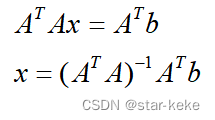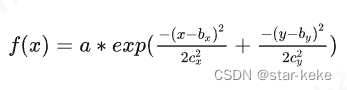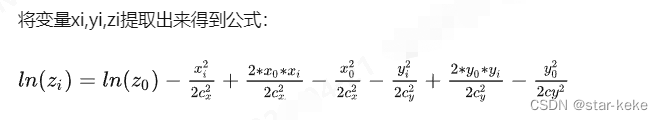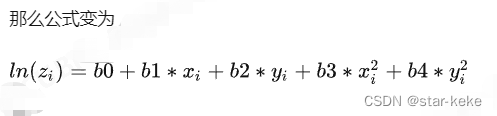本节介绍如何用Eigen求解线性最小二乘方程组。求解Ax=b的最小二乘问题,等价于求解方程
使用Eigen的求解的代码如下:
Eigen::MatrixXd MatX;//样本数据
Eigen::MatrixXd MatY;//观测值
Eigen::MatrixXd MatLS;//待定系数
MatLS = (MatX.transpose() * MatX).inverse() * MatX.transpose() * MatY;直线拟合:
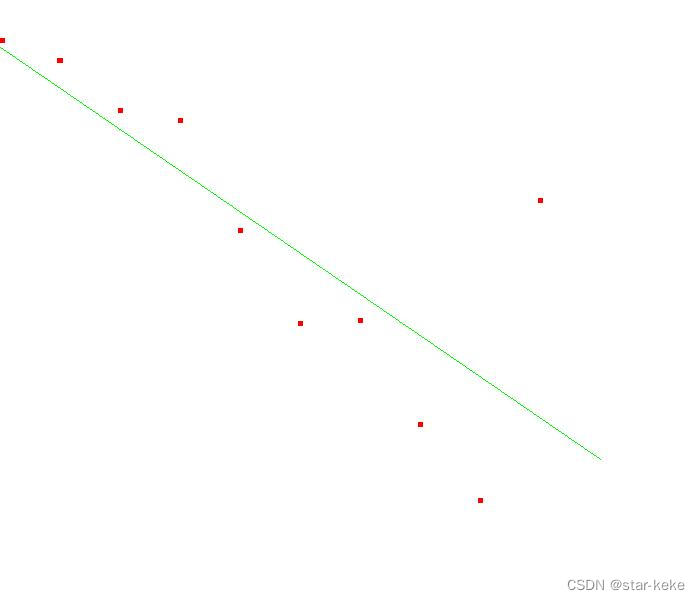
直线方程:y = k*x + b
//y = k*x + b
void least_square_line(double input[][2], int number, double&k, double&b){
Eigen::MatrixXd MatX;
Eigen::MatrixXd MatY;
MatX.resize(number, 2);
MatY.resize(number, 1);
Eigen::MatrixXd MatLS;
MatLS.resize(number, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < number; ++i){
MatX.row(i) = Eigen::Vector2d(input[i][0], 1);
MatY(i, 0) = input[i][1];
}
MatLS = (MatX.transpose()*MatX).inverse()*MatX.transpose()*MatY;
//MatLS = MatX.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(MatY); //也可以用
k = MatLS(0,0);
b = MatLS(1,0);
}曲线拟合:
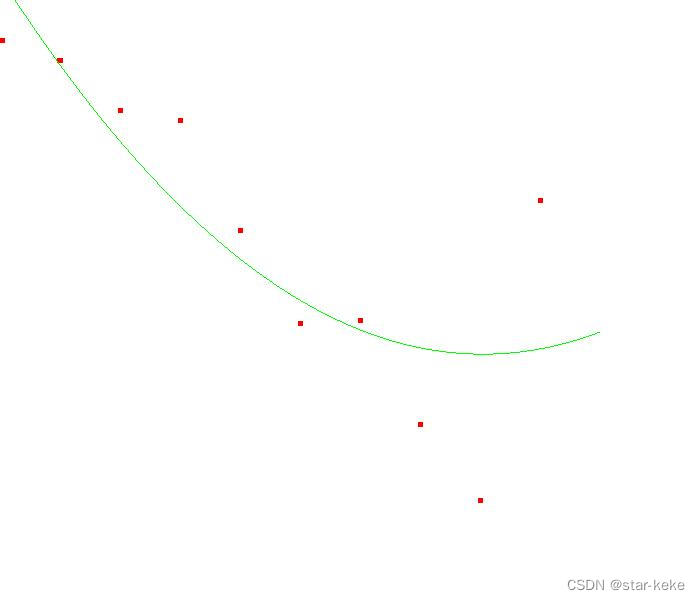
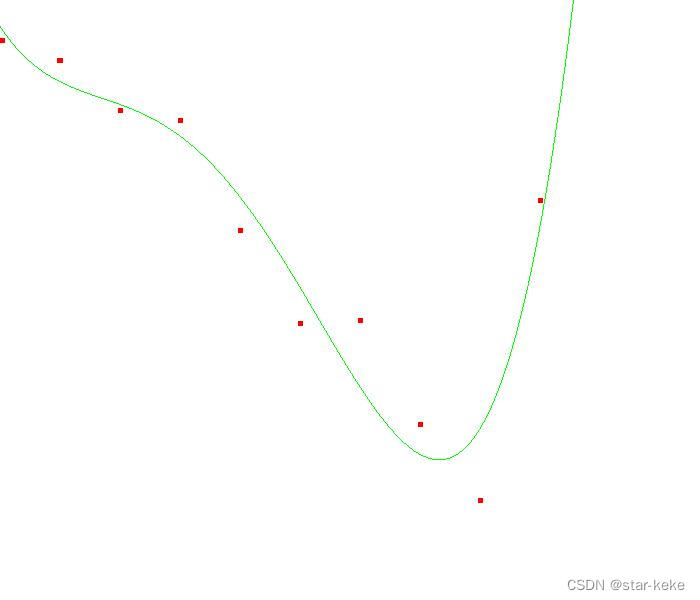
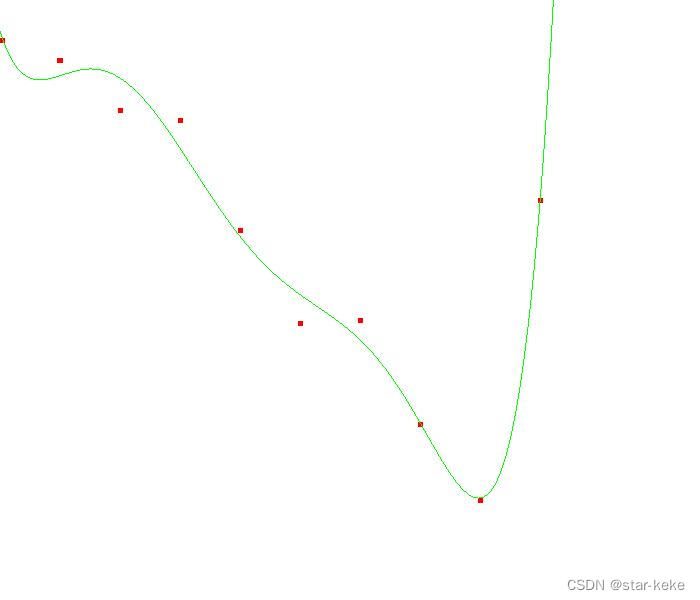
多项式方程:Pn(x)=a(n)x^n+a(n-1)x^(n-1)+…+a(1)x+a(0)
//y = a0 + a1*x + a2*x*x + a3*x*x*x + a4*x*x*x*x + a5*x*x*x*x*x;
void least_square_curve(double input[][2], int number, int jie, std::vector<double>&weight){
Eigen::MatrixXd MatX;
Eigen::MatrixXd MatY;
MatX.resize(number, jie);
MatY.resize(number, 1);
Eigen::MatrixXd MatLS;
MatLS.resize(number, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < number; ++i){
std::vector<double> pows;
for(int j = 0; j < jie; j++){
double p = pow(input[i][0], j);
MatX(i, j) = p;
}
MatY.row(i)[0] = input[i][1];
