1.容器rb_tree
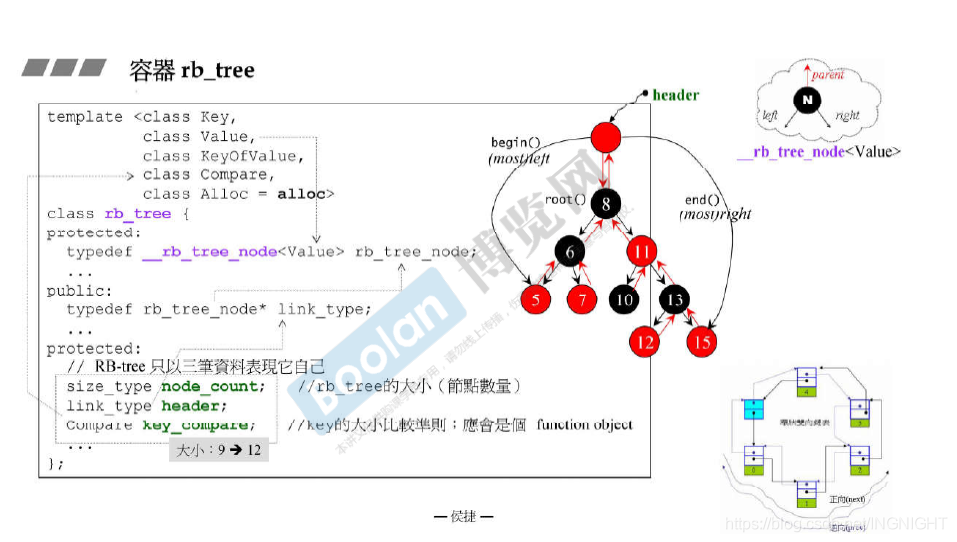
Red-Black tree(红黑树)是平衡二元搜寻树(balanced binary search tree)中常被使用的一种平衡二元搜寻树的特点:排列规则有利于search和insert,并保持适度平衡-无任何节点过深
rb_tree提供遍历操作以及iterators
按正常规则(++ite)遍历,便能获得排序状态(sorted)
我们不应该使用rb_tree的iterators改变元素值(因为元素有其严谨排列规则)。编程里面(programming leve)并未阻绝此事。如此设计是正确的,因为rb_tree即将为set和map服务(做为其底部支持),而map允许元素的data被改变,只有元素的key才是不可被改变的
rb_tree提供两种insertion操作:insert_unique()和insert_equal()。前者表示节点的key一定在整个tree中独一无二,否则安插失败。后者表示节点的key可重复
-
#include <set> -
#include <iostream> -
using namespace std; -
//容器rb_tree -
// key和data合成value(key|value) -
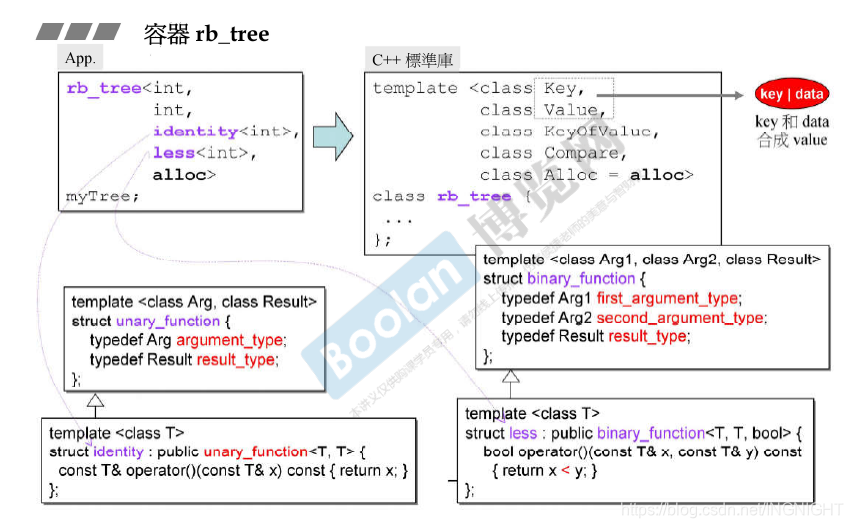
//template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc = alloc> -
//class rb_tree { -
//protected: -
// typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node; -
// ... -
//public: -
// typedef rb_tree_node* link_type; -
//protected: -
// //RB-tree只以三笔表现他自己 -
// size_type node_count; // rb_tree的大小(节点) -
// link_type header; -
// Compare key_compare; //key的大小比较规则,应会是个function object -
//}; -
namespace jj31 -
{ -
