【Android系统启动】 Android Init 进程启动流程源码解析
前言
- 文章源码按照AOSP官网源码android14-releaseInit进程代码进行解读;
- 如有不当之处,麻烦指出作者进行修正
代码位置
- system/core/init/main.cpp
- /system/core/rootdir/init.rc
- /system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
源码解析
main.cpp Init进程入口
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
#if __has_feature(address_sanitizer)
__asan_set_error_report_callback(AsanReportCallback);
#elif __has_feature(hwaddress_sanitizer)
__hwasan_set_error_report_callback(AsanReportCallback);
#endif
// Boost prio which will be restored later
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, -20);
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (argc > 1) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "subcontext")) {
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger);
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap();
return SubcontextMain(argc, argv, &function_map);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "selinux_setup")) {
return SetupSelinux(argv);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "second_stage")) {
return SecondStageMain(argc, argv);
}
}
return FirstStageMain(argc, argv);
}
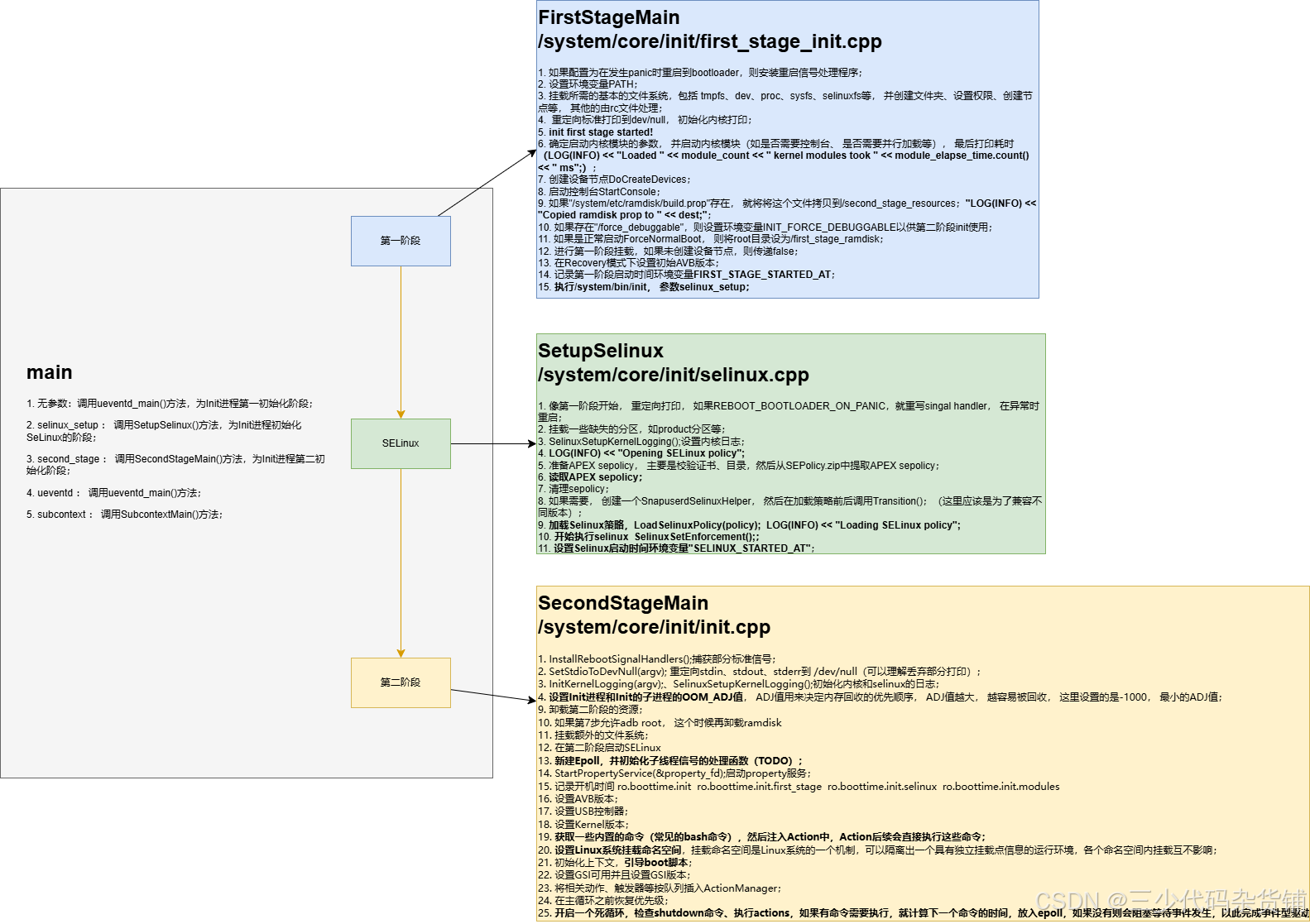
- 可以从Init进程的main入口函数这里看到,Init进程进入后会将优先级设为最高,然后解析参数,根据参数有5种情况:
- 无参数:调用ueventd_main()方法,为Init进程第一初始化阶段;
- “selinux_setup” : 调用SetupSelinux()方法,为Init进程初始化SeLinux的阶段;
- “second_stage” : 调用SecondStageMain()方法,为Init进程第二初始化阶段;
- “ueventd” : 调用ueventd_main()方法,本篇文章不涉及;
- “subcontext” : 调用SubcontextMain()方法,本篇文章不涉及;
- 根据上一篇文章Kernel启动流程种可以看到, 当时调用是没有带参数的,因此这里从
FirstStageMain开始;
// https://cs.android.com/android/kernel/superproject/+/common-android14-5.15:common/init/main.c
if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh"))
return 0;
static int try_to_run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
int ret;
ret = run_init_process(init_filename);
if (ret && ret != -ENOENT) {
pr_err("Starting init: %s exists but couldn't execute it (error %d)\n",
init_filename, ret);
}
return ret;
}
first_stage_init.cpp 第一阶段Init
int FirstStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
// 如果配置为在发生panic时重启到bootloader,则安装重启信号处理程序
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
// 记录启动时间
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// 存储错误信息的容器
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> errors;
#define CHECKCALL(x) \
if ((x) != 0) errors.emplace_back(#x " failed", errno);
// 清除umask
umask(0);
// 清空环境变量
CHECKCALL(clearenv());
// 设置默认PATH
CHECKCALL(setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1));
// 在initramdisk中进行基本的文件系统设置
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755"));
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755));
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755));
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/dm-user", 0755));
CHECKCALL(mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL));
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
CHECKCALL(mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC)));
#undef MAKE_STR
// 不向非特权进程暴露原始命令行
CHECKCALL(chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440));
std::string cmdline;
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/cmdline", &cmdline);
// 不向非特权进程暴露原始bootconfig
chmod("/proc/bootconfig", 0440);
std::string bootconfig;
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/bootconfig", &bootconfig);
gid_t groups[] = {AID_READPROC};
// 设置进程组
CHECKCALL(setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups));
CHECKCALL(mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL));
CHECKCALL(mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL));
// 创建/dev/kmsg设备节点
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11)));
// 如果配置为允许任何人写入kmsg,则创建/dev/kmsg_debug设备节点
if constexpr (WORLD_WRITABLE_KMSG) {
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/kmsg_debug", S_IFCHR | 0622, makedev(1, 11)));
}
// 创建随机数设备节点
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8)));
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9)));
// 创建设备节点
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/ptmx", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(5, 2)));
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/null", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 3)));
// 下面的挂载在第一阶段init中完成,以便第一阶段挂载可以挂载/mnt/{vendor,product}/的子目录。
// 其他挂载,不需要第一阶段挂载,则应该在rc文件中完成。
// 为由vold管理的设备挂载临时文件系统
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/mnt", "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=1000"));
// /mnt/vendor用于挂载特定于供应商的分区,这些分区不能作为供应商分区的一部分,例如,因为它们被以读写方式挂载。
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/mnt/vendor", 0755));
// /mnt/product用于挂载特定于产品的分区,这些分区不能作为产品分区的一部分,例如,因为它们被以读写方式挂载。
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/mnt/product", 0755));
// /debug_ramdisk用于保留调试ramdisk中的额外文件
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/debug_ramdisk", "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=0"));
// /second_stage_resources用于保留从第一阶段到第二阶段init的文件
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", kSecondStageRes, "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=0"))
#undef CHECKCALL
// 将标准输入/输出/错误重定向到/dev/null
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
// 现在/dev上已经挂载了tmpfs,并且我们有了/dev/kmsg,我们实际上可以与外界通信了...
InitKernelLogging(argv);
// 如果存在错误,则记录并终止
if (!errors.empty()) {
for (const auto& [error_string, error_errno] : errors) {
LOG(ERROR) << error_string << " " << strerror(error_errno);
}
LOG(FATAL) << "Init encountered errors starting first stage, aborting";
}
// 记录init第一阶段已启动
LOG(INFO) << "init first stage started!";
// 打开旧的根目录
auto old_root_dir = std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)>{opendir("/"), closedir};
if (!old_root_dir) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not opendir(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
}
struct stat old_root_info;
// 获取旧的根目录信息
if (stat("/", &old_root_info) != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not stat(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
old_root_dir.reset();
}
// 确定是否需要在控制台上输出信息
auto want_console = ALLOW_FIRST_STAGE_CONSOLE ? FirstStageConsole(cmdline, bootconfig) : 0;
// 确定是否要并行加载模块
auto want_parallel =
bootconfig.find("androidboot.load_modules_parallel = \"true\"") != std::string::npos;
// 加载内核模块
boot_clock::time_point module_start_time = boot_clock::now();
int module_count = 0;
if (!LoadKernelModules(IsRecoveryMode() && !ForceNormalBoot(cmdline, bootconfig), want_console,
want_parallel, module_count)) {
if (want_console != FirstStageConsoleParam::DISABLED) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to load kernel modules, starting console";
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load kernel modules";
}
}
// 记录加载的模块数量和时间
if (module_count > 0) {
auto module_elapse_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
boot_clock::now() - module_start_time);
setenv(kEnvInitModuleDurationMs, std::to_string(module_elapse_time.count()).c_str(), 1);
LOG(INFO) << "Loaded " << module_count << " kernel modules took "
<< module_elapse_time.count() << " ms";
}
bool created_devices = false;
// 如果在故障时要求在控制台上输出信息
if (want_console == FirstStageConsoleParam::CONSOLE_ON_FAILURE) {
if (!IsRecoveryMode()) {
// 创建设备节点
created_devices = DoCreateDevices();
if (!created_devices) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create device nodes early";
}
}
// 启动控制台
StartConsole(cmdline);
}
// 如果存在/bootimage_ramdisk.prop,则将其复制到第二阶段
if (access(kBootImageRamdiskProp, F_OK) == 0) {
std::string dest = GetRamdiskPropForSecondStage();
std::string dir = android::base::Dirname(dest);
std::error_code ec;
if (!fs::create_directories(dir, ec) && !!ec) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Can't mkdir " << dir << ": " << ec.message();
}
if (!fs::copy_file(kBootImageRamdiskProp, dest, ec)) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Can't copy " << kBootImageRamdiskProp << " to " << dest << ": "
<< ec.message();
}
LOG(INFO) << "Copied ramdisk prop to " << dest;
}
// 如果存在"/force_debuggable",则设置环境变量INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE以供第二阶段init使用
if (access("/force_debuggable", F_OK) == 0) {
constexpr const char adb_debug_prop_src[] = "/adb_debug.prop";
constexpr const char userdebug_plat_sepolicy_cil_src[] = "/userdebug_plat_sepolicy.cil";
std::error_code ec; // 调用不会抛出异常的重载copy_file()
if (access(adb_debug_prop_src, F_OK) == 0 &&
!fs::copy_file(adb_debug_prop_src, kDebugRamdiskProp, ec)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Can't copy " << adb_debug_prop_src << " to " << kDebugRamdiskProp
