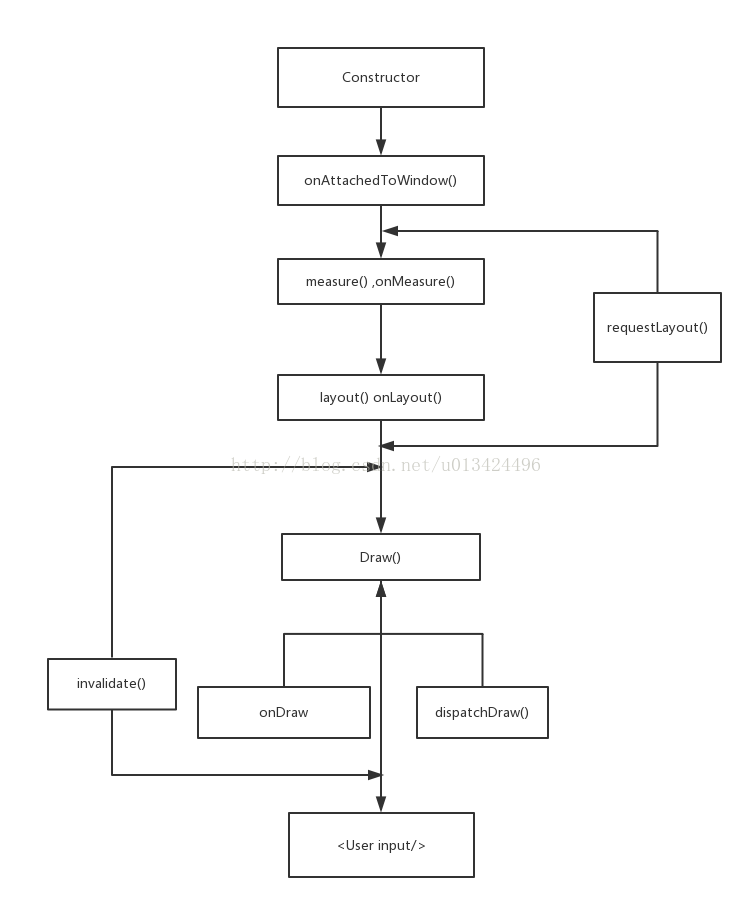
一.ConStructor:
1.首先是在res的values文件夹下创建一个attrs的文件,然后对自定义的控件添加属性
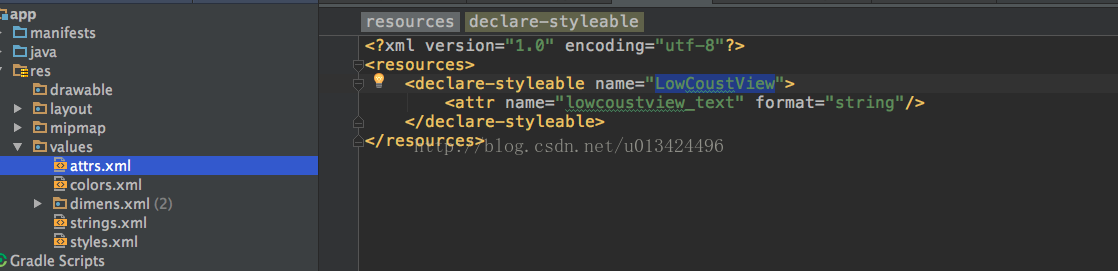
2.然后在两个参数的构造方法中获取这个xml中的属性值,
publicLowCoustView(Context context,AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray array = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.LowCoustView);
String text = array.getString(R.styleable.LowCoustView_lowcoustview_text);
//记得回收
array.recycle();
}二onAttachedToWindow():
三 measure() onMeasure
(1)计算你的view 的内容所需的大小(宽度和高度)
(2)获取你的View MeasureSpec大小和模式(宽度和高度,比如具体的值,wrap_content,match_parent,fill_parent这些)
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}(3)检查MeasureSpec设置和调整View(宽和高)的尺寸模式
// desiredWidth 控件xml或者是动态设置的高度
// MeasureSpec的三种Mode:
// 1.UNSPECIFIED
// 父不没有对子施加任何约束,子可以是任意大小(也就是未指定)
// (UNSPECIFIED在源码中的处理和EXACTLY一样。
// 当View的宽高值设置为0的时候或者没有设置宽高时,模式为UNSPECIFIED
// 2.EXACTLY
// 父决定子的确切大小,子被限定在给定的边界里,忽略本身想要的大小。
// (当设置width或height为match_parent或者是确定值时,模式为EXACTLY,
// 因为子view会占据剩余容器的空间,所以它大小是确定的)
// 3.AT_MOST
// 子最大可以达到的指定大小
// (当设置为wrap_content时,模式为AT_MOST,
// 表示子view的大小最多是多少,这样子view会根据这个上限来设置自己的尺寸)
int width;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = widthSize;
} else if (widthMode == AT_MOST) {
width = Math.min(desiredWidth, widthSize);
} else {
width = desiredWidth;
}四 layout()onLayout
setFrame(left, top, right, bottom),他会返回一个boolean值changed表示view的位置是否有发生了变化,然后遍历子 view 调用onlayout()方法,修改子view的位置了
⚠️ 1.view.getWidth() = right-left; view.getHeight() = bottom - top;这个view.getWidth()和measure中的mMeasuredWidth,也就是 view.getMeasuredWidth()是有区别的, view.getWidth()是整个屏幕中显示的宽,而view.getMeasuredWidth()是指view整个宽度,包块屏幕没显示到的2.view的话改变位置可以直接通过onlayout(),调用就是onlayout(boolean,left,top,left+width,top+height),一般不是继承view的话是不能重写layout()这个方法的
五 dispatchDraw() . draw()和onDraw()
最后我们会处理一些动画,然后导致view会重新绘制,这个时候的话就需要下面这些方法
(1)invalidate()方法
视图,即谁(View的话,只绘制该View ;ViewGroup,则绘制整个ViewGroup)请求invalidate()方法,就绘制该视图。
一般引起invalidate()操作的函数如下:
1、直接调用invalidate()方法,请求重新draw(),但只会绘制调用者本身。
2、setSelection()方法 :请求重新draw(),但只会绘制调用者本身。
3、setVisibility()方法 : 当View可视状态在INVISIBLE转换VISIBLE时,会间接调用invalidate()方法, 继而绘制该View。
4 、setEnabled()方法 : 请求重新draw(),但不会重新绘制任何视图包括该调用者本身。
(2)requestLayout()方法
请求重新布局layout,他会调用measure()和layout()过程,他不会调用draw()过程,也就是不会重新绘制任何视图包括自己。
一般引起requestLayout的操作函数:
1、setVisibility()方法:当View的可视状态在INVISIBLE/ VISIBLE 转换为GONE状态时,会间接调用requestLayout() 和invalidate方 法。
一般引起requestLayout()操作的函数如下:
1、setVisibility()方法:
当View的可视状态在INVISIBLE/ VISIBLE 转换为GONE状态时,会间接调用requestLayout() 和invalidate方法。
同时,由于整个个View树大小发生了变化,会请求measure()过程以及draw()过程,同样地,只绘制需要“重新绘制”的视图。
题外话 引入动画的话
在自定义View中,动画是一帧一帧的过程。这意味着,如果你想使一个圆半径从小变大,你将需要逐步增加半径并调用invalidate()来重绘它。
在自定义View动画中,ValueAnimator是你的好朋友。下面这个类将帮助你从任何值开始执行动画到最后,甚至支持Interpolator(如果需要)。
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt( 0, 100);animator.setDuration( 1000);animator.setInterpolator( new DecelerateInterpolator());animator.addUpdateListener( new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {int newRadius = ( int) animation.getAnimatedValue();postInvalidate();}});animator.start();
参考文章
https://hackernoon.com/android-draw-a-custom-view-ef79fe2ff54b