void test_Rb_tree() -
{ -
//G2.9 vs. G4.9 : -
//rb_tree => _Rb_tree, -
//identity<> => _Identity<> -
//insert_unique() => _M_insert_unique() -
//insert_equal() => _M_insert_equal() -
cout << "\ntest_Rb_tree().......... \n"; -
_Rb_tree<int, int, _Identity<int>, less<int> > itree; -
cout << itree.empty() << endl; //1 -
cout << itree.size() << endl; //0 -
itree._M_insert_unique(3); -
itree._M_insert_unique(8); -
itree._M_insert_unique(5); -
itree._M_insert_unique(9); -
itree._M_insert_unique(13); -
itree._M_insert_unique(5); //no effect, since using insert_unique(). -
cout << itree.empty() << endl; //0 -
cout << itree.size() << endl; //5 -
cout << itree.count(5) << endl; //1 -
itree._M_insert_equal(5); -
itree._M_insert_equal(5); -
cout << itree.size() << endl; //7, since using insert_equal(). -
cout << itree.count(5) << endl; //3 -
} -
} -
int main() { -
jj31::test_Rb_tree(); -
return 0; -
}
2.容器map,multimap
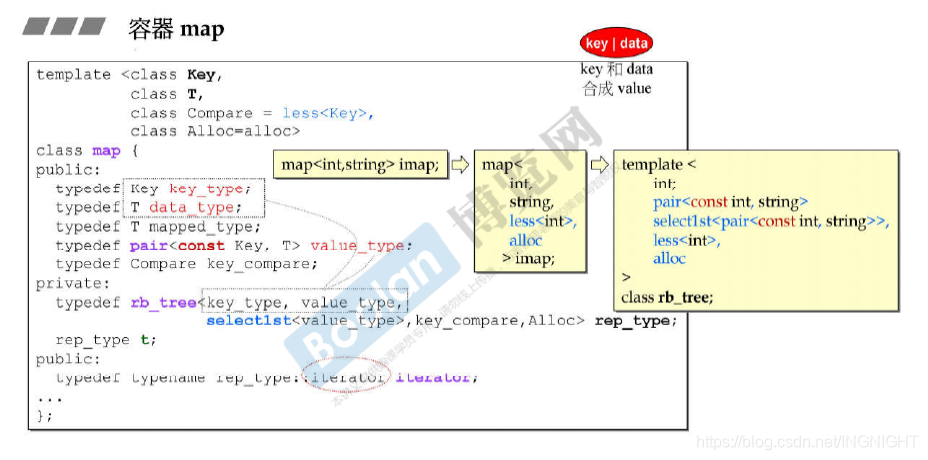
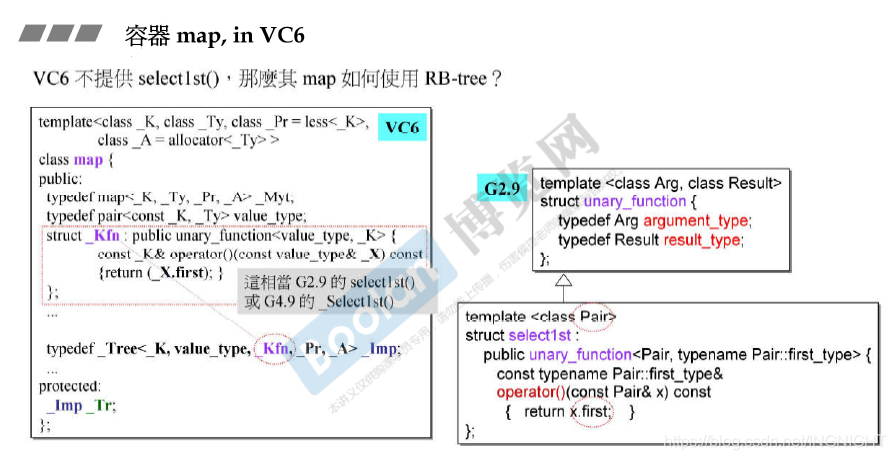
(1)map/multimap以rb_tree为底层结构,因此有元素自动排序特性,排序的依据是key.