<< ": " << ec.message();
}
if (access(userdebug_plat_sepolicy_cil_src, F_OK) == 0 &&
!fs::copy_file(userdebug_plat_sepolicy_cil_src, kDebugRamdiskSEPolicy, ec)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Can't copy " << userdebug_plat_sepolicy_cil_src << " to "
<< kDebugRamdiskSEPolicy << ": " << ec.message();
}
// 设置环境变量INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE
setenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE", "true", 1);
}
// 如果是正常启动,则准备切换根文件系统
if (ForceNormalBoot(cmdline, bootconfig)) {
// 创建/first_stage_ramdisk目录
mkdir("/first_stage_ramdisk", 0755);
// 准备切换根文件系统
PrepareSwitchRoot();
// 必须使用挂载点作为目标调用SwitchRoot(),因此在此处将目标目录绑定到自身。
if (mount("/first_stage_ramdisk", "/first_stage_ramdisk", nullptr, MS_BIND, nullptr) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Could not bind mount /first_stage_ramdisk to itself";
}
// 切换根文件系统
SwitchRoot("/first_stage_ramdisk");
}
// 进行第一阶段挂载,如果未创建设备节点,则传递false
if (!DoFirstStageMount(!created_devices)) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to mount required partitions early ...";
}
// 获取新的根目录信息
struct stat new_root_info;
if (stat("/", &new_root_info) != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not stat(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
old_root_dir.reset();
}
// 如果旧的根目录存在且新的根目录设备号与旧的不同,则释放ramdisk
if (old_root_dir && old_root_info.st_dev != new_root_info.st_dev) {
FreeRamdisk(old_root_dir.get(), old_root_info.st_dev);
}
// 在恢复模式下设置初始AVB版本
SetInitAvbVersionInRecovery();
// 设置环境变量,记录第一阶段启动时间
setenv(kEnvFirstStageStartedAt, std::to_string(start_time.time_since_epoch().count()).c_str(),
1);
// 设置selinux init的路径和参数
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "selinux_setup", nullptr};
// 打开/dev/kmsg,重定向标准输出和标准错误到其上,并关闭文件描述符
auto fd = open("/dev/kmsg", O_WRONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO);
close(fd);
// 执行selinux init
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
// 如果execv()返回,说明出现了错误,此时记录错误并终止
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
return 1;
}
上面代码的注释部分是原文翻译,部分是自己加上去。可以看到第一阶段做了如下工作:
- InstallRebootSignalHandlers : 实际上监听Linux的Signal,当收到这些Signal时,重启Bootloader,如果REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC不为true,则不会处理;
- 设置基本的环境, 如设置环境变量、挂载基本的文件系统、挂载设备节点、初始化日志等等,并监听是否出错,如果出错则停止;
- 加载内核模块:根据配置加载内核模块,可以选择是否并行加载模块,并记录加载模块的数量和时间。
- 创建设备节点和启动控制台:根据配置决定是否在控制台上输出信息,如果配置为在故障时输出信息,则创建设备节点并启动控制台。
- 复制 ramdisk 属性文件:如果存在
/bootimage_ramdisk.prop文件,则将其复制到第二阶段用于使用。 - 设置调试模式:如果存在
/force_debuggable文件,则设置环境变量INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE为true,并复制相关属性文件到调试 ramdisk。 - 准备切换根文件系统:如果是正常启动,创建
/first_stage_ramdisk目录并准备切换根文件系统。 - 进行第一阶段挂载:进行第一阶段的文件系统挂载。
- 释放旧的 ramdisk:如果旧的根目录存在且新的根目录设备号与旧的不同,则释放 ramdisk。
- 设置初始 AVB 版本:在恢复模式下设置初始 Android Verified Boot (AVB) 版本。
- 设置环境变量:记录第一阶段启动时间。
- 执行 SELinux 初始化:设置 SELinux 初始化的路径和参数,并执行 SELinux 初始化。
那么下一步去查看SeLinux的初始化吧。
selinux.cpp SeLinux初始化
// SELinux设置过程围绕着snapuserd进行精心编排。策略必须从动态分区加载,在OTA期间,这些分区无法在没有snapuserd的情况下读取。
// 但是,随着以内核特权运行的snapuserd,加载策略将立即触发审核。
//
// 我们使用五个步骤来解决这个问题:
// (1) 在snapuserd运行时将策略读入字符串中。
// (2) 重写快照设备映射表,生成新的dm-user设备并刷新I/O。
// (3) 终止snapuserd,因为它不再有任何dm-user设备可以附加。
// (4) 加载sepolicy并在/dev中执行关键的restorecon,小心避免读取/system中的任何内容。
// (5) 重新启动snapuserd并将其附加到步骤(2)中的dm-user设备上。
//
// 在此序列之后,可以安全地启用强制模式并继续引导。
int SetupSelinux(char** argv) {
SetStdioToDevNull(argv); // 设置标准输入/输出/错误到/dev/null
InitKernelLogging(argv); // 初始化内核日志记录
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) { // 如果在发生panic时重新引导引导加载程序
InstallRebootSignalHandlers(); // 安装重新引导信号处理程序
}
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now(); // 记录启动时间点
MountMissingSystemPartitions(); // 挂载缺失的系统分区
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging(); // SELinux设置内核日志记录
LOG(INFO) << "Opening SELinux policy"; // 记录打开SELinux策略
PrepareApexSepolicy(); // 准备APEX sepolicy
// 在潜在终止snapuserd之前读取策略
std::string policy;
ReadPolicy(&policy);
CleanupApexSepolicy(); // 清理APEX sepolicy
auto snapuserd_helper = SnapuserdSelinuxHelper::CreateIfNeeded(); // 创建snapuserd SELinux帮助器
if (snapuserd_helper) {
// 终止旧的snapuserd以避免审核消息。在此之后,我们不能从/system(或其他动态分区)读取,直到调用FinishTransition()为止。
snapuserd_helper->StartTransition(); // 开始转换
}
LoadSelinuxPolicy(policy); // 加载SELinux策略
if (snapuserd_helper) {
// 在启用强制之前,完成挂起的snapuserd转换。
snapuserd_helper->FinishTransition(); // 完成转换
snapuserd_helper = nullptr;
}
// 此restorecon在SelinuxSetEnforcement之前有意执行,因为在将SELinux设置为强制模式后,从tmpfs转换文件到*_contexts_file上下文所需的权限不应授予任何进程。
if (selinux_android_restorecon("/dev/selinux/", SELINUX_ANDROID_RESTORECON_RECURSE) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "restorecon failed of /dev/selinux failed"; // 恢复失败,终止
}
SelinuxSetEnforcement(); // 设置SELinux执行
// 我们在内核域中,希望转换到init域。保存SELabel在其xattrs中的文件系统,例如ext4,此处不需要显式的restorecon,但其他文件系统需要。特别是对于A/B设备的恢复镜像等ramdisk。
if (selinux_android_restorecon("/system/bin/init", 0) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "restorecon failed of /system/bin/init failed"; // 恢复失败,终止
}
// 设置环境变量,记录SELinux启动时间
setenv(kEnvSelinuxStartedAt, std::to_string(start_time.time_since_epoch().count()).c_str(), 1);
const char* path = "/system/bin/init"; // 第二阶段init的路径
const char* args[] = {path, "second_stage", nullptr}; // 第二阶段init的参数
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args)); // 执行第二阶段init
// 如果execv()返回,则出现错误,记录并终止
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
return 1;
}
这里做的工作有:
- 初始化日志并设置标准输入/输出/错误到
/dev/null; - 如果配置为在发生 panic 时重启到 bootloader,则捕获信号并重启(跟上面第一阶段一样);
- 记录启动时间点;
- 挂载缺失的系统分区;
- 设置内核日志记录和打开 SELinux 策略;
- 准备 APEX sepolicy 并读取策略,执行相关转换;
- 执行必要的恢复操作,包括设置 SELinux 强制模式;
- 执行第二阶段 init。
init.cpp - SecondStageMain 第二阶段Init
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers(); // 如果发生 panic,安装重新引导信号处理程序
}
// 等到 signalfd 注册之前,不应启动任何线程。
// 如果确实需要这些线程,每个线程都应确保阻塞 SIGCHLD 信号。
// 参见 b/223076262
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now(); // 记录启动时间点
trigger_shutdown = [](const std::string& command) { shutdown_state.TriggerShutdown(command); };
SetStdioToDevNull(argv); // 设置标准输入/输出/错误到 /dev/null
InitKernelLogging(argv); // 初始化内核日志记录
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!"; // 记录第二阶段初始化开始
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging(); // 设置 SELinux 内核日志记录
// 更新 $PATH(如果第二阶段 init 新于第一阶段 init,则设置)
if (setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Could not set $PATH to '" << _PATH_DEFPATH << "' in second stage"; // 设置 $PATH 失败,终止
}
// 初始化不应因为对其他进程的依赖而崩溃,因此我们忽略 SIGPIPE 并直接在调用点处理 EPIPE。
