LeetCode-算法:201-300(Python)
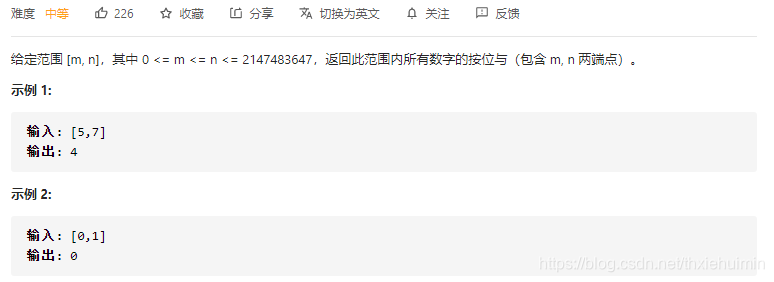
- 201. 数字范围按位与(中等)
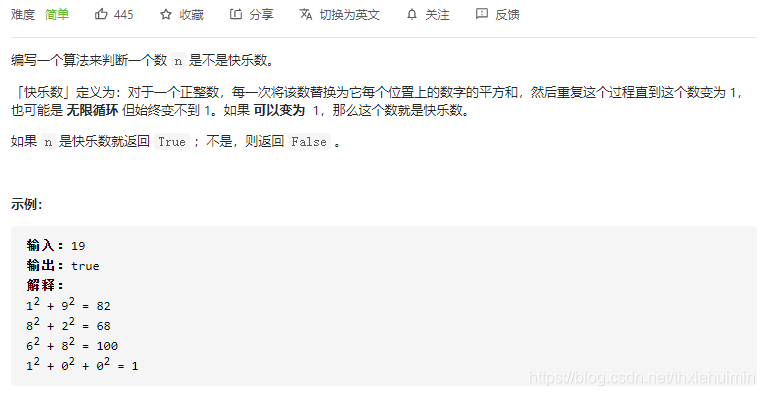
- 202. 快乐数(简单)
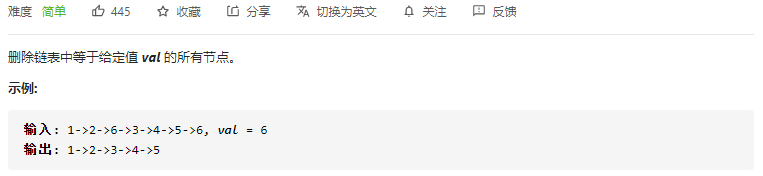
- 203. 移除链表元素(简单)
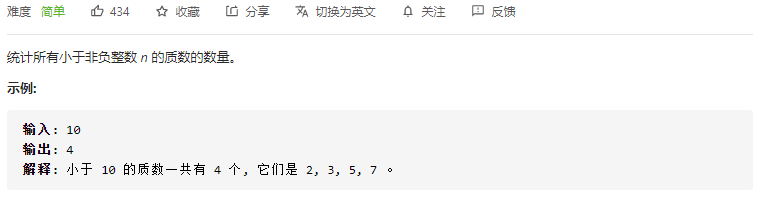
- 204. 计数质数(简单)
- 205. 同构字符串(简单)
- 206. 反转链表(简单)
- 207. 课程表(中等)
- 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)(中等)
- 209. 长度最小的子数组(中等)
- 210. 课程表 II(中等)
- 211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计(中等)
- 212. 单词搜索 II(困难)
- 213. 打家劫舍 II(中等)
- 214. 最短回文串(困难)
- 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素(中等)
- 216. 组合总和 III(中等)
- 217. 存在重复元素(简单)
- 218. 天际线问题(困难)
- 219. 存在重复元素 II(简单)
- 220. 存在重复元素 III(中等)
- 221. 最大正方形 (中等)
- 222. 完全二叉树的节点个数(中等)
- 223. 矩形面积(中等)
- 224. 基本计算器(困难)
- 225. 用队列实现栈(简单)
- 226. 翻转二叉树(简单)
- 227. 基本计算器 II(中等)
- 228. 汇总区间(简单)
- 229. 求众数 II(中等)
- 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素(中等)
- 231. 2的幂(简单)
- 232. 用栈实现队列(简单)
- 233. 数字 1 的个数(困难)
- 234. 回文链表(简单)
- 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先(简单)
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先(中等)
- 237. 删除链表中的节点 (简单)
- 238. 除自身以外数组的乘积(中等)
- 239. 滑动窗口最大值(困难)
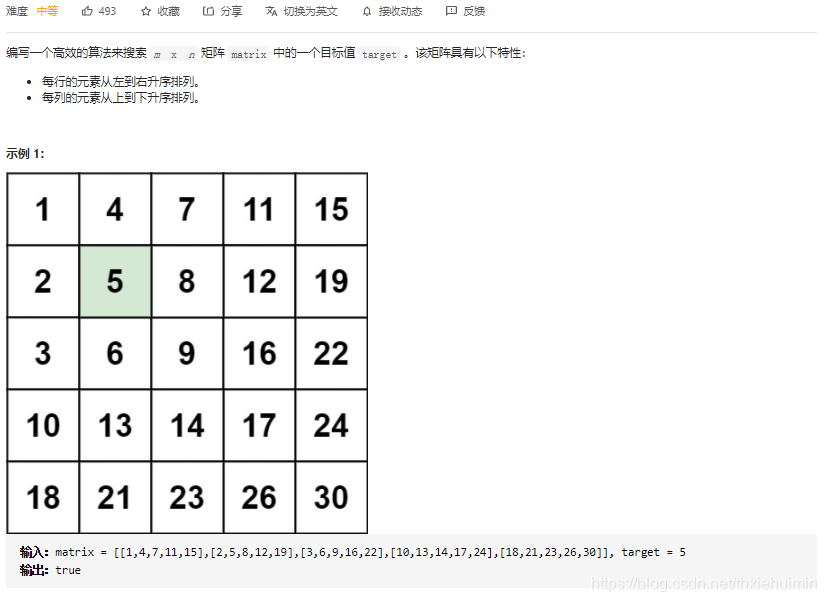
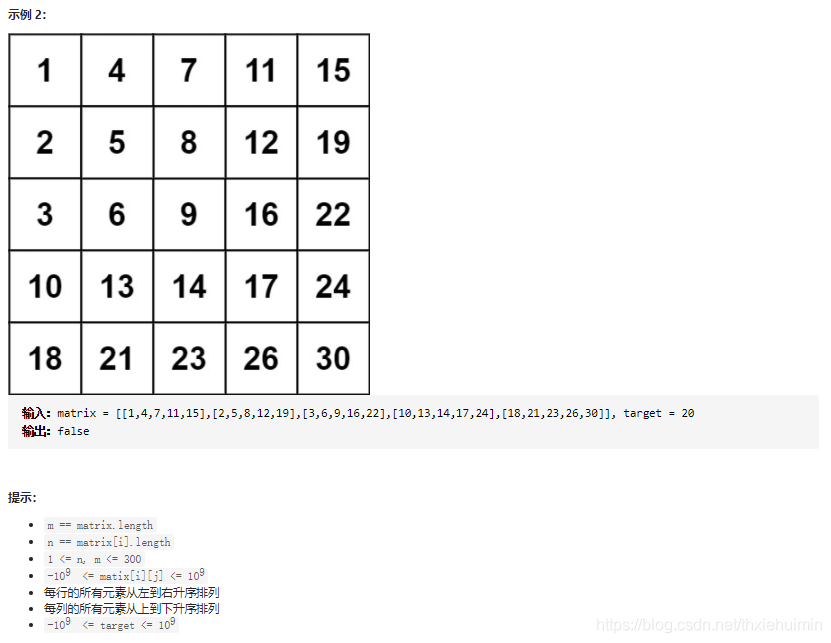
- 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II (中等)
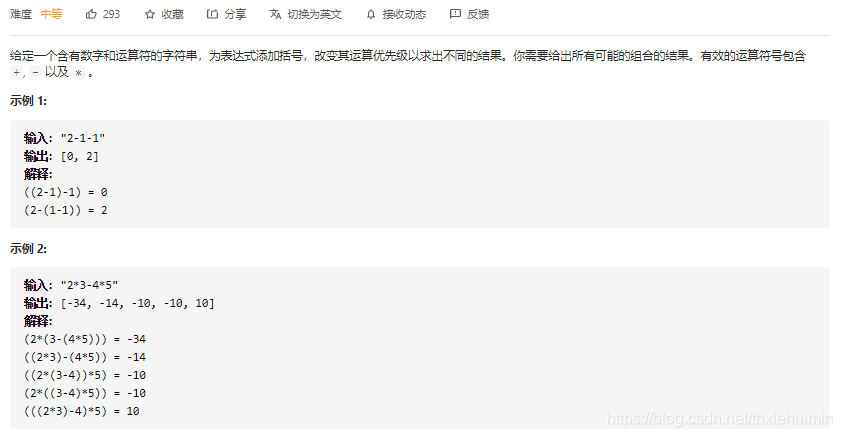
- 241. 为运算表达式设计优先级(中等)
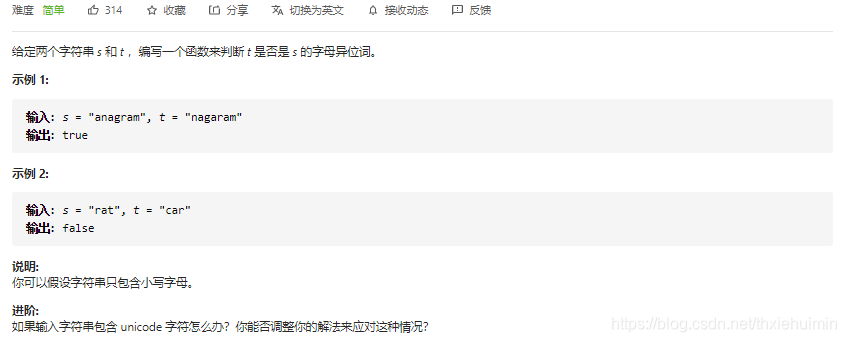
- 242. 有效的字母异位词(简单)
- 243-256(无)
- 257. 二叉树的所有路径(简单)
- 258. 各位相加(简单)
- 259(无)
- 260. 只出现一次的数字 III(中等)
- 261 以图判树(中等)-无
- 262 行程和用户(困难)
- 263. 丑数(简单)
- 264. 丑数 II (中等)
- 265-267(无)
- 268. 丢失的数字(简单)
- 269-272(无)
- 273. 整数转换英文表示(困难)
- 274. H 指数(中等)
- 275. H 指数 II(中等)
- 276-277(无)
- 278. 第一个错误的版本(简单)
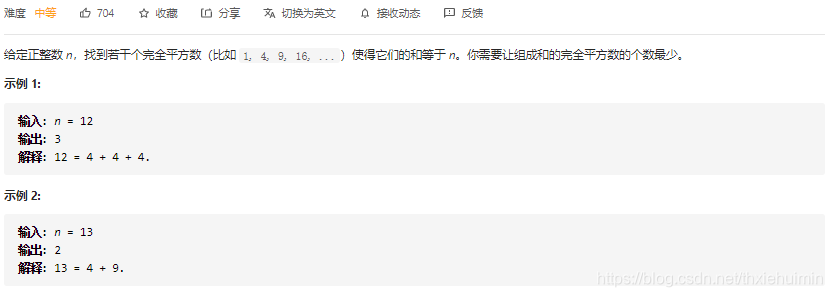
- 279. 完全平方数(中等)
- 280-281(无)
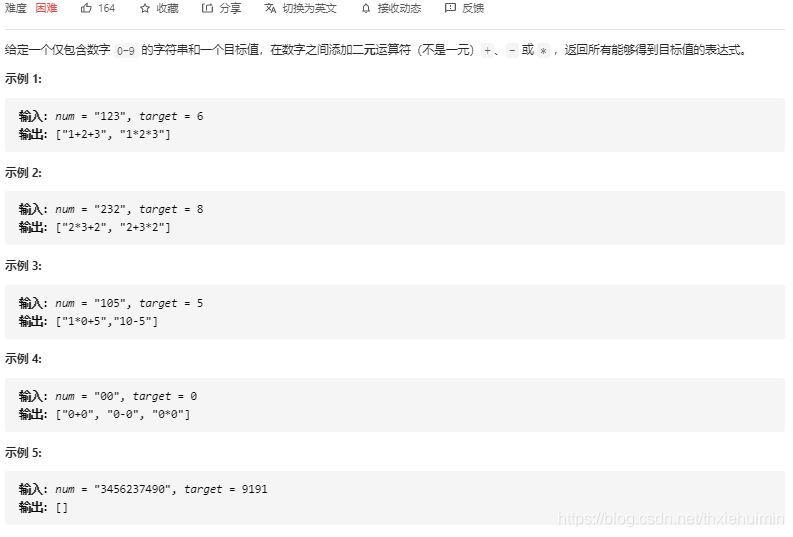
- 282. 给表达式添加运算符(困难)
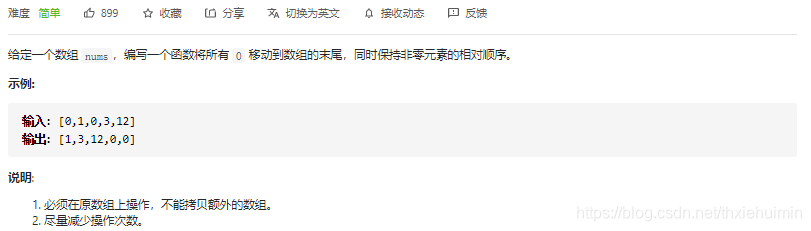
- 283. 移动零(简单)
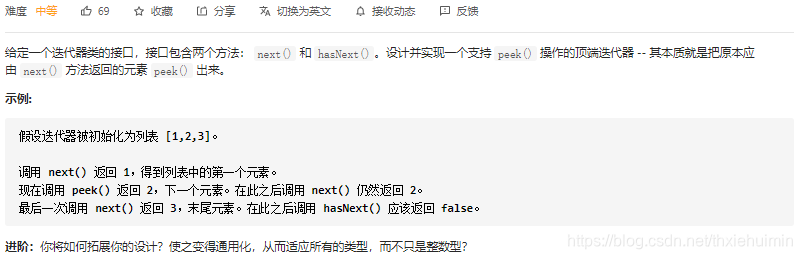
- 284. 顶端迭代器(中等)
- 285(无)
- 286(无)
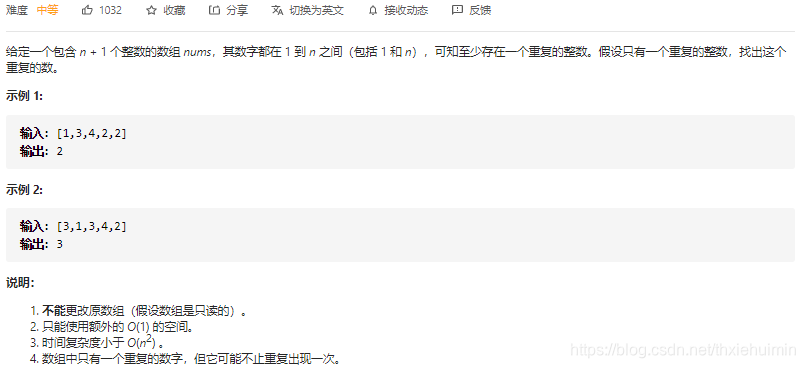
- 287. 寻找重复数(中等)
- 288(无)
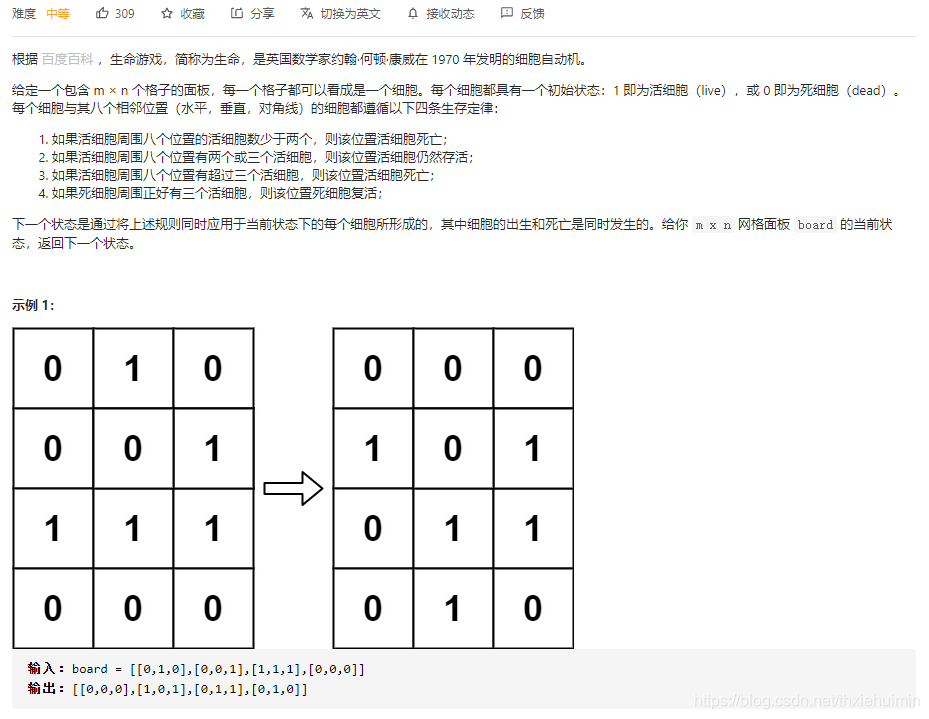
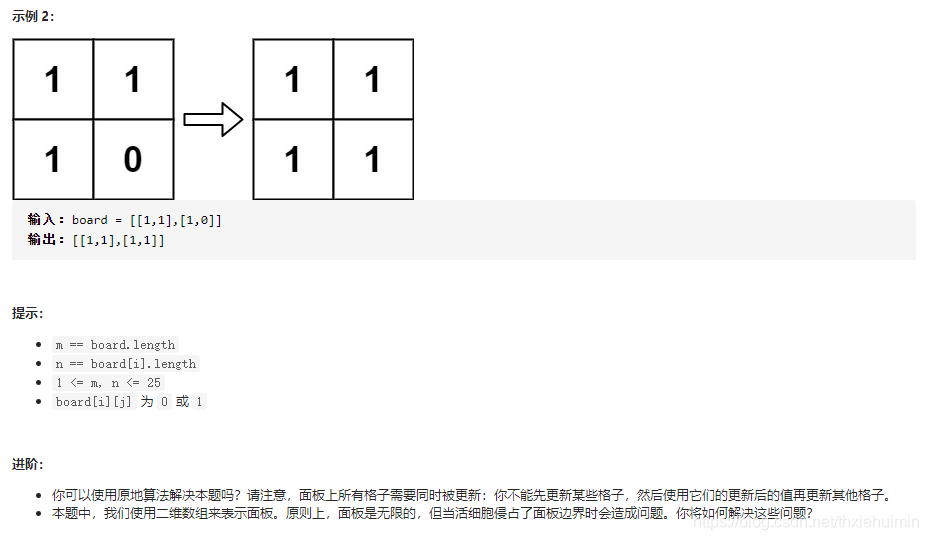
- 289. 生命游戏(中等)
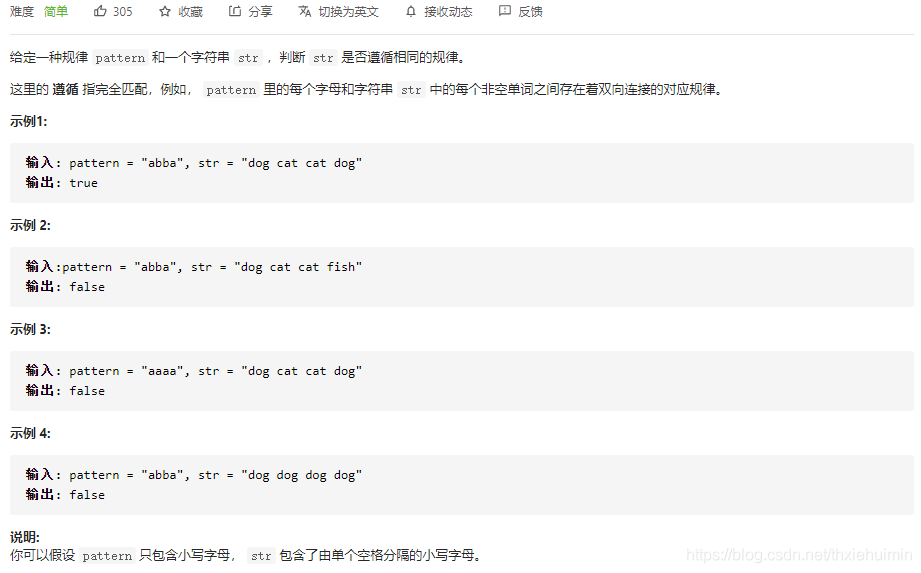
- 290. 单词规律(简单)
- 291(无)
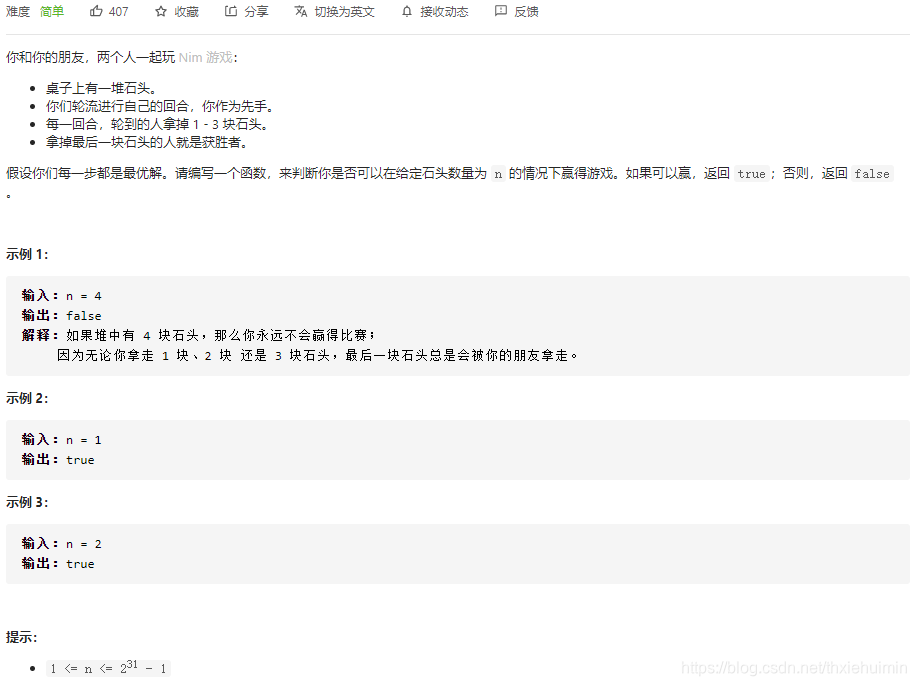
- 292. Nim 游戏(简单)
- 293(无)
- 294(无)
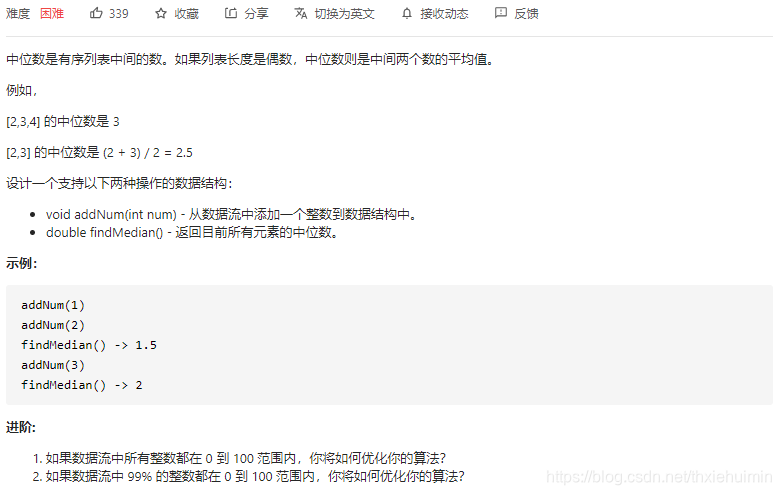
- 295. 数据流的中位数(困难)
- 296(无)
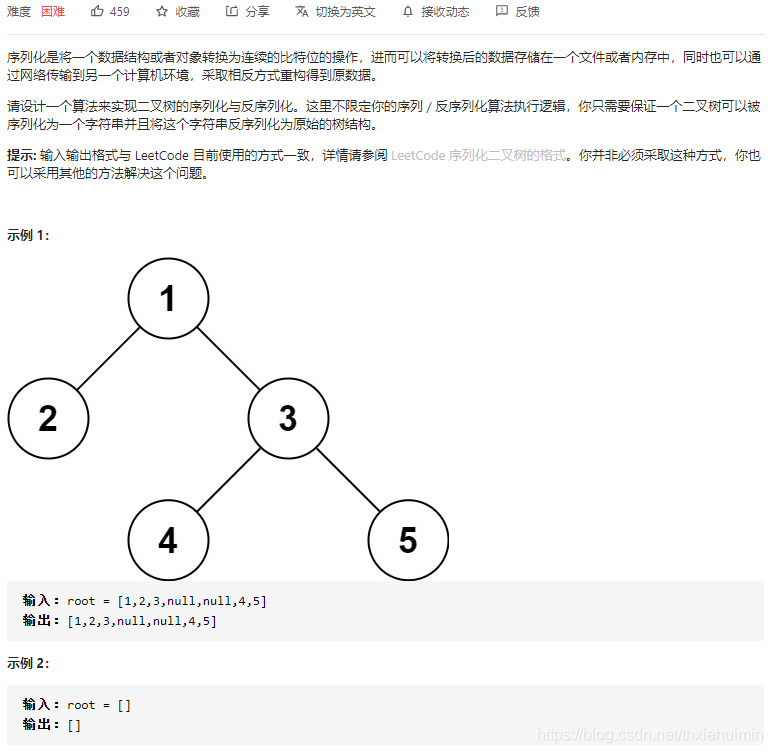
- 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化(困难)
- 298(无)
- 299. 猜数字游戏 (中等)
- 300. 最长递增子序列(中等)
201. 数字范围按位与(中等)
思路
x
x
x和
x
+
1
x+1
x+1的二进制在某一位后面的数为相反数,相与后均为0。m,n分别右移一位,抹掉m,n的右边一位时,tail加1,得到m,n相等的前缀,共抹掉tail位,左移tail位补充为0
栗子:
| 十进制 | 二进制 |
|---|---|
| 5 | 0000 0101 |
| 6 | 0000 0110 |
| & | 0000 0100 |
| 7 | 0000 0111 |
| & | 0000 0100 |
| 十进制 | 二进制 | m,n,ans | tail |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5>>=1 | 0000 0010 | m=2 | tail=1 |
| 7>>=1 | 0000 0011 | n=3 | tail=1 |
| 2>>=1 | 0000 0001 | m=1 | tail=2 |