(2)map/multimap提供"遍历"操作及iterators,按正常规则(++ite)遍历,便能获得排序状态(sorted)
(3)我们无法使用map/multimap的iterators改变元素的key(因为key有其严谨的排列规则),但可以用它改变元素的data,
因此,map/multimap内部自动将user指定的key type设为const,如此禁止user对元素的key赋值,map不允许迭代器来改key
(4)map元素的key必须独一无二,因此其insert()用的是rb_tree的insert_unique
multimap元素的key可以重复,因此其insert()用的是rb_tree的insert_equal
-
template <class _Key, class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Alloc> -
class map { -
public: -
// typedefs: -
typedef _Key key_type; -
typedef _Tp data_type; -
typedef _Tp mapped_type; -
typedef pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type; -
// key|data,key和data合成value -
// map/multimap内部自动将user指定的key type设为const,如此禁止user对元素的key赋值 -
typedef _Compare key_compare; -
private: -
typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, -
_Select1st<value_type>, key_compare, _Alloc> _Rep_type; -
_Rep_type _M_t; // red-black tree representing map -
public: -
typedef typename _Rep_type::iterator iterator; -
}; -
map<int, string> imap -> map<int, string, less<int>, alloc> imap -> -
template<int, pair<const int, string>, select1st<pair<const int, string>>, less<int>, alloc> class rb_tree;
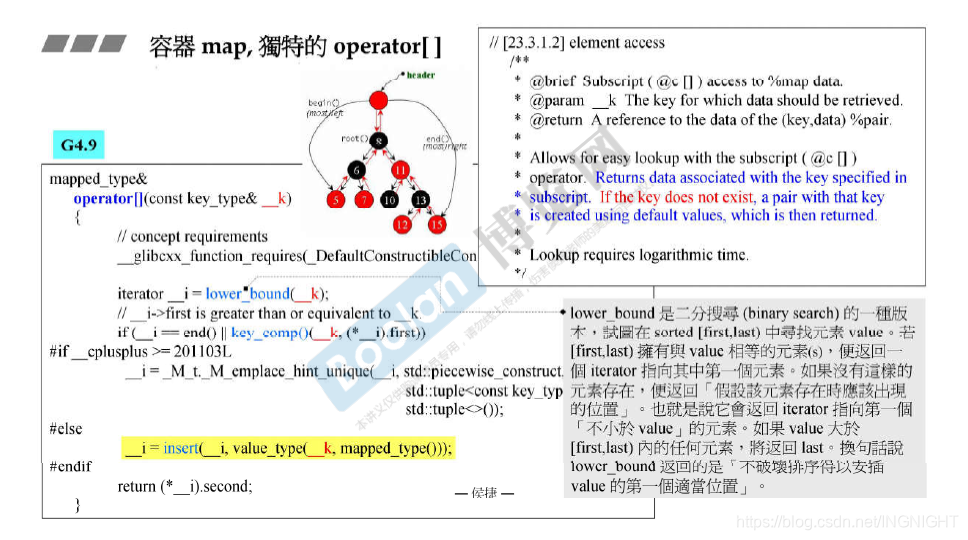
3.容器map,独特的operator[]
返回与下标中指定的键关联的数据
如果key不存在,则使用默认值创建具有key的对,然后返回该值
-
_Tp& operator[](const key_type& __k) { -
iterator __i = lower_bound(__k); -
// __i->first is greater than or equivalent to __k. -
if (__i == end() || key_comp()(__k, (*__i).first)) -
__i = insert(__i, value_type(__k, _Tp())); -
return (*__i).second; -
}
lower_bound是二分搜寻的一种版本,试图在sorted[first, last)中寻找元素value
若[first, last)拥有value相等的元素(s),便返回一个iterator指向其中第一个元素
如果没有这样的元素存在,便返回假设该元素存在时应该出现的位置
lower_bound返回的是 不破坏排序得以安插value的第一个适当位置
-
#include <map> -
#include <stdexcept> -
#include <string> -
#include <cstdlib> //abort() and rand() and RAND_MAX -
#include <cstdio> //snprintf() -
#include <iostream> -
#include <ctime> -
using namespace std; -
namespace jj14 -
{ -
long get_a_target_long() -
{ -
long target=0; -
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): "; -
cin >> target; -
return target; -
} -
void test_map(long& value) -
{ -
cout << "\ntest_map().......... \n"; -
map<long, string> c; -