// 请注意,将信号设置为 SIG_IGN 是继承的,但自定义信号处理程序不是。
// 由于我们不希望为子进程忽略 SIGPIPE,因此为信号处理程序设置一个空操作函数。
{
struct sigaction action = {.sa_flags = SA_RESTART};
action.sa_handler = [](int) {};
sigaction(SIGPIPE, &action, nullptr);
}
// 设置 init 及其派生子进程的 oom_adj。
if (auto result = WriteFile("/proc/1/oom_score_adj", StringPrintf("%d", DEFAULT_OOM_SCORE_ADJUST));
!result.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write " << DEFAULT_OOM_SCORE_ADJUST
<< " to /proc/1/oom_score_adj: " << result.error(); // 写入 oom_adj 失败,记录错误
}
// 设置一个所有进程都可以访问的会话密钥环。
// 它将保存诸如 FBE 加密密钥等内容。没有进程应该覆盖其会话密钥环。
keyctl_get_keyring_ID(KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
// 表示引导正在进行中,以通知后台固件加载程序等。
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
// 查看是否需要加载调试属性以允许在设备解锁时 adb root。
const char* force_debuggable_env = getenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE");
bool load_debug_prop = false;
if (force_debuggable_env && AvbHandle::IsDeviceUnlocked()) {
load_debug_prop = "true"s == force_debuggable_env;
}
unsetenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE"); // 清除环境变量
// 当不需要时,卸载调试 ramdisk,以防止属性服务从中读取 .prop 文件。
if (!load_debug_prop) {
UmountDebugRamdisk();
}
PropertyInit(); // 初始化属性服务
// 在属性服务读取 .prop 文件后,卸载第二阶段资源。
UmountSecondStageRes();
// 当需要时,在属性服务读取 .prop 文件后卸载调试 ramdisk。
if (load_debug_prop) {
UmountDebugRamdisk();
}
// 挂载第二阶段 init 所需的额外文件系统。
MountExtraFilesystems();
// 现在为第二阶段设置 SELinux。
SelabelInitialize(); // 初始化 SELinux 标签
SelinuxRestoreContext(); // 恢复 SELinux 上下文
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error(); // 打开 epoll 失败,终止
}
// 在响应其他待处理函数之前,我们总是先收集子进程。
// 这是为了防止竞争,其他守护进程在服务退出后看到并要求 init 通过 ctl.start 启动它,而 init 尚未收集它。
epoll.SetFirstCallback(ReapAnyOutstandingChildren);
InstallSignalFdHandler(&epoll); // 安装信号描述符处理程序
InstallInitNotifier(&epoll); // 安装初始化通知程序
StartPropertyService(&property_fd); // 启动属性服务
// 记录初始化阶段启动时间,以便 bootstat 记录。
RecordStageBoottimes(start_time);
// 设置 libavb 版本以进行框架限定的 OTA 匹配(在 Treble 构建中)。
if (const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION"); avb_version != nullptr) {
SetProperty("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
}
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION"); // 清除环境变量
fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all(); // 挂载所有 vendor overlay
export_oem_lock_status(); // 导出 OEM 锁定状态
MountHandler mount_handler(&epoll); // 挂载处理器
SetUsbController(); // 设置 USB 控制器
SetKernelVersion(); // 设置内核版本
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap(); // 获取内置函数映射
Action::set_function_map(&function_map); // 设置动作函数映射
if (!SetupMountNamespaces()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "SetupMountNamespaces failed"; // 设置 mount namespaces 失败,终止
}
InitializeSubcontext(); // 初始化子上下文
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance(); // 获取动作管理器实例
ServiceList& sm = ServiceList::GetInstance(); // 获取服务列表实例
LoadBootScripts(am, sm); // 加载引导脚本
// 默认情况下,启用此项并允许 INFO 日志被丢弃,将会增加 0.2s 的 Nexus 9 启动时间,因此默认禁用。
if (false) DumpState(); // 打印状态信息
// 在脚本开始运行之前,使 GSI 状态可用。
auto is_running = android::gsi::IsGsiRunning() ? "1" : "0";
SetProperty(gsi::kGsiBootedProp, is_running); // 设置 GSI 启动属性
auto is_installed = android::gsi::IsGsiInstalled() ? "1" : "0";
SetProperty(gsi::kGsiInstalledProp, is_installed); // 设置 GSI 已安装属性
if (android::gsi::IsGsiRunning()) {
std::string dsu_slot;
if (android::gsi::GetActiveDsu(&dsu_slot)) {
SetProperty(gsi::kDsuSlotProp, dsu_slot); // 设置 DSU 槽位属性
}
}
// 将内置动作排入队列以启动 cgroups 设置等。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetupCgroupsAction, "SetupCgroups");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(TestPerfEventSelinuxAction, "TestPerfEventSelinux");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(ConnectEarlyStageSnapuserdAction, "ConnectEarlyStageSnapuserd");
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// 将一个动作排入队列,等待冷启动完成,以便我们知道 ueventd 已设置所有 /dev...
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ...以便我们可以开始排队需要来自 /dev 的东西的动作。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits");
Keychords keychords;
am.QueueBuiltinAction(
[&epoll, &keychords](const BuiltinArguments& args) -> Result<void> {
for (const auto& svc : ServiceList::GetInstance()) {
keychords.Register(svc->keycodes());
}
keychords.Start(&epoll, HandleKeychord);
return {};
},
"KeychordInit");
// 触发所有引导动作以启动系统。
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// 在充电模式下不要挂载文件系统或启动核心系统服务。
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// 基于属性当前状态运行所有属性触发器。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
// 在主循环之前恢复优先级。
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, 0);
while (true) {
// 默认情况下,睡眠直到发生事件。
// 不要将 far_future 转换为 std::chrono::milliseconds,因为这会触发溢出。
// boot_clock 的单位是 1ns。
const boot_clock::time_point far_future = boot_clock::time_point::max();
boot_clock::time_point next_action_time = far_future;
auto shutdown_command = shutdown_state.CheckShutdown(); // 检查是否有关机命令
if (shutdown_command) {
LOG(INFO) << "Got shutdown_command '" << *shutdown_command
<< "' Calling HandlePowerctlMessage()";
HandlePowerctlMessage(*shutdown_command); // 处理关机消息
}
if (!(prop_waiter_state.MightBeWaiting() || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand(); // 执行一个命令
// 如果还有更多工作要做,立即再次唤醒。
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) {
next_action_time = boot_clock::now();
}
}
// 由于上面的代码检查了待处理的动作,因此在下面的 Epoll::Wait() 调用之前,不得有新的动作排队,
// 而没有调用 WakeMainInitThread()。
if (!IsShuttingDown()) {
auto next_process_action_time = HandleProcessActions(); // 处理进程动作
// 如果有需要重新启动的进程,请及时唤醒。
if (next_process_action_time) {
next_action_time = std::min(next_action_time, *next_process_action_time);
}
}
std::optional<std::chrono::milliseconds> epoll_timeout;
if (next_action_time != far_future) {
epoll_timeout = std::chrono::ceil<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
std::max(next_action_time - boot_clock::now(), 0ns));
}
auto epoll_result = epoll.Wait(epoll_timeout); // 等待 epoll 事件
if (!epoll_result.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << epoll_result.error(); // 记录 epoll 错误
}
if (!IsShuttingDown()) {
HandleControlMessages(); // 处理控制消息
SetUsbController(); // 设置 USB 控制器
}
}
return 0;
}
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list);
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init/hw/init.rc");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/system/etc/init");
}
// late_import is available only in Q and earlier release. As we don't
// have system_ext in those versions, skip late_import for system_ext.