}
MatLS = (MatX.transpose()*MatX).inverse()*MatX.transpose()*MatY;
for(int i = 0; i < jie; i++)
weight.push_back(MatLS(i, 0)) ;
}3阶多项式
5阶多项式:
7阶多项式:
平面拟合:
平面方程:Ax+By+Cz+D=0
//z = A*x + B*y + C
void Least_squares_plane(double input[][3], int number, double& A, double& B, double& C)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd MatX;
Eigen::MatrixXd MatY;
MatX.resize(number, 3);
MatY.resize(number, 1);
Eigen::MatrixXd MatLS;
MatLS.resize(number, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < number; ++i) {
MatX.row(i) = Eigen::RowVector3d(input[i][0], input[i][1],1);
MatY.row(i)[0] = input[i][2];
}
MatLS = (MatX.transpose() * MatX).inverse() * MatX.transpose() * MatY;
A = MatLS(0, 0);
B = MatLS(1, 0);
C = MatLS(2, 0);
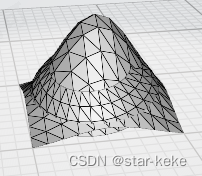
}以该3D模型的每个三角形面片的顶点为观测数据:
拟合的平面如下:
高斯拟合:
高斯函数
//ln(z) = A + B*x + C*y + D*x*x + E*y*y
//z = exp(A + B*x + C*y + D*x*x + E*y*y)
void Least_squares_gaussian(double input[][3], int number, double& A, double& B, double& C, double& D, double& E)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd MatX;
Eigen::MatrixXd MatY;
MatX.resize(number, 5);
MatY.resize(number, 1);
Eigen::MatrixXd MatLS;
MatLS.resize(number, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < number; ++i) {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 5, 1> row;
row << 1 , input[i][0] , input[i][1] , input[i][0] * input[i][0] , input[i][1] * input[i][1];
MatX.row(i) = row;
MatY.row(i)[0] = log(input[i][2]);
}
MatLS = (MatX.transpose() * MatX).inverse() * MatX.transpose() * MatY;
A = MatLS(0, 0);
B = MatLS(1, 0);
C = MatLS(2, 0);
D = MatLS(3, 0);
E = MatLS(4, 0);
}同样以该3D模型的顶点为观测数据
拟合高斯面如下: