Eigen
1.使用Map函数,c++数组与 eigen矩阵的转换
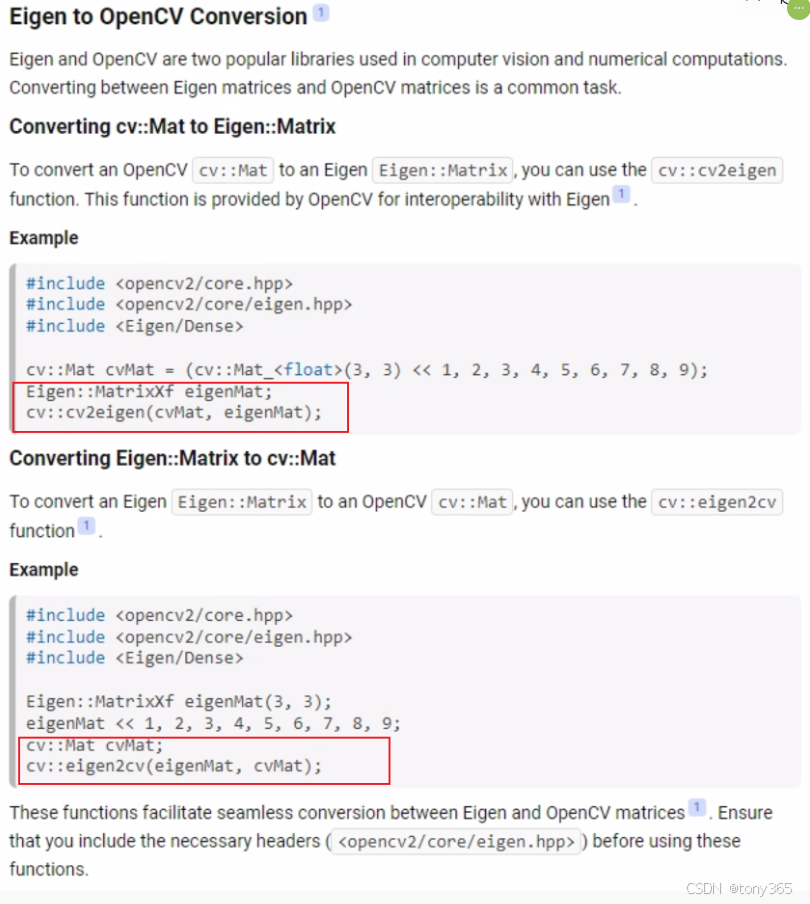
2.eigen矩阵与opencv互转
3.eigen使用总结
https://zxl19.github.io/eigen-note/
https://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox/group__QuickRefPage.html
4.eigen visual studio 和 ubuntu上
a.ubuntu上只需要CMakeLists.txt中添加
include_directories(“/home/xx/software/eigen-3.4.0”)
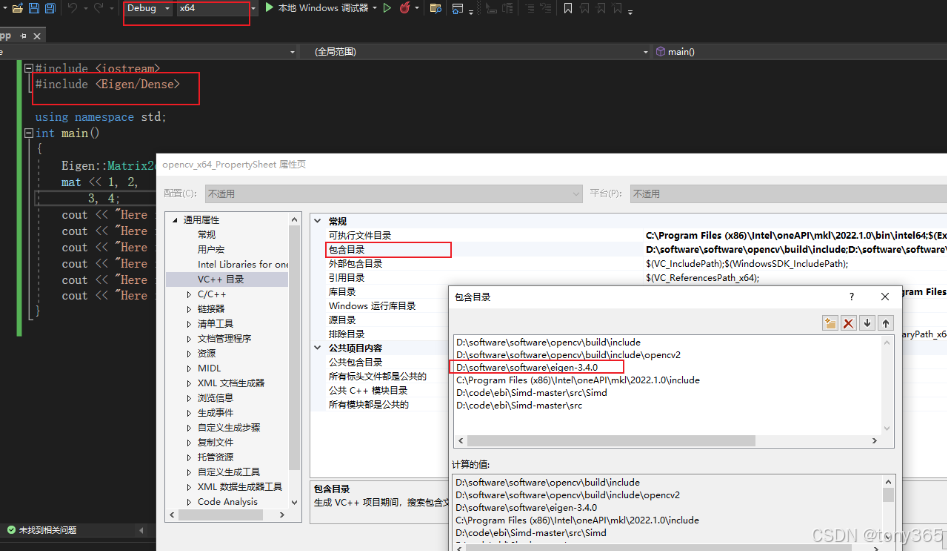
b.eigen 库在visual studio中的使用:
只需要添加包含目录即可
1)
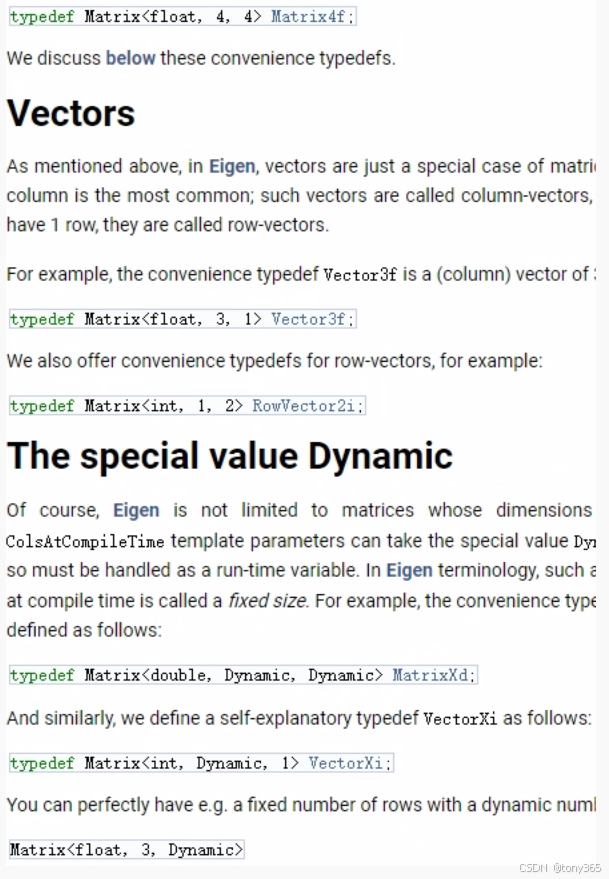
在eigen中, matrices 和 vectors都是 Matrix template class的对象。
Vectors 是matrices的特殊case:行数为1或者列数为1
模板类一共有六个参数,一般使用前三个参数就足够了。比如
2)
Dynamic关键字 指示动态矩阵动态向量。 动态是运行时才知道size大小。
静态时编译时就知道size大小。一般比较小的矩阵可以使用静态。
静态和动态类似于:
int a[16];
int *a = new int[1000*1000];
3)初始化的方法
4)元素获取
用括号
m(1,2) //第2行第3列
5)resize
m.rows() m.cols() m.size()
resize 只能操作固定size的矩阵,如果resize后数量不变则无操作,数量变化会删除原来的数据
