一、java.lang.Object()
在 Java 中, Object 类是所有类的父类,也就是说 Java 的所有类都继承了 Object,子类可以使用 Object 的所有方法。
Object 类是在 java.lang 包中,编译时会自动导入,我们创建一个类时,如果没有明确继承一个父类,那么它就会自动继承 Object,成为 Object 的子类。
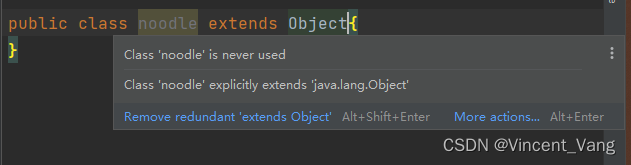
Object 类可以 显式继承 ,也可以 隐式继承 :
显式继承
隐式继承:
二、 toString() 方法
1.基本信息
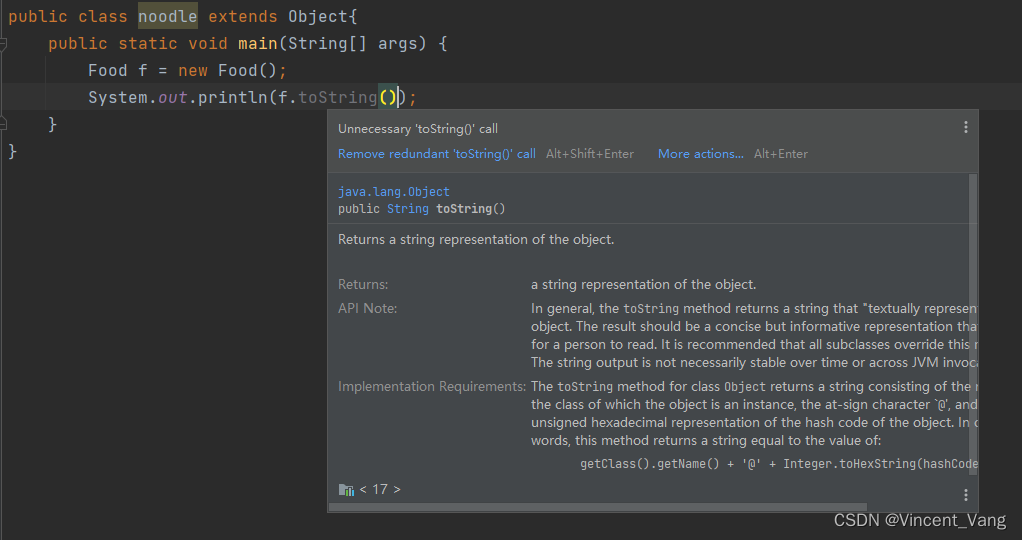
toString() 一个 public (公共的)修饰的一个方法,在 java.lang.Object 类中。
用来获得指定实例(对象)的描述信息(即用一个字符串描述一个实例)。
Returns a string representation of the object.
API Note:
In general, the method returns a string that “textually represents” this object. The result should be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a person to read. It is recommended that all subclasses override this method. The string output is not necessarily stable over time or across JVM invocations.
toStringImplementation Requirements:
The method for class returns a string consisting of the name of the class of which the object is an instance, the at-sign character `', and the unsigned hexadecimal representation of the hash code of the object. In other words, this method returns a string equal to the value of:
toStringObject@
getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
其返回类型为 String类型 ,是由其实例的名称 + @ + 对象的哈希码(无符号)的十六进制组成。
运行结果:
打印的结果为: 包名 + 类名 @ 对象的哈希码
2.重写 toString() 方法
对 toString() 未进行重写时,调用其方法时,打印出来的结果是一个由 包名 + 类名 @ 对象的哈希码 ,于是我们对 toString() 方法进行重写:
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Food{" + kind