parser.ParseConfig("/system_ext/etc/init");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/vendor/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/odm/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/product/etc/init");
}
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
}
}
- InstallRebootSignalHandlers();捕获部分标准信号;
- SetStdioToDevNull(argv); 重定向stdin、stdout、stderr到 /dev/null(可以理解丢弃部分打印);
- InitKernelLogging(argv);、SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();初始化内核和selinux的日志;
- 设置Init进程和Init的子进程的OOM_ADJ值, ADJ值用来决定内存回收的优先顺序, ADJ值越大, 越容易被回收, 这里设置的是-1000, 最小的ADJ值;
- 卸载第二阶段的资源;
- 如果第7步允许adb root, 这个时候再卸载ramdisk
- 挂载额外的文件系统;
- 在第二阶段启动SELinux
- 新建Epoll,并初始化子线程信号的处理函数(TODO);
- StartPropertyService(&property_fd);启动property服务;
- 记录开机时间 ro.boottime.init ro.boottime.init.first_stage ro.boottime.init.selinux ro.boottime.init.modules
- 设置AVB版本;
- 设置USB控制器;
- 设置Kernel版本;
- 获取一些内置的命令(常见的bash命令),然后注入Action中,Action后续会直接执行这些命令;
- 设置Linux系统挂载命名空间,挂载命名空间是Linux系统的一个机制,可以隔离出一个具有独立挂载点信息的运行环境,各个命名空间内挂载互不影响;
- 初始化上下文,引导boot脚本;这里会从
/system/etc/init/hw/init.rc、/system/etc/init等位置查找; - 设置GSI可用并且设置GSI版本;
- 将相关动作、触发器等按队列插入ActionManager;
- 在主循环之前恢复优先级;
- 开启一个死循环,检查shutdown命令、执行actions,如果有命令需要执行,就计算下一个命令的时间,放入epoll,如果没有则会阻塞等待事件发生,以此完成事件型驱动;
启动zygote
init.rc文件中命令执行了start zygote
start zygote
Q&A
Init进程启动分为几个阶段?每个阶段做了什么事情?
普遍认为2个阶段,但是从代码看也可以分为3个或者4个阶段。 第一阶段->selinux->第二阶段->uventd。第一个阶段,第一个阶段主要做了一些挂载基本文件系统、设置环境变量等的操作,第二阶段则挂在了额外的文件系统,使用epoll实现了一个事件驱动型的功能,加载和执行.rc文件中的命令;
Init如何启动zygote?
在init.rc文件中, on zygote-start的地方, 写了start zygote, start是android内置的命令,在解析rc文件之前就已经将这些方法放到代码中了,命令会执行start方法,将zygote拉起来;
Init如何解析.rc文件?
Init进程在第二阶段启动过程中,会调用LoadBootScripts方法,方法内部有Parser等工具类,将文件内容一一解析,然后会被放到actionmanager中执行。
PS:代码中epoll的使用和原理还不大懂,后续需要填坑…(哈哈,其实别的也很多不懂)
参考
- https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/+/android14-release:
- 源码详解Android 9.0§ 系统启动流程之init进程(第二阶段)_android 开机第二阶段-CSDN博客