| 3>>=1 | 0000 0001 | n=1 | tail=2 |
| 1<<=2 | 0000 0100 | ans=4 | tail=2 |
class Solution(object):
def rangeBitwiseAnd(self, m, n):
"""
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
tail = 0
while m!=n:
m >>= 1
n >>= 1
tail += 1
return m<<tail
202. 快乐数(简单)
思路
计算各位数的平方和是否等于1,不等于1时,查看该平方和是否曾经出现过,曾经出现表示出现循环,返回False。未出现则继续计算;如果平方和等于1则返回True
class Solution(object):
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
visited = [n]
while n!=1:
sum_squares = 0
while n!=0:
sum_squares += (n%10)**2
n //=10
n = sum_squares
if sum_squares not in visited:
visited.append(sum_squares)
else:
return False
return True
203. 移除链表元素(简单)
思路
见备注
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type val: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return head
pre = head
while pre and pre.val == val: # 当第一个结点等于val时移除
pre=pre.next
rehead = pre
cur = pre.next if pre else None
while cur:
if cur.val == val: # 当结点等于val时移除
pre.next = cur.next
cur = pre.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return rehead
思路
哨兵
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type val: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
pre = ListNode(0) # 哨兵
pre.next = head
rehead, cur = pre, pre.next
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = pre.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return rehead.next
204. 计数质数(简单)
思路
厄拉多塞筛法
class Solution(object):
def countPrimes(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n < 2:
return 0
ans = 0
isPrime = [True]*(n+1)
isPrime[0], isPrime[1]=False, False
for i in range(2, n):
if isPrime[i]: # 当i为质数时,将i的倍数置为非质数(False)
ans += 1
for j in range(i+i, n+1, i):
isPrime[j]=False
return ans
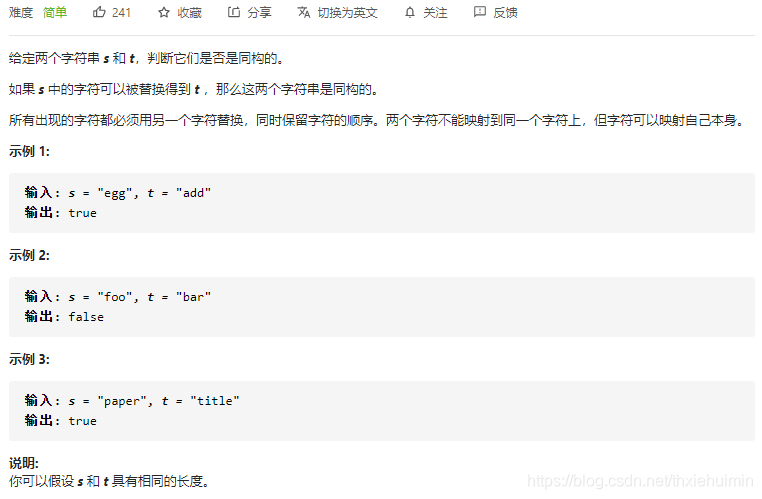
205. 同构字符串(简单)
思路
见备注
class Solution(object):
def isIsomorphic(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
visited = dict()
n = len(s)
for i in range(n):
if s[i] not in visited: # s[i]未访问过时,添加至visited中
if t[i] in visited.values(): # t[i]已出现在visited的values时,说明已经有映射的字符(对应的s[i]应在visited中),因此返回False
return False
visited[s[i]] = t[i]
else:
if visited[s[i]] != t[i]: # s[i]已访问过,映射的字符与t[i]不相等,返回False
return False
return True
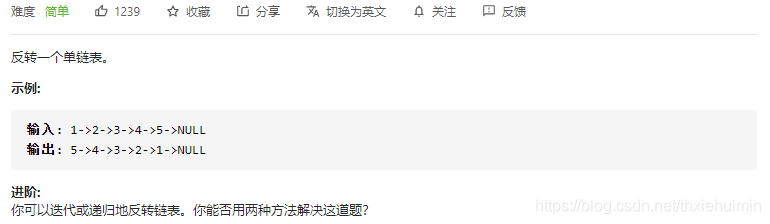
206. 反转链表(简单)
思路
迭代
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
pre, cur = None, head
while cur!=None:
cur_next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = cur_next
return pre
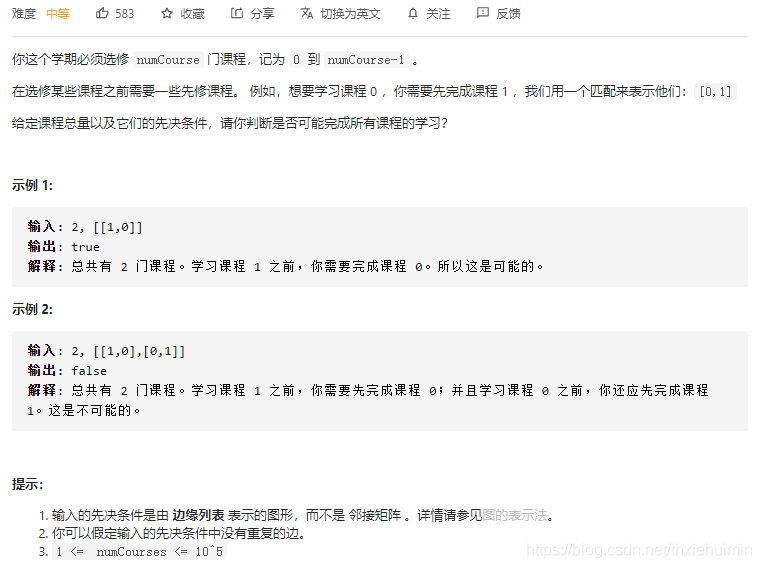
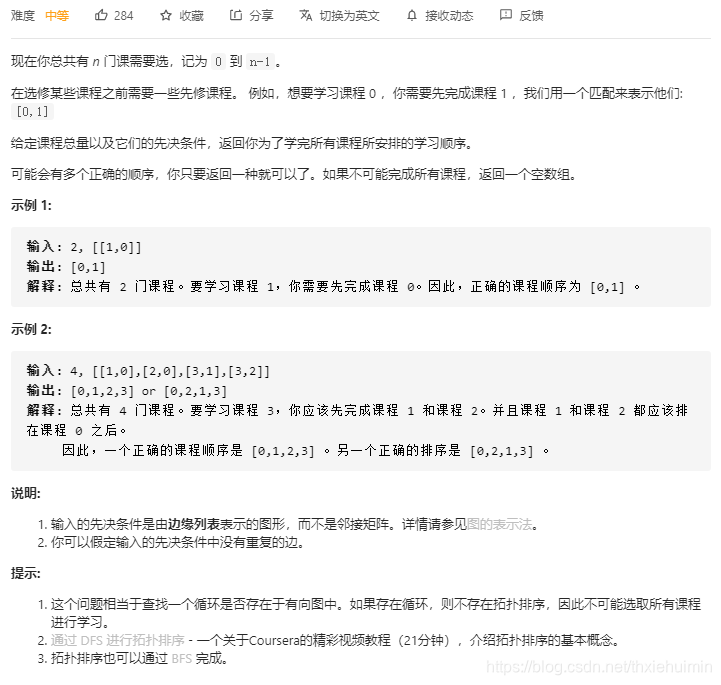
207. 课程表(中等)
思路
广度优先遍历,见代码备注
class Solution(object):
def canFinish(self, numCourses, prerequisites):
"""
:type numCourses: int
:type prerequisites: List[List[int]]
:rtype: bool
"""
edges = collections.defaultdict(list)
indegree = [0]*numCourses
for lesson in prerequisites:
edges[lesson[1]].append(lesson[0]) # 学习lesson[0]前需要学习lesson[1]
indegree[lesson[0]]+= 1 # lesson[0]的入度加1
# 当课程的入度为0时,添加至队列中,即该课程无先修课程
queue = [l for l in range(numCourses) if indegree[l]==0]
learned = 0
while queue:
prerequisite = queue.pop(0) # 取出队列第一个课程
learned += 1 # 可以学习的课程数加1
for cur in edges[prerequisite]: # edges[prerequisite]为cur的先修课程
indegree[cur] -= 1 # cur当前课程的入度减1
if indegree[cur] == 0: # 当前课程入度为0时,添加至队列中
queue.append(cur)
return learned==numCourses # 返回学习的课程数是否等于总课程数
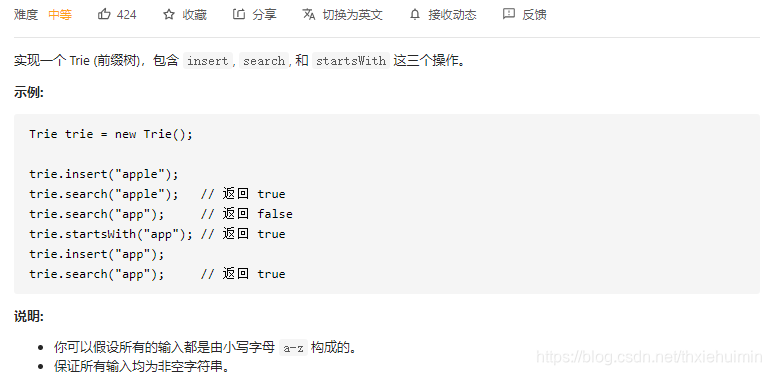
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)(中等)
思路
见代码备注
class Trie(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.root = {"is_end":True}
def insert(self, word):
"""
Inserts a word into the trie.
:type word: str
:rtype: None
"""
node = self.root
# 如word="apple" 得到{'is_end': True, 'a': {'p': {'p': {'l': {'e': {'is_end': True}}}}}}
for c in word:
if c in node.keys(): # 字母存在前缀树中时,node指向改字母
node = node[c]
else: # 字母不存在前缀树中时,添加字母至前缀树中,并将node指向该字母
node[c] = dict()
node = node[c]
node["is_end"] = True
def search(self, word):
"""
Returns if the word is in the trie.
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
node = self.root
for c in word:
if c in node.keys():
node = node[c]
else:
return False
if "is_end" in node.keys(): # word是否存在前缀树中
return True
else:
return False
def startsWith(self, prefix):
"""
Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix.
:type prefix: str
:rtype: bool
"""
node = self.root
for c in prefix:
if c in node.keys():
node = node[c]
else:
return False
return True # prefix存在前缀树中
# Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = Trie()
# obj.insert(word)
# param_2 = obj.search(word)
# param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix)
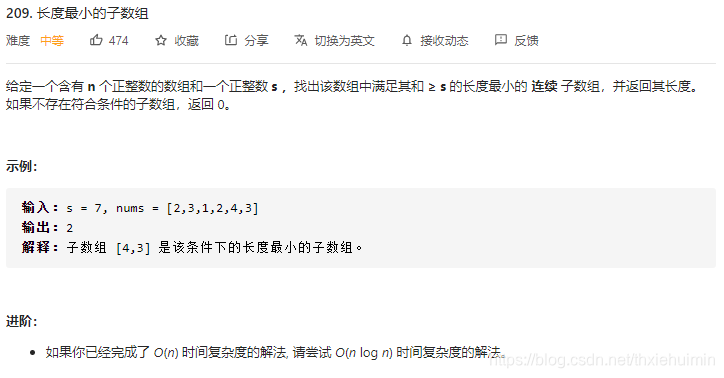
209. 长度最小的子数组(中等)
思路
双指针:
i指向0,j往右滑动。符合题目要求时,当ans为0时,计算符合要求的子数组长度,ans不为0时,比较原ans和新计算的值取其较小值
class Solution(object):
def minSubArrayLen(self, s, nums):
"""
:type s: int
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
i, ans, sumNums = 0, 0, 0
for j in range(len(nums)):
sumNums += nums[j]
while sumNums>=s:
ans = j-i+1 if ans==0 else min(ans, j-i+1)
sumNums -= nums[i]
i += 1
return ans
210. 课程表 II(中等)
思路
参考 207. 课程表
class Solution(object):
def findOrder(self, numCourses, prerequisites):
"""
:type numCourses: int
:type prerequisites: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
edges = collections.defaultdict(list)
indegrees = [0]*numCourses # 每节课的入度
for lesson in prerequisites:
edges[lesson[1]].append(lesson[0])
indegrees[lesson[0]] += 1
queue = [l for l in range(numCourses) if indegrees[l]==0]
learned = list()
while queue:
prerequisite = queue.pop(0)
learned.append(prerequisite)
for cur in edges[prerequisite]:
indegrees[cur] -= 1
if indegrees[cur] == 0:
queue.append(cur)
if len(learned) == numCourses:
return learned
else:
return []
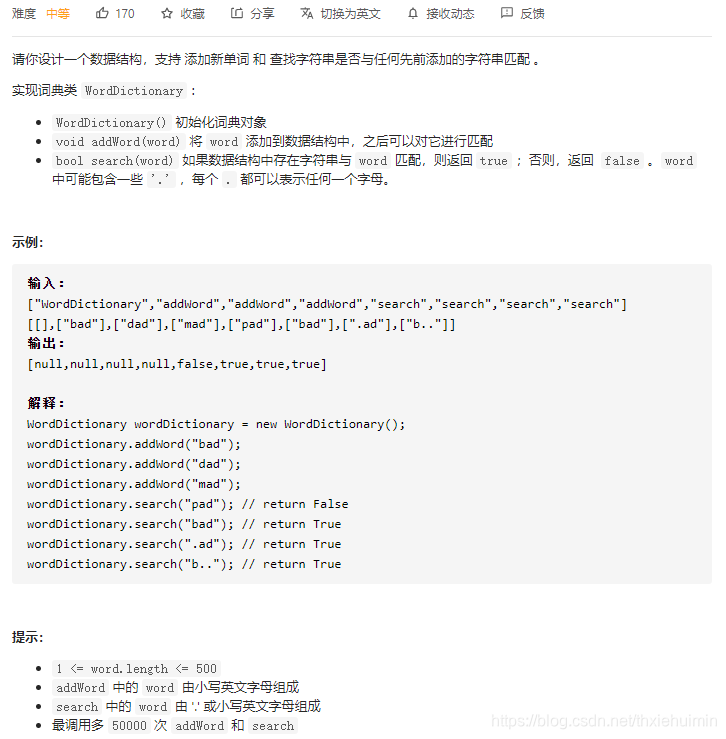
211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计(中等)
思路
参考 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
class WordDictionary(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.root = {"is_end":dict()}
def addWord(self, word):
"""
Adds a word into the data structure.