6)赋值操作
a = b //相当于把b copy到 a, 如果ab大小不同,会有resize的操作。
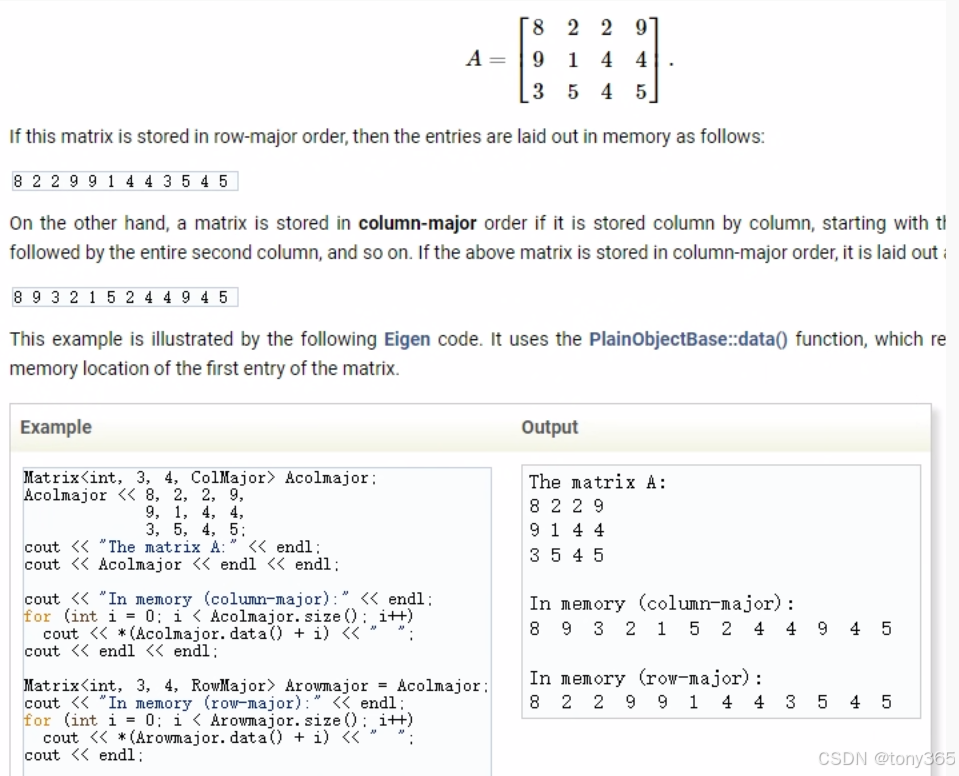
7)存储顺序
column major or row major
如果没有指定,默认是 ColMajor。
且两者可以互相转换,转换方法如下:
=======================================================================
8)算术操作
加减操作。必须类型(Scalar)相同,size相同。
矩阵与scalar的乘法,除法操作。
9)算术表达式
下面是可行的,而且可以更好的被优化
a = 3*b + 4*c - x/2;
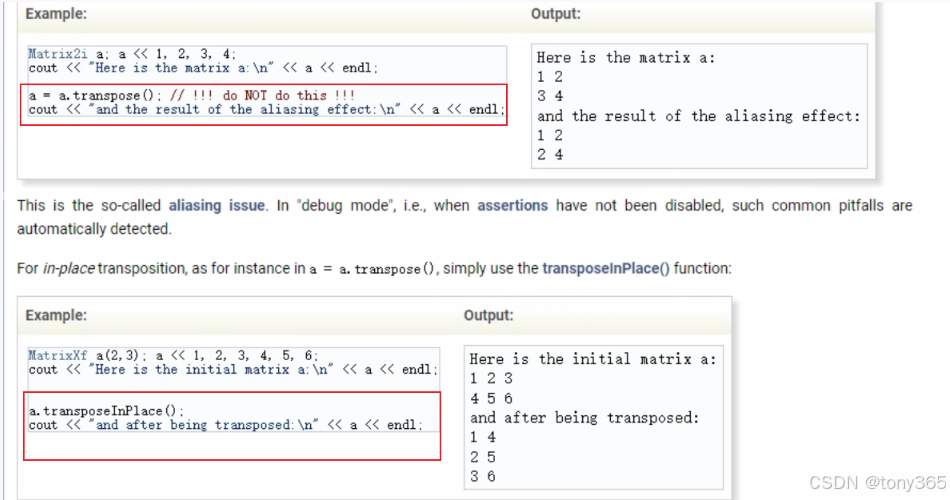
10) 转置
11) 矩阵相乘
c = a * b -> [m,n] @ [n,m] = [m, m]
12)内积
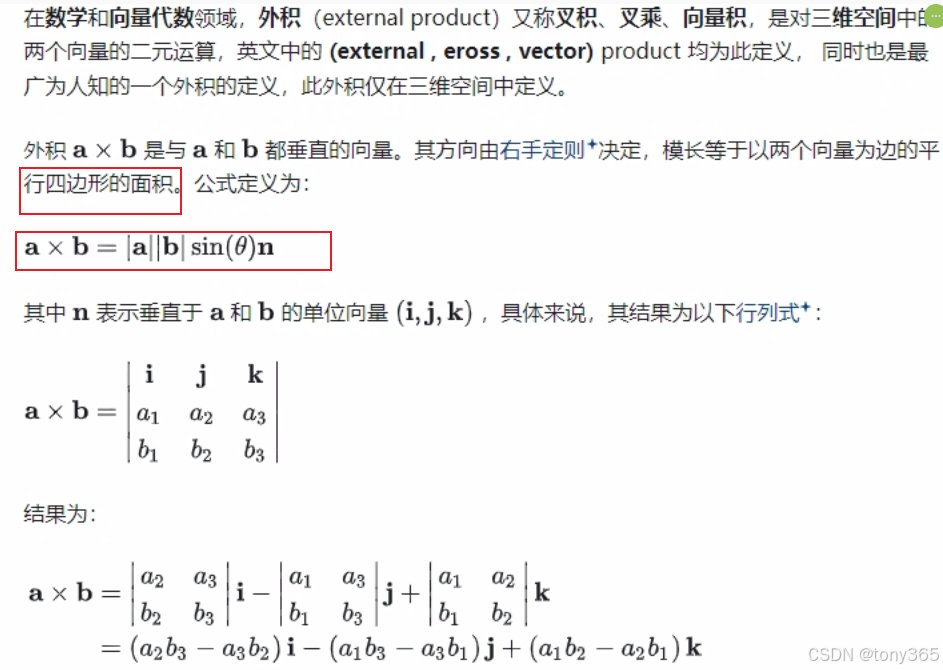
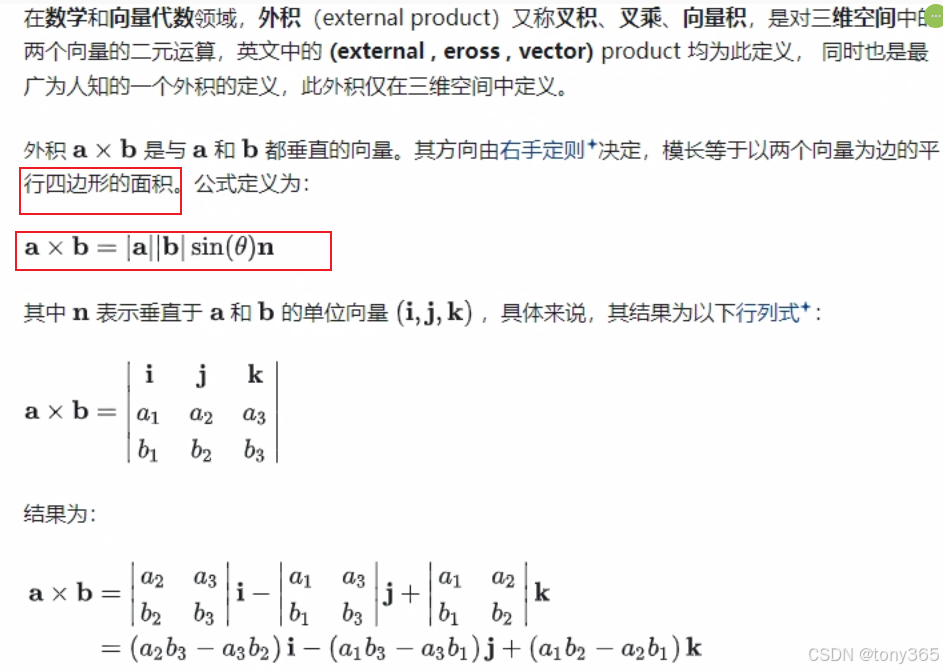
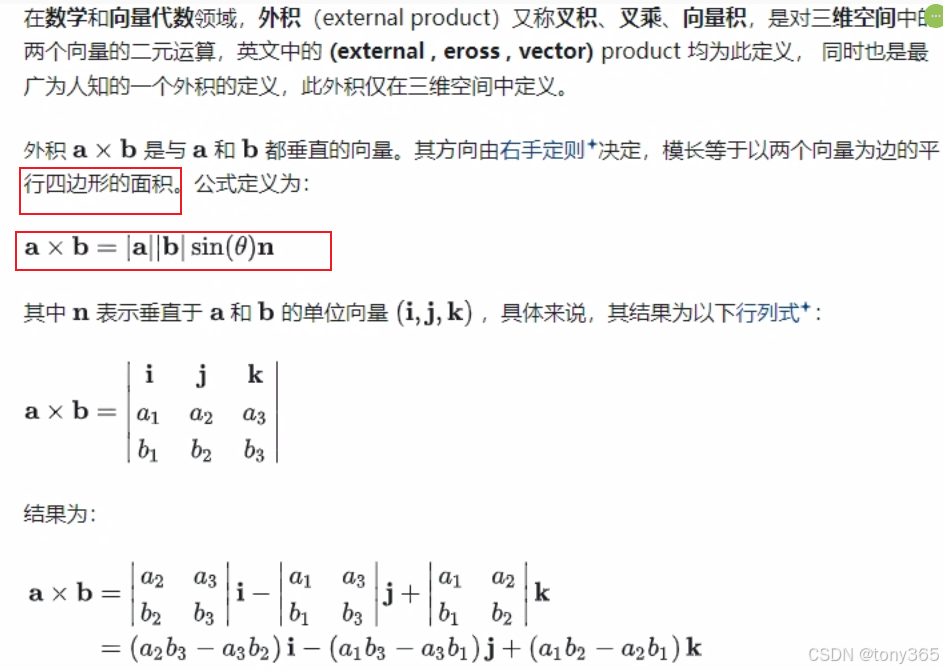
13)外积
14)eigen中内积和外积分别是 dot, cross
dot适用于任意长度的向量
cross只适用于长度为3的vector
15)reduction 操作
===============================================================================
array class
16)array
matrix目的是为了线性集合操作,比如矩阵相乘。
Array 可以更好的执行 element-wise 操作。