char buf[10]; -
clock_t timeStart = clock(); -
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) -
{ -
try { -
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); -
c[i] = string(buf); -
} -
catch(exception& p) { -
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl; -
abort(); -
} -
} -
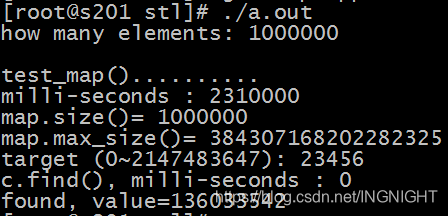
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; -
cout << "map.size()= " << c.size() << endl; -
cout << "map.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970 -
long target = get_a_target_long(); -
timeStart = clock(); -
auto pItem = c.find(target); -
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; -
if (pItem != c.end()) -
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl; -
else -
cout << "not found! " << endl; -
c.clear(); -
} -
} -
int main() { -
long value; -
cout << "how many elements: "; -
cin >> value; -
jj14::test_map(value); -
}
4.map容器迭代器失效问题
-
#include <iostream> -
#include <map> -
using namespace std; -
class Key { -
public: -
explicit Key(int num):_num(num) { -
} -
int get_num() const { -
return _num; -
} -
bool operator < (const Key& k) const { -
return get_num() < k.get_num() ? true : false; -
} -
public: -
int _num; -
}; -
class CompareKey : public binary_function<Key, Key, bool> { -
public: -
bool operator()(const Key& k1, const Key& k2) { -
return k1.get_num() < k2.get_num() ? true : false; -
} -
}; -
int main() { -
//std::map<Key, int, CompareKey> table; -
std::map<Key, int> table; -
table.insert(std::pair<Key, int>(Key(0), 1)); -
table.insert(std::pair<Key, int>(Key(1), 1)); -
table.insert(std::pair<Key, int>(Key(3), 1)); -
table.insert(std::pair<Key, int>(Key(4), 1)); -
table.insert(std::pair<Key, int>(Key(5), 1)); -
cout << table.begin()->first.get_num() << std::endl; -
cout << table.rbegin()->first.get_num() << std::endl; -
auto ite = table.lower_bound(Key(1)); -
cout << ite->first.get_num() << std::endl;; -
ite = table.lower_bound(Key(2)); -
cout << ite->first.get_num() << std::endl;; -
ite = table.upper_bound(Key(2)); -
cout << ite->first.get_num() << std::endl;; -
ite = table.upper_bound(Key(1)); -
cout << ite->first.get_num() << std::endl;; -
}