:type word: str
:rtype: None
"""
node = self.root
for c in word:
if c in node.keys():
node = node[c]
else:
node[c] = dict()
node = node[c]
node["is_end"] = dict()
def search(self, word):
"""
Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
:type word: str
:rtype: bool
"""
return self.__search(word, self.root)
def __search(self, word, trie): # 回溯
if not word: # word是否存在前缀树trie中
if "is_end" in trie.keys():
return True
return False
if word[0] == ".": # 当字符为“.”时,对比下一个字符
for c in trie:
if self.__search(word[1:], trie[c]):
return True
elif word[0] in trie.keys(): # 当字符存在trie时,对比下一个字符
if self.__search(word[1:], trie[word[0]]):
return True
return False
# Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = WordDictionary()
# obj.addWord(word)
# param_2 = obj.search(word)
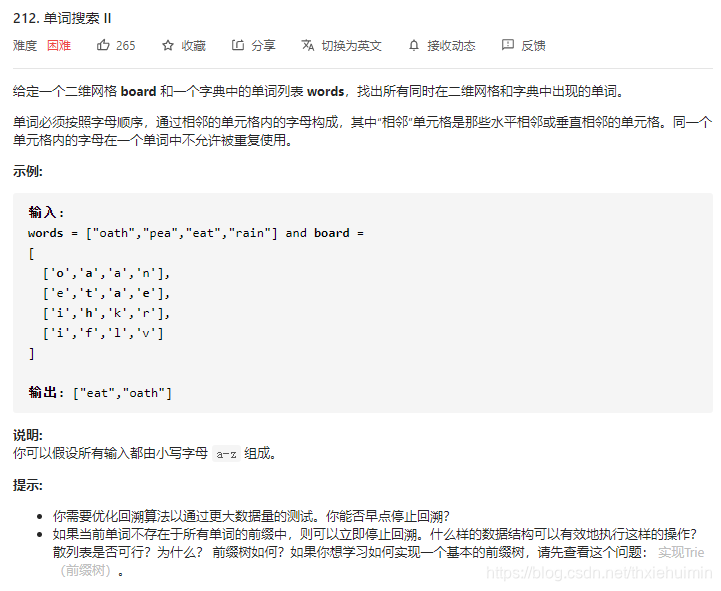
212. 单词搜索 II(困难)
思路
- 将words以前缀树结构Trie保存起来
- 在board中寻找word,参考 211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计 的search()
class Solution(object):
def findWords(self, board, words):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:type words: List[str]
:rtype: List[str]
"""
def search(row, col, trie): # 回溯
curNode = trie[board[row][col]] # 指向trie当前结点
visited.append((row, col)) # 添加已访问的结点
if "is_end" in curNode.keys(): # 指向is_end时,存在该单词,保存在ans中
if curNode["is_end"] not in ans: # 去重
ans.append(curNode["is_end"])
for i, j in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]: # 上下左右
newRow, newCol = row+i, col+j
if 0 <= newRow < m and 0 <= col + j < n: # 在合法范围内移动
if (newRow, newCol) not in visited: # 在该单词内未访问过的点
if board[newRow][newCol] in curNode.keys(): # 字符匹配
search(newRow, newCol, curNode)
visited.pop()
trie = dict()
for word in words:
node = trie
for c in word:
node = node.setdefault(c, dict())
node["is_end"] = word
ans = list()
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
for i in range(m): # 遍历board,当board[i][j]出现在trie时,查找对应的单词
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j] in trie:
visited = []
search(i, j, trie)
return ans
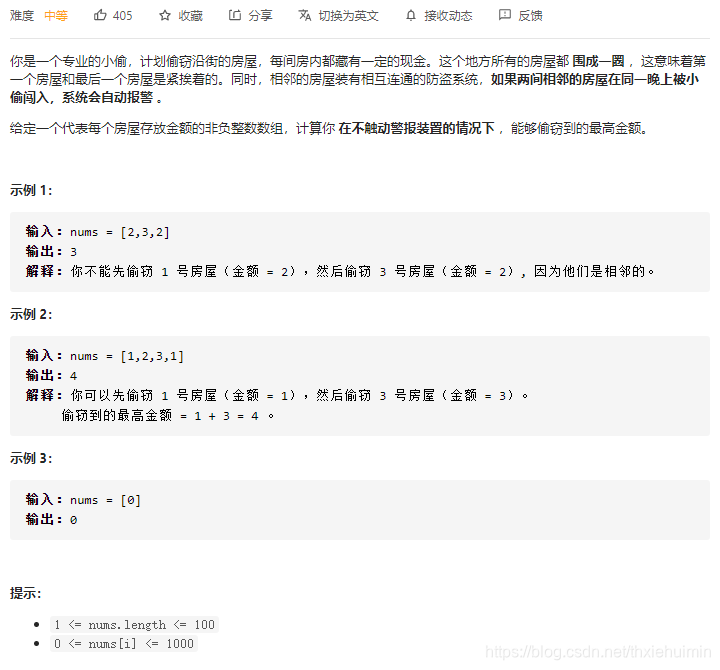
213. 打家劫舍 II(中等)
思路
- 参考 198. 打家劫舍
- 1~nums.length(去掉第一个房屋) 和 0~nums.length-1(去掉最后一个房屋)分别遍历一次
class Solution(object):
def rob(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
return max(self.__rob(nums[:n-1]), self.__rob(nums[1:n])) if n>1 else nums[0]
def __rob(self, nums):
pre, cur = 0, 0
for num in nums:
# i-2(pre)房屋得到的现金和i房屋相加 与 i-1(cur)(不能与i房屋相加)能得到的现金相比较选择较大值
cur, pre = max(num+pre, cur), cur
return cur
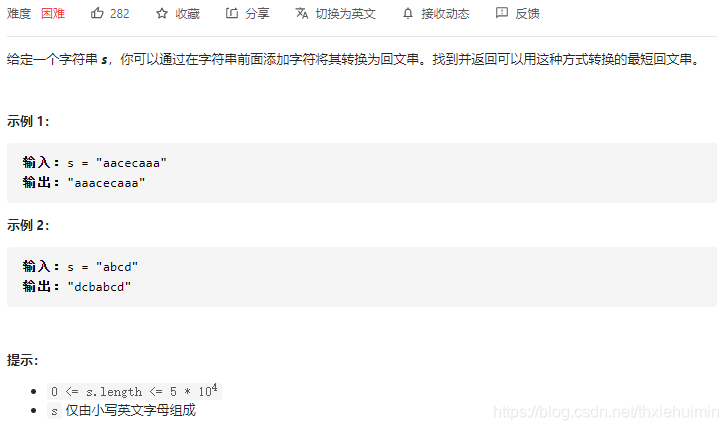
214. 最短回文串(困难)
思路
找出s本身最长回文串s[:i],剩下s[i:]为非回文,将s[i:]逆序后拼接在s字符串前即可
栗子:
s = “abcd”
s的最长回文串s[:i]:“a”
s剩下字符为非回文串s[i:]:“bcd”–>“dcb”(逆序)
将s[i:]逆序拼接在s字符串前:“dcbabcd”
class Solution(object):
def shortestPalindrome(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
r = s[::-1]
if r == s:
return s
for i in range(1, len(s)):
if s[:-i] == r[i:]:
return r[:i]+s
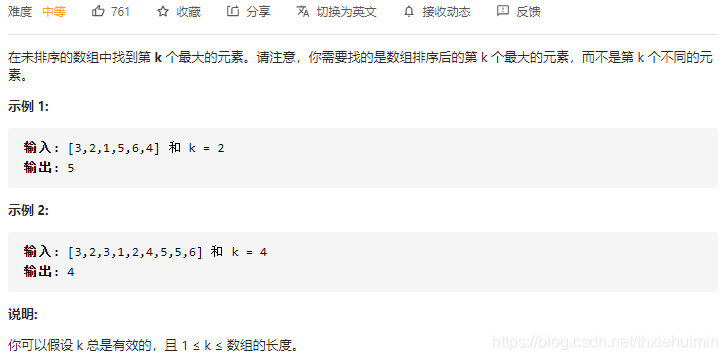
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素(中等)
思路
排序后输入倒数第k个
class Solution(object):
def findKthLargest(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
def quickSort(nums, left, right): # 快排
if left < right:
i, j = left, right
key = nums[i]
while i < j:
while i < j and nums[j] > key:
j -= 1
nums[i] = nums[j]
while i < j and nums[i] <= key:
i += 1
nums[j] = nums[i]
nums[i] = key
quickSort(nums, left, i-1)
quickSort(nums, i+1, right)
quickSort(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
return nums[-k]
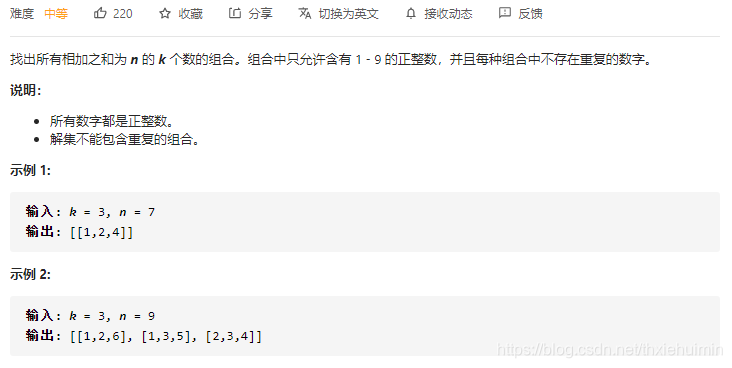
216. 组合总和 III(中等)
思路
参考 39. 组合总和 和 40. 组合总和 II 回溯
index:[1-9]
sub:[1-9]的子集
sumn:sub子集的和
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum3(self, k, n):
"""
:type k: int
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def solve(index, sub, sumn): # 回溯
if sumn == n and len(sub)==k:
if sub not in ans:
ans.append(sub)
return
if sumn > n or index > 9 or len(sub) > k:
return
if sumn + index <=n:
solve(index+1, sub+[index], sumn+index) # 将index添加至sub中
solve(index+1, sub, sumn)
ans = list()
solve(1, [], 0)
return ans
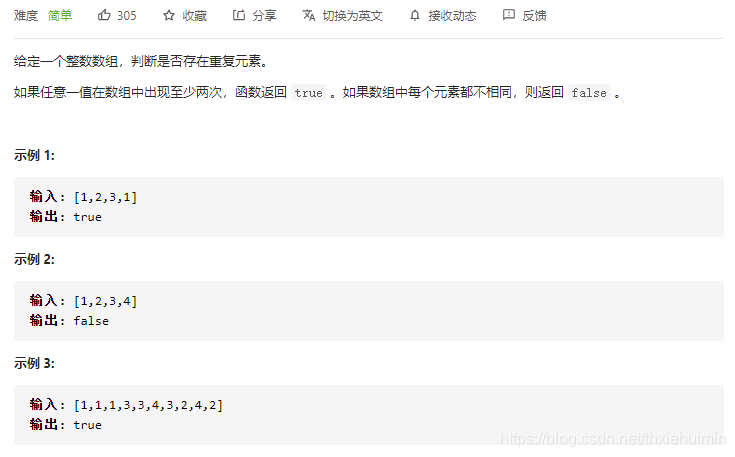
217. 存在重复元素(简单)
思路
- 出现重复的数即返回True
- 不存在重复的数返回False
class Solution(object):
def containsDuplicate(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
nonrepeat = set()
for num in nums:
if num in nonrepeat:
return True
else:
nonrepeat.add(num)
return False
218. 天际线问题(困难)
思路
- 将所有x轴坐标添加至x中,左端点高度记录为负,右端点高度记录为正
- 遍历x轴的端点,遇到左端点,将高度入堆heights。遇到右端点,将高度出堆heights(heights为最小堆,高度加负号即为最大堆)
列表排序:
x.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], -x[1]))
heapq:是一种优先队列。优先队列让你能够以任意顺序添加对象,并随时(可能是在两次添加对象之间)找出(并删除)最小的元素。它们虽然不是严格排序的,但必须保证一点:位置i处的元素总是大于位置i // 2处的元素(反过来说就是小于位置2 * i和2 * i + 1处的元素)。这是底层堆算法的基础,称为堆特征(heap property)
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| heappush(heap,x) | 将x压入堆中 |
| heappop(heap) | 从堆中弹出最小的元素 |
| heapify(heap) | 让列表具备堆特征 |
| heapreplace(heap,x) | 弹出最小的元素,并将x压入堆中 |
| nlargest(n, iter) | 返回iter中n个最大的元素 |
| nsmallest(n, iter) | 返回iter中n个最小的元素 |
import heapq
class Solution(object):
def getSkyline(self, buildings):
"""
:type buildings: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
x = list()
heights = [0] # 保存当前位置的所有高度
last = [0, 0] # 保存上个位置转折点的横左边和高度
visited = list() # 保存右端点位置的高度
ans =[[0,0]]
for building in buildings:
x.append([building[0], -building[2]]) # 记录左端点,高度为负
x.append([building[1], building[2]]) # 记录右端点,高度为正
x.sort() # 对x列表排序
for point in x:
if point[1] < 0: # 左端点,将高度如入最小堆(最小值始终在第一位)
heapq.heappush(heights, point[1])
else: # 右端点,移除该端点对应的高度
visited.append(point[1])
while visited and -heights[0] in visited:
tmp = -heights[0]
heapq.heappop(heights)
visited.remove(tmp)
maxHeight = -heights[0]
# 转折点:上一个位置的高度不等于当前位置的最高高度,更新last,将last添加至ans中
if last[-1] != maxHeight:
last = [point[0], maxHeight]
# 该位置的横坐标与ans中最后一个转折点的横坐标相同,去除ans中最后一个转折点
if point[0] == ans[-1][0]:
ans.pop()
if not ans:
ans.append(last[:])
# 最高高度与ans中最后一个转折点的高度不相同时,添加至答案中
elif maxHeight != ans[-1][1]:
ans.append(last[:])
if [0, 0] in ans:
return ans[1:]
return ans
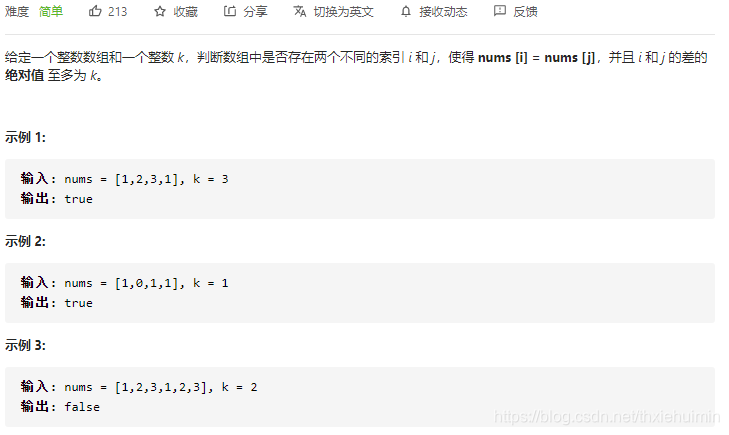
219. 存在重复元素 II(简单)
思路
- 创建visited集合,保存nums长度为k的集合
- 遍历nums的数,判断是否在visited中,是则返回True,否则添加至visited中
class Solution(object):
def containsNearbyDuplicate(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: bool
"""
visited = set()
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] in visited: # nums[i]存在visited中返回True
return True
else:
visited.add(nums[i]) # nums[i]不存在visited中,添加nums[i]至visited中
if len(visited) > k: # 当visited长度大于k时,弹出nums[i-k]
visited.remove(nums[i-k])
return False # 没有符合条件的重复元素
思路
- 判断nums长度小于等于k时是否存在重复元素
- 判断nums倒数k个元素内是否存在重复元素
- 判断nums[:n-k]中是否存在符合条件的重复元素
- 没有符合条件的重复元素返回False
class Solution(object):
def containsNearbyDuplicate(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: bool
"""
n = len(nums)
if n <= k:
if len(set(nums)) != n: # nums长度小于等于k时存在重复元素
return True
else:
if len(set(nums[n-k:])) != k: # nums倒数k个元素内存在重复元素
return True
for i in range(n-k):
if nums[i] in nums[i+1:i+k+1]: # nums[:n-k]中存在符合条件的重复元素
return True
return False # 没有符合条件的重复元素
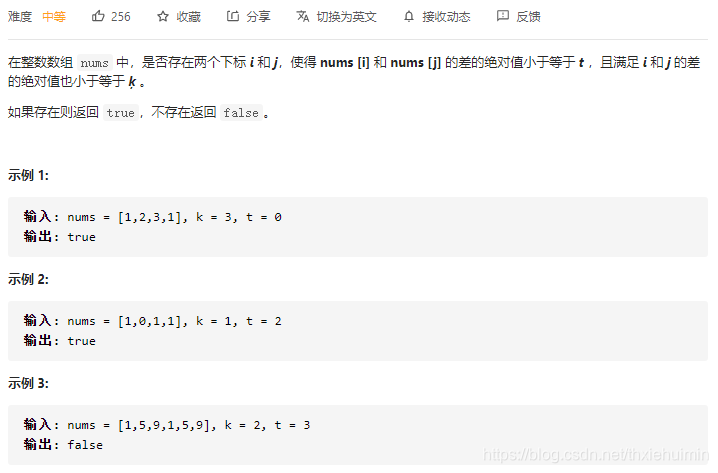
220. 存在重复元素 III(中等)
思路
参考 219. 存在重复元素 II (简单)
- 创建visited集合,保存nums长度为k的集合
- 遍历nums的数,判断nums[i]和在visited中num差的绝对值是否小于等于t,是则返回True,否则添加至visited中
class Solution(object):
def containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(self, nums, k, t):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:type t: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if k == 10000: # 放弃治疗
return False
visited = set()
for i in range(len(nums)):
for num in visited:
if nums[i]-t <= num <= nums[i] + t:
return True
visited.add(nums[i])
if len(visited) > k:
visited.remove(nums[i-k])
return False
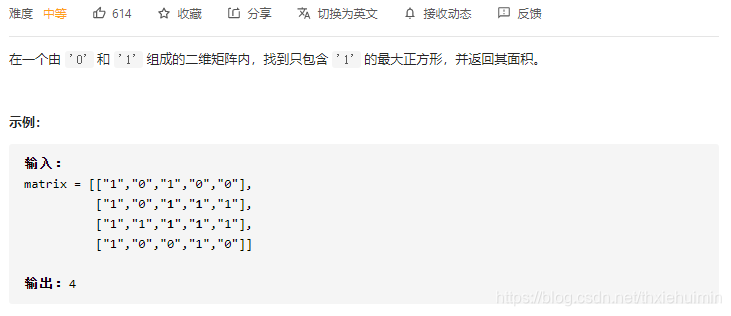
221. 最大正方形 (中等)
思路
动态规划
- 创建dp数组,第一行和第一列为1时,最大正方形变成为1,否则为0
- matrix[r][c]为1时,dp[r][c]的值由其左方、上方和左上方的三个相邻位置的dp值的最小值加1得到,状态转移方程:
d p [ r ] [ c ] = m i n ( d p [ r − 1 ] [ c ] , d p [ r ] [ c − 1 ] , d p [ r − 1 ] [ c − 1 ] ) + 1 dp[r][c] = min(dp[r-1][c], dp[r][c-1], dp[r-1][c-1]) + 1 dp[r][c]=min(dp[r−1][c],dp[r][c−1],dp[r−1][c−1])+1
class Solution(object):
def maximalSquare(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[str]]
:rtype: int
"""
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return 0
m, n, maxSide = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]), 0
dp = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
for r in range(m):
for c in range(n):
if matrix[r][c] == "1": # 遇到1的时候
if r==0 or c==0: # 第一行与第一列
dp[r][c] = 1
else:
# 左方、上方和左上方的最小值加1
dp[r][c] = min(dp[r-1][c], dp[r][c-1], dp[r-1][c-1]) + 1
maxSide = max(maxSide, dp[r][c])
return maxSide*maxSide
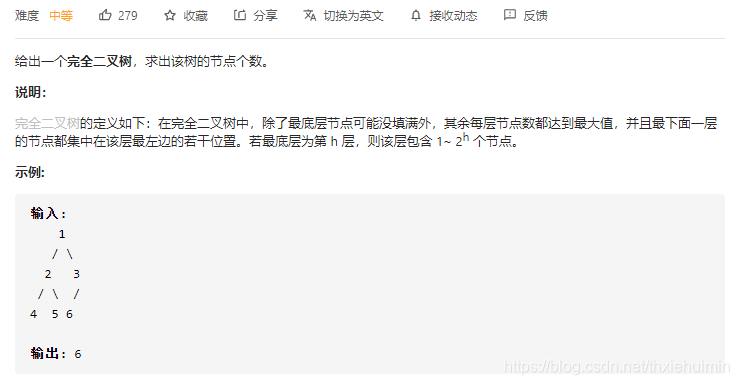
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数(中等)
思路
先序遍历计算节点数
class Solution(object):
def countNodes(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
def preorder(root):
return 0 if not root else 1 + preorder(root.left) + preorder(root.right)
return preorder(root)
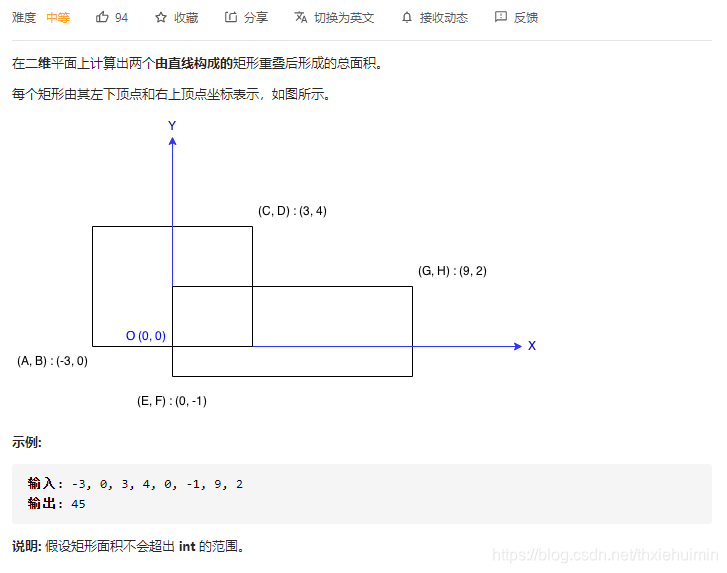
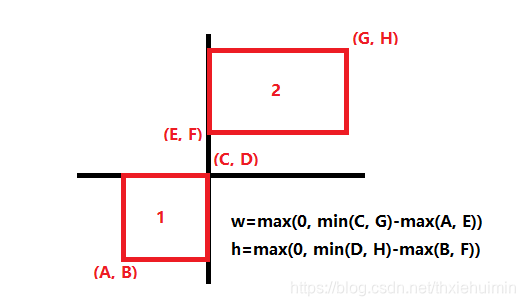
223. 矩形面积(中等)
思路
矩形1面积+矩形2面积-相交面积
矩形面积:(A, B)为左下角, (C, D)为右上角,面积为(C-A)*(D-B)
相交面积:
w
×
h
w \times h
w×h
相交的x坐标宽度w:矩形1和矩形2右上角x坐标较小值min(C, G)减矩形1和矩形2左下角x坐标较大值max(A, E),不相交时为负取0,即
w
=
m
a
x
(
0
,
m
i
n
(
C
,
G
)
−
m
a
x
(
A
,
E
)
)
w=max(0, min(C, G)-max(A, E))
w=max(0,min(C,G)−max(A,E))
相交的y坐标高度h:矩形1和矩形2右上角y坐标较小值min(D, H)减矩形1和矩形2左下角y坐标较大值max(B, F),不相交时为负取0,即
h
=
m
a
x
(
0
,
m
i
n
(
D
,
H
)
−
m
a
x
(
B
,
F
)
)
h=max(0, min(D, H)-max(B, F))
h=max(0,min(D,H)−max(B,F))
class Solution(object):
def computeArea(self, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H):
"""
:type A: int
:type B: int
:type C: int
:type D: int
:type E: int
:type F: int
:type G: int
:type H: int
:rtype: int
"""
w = max(0, min(C, G)-max(A, E))
h = max(0, min(D, H)-max(B, F))
return (C-A)*(D-B)+(G-E)*(H-F)-w*h
224. 基本计算器(困难)
思路
- 遍历s字符串,遇到数字,构建为操作数operand
- 遇到运算符+/-时,ans累加+/-号前的操作数operand
- 遇到左括号(,将已计算的ans和运算符sign入栈,即stack=[ans, sign]。重置ans和sign继续步骤1,2计算括号内的公式
- 遇到右括号),ans累加右括号)前的操作数,得到括号内的运算结果后,运算符sign出栈,为括号前的正负符号。括号前的运算结果出栈然后累加,即stack.pop()+/-(ans)。
- 返回ans累加最后一个数,即ans+/-operand
class Solution(object):
def calculate(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
operand = 0 # 操作数
sign = 1 # 1为正式,0为负数
ans = 0
stack = list()
for c in s:
if c.isdigit(): # 字符为数字,添加至操作数中
operand = operand*10+int(c)
elif c=="+":
ans += sign*operand # ans累加正号前一个数
sign, operand = 1, 0 # 将sign至为1,operand归0
elif c=="-":
ans += sign*operand # ans累加负号前一个数
sign, operand = -1, 0 # 将sign至为-1,operand归0
elif c=="(":
stack.append(ans) # (前得到的运算结果入栈
stack.append(sign) # sign运算符入栈
ans, sign = 0, 1
elif c==")":
ans += sign*operand
ans *=stack.pop() # 运算符sign出栈,为括号前的正负符号
ans += stack.pop()
operand = 0
return ans+sign*operand
225. 用队列实现栈(简单)
思路
所见即所得
class MyStack(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.a = list()
def push(self, x):
"""
Push element x onto stack.
:type x: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.a.append(x)
def pop(self):
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
:rtype: int
"""
return self.a.pop()
def top(self):
"""
Get the top element.
:rtype: int
"""
return self.a[-1]
def empty(self):
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
:rtype: bool
"""
return not self.a
# Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyStack()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.top()
# param_4 = obj.empty()
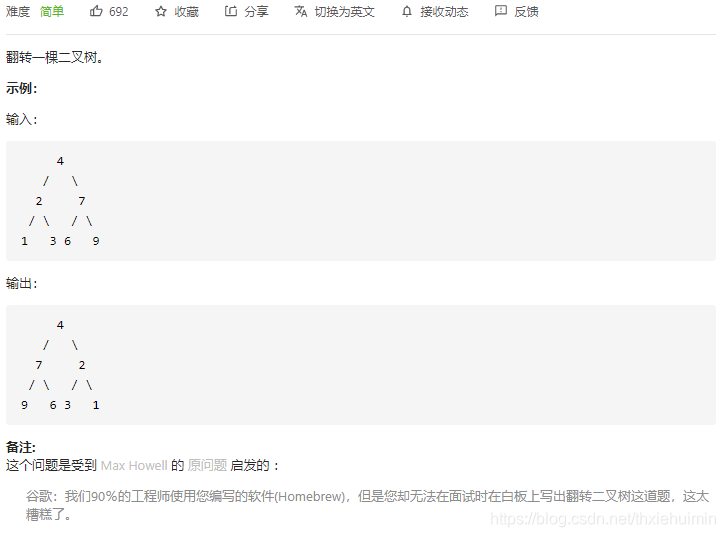
226. 翻转二叉树(简单)
思路
递归
class Solution(object):
def invertTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root:
return root
right = self.invertTree(root.left)
left = self.invertTree(root.right)
root.left, root.right = left, right
return root
227. 基本计算器 II(中等)
思路
参考 224. 基本计算器(困难)
- 在第一个字符前添加运算符+,如s=“3+2*2"可以得到+3+2+2,成对的,创建stack,遇到运算符±时或到最后一个字符时(i=len(s)-1),将前一个数压入stack中,如遍历到s[1]=”+"时,将operand=3压入stack中
- 遇到运算符为*/时,栈顶元素与当前operand相乘或相除
- 将栈内元素累加得到结果
class Solution(object):
def calculate(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
operand = 0
sign = "+"
stack = list()
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i].isdigit():
operand = operand*10+int(s[i])
if s[i] in ["+", "-", "*", "/"] or i == len(s)-1:
if sign == "+":
stack.append(operand)
elif sign == "-":
stack.append(-operand)
elif sign == "*" or sign == "/":
stack[-1] = stack[-1]*operand if sign == "*" else int(stack[-1]*1.0/operand)
operand = 0
sign = s[i]
return sum(stack)
228. 汇总区间(简单)
思路
- 初始化j=0,遍历nums的数,当nums[i+1]等于nums[i]+1时,说明是在同一区间,i往后遍历直到nums[i+1]不等于nums[i]+1;
- 当nums[i+1]不等于nums[i]+1时,若i坐标与j一致时,说明nums[i]为单独一个数,没有连续区间。若i不等于j时,j为区间开始坐标,i为区间结束坐标,添加区间至ans后,更新j坐标为i+1
class Solution(object):
def summaryRanges(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[str]
"""
n = len(nums)
ans = list()
j = 0
for i in range(n):
if i+1 < n and nums[i+1]==nums[i]+1:
continue
if i == j:
ans.append(str(nums[j]))
else:
ans.append(str(nums[j]) + "->" + str(nums[i]))
j = i+1
return ans
229. 求众数 II(中等)
思路
摩尔投票法(两个阶段:1.对抗阶段 2.计数阶段)
- 对抗阶段:获选人的票数互相低消
- 计数阶段:计算剩下的候选人的票数是否符合要求
一个大小为n的整数数组,超过 ⌊ n/3 ⌋ 次的元素最多有2个,选出两个候选人,确定票数是否满足大于 N/3
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ans = list()
n = len(nums)
if not nums:
print(ans)
cand1, cand2, count1, count2 = nums[0], nums[0], 0, 0
# 1.对抗阶段:获选人的票数互相低消
for num in nums:
if cand1==num: # 候选人cand1与num相等时,count1票数增加1
count1 += 1
elif cand2==num: # 候选人cand2与num相等时,count2票数增加1
count2 += 1
elif count1==0: # 候选人cand1的票数为0时,更换候选人cand1为num
cand1 = num
count1 += 1
elif count2==0: # 候选人cand2的票数为0时,更换候选人cand2为num
cand2 = num
count2 += 1
else: # 候选人cand1和cand2的与num不相等时,低消票数
count1 -= 1
count2 -= 1
# 2.计数阶段:计算剩下的候选人的票数是否符合要求
count1, count2 = 0, 0 # 初始化两个候选人的票数为0
for num in nums:
if cand1==num:
count1 += 1
elif cand2==num:
count2 += 1
if count1 > n//3:
ans.append(cand1)
if count2 > n//3:
ans.append(cand2)
return ans
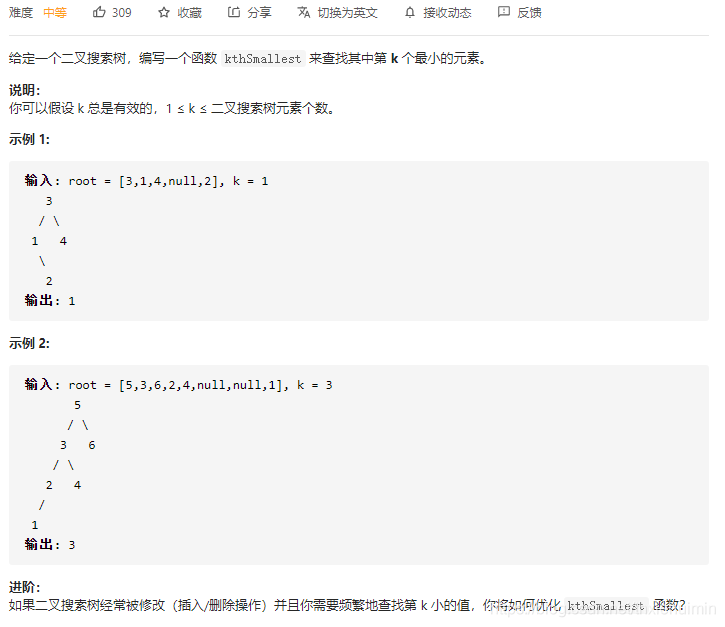
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素(中等)
思路
中序遍历二叉搜索树返回第k-1个
class Solution(object):
def inorder(self, root):
return [] if not root else self.inorder(root.left) + [root.val] + self.inorder(root.right)
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
return self.inorder(root)[k-1]
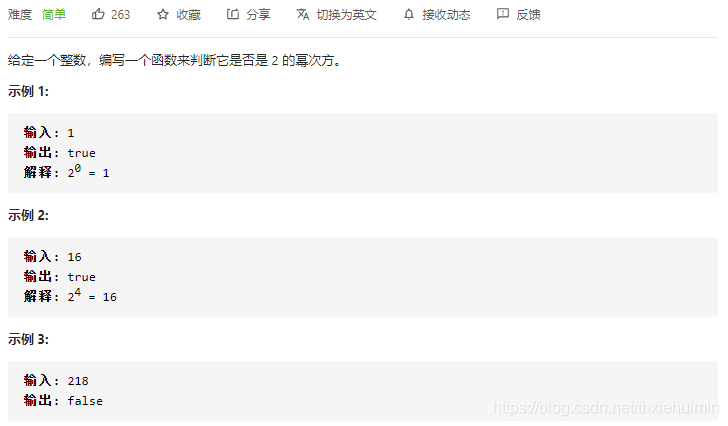
231. 2的幂(简单)
思路
2的幂次方n二进制为1000…,其n-1的二进制为0111…,与操作后得到0,即为2的幂次方
class Solution(object):
def isPowerOfTwo(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if n==0:
return False
return True if n&n-1==0 else False
232. 用栈实现队列(简单)
思路
参考225. 用队列实现栈(简单)
class MyQueue(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.a = list()
def push(self, x):
"""
Push element x to the back of queue.
