题目描述
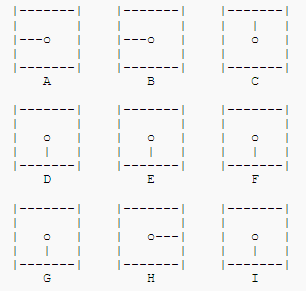
考虑将如此安排在一个 3 x 3 行列中的九个时钟:
目标要找一个最小的移动顺序将所有的指针指向12点。下面原表格列出了9种不同的旋转指针的方法,每一种方法都叫一次移动。选择1到9号移动方法,将会使在表格中对应的时钟的指针顺时针旋转90度。
移动方法 受影响的时钟
1 ABDE
2 ABC
3 BCEF
4 ADG
5 BDEFH
6 CFI
7 DEGH
8 GHI
9 EFHI
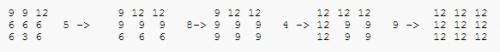
Example
[但这可能不是正确的方法,请看下面]
输入格式
第1-3行: 三个空格分开的数字,每个数字表示一个时钟的初始时间,3,6,9,12。数字的含意和上面第一个例子一样。
输出格式
单独的一行包括一个用空格分开的将所有指针指向12:00的最短移动顺序的列表。
如果有多种方案,输出那种使其连接起来数字最小的方案。(举例来说5 2 4 6 < 9 3 1 1)。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
9 9 12 6 6 6 6 3 6
输出 #1复制
4 5 8 9
说明/提示
题目翻译来自NOCOW。
USACO Training Section 1.4
我说它是暴力枚举,你信吗。。。。。。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node{ int state[9]; string ans; }; const bool movement[9][9] = { {1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0}, {1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0}, {1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0}, {0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0}, {0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1}, {0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0}, {0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1}, {0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1} }; int state[9]; inline bool checkOK(int state[]){ for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ if(state[i] != 4) return false; } return true; } string ans = ""; bool vis[5][5][5][5][5][5][5][5][5]; queue<node> q; void bfs(){ node tt; for(int j=0;j<9;j++){ tt.state[j] = state[j]; } tt.ans = ""; q.push(tt); while(!q.empty()){ node now = q.front(); q.pop(); if(checkOK(now.state)){ ans = now.ans; return; } for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ node nextn=now; for(int k=0;k<9;k++){ nextn.state[k]=(nextn.state[k]+movement[i][k])%5; if(nextn.state[k] == 0) nextn.state[k] = 1; } nextn.ans += (char)('0'+i+1); if(!vis[nextn.state[0]][nextn.state[1]][nextn.state[2]][nextn.state[3]][nextn.state[4]][nextn.state[5]][nextn.state[6]][nextn.state[7]][nextn.state[8]]){ q.push(nextn); vis[nextn.state[0]][nextn.state[1]][nextn.state[2]][nextn.state[3]][nextn.state[4]][nextn.state[5]][nextn.state[6]][nextn.state[7]][nextn.state[8]] = true; } } } } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ int time; cin>>time; state[i] = time / 3; } memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); bfs(); for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++){ if(i == 0){ cout << ans[i]; }else{ cout << " " << ans[i]; } } return 0; }