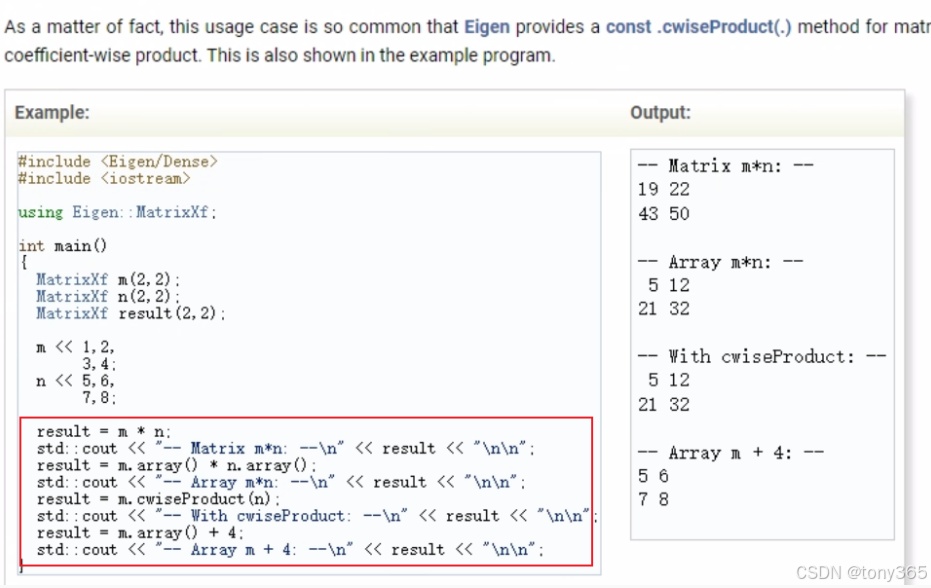
比如对矩阵+上一个数,或者两个矩阵对应元素相乘。
定义
对应元素 加,减,乘的操作略
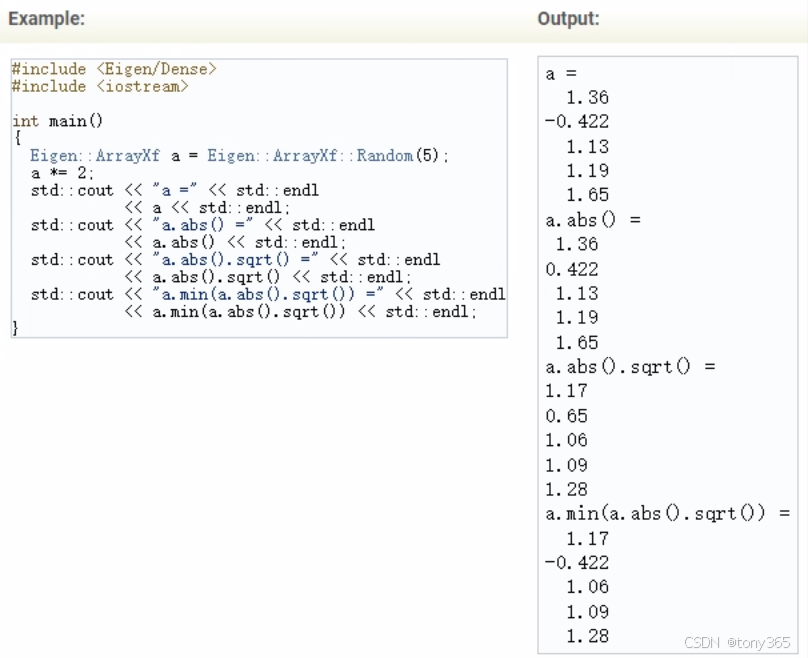
对应元素 abs, sqrt, min, max
17) array 和matrix
两个类的操作是不能互通的。因此如果你既想要矩阵相乘,又想要对应元素相乘,这个时候要首先进行转换。
.array() 和 .matrix() 可以是左值也可以是右值。而且基本上没有耗时
=======================================================================================
对于matrix
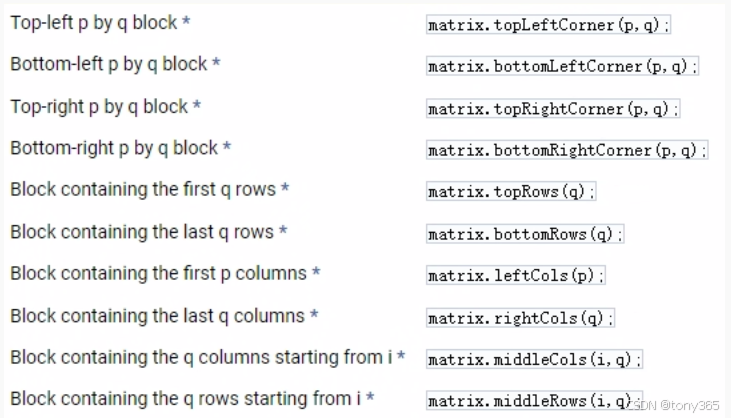
18)matrix : block(), row(), col() 和其他
block 输入 起始坐标(row,col)和对应高度宽度(height, width),输出矩形数据
m.row(i)
m.col(j)
其他取矩阵的操作
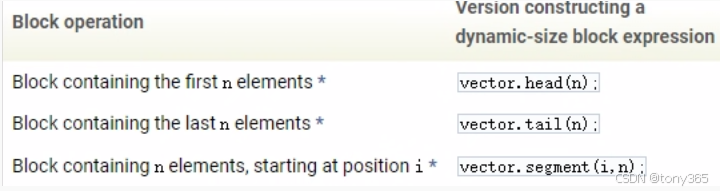
19)vector: head(), tail(), segment()
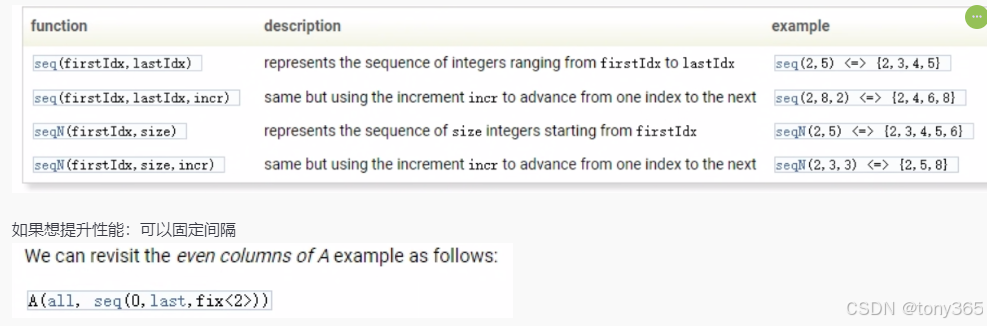
20)slicing和indexing 操作
21)根据索引提取列
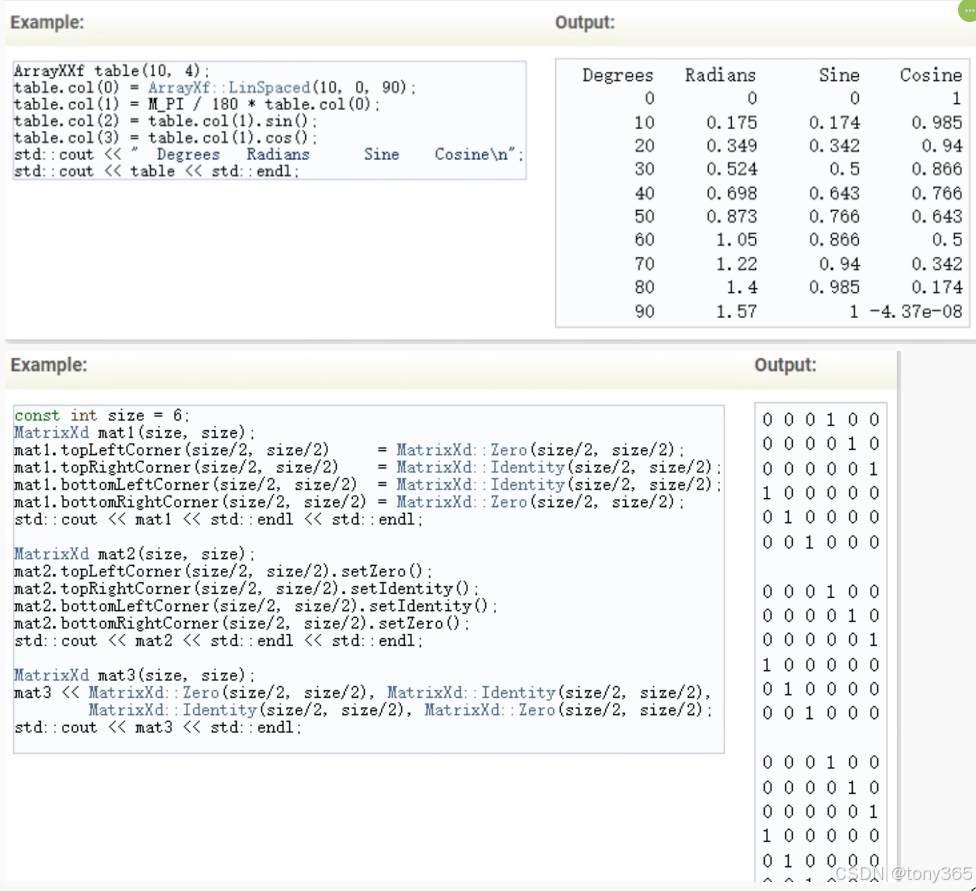
22)一些初始化方法
23) 其他示例
// case1 reduction
// case2 范数
// case3, 按照行或者列进行reduction
// case4: 布尔 all, any, count 操作
// case5: partial recuctions
// case6: broadcasting
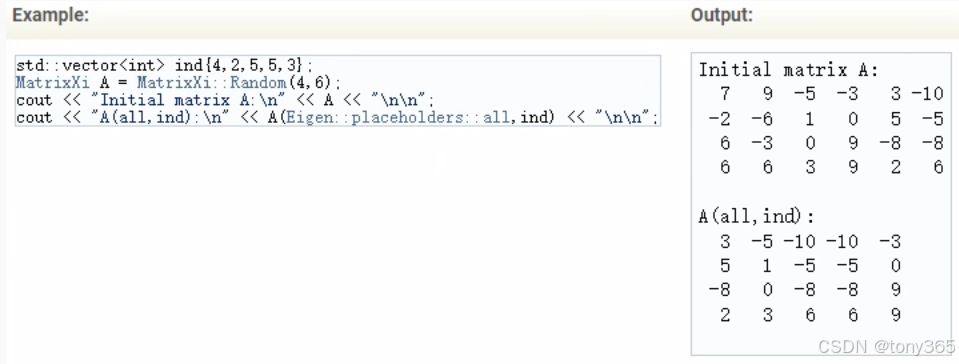
// case7: index:A({2, 1}, { 4,2,5,5,3 }) 先索引行,再选列
// case8: reshape 特点是默认按照col优先的储存顺序
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
// case1 reduction
Eigen::Matrix2d mat;
mat << 1, 2,
3, 4;
cout << "Here is mat.sum(): " << mat.sum() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.prod(): " << mat.prod() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.mean(): " << mat.mean() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.minCoeff(): " << mat.minCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.maxCoeff(): " << mat.maxCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.trace(): " << mat.trace() << endl;//等价于mat.diagonal().sum()
// case2 范数
Eigen::VectorXf v(2);
Eigen::MatrixXf m(2, 2), n(2, 2);
v << -1,
2;