:type x: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.a.append(x)
def pop(self):
"""
Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.
:rtype: int
"""
return self.a.pop(0)
def peek(self):
"""
Get the front element.
:rtype: int
"""
return self.a[0]
def empty(self):
"""
Returns whether the queue is empty.
:rtype: bool
"""
return not self.a
# Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyQueue()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.peek()
# param_4 = obj.empty()
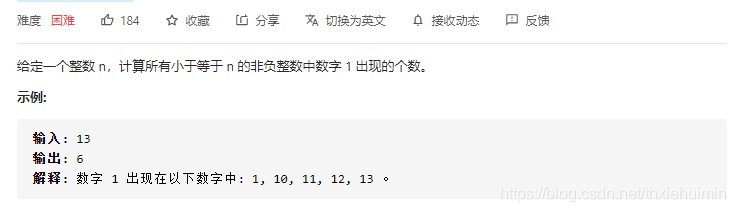
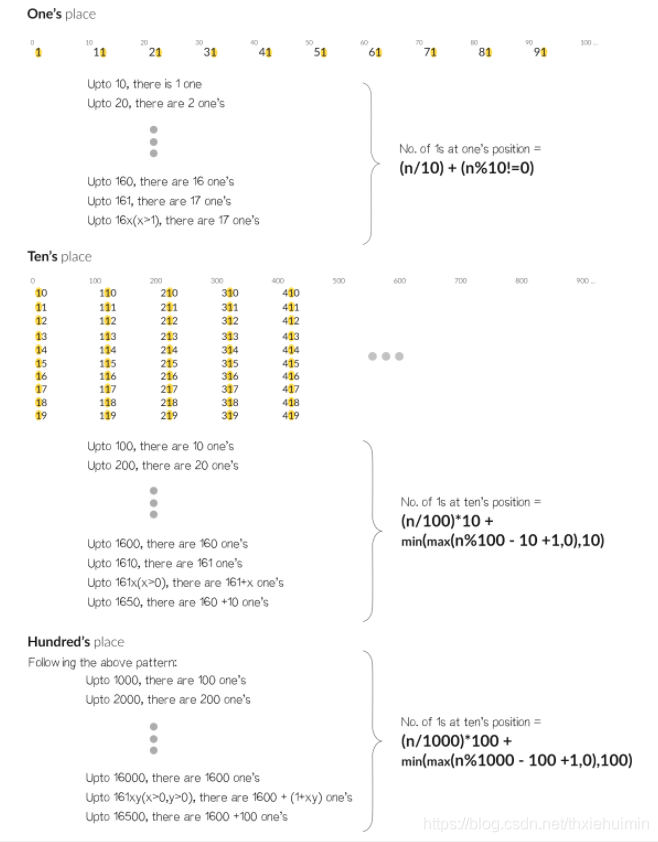
233. 数字 1 的个数(困难)
思路
分别计算n在个位(1个),十位(每十位的个位出现1次,如11,21,31…),百位(每百位的十位出现10次,如110,111,112…210,211,212…)…的1出现的个数后累加求和
由规律得到公式:
(
n
/
10
∗
i
)
∗
i
+
m
i
n
(
m
a
x
(
n
%
10
∗
i
−
i
+
1
,
0
)
,
i
)
(n/10*i)*i+min(max(n\%10*i-i+1, 0), i)
(n/10∗i)∗i+min(max(n%10∗i−i+1,0),i)
class Solution(object):
def countDigitOne(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
i, ans = 1, 0
while i <= n:
ans =ans + (n//(10*i))*i+min(max(n%(10*i)-i+1, 0), i)
i *= 10
return ans
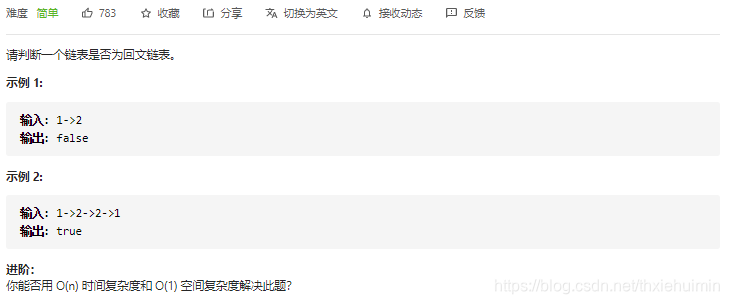
234. 回文链表(简单)
思路
将结点的值保存在列表中,判别是否回文
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
tmp = head
ans = list()
while tmp:
ans.append(tmp.val)
tmp = tmp.next
return ans==ans[::-1]
思路
- 用快慢指针找到链表的中间结点
- 反转链表后半部分
- 判断是否回文,对比链表的前半部分和反转的后部分是否相同
class Solution(object):
# 快慢指针, slow指向链表中间
def halfList(self, head):
slow, fast = head, head
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# 206. 反转链表(简单)
def reverseList(self, head):
p, c = None, head
while c:
n = c.next
c.next = p
p = c
c = n
return p
def isPalindrome(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not head or head.next==None:
return True
first = head # 链表前半部分
slow = self.halfList(head) # 找到中间结点
second_start = self.reverseList(slow.next) # 反转链表后半部分
second = second_start # 链表后半部分
while second!=None: # 判断是否回文,对比链表的前半部分和反转的后部分是否相同
if first.val != second.val:
return False
first = first.next
second = second.next
# 还原链表
first.next = self.reverseList(second_start)
return True
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先(简单)
思路
遍历二叉搜索树,当遍历的结点x均大于p和q时,p和q均在x的左子树中;当x均小于p和q时,p和q均在x的右子树中;否则x未p和q的分叉点,即最近的公共祖先
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
x = root
while x:
if p.val < x.val and q.val < x.val:
x = x.left
elif p.val > x.val and q.val > x.val:
x = x.right
else:
return x
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先(中等)
思路
递归:后续遍历(左-右-根)
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
ans = None
def helper(self, root, p, q):
if not root:
return False
left = self.helper(root.left, p, q)
right = self.helper(root.right, p, q)
if (left and right) or ((root.val==p.val or root.val==q.val) and (right or left)):
self.ans = root
# p/q分别存在左右子树中 或 遍历的结点为p/q
return left or right or (root.val==p.val or root.val==q.val)
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
self.helper(root, p, q)
return self.ans
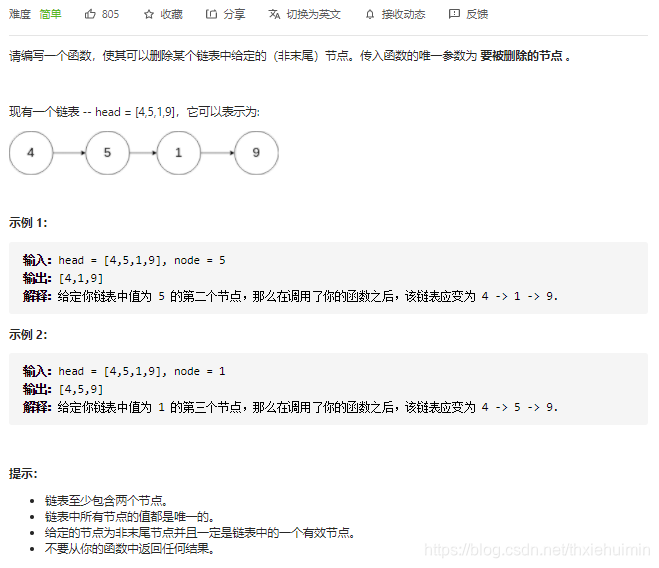
237. 删除链表中的节点 (简单)
思路
就酱
class Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, node):
"""
:type node: ListNode
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
"""
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next
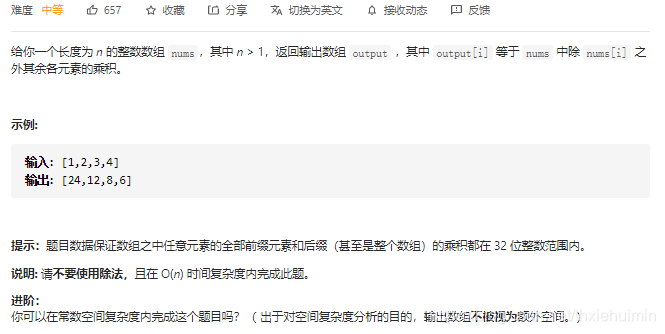
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积(中等)
思路
遍历两遍:
第一遍: 计算从左0到i-1的乘积L存在输出数组output[i]中,即output[i]=L(nums[i-1]*output[i-1])
第二遍: 计算从右n-1到i+1的乘积R,更新output[i]=output[i]R,即output[i] = LR(L:i坐标左边数字的乘积,R:i右边数字的乘积)
class Solution(object):
def productExceptSelf(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
n = len(nums)
output = [1 for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(1, n):
output[i] = nums[i-1]*output[i-1]
R = 1
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
output[i] = output[i]*R
R *= nums[i]
return output
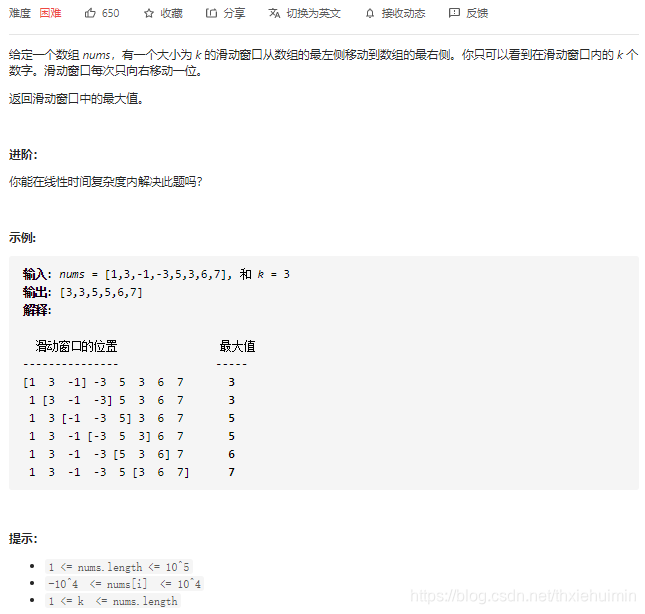
239. 滑动窗口最大值(困难)
思路
双向队列:
- 处理前k个元素,得到值最大的坐标maxIdx
- 遍历数组:将最大值坐标maxIdx保存在队列头部,当该坐标滑出窗口范围后,将其移出队列;2. 遍历当前值时,将比当前值小的索引移出队列后,将当前值索引添加至双向队列中。最后将队列头部添加至输出队列中
class Solution(object):
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
n = len(nums)
if n*k==0:
return []
if k==1:
return nums
if n <=k:
return [max(nums)]
maxIdx, queue = 0, list() # 创建窗口最大值的索引和双向队列
for i in range(k):
while queue and nums[i] > nums[queue[-1]]: # 将比当前值小的索引移出队列
queue.pop()
queue.append(i) # 将当前值索引添加至双向队列中
if nums[i] > nums[maxIdx]: # 得到值最大的坐标maxIdx
maxIdx = i
ans = [nums[maxIdx]]
for i in range(k, n):
if queue and queue[0] == i-k: # 最大值坐标为i-k时不在窗口范围内(窗口范围为[i-k+1, i+1]),将其移除
queue.pop(0) # 移除队列头部
while queue and nums[i] > nums[queue[-1]]: # 将比当前值小的索引移出队列
queue.pop() # 移除队列尾部
queue.append(i) # 将当前值索引添加至双向队列中
ans.append(nums[queue[0]]) # 队列头部添加至输出队列中
return ans
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II (中等)
思路
就酱
class Solution(object):
def searchMatrix(self, matrix, target):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:type target: int
:rtype: bool
"""
for i in range(len(matrix)):
if target in matrix[i]:
return True
return False
241. 为运算表达式设计优先级(中等)
思路
递归
class Solution(object):
def diffWaysToCompute(self, input):
"""
:type input: str
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if input.isdigit(): # 纯数字时直接返回
return [int(input)]
ans = list()
for i, c in enumerate(input): # 遍历字符串
if c in ["+", "-", "*"]: # 字符是运算符时运算
left = self.diffWaysToCompute(input[:i]) # 求左边的操作数
right = self.diffWaysToCompute(input[i+1:]) # 求右边的操作数
for l in left:
for r in right:
if c == "+":
ans.append(l+r)
elif c == "-":
ans.append(l-r)
elif c == "*":
ans.append(l*r)
return ans
242. 有效的字母异位词(简单)
思路
哈希
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
sList=[0 for _ in range(26)]
tList=[0 for _ in range(26)]
for c in s:
sList[ord(c)-97] += 1
for c in t:
tList[ord(c)-97] += 1
return sList==tList
思路
排序
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
return sorted(s)==sorted(t)
243-256(无)
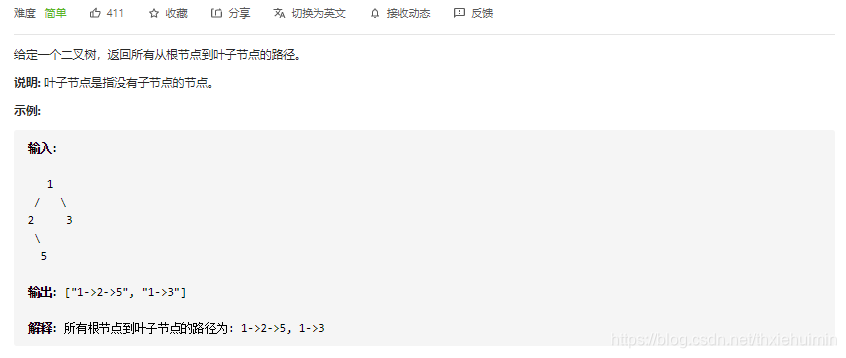
257. 二叉树的所有路径(简单)
思路
深度优先搜索
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ans = list()
def dfs(self, root, path):
if not root:
return []
path.append(str(root.val))
if not root.left and not root.right: # 叶子节点
self.ans.append("->".join(path))
else:
self.dfs(root.left, path)
self.dfs(root.right, path)
path.pop()
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[str]
"""
self.dfs(root, list())
return self.ans
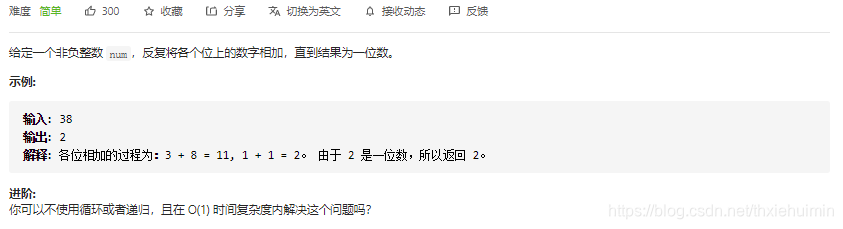
258. 各位相加(简单)
思路
普通循环计算
class Solution(object):
def addDigits(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: int
"""
ans = 0
while num>0:
ans += num%10
num //=10
if num == 0 and ans > 9: # ans大于9重新初始化num和ans
num = ans
ans = 0
return ans
259(无)
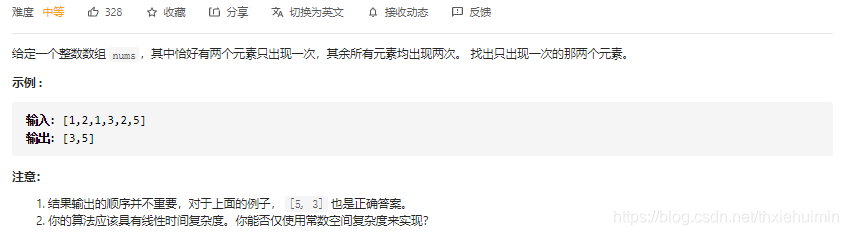
260. 只出现一次的数字 III(中等)
思路
- 创建visited1, visited2集合
- 未出现过的num添加至visited1中(全部数字),出现过的num添加至visited2中(出现两次的数)
- 返回visited1和visited2的差集
class Solution(object):
def singleNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
visited1, visited2 = set(), set()
for num in nums:
if num not in visited1:
visited1.add(num)
else:
visited2.add(num)
return list(visited1-visited2)
261 以图判树(中等)-无
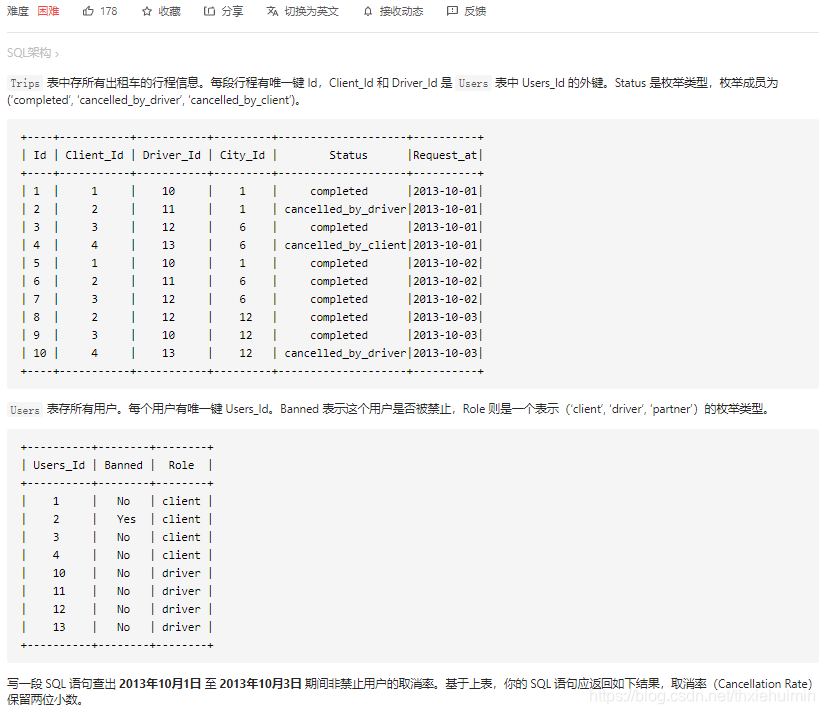
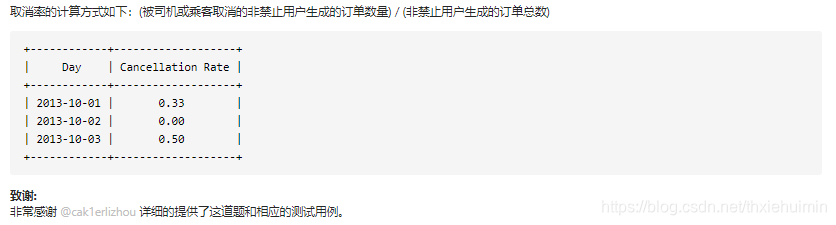
262 行程和用户(困难)
思路
- 对 client_id 和 driver_id 各自关联的 users_id,同时检测是否被禁止
- 按日期分组,统计每组的总行程数,取消行程数
- 取消率=每组取消的行程数/每组总行程数
# Write your MySQL query statement below
SELECT T.request_at AS `Day`,
ROUND(
SUM(
IF(T.STATUS='completed',0,1)
)
/
COUNT(T.STATUS),
2
) AS `Cancellation Rate`
FROM Trips AS T
JOIN Users AS U1 ON (T.client_id = U1.users_id AND U1.banned='No')
JOIN Users AS U2 ON (T.driver_id = U2.users_id AND U2.banned='No')
WHERE T.request_at BETWEEN '2013-10-01' AND '2013-10-03'
GROUP BY T.request_at
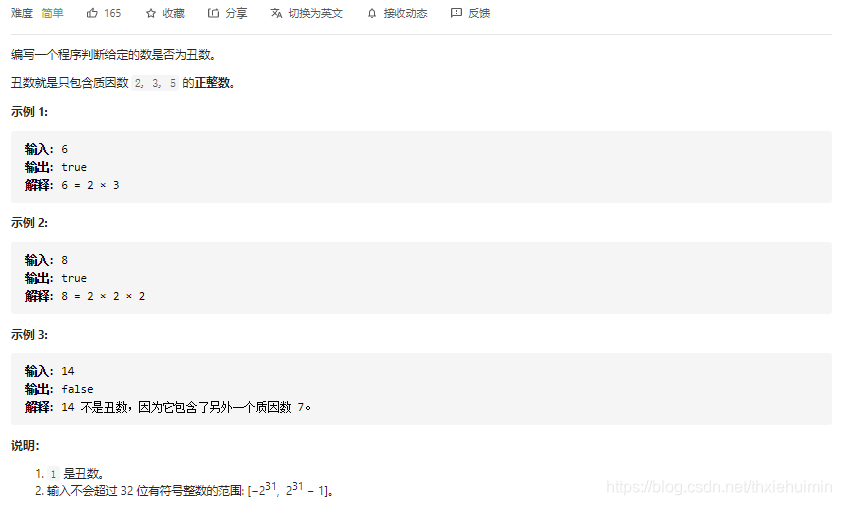
263. 丑数(简单)
思路
循环整除5, 3, 2后等于1为丑数,等于0不为丑数
class Solution(object):
def isUgly(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if num == 0:
return False
while num%5==0:
num //= 5
while num%3==0:
num //=3
while num%2==0:
num >>=1 # 二进制左移1位,即为除以2
return num == 1
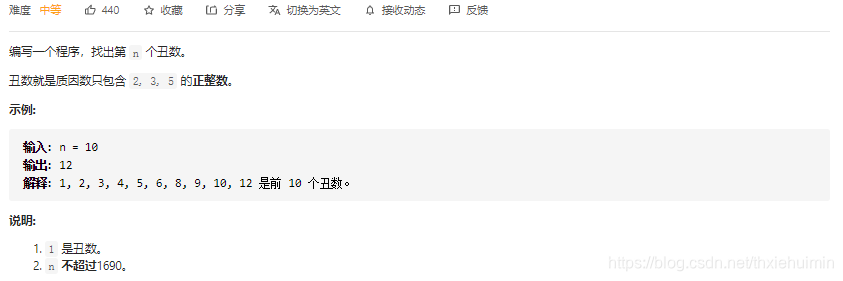
264. 丑数 II (中等)
思路
参考 263. 丑数(简单)
动态规划:
- 创建数组uglyNums添加第一个丑数,创建指针idx2, idx3, idx5初始化为0
- 往数组添加丑数:添加min(2uglyNums[idx2], 3uglyNums[3], 5*uglyNums[5])至nums中,得到从小到大排列的丑数数组uglyNums,并将对应的指针右移
- 当数组长度为n时,返回数组最后一个数即为uglyNum
class Solution(object):
def nthUglyNumber(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
uglyNums = [1]
idx2, idx3, idx5 = 0, 0, 0
for _ in range(1, n):
uglyNum = min(uglyNums[idx2]*2, uglyNums[idx3]*3, uglyNums[idx5]*5)
uglyNums.append(uglyNum)
if uglyNum == uglyNums[idx2]*2:
idx2 += 1
if uglyNum == uglyNums[idx3]*3:
idx3 += 1
if uglyNum == uglyNums[idx5]*5:
idx5 += 1
return uglyNums[-1]
265-267(无)
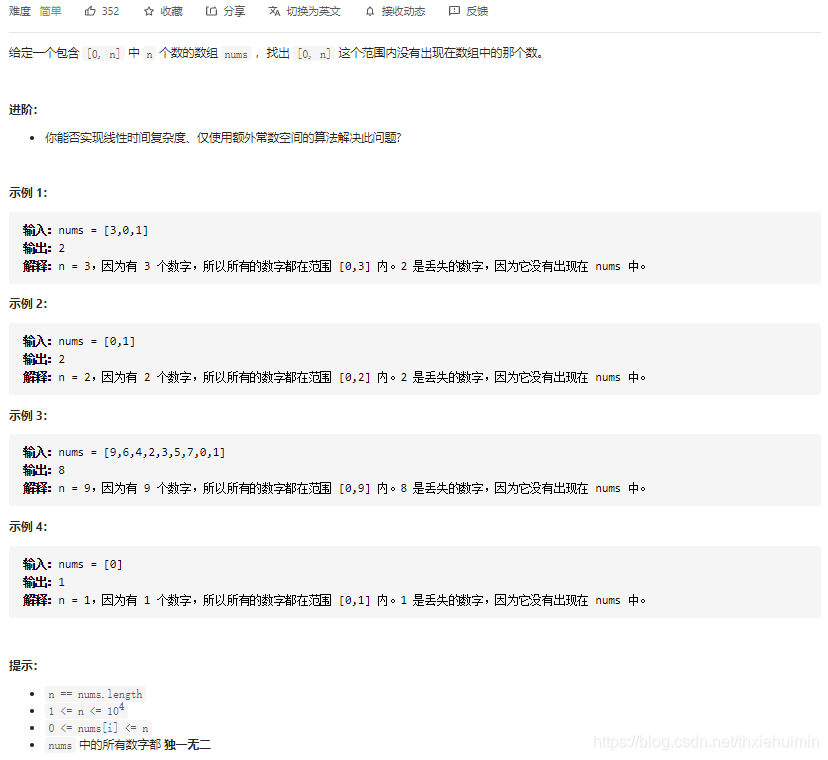
268. 丢失的数字(简单)
思路
参考 136. 只出现一次的数字
nums里的数和下标做异或操作:
初始化missingNum为len(nums)
没有出现的数字和下标异或:0^i = i
数字num和下标i相同时异或:num[i] ^ i = 0
class Solution(object):
def missingNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
missingNum = n
for i in range(n):
missingNum ^= nums[i] ^ i
return missingNum
思路
就酱
class Solution(object):
def missingNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
for num in range(len(nums)+1):
if num not in nums:
return num
269-272(无)
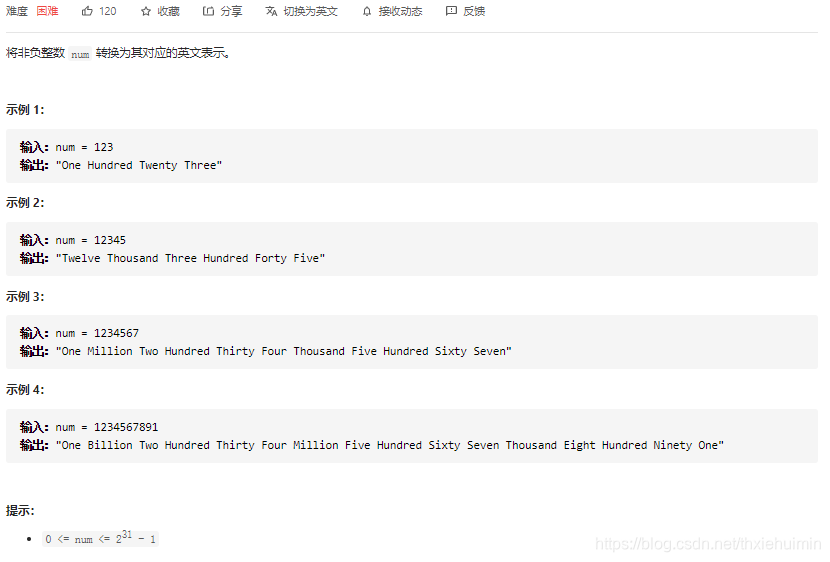
273. 整数转换英文表示(困难)
思路
就酱
class Solution(object):
def numberToWords(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: str
"""
to19 = ['One', 'Two', 'Three', 'Four', 'Five', 'Six', 'Seven', 'Eight', 'Nine', 'Ten', 'Eleven',
'Twelve', 'Thirteen', 'Fourteen', 'Fifteen', 'Sixteen', 'Seventeen', 'Eighteen', 'Nineteen']
tens = ['Twenty', 'Thirty', 'Forty', 'Fifty', 'Sixty', 'Seventy', 'Eighty', 'Ninety']
def helper(num):
if num < 20:
return to19[num-1:num] # 返回列表
if num < 100:
return [tens[num//10-2]] + helper(num%10)
if num < 1000:
return [to19[num//100-1]] + ['Hundred'] + helper(num%100)
for p, word in enumerate(['Thousand', 'Million', 'Billion']):
if num < 1000**(p+2):
return helper(num//1000**(p+1)) + [word] + helper(num%(1000**(p+1)))
return ' '.join(helper(num)) or 'Zero'
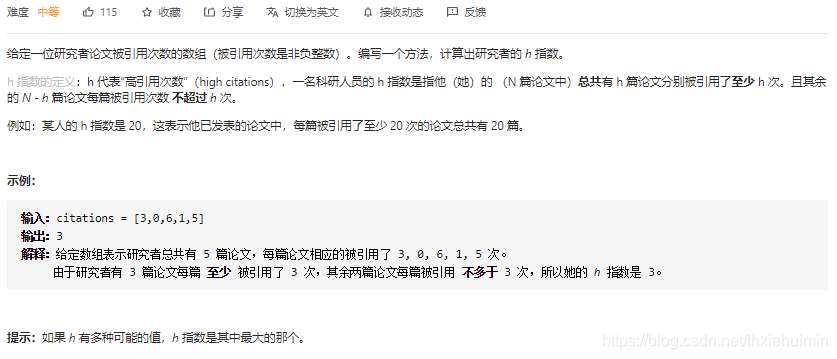
274. H 指数(中等)
思路
- 对citations排序,查找符合条件的h值并返回
- 没有符合条件的h值,返回0
class Solution(object):
def hIndex(self, citations):
"""
:type citations: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
citations.sort()
n = len(citations)
for i in range(n):
if citations[i]>=n-i:
return n-i
return 0
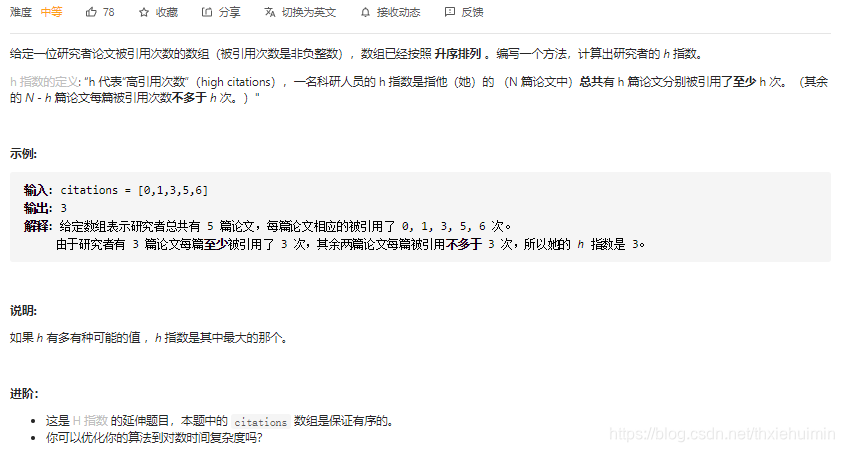
275. H 指数 II(中等)
思路
参考 274. H 指数(中等)
class Solution(object):
def hIndex(self, citations):
"""
:type citations: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(citations)
for i in range(n):
if citations[i]>=n-i:
return n-i
return 0
276-277(无)
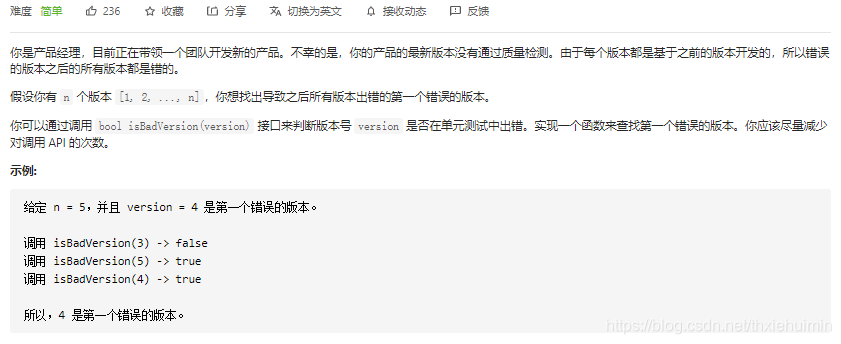
278. 第一个错误的版本(简单)
思路
二分查找
class Solution(object):
def firstBadVersion(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
l, r = 1, n
while l<=r:
mid = (l+r)//2
if isBadVersion(mid):
r = mid-1
else:
l = mid+1
return l
279. 完全平方数(中等)
思路
动态规划:
- 初始化dp数组为最大值float(int)
- 动态方程:
d p ( n ) = m i n ( d p [ i ] , d p ( n − k ) + 1 ) ∀ k ∈ s q u a r e N u m s dp(n)=min(dp[i], dp(n-k) + 1) \quad\quad\forall k\in squareNums dp(n)=min(dp[i],dp(n−k)+1)∀k∈squareNums
import math
class Solution(object):
def numSquares(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
squareNums = [i**2 for i in range(1, int(math.sqrt(n)+1))]
dp = [float("inf") for _ in range(n+1)]
dp [0]= 0
for i in range(1, n+1):
for k in squareNums:
if i - k >= 0:
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i-k]+1)
return dp[-1]
280-281(无)
282. 给表达式添加运算符(困难)
思路
回溯:
- 考虑所有有效表达式
- 创建index在num到目前为止构建表达式的值的位置
- 递归调用±*
- 检验表达式
class Solution(object):
def addOperators(self, num, target):
"""
:type num: str
:type target: int
:rtype: List[str]
"""
def helper(index, pre, cur, numSum, s):
if index == n:
if numSum == target and cur == 0:
ans.append("".join(s[1:]))
return
cur = cur*10+int(num[index])
if cur > 0:
helper(index+1, pre, cur, numSum, s)
s.append('+') # 加
s.append(str(cur))
helper(index+1, cur, 0, numSum+cur, s)
s.pop()
s.pop()
if s:
s.append('-') # 减
s.append(str(cur))
helper(index+1, -cur, 0, numSum-cur, s)
s.pop()
s.pop()
s.append('*') # 乘
s.append(str(cur))
# 乘,用表达式的值减去pre再加上pre*cur, 如123,1+2*3-->(1+2)-2+(2*3),保证乘法的优先级
helper(index+1, pre*cur, 0, numSum-pre+(pre*cur), s)
s.pop()
s.pop()
n = len(num)
ans = list()
helper(0, 0, 0, 0, list())
return ans
283. 移动零(简单)
思路
设置游标i为0,遍历数组nums,不为0的数字存储在数组前端,剩余的位置均为0
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
i = 0
for j in range(len(nums)):
if nums[j] != 0:
nums[i] = nums[j]
i += 1
for k in range(i, len(nums)):
nums[k] = 0
思路
设置游标i为0,遍历数组nums,当nums[j]不为0时和nums[i]交换,i往右移动
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
i = 0
for j in range(len(nums)):
if nums[j] != 0:
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
i += 1
284. 顶端迭代器(中等)
思路
peek: 查看cache是否为空,不为空时直接返回,为空时执行next操作并记录值,返回该值
# Below is the interface for Iterator, which is already defined for you.
#
# class Iterator(object):
# def __init__(self, nums):
# """
# Initializes an iterator object to the beginning of a list.
# :type nums: List[int]
# """
#
# def hasNext(self):
# """
# Returns true if the iteration has more elements.
# :rtype: bool
# """
#
# def next(self):
# """
# Returns the next element in the iteration.
# :rtype: int
# """
class PeekingIterator(object):
def __init__(self, iterator):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
:type iterator: Iterator
"""
self.iterator = iterator
self.cache = None
def peek(self):
"""
Returns the next element in the iteration without advancing the iterator.
:rtype: int
"""
if self.cache:
return self.cache
else:
self.cache = self.iterator.next()
return self.cache
def next(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
if not self.cache:
return self.iterator.next()
temp = self.cache
self.cache = None
return temp
def hasNext(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
return self.cache != None or self.iterator.hasNext()
# Your PeekingIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
# iter = PeekingIterator(Iterator(nums))
# while iter.hasNext():
# val = iter.peek() # Get the next element but not advance the iterator.
# iter.next() # Should return the same value as [val].
285(无)
286(无)
287. 寻找重复数(中等)
思路
- 排序
- 返回相邻相等的数
class Solution(object):
def findDuplicate(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
nums.sort()
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i]==nums[i-1]:
return nums[i]
288(无)
289. 生命游戏(中等)
思路
- 遍历board,得到当前位置周围8高位置的活细胞数,根据条件添加需要细胞存活发生变化的坐标到change数组中
- 遍历change数组,修改board对应位置细胞的存活状态
class Solution(object):
def gameOfLife(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[int]]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
change = list()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
liveNum = 0
for tmp_i, tmp_j in [(-1,-1),(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,-1),(0,1),(1,-1),(1,0),(1,1)]:
x, y = i+tmp_i, j+tmp_j
if 0<=x<m and 0<=y<n:
if board[x][y] == 1:
liveNum += 1
if board[i][j] == 1:
if liveNum < 2 or liveNum > 3:
change.append((i,j))
else:
if liveNum==3:
change.append((i, j))
for i, j in change:
board[i][j] = 0 if board[i][j]==1 else 1
return board
290. 单词规律(简单)
思路
- pattern和s长度不相等,返回False
- 遍历pattern,创建字典得到pattern和s的对应关系,patter[i]不在mapping时,校验s[i]是否在mapping中,是则返回False,否则添加至mapping中。patter[i]存在mapping时,对应不上返回False
- 遍历结束,返回True
class Solution(object):
def wordPattern(self, pattern, s):
"""
:type pattern: str
:type s: str
:rtype: bool
"""
mapping = dict()
s = s.split()
if len(s) != len(pattern):
return False
for i in range(len(pattern)):
if pattern[i] not in mapping:
if s[i] not in mapping.values():
mapping[pattern[i]] = s[i]
else:
return False
else:
if mapping[pattern[i]] != s[i]:
return False
return True
291(无)
292. Nim 游戏(简单)
思路
留下4个石头就一定会输
class Solution(object):
def canWinNim(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
return n%4!=0
293(无)
294(无)
295. 数据流的中位数(困难)
思路
- __init__初始化nums
- addNum添加num
- findMedian返回中位数,有奇个数返回中位数,偶个数返回2个中位数的平均值
class MedianFinder(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.nums = list()
def addNum(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: None
"""
self.nums.append(num)
def findMedian(self):
"""
:rtype: float
"""
self.nums.sort()
n = len(self.nums)
mid = n//2
if n%2!=0:
return self.nums[mid]
else:
return (self.nums[mid-1]+self.nums[mid])/2.0
# Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MedianFinder()
# obj.addNum(num)
# param_2 = obj.findMedian()
296(无)
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化(困难)
思路
先序序列化
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
return "X," if not root else str(root.val)+',' + self.serialize(root.left) + self.serialize(root.right)
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
data = data.split(',')
return self.buildTree(data)
def buildTree(self, data):
val = data.pop(0)
if val == "X":
return None
node = TreeNode(val)
node.left = self.buildTree(data)
node.right = self.buildTree(data)
return node
298(无)
299. 猜数字游戏 (中等)
思路
- 第一遍遍历求公牛数A并修改secret,guess对应位置的字符
- 第二遍遍历求奶牛数B并修改secret对应位置的字符
- 返回对应的公牛数和奶牛数
class Solution(object):
def getHint(self, secret, guess):
"""
:type secret: str
:type guess: str
:rtype: str
"""
A, B = 0, 0
secret, guess = list(secret), list(guess)
for i in range(len(secret)):
if secret[i] == guess[i]:
A+=1
secret[i] = 'A'
guess[i] = 'G'
for i in range(len(secret)):
if secret[i] != guess[i]:
if guess[i] in secret:
B += 1
secret[secret.index(guess[i])] = "B"
return str(A)+'A'+str(B)+'B'
300. 最长递增子序列(中等)
思路
动态规划:
nums[i]大于nums[j]时dp[i]=max(dp[i], dp[j]+1)
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
dp = [1]*n
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(i):
if nums[i]>nums[j]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1)
return max(dp)