m << 1, -2,
-3, 4;
std::cout << "v.squaredNorm() = " << v.squaredNorm() << std::endl; // 所有元素平方后求和
std::cout << "v.norm() = " << v.norm() << std::endl; // 所有元素平方后求和,再求根
std::cout << "v.lpNorm<1>() = " << v.lpNorm<1>() << std::endl; // 1范数,所有元素绝对值求和
std::cout << "v.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << v.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() << std::endl; // 无穷范数,所有元素的绝对值最大值
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "m.squaredNorm() = " << m.squaredNorm() << std::endl;
std::cout << "m.norm() = " << m.norm() << std::endl;
std::cout << "m.lpNorm<1>() = " << m.lpNorm<1>() << std::endl;
std::cout << "m.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << m.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>() << std::endl;
// case3, 按照行或者列进行reduction
//Eigen::MatrixXf m(2, 2);
m << 1, -2,
-3, 4;
std::cout << "1-norm(m) = " << m.cwiseAbs().colwise().sum()
<< " == " << m.colwise().lpNorm<1>() << std::endl;
std::cout << "infty-norm(m) = " << m.cwiseAbs().rowwise().sum()
<< " == " << m.rowwise().lpNorm<1>() << std::endl;
// case 4: 布尔 all, any, count 操作
//all() returns true if all of the coefficients in a given Matrix or Array evaluate to true .
//any() returns true if at least one of the coefficients in a given Matrix or Array evaluates to true .
//count() returns the number of coefficients in a given Matrix or Array that evaluate to true.
Eigen::ArrayXXf a(2, 2);
a << 1, 2,
3, 4;
std::cout << "(a > 0).all() = " << (a > 0).all() << std::endl; //1
std::cout << "(a > 0).any() = " << (a > 0).any() << std::endl; //1
std::cout << "(a > 0).count() = " << (a > 0).count() << std::endl;//4
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "(a > 2).all() = " << (a > 2).all() << std::endl; //0
std::cout << "(a > 2).any() = " << (a > 2).any() << std::endl; //1
std::cout << "(a > 2).count() = " << (a > 2).count() << std::endl;//2
// case5: partial recuctions
Eigen::MatrixXf mat24(2, 4);
mat24 << 1, 2, 6, 9,
3, 1, 7, 2;
std::cout << "Column's maximum: " << std::endl
<< mat24.colwise().maxCoeff() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Row's maximum: " << std::endl
<< mat24.rowwise().maxCoeff() << std::endl;
// case6: broadcasting
Eigen::MatrixXf matf(2, 4);
Eigen::VectorXf vf(2);
matf << 1, 2, 6, 9,
3, 1, 7, 2;
vf << 0,
1;
//add v to each column of m
matf.colwise() += vf;
std::cout << "Broadcasting result: " << std::endl;
std::cout << matf << std::endl;
// case7: index
Eigen::MatrixXi A = Eigen::MatrixXi::Random(4, 6);
cout << "Initial matrix A:\n" << A << "\n\n";
cout << "A(all,{4,2,5,5,3}):\n" << A(Eigen::all, { 4,2,5,5,3 }) << "\n\n";
cout << "A({2,1},{4,2,5,5,3}):\n" << A({2, 1}, { 4,2,5,5,3 }) << "\n\n";
// case8: reshape 特点是默认按照col优先的储存顺序
// m.reshaped<RowMajor>().transpose() 按照行顺序重新排列为1D linear. 然后转置
// stl 应用2D arrays或matrices. 比如对行或者列进行排序
A = ArrayXXi::Random(4, 4);
cout << "initial array A:" << A << "\n";
for (auto row : A.rowwise()) {
cout << row << endl;
std::sort(row.begin(), row.end());
}
cout << "sort row array A:" << A << "\n";
for (auto col : A.colwise()) {
std::sort(col.begin(), col.end());
}
cout << "sort col array A:" << A << "\n";
24)最小二乘法解线性方程组
下面两种方法分别是QR分解和正则化的方法求解,后者速度更快精度略低。
A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(b)
(A.transpose()*A).ldlt().solve(A.transpose()*b)