以下答案纯属个人愚见,作为IT新手,算法代码中难免有逻辑漏洞和其他不足之处,欢迎朋友你点评拍砖,交流争辩能极大开阔思维,愿一起加油进步!^_^
1.1.19 在计算机上运行以下程序:
1 public class Fibonacci { 2 3 public static long F(int N) { 4 if(0 == N) 5 return 0; 6 if(1 == N) 7 return 1; 8 return F(N - 1) + F(N - 2); 9 } 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 for(int N = 0; N < 100; ++N) 13 StdOut.println(N + " " + F(N)); 14 } 15 16 }
计算机用这段程序在一个小时之内能够得到F(N) 结果的最大N 值是多少?开发F(N) 的一 个更好的实现,用数组保存已经计算过的值。
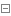
1 public class Fibonacci { 2 3 // Fibonacci数列计算,时间空间复杂度优化版 4 private static int M = 100; 5 private static long[] fib = new long[M]; 6 public static long fibonacciOptimization(int N) { 7 if(0 == N) 8 fib[0] = 0; 9 else if(1 == N) 10 fib[1] = 1; 11 else 12 fib[N] = fib[N - 1] + fib[N -2]; 13 return fib[N]; 14 } 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 for(int N = 0; N < 100; ++N) { 18 fib[N] = fibonacciOptimization(N); 19 StdOut.println(N + "\t" + fib[N]); 20 } 21 } 22 23 }
1.1.20 编写一个递归的静态方法计算 ln( N! ) 的值。


1 public static long factorial(int M) { 2 if(0 == M || 1 == M) 3 return 1; 4 else 5 return M * factorial(M - 1); 6 } 7 8 public static double ln(int N) { 9 return Math.log(factorial(N)); 10 } 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 double val = ln(4); 14 StdOut.println(val); 15 }
1.1.21 编写一段程序,从标准输入按行读取数据,其中每行都包含一个名字和两个整数。然后用printf() 打印一张表格,每行的若干列数据包括名字、两个整数和第一个整数除以第二个整数的结果,精确到小数点后三位。可以用这种程序将棒球球手的击球命中率或者学生的考试分数制成表格。


1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 int M = 3; 3 int index = 0; 4 String[] strs = new String[M]; 5 while(index < M) 6 strs[index++] = StdIn.readLine(); 7 for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; ++i) { 8 String[] arr = strs[i].split("\\s+"); 9 double temp = Double.parseDouble(arr[1]) / Double.parseDouble(arr[2]); 10 StdOut.printf("%-10s %-10s %-10s %-13.3f\n", arr[0], arr[1], arr[2], temp); 11 }; 12 }
1.1.22 使用1.1.6.4 节中的rank() 递归方法重新实现BinarySearch 并跟踪该方法的调用。每当该方法被调用时,打印出它的参数lo 和hi 并按照递归的深度缩进。提示:为递归方法添加一个参数来保存递归的深度。


1 /** 2 * 递归查找关键词的索引 3 * @param key 4 * @param arr 5 * @param low 6 * @param high 7 * @return 8 */ 9 public static int rank(int key, int[] arr, int low, int high, int depth) { 10 printCallInfo(low, high, depth); 11 if(low > high) 12 return -1; 13 int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1); 14 if(key < arr[mid]) 15 return rank(key, arr, low, mid - 1, depth + 1); 16 else if(key > arr[mid]) 17 return rank(key, arr, mid + 1, high, depth + 1); 18 else 19 return mid; 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 二分查找 : 递归描述 24 * @param key 25 * @param arr 26 * @return 27 */ 28 public static int binarySearch(int key, int[] arr, int depth) { 29 return rank(key, arr, 0, arr.length - 1, depth); 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 打印缩进 34 * @param indents 缩进数 35 */ 36 private static void printIndent(final int indents) { 37 for(int i = 0; i < indents; ++i) 38 StdOut.print("----------"); 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * 打印调用信息 43 * @param low 44 * @param high 45 * @param depth 46 */ 47 private static void printCallInfo(int low, int high, int depth) { 48 StdOut.print(depth + "\t"); 49 printIndent(depth); 50 StdOut.println(low + "\t" + high); 51 } 52 53 public static void main(String[] args) { 54 int N = 1024; 55 int[] arr = new int[N]; 56 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) 57 arr[i] = StdRandom.uniform(N * 50); 58 // 排序 59 Arrays.sort(arr); 60 // 从随机数组中随机抽取一个元素作为关键字 61 // 输出随机数组 62 StdOut.print("seq = "); 63 for(int i = 0 ; i < N; ++i) 64 StdOut.print(arr[i] + "\t"); 65 int key = arr[StdRandom.uniform(N)]; 66 StdOut.println("\nkey = " + key); 67 StdOut.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"); 68 binarySearch(key, arr, 0); 69 }
1.1.23 为BinarySearch 的测试用例添加一个参数:+ 打印出标准输入中不在白名单上的值;-,则打印出标准输入中在白名单上的值。


1 /** 2 * 二分查找 : 非递归描述 3 * @param key 关键字 4 * @param arr 数组 5 * @return 若找到则返回true,否则返回false 6 */ 7 public static boolean BinaryLookup(int key, int[] arr) { 8 int low = 0; 9 int high = arr.length - 1; 10 while(low <= high) { 11 int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1); 12 if(key < arr[mid]) 13 high = mid - 1; 14 else if(key > arr[mid]) 15 low = mid + 1; 16 else 17 return true; 18 } 19 return false; 20 } 21 22 public static void main(String[] args) { 23 // “ + ” --> 打印出标准输入中不在白名单上的值, 24 // “ - ” --> 打印出标准输入中在白名单上的值 25 char symbol = '-'; 26 int[] whitelist = new In(args[0]).readAllInts(); 27 Arrays.sort(whitelist); 28 while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) { 29 int key = StdIn.readInt(); 30 boolean found = BinaryLookup(key, whitelist); 31 if('+' == symbol && !found) 32 StdOut.println(key); 33 if('-' == symbol && found) 34 StdOut.println(key); 35 } 36 }
测试命令:java xxx tinyW.txt < tinyT.txt
1.1.24 给出使用欧几里德算法计算105 和24 的最大公约数的过程中得到的一系列p 和q 的值。扩展该算法中的代码得到一个程序Euclid,从命令行接受两个参数,计算它们的最大公约数并打印出每次调用递归方法时的两个参数。使用你的程序计算1 111 111 和1 234 567 的最大公约数。


1 /** 2 * 打印缩进 3 * @param indents 缩进数 4 */ 5 private static void printIndents(final int indents) { 6 for(int i = 0; i < indents; ++i) 7 StdOut.print("----------"); 8 } 9 10 /** 11 * 打印调用信息 12 * @param p 13 * @param q 14 * @param depth 15 */ 16 private static void printCallInfo(int p, int q, int depth) { 17 StdOut.print(depth + "\t"); 18 printIndents(depth); 19 StdOut.println(p + " " + q); 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 使用2300多年前的欧几里得算法求解两数的最大公约数 24 * @param p 数一 25 * @param q 数二 26 * @return 最大公约数 27 */ 28 public static int Euclid(int p, int q, int depth) { 29 printCallInfo(p, q, depth); 30 if(q == 0) 31 return p; 32 int r = p % q; 33 return Euclid(q, r, depth+1); 34 } 35 36 public static void main(String[] args) { 37 int p = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); 38 int q = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 39 int gcd = Euclid(p, q, 0); 40 StdOut.println("\n" + p + " 和 " + q + " 的最大公约数是: " + gcd); 41 }
1.1.25 使用数学归纳法证明欧几里德算法能够计算任意一对非负整数p 和q 的最大公约数。
提高题
1.1.26 将三个数字排序。假设a、b、c 和t 都是同一种原始数字类型的变量。证明以下代码能够将a、 b、c 按照升序排列:
if (a > b) { t = a; a = b; b = t; } // 保证a为a、b两数的较小者
if (a > c) { t = a; a = c; c = t; } // 保证a为a、b、c三数中的最小者
if (b > c) { t = b; b = c; c = t; } // 保证b为比a大的b、c两数的较小者,从而必有c为三数中的最大者
1.1.27 二项分布。估计用以下代码计算binomial(100, 50) 将会产生的递归调用次数:
1 public static double binomial(int N,int k, double p) { 2 if(N == 0 && k == 0) 3 return 1.0; 4 if(N < 0 || k < 0) 5 return 0.0; 6 return (1.0 - p) * binomial(N-1, k, p) + p * binomial(N-1, k-1, p); 7 }
将已经计算过的值保存在数组中并给出一个更好的实现。
思路:用二维数组存储已计算的概率,下次需要时则直接取出即可,免去了再花时间去完成同样的计算,例如:binom[N][k] = (1.0 - p) * binomial(N - 1, k, p) + p * binomial(N - 1, k - 1, p);


1 private static int binom_N = 100; 2 3 private static int binom_k = 50; 4 5 private static double[][] binom = new double[binom_N + 1][binom_k + 1]; 6 7 private static double binomial(int N, int k, double p) { 8 if(N < 0 || k < 0) { 9 return 0.0; 10 } else if(N == 0 && k == 0) { 11 if(binom[N][k] == -1.0) 12 binom[N][k] = 1.0; 13 } else { 14 if (binom[N][k] == -1.0) 15 binom[N][k] = (1.0 - p) * binomial(N - 1, k, p) + p * binomial(N - 1, k - 1, p); 16 } 17 return binom[N][k]; 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 // 数组binom初始化 22 for(int i = 0; i < binom_N + 1; ++i) 23 for(int j = 0; j < binom_k + 1; ++j) 24 binom[i][j] = -1.0; 25 // 计算概率 26 double res = binomial(binom_N, binom_k, 0.25); 27 StdOut.println(res); 28 }
1.1.28 删除重复元素。修改BinarySearch 类中的测试用例来删去排序之后白名单中的所有重复元素。


1 /** 2 * 统计数组arr中重复元素个数 3 * @param arr 4 * @return 重复元素个数 5 */ 6 public static int countRepeated(int[] arr) { 7 int cnt = 0; 8 for (int i = 0; i < (arr.length - 1); ++i) 9 if (arr[i + 1] == arr[i]) 10 ++ cnt; 11 return cnt; 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * 去掉重复的元素,并拷贝其余元素 16 * @param original 原始数组 17 * @param repeatedCnt 重复的元素个数 18 * @return 去重后的数组拷贝 19 */ 20 public static int[] copy(int[] original, int repeatedCnt) { 21 int[] res = new int[original.length - repeatedCnt]; 22 int cntIdx = 0; 23 res[cntIdx ++] = original[0]; 24 for(int i = 1; i < original.length; ++i) 25 if(original[i] == original[i-1]) 26 continue; 27 else 28 res[cntIdx ++] = original[i]; 29 return res; 30 } 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) { 33 int[] whitelist = new In(args[0]).readAllInts(); 34 // 白名单排序并输出 35 Arrays.sort(whitelist); 36 for(int i = 0; i < whitelist.length; ++i) 37 StdOut.print(whitelist[i] + "\t"); 38 StdOut.println(); 39 // 统计重复元素个数并去重 40 int cnt = countRepeated(whitelist); 41 int[] res = copy(whitelist, cnt); 42 // 输出去重后的数组 43 for(int i = 0; i < res.length; ++i) 44 StdOut.print(res[i] + "\t"); 45 }
1.1.29 等值键。为BinarySearch 类添加一个静态方法rank(),它接受一个键和一个整型有序数组(可能存在重复键)作为参数并返回数组中小于该键的元素数量,以及一个类似的方法count() 来返回数组中等于该键的元素的数量。注意:如果i 和j 分别是rank(key,a) 和count(key,a)的返回值,那么a[i..i+j-1] 就是数组中所有和key 相等的元素。看法:只有当key在数组中时才这样子。


1 /** 2 * 二分查找统计 3 * @param key 待查找关键字 4 * @param arr 待查找数组 5 * @return 返回小于key的个数即比等于key的第一个元素的索引值,若找不到则返回-1 6 */ 7 private static int countLowers(int key, int[] arr) { 8 int low = 0; 9 int high = arr.length - 1; 10 while(low <= high) { 11 int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1); 12 if(key < arr[mid]) 13 high = mid - 1; 14 else if(key > arr[mid]) 15 low = mid + 1; 16 else { 17 while(mid > 0 && arr[mid] == arr[mid - 1]) // 注意判断条件的先后顺序 18 -- mid; 19 return mid; 20 } 21 } 22 return low; // -1; 根据算法原理可知low是小于key的个数 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * 统计与key相等的个数 27 * @param key 待查找关键字 28 * @param arr 待查找数组 29 * @return 返回与key相等的个数 30 */ 31 private static int countEquals(int key, int[] arr) { 32 int lowers = countLowers(key, arr); 33 int idx = lowers; 34 if(idx == arr.length || key != arr[idx]) // 注意判断条件的先后顺序 35 return 0; 36 37 int cnt = 1; 38 while((idx < arr.length - 1) && (arr[idx] == arr[idx + 1])) { // 注意判断条件的先后顺序 39 ++ cnt; 40 ++ idx; 41 } 42 return cnt; 43 } 44 45 public static void main(String[] args) { 46 // 从文件读取数据 47 In in = new In("./data/tinyW.txt"); 48 int[] whiteList = in.readAllInts(); 49 // 排序并打印输出 50 Arrays.sort(whiteList); 51 for(int idx = 0; idx < whiteList.length; ++idx) 52 StdOut.print(whiteList[idx] + "\t"); 53 StdOut.println(); 54 // 从控制台读取关键字 55 int key = StdIn.readInt(); 56 int lowers = countLowers(key, whiteList); 57 StdOut.println("小于\t" + key + "\t的个数是:\t" + lowers); 58 int equals = countEquals(key, whiteList); 59 StdOut.println("等于\t" + key + "\t的个数是:\t" + equals); 60 }
1.1.30 数组练习。编写一段程序,创建一个N×N 的布尔数组a[][]。其中当i 和j 互质时(没有相同因子),a[i][j] 为true,否则为false。


1 /** 2 * 判断两数是否互质,若两数的最大公约数是1则两数互质 3 * @param a 4 * @param b 5 * @return 若互质则true,否则false 6 */ 7 private static boolean isCoprime(int a, int b) { 8 for(int i = 2; i < Math.sqrt(a); ++i) { 9 if(a % i == 0 && b % i == 0) 10 return false; 11 } 12 return true; 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * 使用2300多年前的欧几里得算法求解两数的最大公约数 17 * @param p 数一 18 * @param q 数二 19 * @return 最大公约数 20 */ 21 private static int gcd(int p, int q) { 22 if(q == 0) 23 return p; 24 int r = p % q; 25 return gcd(q, r); 26 } 27 28 private static boolean[][] boolArray(int N) { 29 // 创建NxN的布尔二维数组 30 boolean[][] boolArr = new boolean[N][N]; 31 for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) 32 for(int j = 1; j <= N; ++j) 33 if(1 == gcd(i, j)) 34 boolArr[i - 1][j - 1] = true; 35 else 36 boolArr[i - 1][j - 1] = false; 37 return boolArr; 38 } 39 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 int N = 5; 42 boolean[][] boolArr = boolArray(N); 43 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { 44 for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) 45 StdOut.print(boolArr[i][j] + "\t"); 46 StdOut.println(); 47 } 48 }
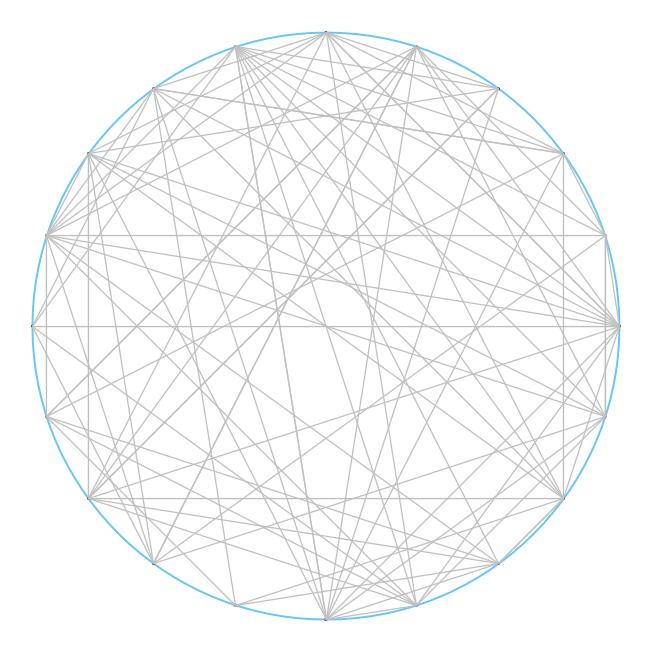
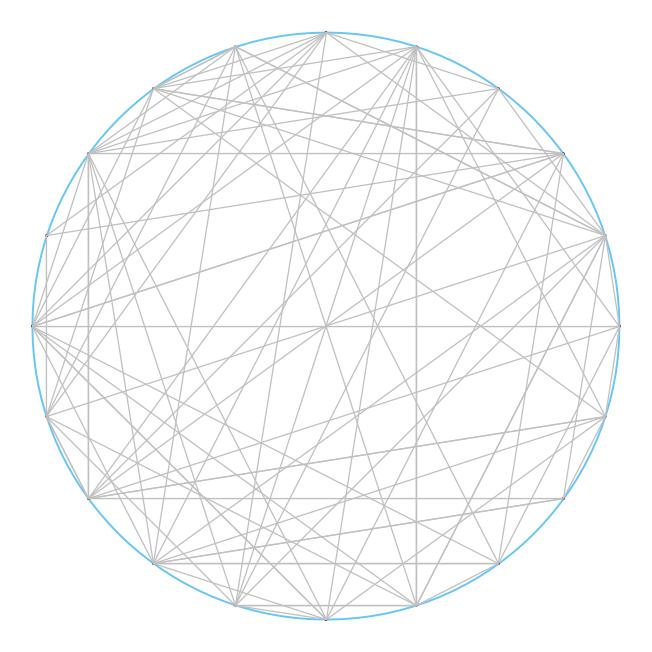
1.1.31 随机连接。编写一段程序,从命令行接受一个整数N 和double 值p(0 到1 之间)作为参数,在一个圆上画出大小为0.05 且间距相等的N 个点,然后将每对点按照概率p 用灰线连接。


1 /** 2 * 画圆 3 * @param x 圆心x坐标 4 * @param y 圆心y坐标 5 * @param r 半径r 6 */ 7 private static void drawCircle(double x, double y, double r) { 8 StdDraw.setXscale(0, 2 * x); 9 StdDraw.setYscale(0, 2 * y); 10 StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.003); 11 StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BOOK_LIGHT_BLUE); 12 StdDraw.circle(x, y, r); 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * 在圆上描点 17 * @param x0 圆心x坐标 18 * @param y0 圆心y坐标 19 * @param r 半径r 20 * @param N N个点 21 */ 22 private static double[][] drawPoints(double x0, double y0, double r, int N) { 23 double[][] points = new double[N][2]; 24 StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.005); 25 StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BOOK_RED); 26 for(int idx = 0; idx < N; ++idx) { 27 double x = x0 + r * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * idx / N); 28 double y = y0 + r * Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * idx / N); 29 StdDraw.point(x, y); 30 points[idx][0] = x; 31 points[idx][1] = y; 32 } 33 return points; 34 } 35 36 /** 37 * 以概率p随机连接顶点集points中的点 38 * @param points 点集 39 * @param p 概率p 40 */ 41 private static void randomLinkPoints(double[][] points, double p) { 42 StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.002); 43 StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.LIGHT_GRAY); 44 int length = points.length; 45 for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) 46 for(int j = 0; j < length; ++j) 47 if(true == StdRandom.bernoulli(p)) 48 StdDraw.line(points[i][0], points[i][1], points[j][0], points[j][1]); // 应该再建立一个包含x坐标和y坐标的数据结构 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * 在圆上画N个点然后每两点间以概率p连接 53 * @param N N个点 54 * @param p 概率p 55 */ 56 private static void randomLink(int N, double p) { 57 double x = 10.0; 58 double y = 10.0; 59 double r = 9.0; 60 drawCircle(x, y, r); 61 double[][] points = drawPoints(x, y, r, N); 62 randomLinkPoints(points, p); 63 } 64 65 public static void main(String[] args) { 66 randomLink(20, 0.2); 67 }
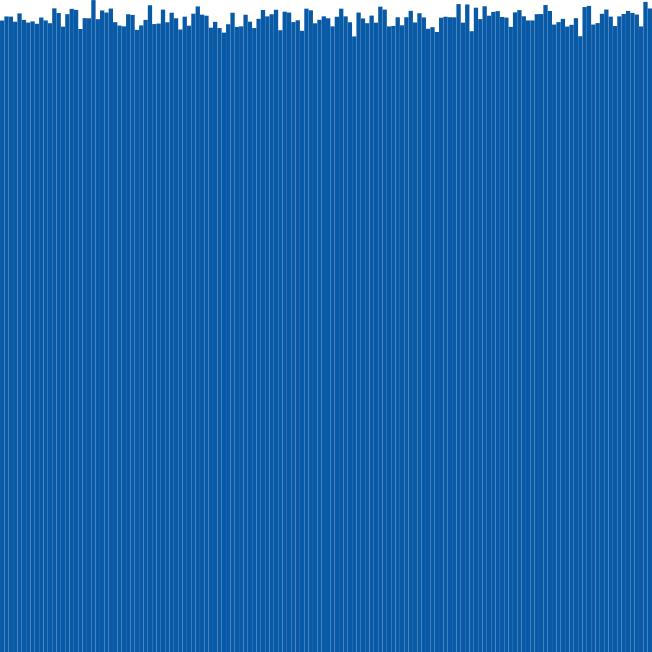
1.1.32 直方图。假设标准输入流中含有一系列double 值。编写一段程序,从命令行接受一个整数N 和两个double 值l 和r。将(l,r) 分为N 段并使用StdDraw 画出输入流中的值落入每段的数量的直方图。


1 /** 2 * 数据柱状图 3 * @param N 4 * @param l 5 * @param r 6 * @param arr 7 */ 8 private static void dataHistogram(int N, double l, double r, double[] arr) { 9 int length = arr.length; 10 int[] statistics = new int[N]; 11 double interval = (r - l) / N; 12 // 统计数据分布 13 for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 14 double remain = arr[i] - l; 15 int idx = (int)(remain / interval); 16 ++ statistics[idx]; 17 } 18 // 查找统计结果中最大值,用于绘制直方图时计算柱状图高时 19 double max = statistics[0]; 20 for(int i = 1; i < statistics.length; ++i) { 21 if(max < statistics[i]) 22 max = statistics[i]; 23 } 24 // 绘制直方图 25 StdDraw.setXscale(l, r); 26 StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BOOK_BLUE); 27 double x0 = l + interval / 2.0; 28 for(int i = 0; i < statistics.length; ++i) { 29 double x = x0 + i * interval; 30 double y = statistics[i] / (max + 1) / 2.0; 31 double hw = 0.99 * interval / 2.0; 32 double hh = y; 33 StdDraw.filledRectangle(x, y, hw, hh); 34 } 35 } 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 In in = new In("./data/largeW.txt"); 39 double[] whiteList = in.readAllDoubles(); 40 double min = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; 41 double max = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY; 42 for(int i = 0; i < whiteList.length; ++i) { 43 if(min > whiteList[i]) 44 min = whiteList[i]; 45 if(max < whiteList[i]) 46 max = whiteList[i]; 47 } 48 // 从控制台读取应该将数据分割的段数 49 StdOut.print("将数据分割的段数:"); 50 int N = StdIn.readInt(); 51 dataHistogram(N, min, max + 10.0, whiteList); 52 }
此图也反映了伪随机数是均匀分布的。
1.1.33 矩阵库。编写一个Matrix 库并实现以下API: <这道题考虑不周,请读者先略过>
public class Matrix
- static double dot(double[ ] x, double[ ] y) 向量点乘
- static double[ ][ ] multiple(double[ ][ ] a, double[ ][ ] b) 矩阵和矩阵之积
- static double[ ][ ] transpose(double[ ][ ] a) 转置矩阵
- static double[ ] multiple(double[ ][ ] a, double[ ] x) 矩阵和向量之积
- static double[ ] multiple(double[ ] y, double[ ][ ] a) 向量和矩阵之积
编写一个测试用例,从标准输入读取矩阵并测试所有方法。


1 /** 2 * 向量点乘 3 * @param x x向量 4 * @param y y向量 5 * @return 向量点乘 6 */ 7 public static double dot(double[] x, double[] y) { 8 // 点乘必须是向量a的长度等于向量b的长度才能运算 9 if(x.length != y.length) 10 System.exit(-1); 11 double res = 0.0; 12 for(int i = 0; i < x.length; ++i) 13 res += x[i] * y[i]; 14 return res; 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * 矩阵和矩阵之积 19 * @param a 20 * @param b 21 * @return 22 */ 23 public static double[][] multiple(double[][] a, double[][] b) { 24 // 只有矩阵a的列数等于矩阵b的行数时,相乘才有意义 25 if(a[0].length != b.length) 26 System.exit(-1); 27 double[][] matrix = new double[a.length][b[0].length]; 28 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) 29 for (int j = 0; j < b[0].length; ++j) 30 for (int k = 0; k < b.length; ++k) 31 matrix[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; 32 return matrix; 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * 矩阵和向量之积 37 * @param a 38 * @param x 39 * @return 40 */ 41 public static double[] multiple(double[][] a, double[] x) { 42 if(a[0].length != x.length) 43 System.exit(-1); 44 double[] matrix = new double[x.length]; 45 for(int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) 46 for(int j = 0; j < x.length; ++j) 47 matrix[i] += a[i][j] * x[j]; 48 return matrix; 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * 向量和矩阵之积 53 * @param y 54 * @param a 55 * @return 56 */ 57 public static double[] multiple(double[] y, double[][] a) { 58 double[] matrix = new double[y.length]; 59 for(int i = 0; i < y.length; ++i) 60 for(int j = 0; j < a[i].length; ++j) 61 matrix[i] += y[j] * a[j][i]; 62 return matrix; 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * 转置矩阵 67 * @param a 68 * @return 69 */ 70 public static double[][] transpose(double[][] a) { 71 for(int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) 72 for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j) { 73 double temp = a[i][j]; 74 a[i][j] = a[j][i]; 75 a[j][i] = temp; 76 } 77 return a; 78 } 79 80 public static void main(String[] args) { 81 StdOut.println("-------- 向量点乘 ---------"); 82 double[] a0 = {1, 2, 3}; 83 double[] b0 = {4, 5, 6}; 84 double res0 = dot(a0, b0); 85 StdOut.println(res0); 86 87 StdOut.println("-------- 矩阵乘法 ---------"); 88 double[][] a1 = { 89 {1, 2}, 90 {3, 4}, 91 {5, 6} 92 }; 93 double[][] b1 = { 94 {1, 2, 3}, 95 {4, 5, 6} 96 }; 97 double[][] res1 = multiple(a1, b1); 98 for(int i = 0; i < res1.length; ++i) { 99 for (int j = 0; j < res1[i].length; ++j) 100 StdOut.printf("%-10.3f", res1[i][j]); 101 StdOut.println(); 102 } 103 104 StdOut.println("-------- 矩阵转置 ---------"); 105 double[][] a2 = { 106 {1, 2, 3}, 107 {4, 5, 6}, 108 {7, 8, 9} 109 }; 110 double[][] c2 = transpose(a2); 111 for(int i = 0; i < a2.length; ++i) { 112 for (int j = 0; j < a2[i].length; ++j) 113 StdOut.printf("%-10.3f", a2[i][j]); 114 StdOut.println(); 115 } 116 117 StdOut.println("----- 矩阵和向量之积 ------"); 118 double[][] a3 = { 119 {1, 2, 3}, 120 {4, 5, 6}, 121 {7, 8, 9} 122 }; 123 double[] b3 = {1, 2, 3}; 124 double[] c3 = multiple(a3, b3); 125 for(int i = 0; i < c3.length; ++i) 126 StdOut.printf("%-10.3f\n", c3[i]); 127 128 StdOut.println("----- 向量和矩阵之积 ------"); 129 double[] a4 = {1, 2, 3}; 130 double[][] b4 = { 131 {1, 2, 3}, 132 {4, 5, 6}, 133 {7, 8, 9} 134 }; 135 double[] c4 = multiple(a4, b4); 136 for(int i = 0; i < c4.length; ++i) 137 StdOut.printf("%-10.3f", c4[i]); 138 }
1.1.34 过滤。以下哪些任务需要(在数组中,比如)(1)保存标准输入中的所有值?哪些可以(2)被实现为一个过滤器且仅使用固定数量的变量和固定大小的数组(和N无关)?在每个
问题中,输入都来自于标准输入且含有N个0到1的实数。
- 打印出最大和最小的数 (2)
- 打印出所有数的中位数 (1)
- 打印出第 k 小的数,k 小于100 (2)
- 打印出所有数的平方和 (2)
- 打印出 N 数的平均值 (2)
- 打印出大于平均值的数的百分比 (1)
- 将 N 个数按照升序打印 (1)
- 将 N 个数按照随机顺序打印 (1)
实验题
1.1.35 模拟掷骰子。以下代码能够计算每种两个骰子之和的准确概率分布:
1 int SIDES = 6; 2 double[] dist = new double[2 * SIDES + 1]; 3 for(int i = 1; i <= SIDES; i++) 4 for(int j = 1; j <= SIDES; j++) 5 dist[i+j] += 1.0; 6 for (int k = 2; k <= 2*SIDES; k++) 7 dist[k] /= 36.0;
dist[i] 的值就是两个骰子之和为i 的概率。用实验模拟N 次掷骰子,并在计算两个1 到 6 之间的随机整数之和时记录每个值的出现频率以验证它们的概率。N 要多大才能够保证你的经验数据和准确数据的吻合程度达到小数点后三位?


1 // 色子有六面,数值分别是1、2、3、4、5、6 2 private static int sides = 6; 3 4 /** 5 * 打印 6 * @param dist 待输出数组 7 */ 8 private static void print(double[] dist) { 9 for(int i = 2; i <= 2 * sides; ++i) 10 StdOut.println(dist[i]); 11 StdOut.println("-------------------------"); 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * 根据统计数据计算概率值 16 * @param dist 统计数据数组 17 * @return 概率数组 18 */ 19 private static double[] computeProbability(double[] dist, int testTimes) { 20 for(int i = 2; i <= 2 * sides; ++i) 21 dist[i] /= (1.0 * testTimes); 22 return dist; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * 两个色子之和的理论概率值 27 * @return 理论概率值 28 */ 29 private static double[] theoreticalValue() { 30 double[] dist = new double[2 * sides + 1]; 31 // 统计值出现的理论次数 32 for(int i = 1; i <=sides; ++i) 33 for(int j = 1; j <= sides; ++j) 34 dist[i+j] += 1.0; 35 // 计算理论概率 36 dist = computeProbability(dist, 36); 37 return dist; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 用随机数模拟掷色子并统计求出试验概率 42 * @param N 抛掷次数 43 * @return 试验概率 44 */ 45 private static double[] simulate(int N) { 46 double[] dist = new double[2 * sides + 1]; 47 // 做N次随机试验模拟抛色子,并统计数据 48 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { 49 int a = StdRandom.uniform(1, 6 + 1); 50 int b = StdRandom.uniform(1, 6 + 1); 51 dist[a + b] += 1.0; 52 } 53 // 计算试验概率值 54 dist = computeProbability(dist, N); 55 return dist; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * 试验概率值能否与理论概率值至少匹配到小数点后三位数 60 * @param dist0 理论概率值 61 * @param dist1 试验概率值 62 * @return 能匹配到小数点后三位数则返回true,否则返回false 63 */ 64 private static boolean isMatch(double[] dist0, double[] dist1) { 65 for(int i = 2; i <= 2 * sides; ++i) 66 if(Math.abs(dist0[i] - dist1[i]) >= 0.0001) 67 return false; 68 return true; 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * 测试得到符合要求的试验次数N 73 * @param initTimes 试验初始次数值 74 * @param dist0 理论概率 75 * @return 符合要求的试验次数 76 */ 77 private static int testGetN(int initTimes, double[] dist0) { 78 int N = initTimes; 79 boolean match = false; 80 while(!match) { 81 double[] dist1 = simulate(N); 82 match = isMatch(dist0, dist1); 83 if(match) 84 print(dist1); 85 // 当前N不合要求,则将N扩大10倍 86 N *= 10; 87 } 88 return N; 89 } 90 91 public static void main(String[] args) { 92 double[] dist0 = theoreticalValue(); 93 print(dist0); 94 int initTimes = 1000000; 95 int N = testGetN(initTimes, dist0); 96 StdOut.println("至少试验次数的数量级: o(" + N + ")"); 97 }
1.1.36 乱序检查。通过实验检查表1.1.10 中的乱序代码是否能够产生预期的效果。编写一个程序ShuffleTest,接受命令行参数M 和N,将大小为M 的数组打乱N 次且在每次打乱之前都将数组重新初始化为a[i] = i。打印一个M×M 的表格,对于所有的列j,行i 表示的是i 在打乱后落到j 的位置的次数。数组中的所有元素的值都应该接近于N/M。
1.1.37 糟糕的打乱。假设在我们的乱序代码中你选择的是一个0 到N-1 而非i 到N-1 之间的随机整数。证明得到的结果并非均匀地分布在N! 种可能性之间。用上一题中的测试检验这个版本。
1.1.38 二分查找与暴力查找。根据1.1.10.4 节给出的暴力查找法编写一个程序bruteForceSearch,在你的计算机上比较它和BinarySearch 处理largeW.txt 和largeT.txt 所需的时间。


1 /** 2 * 二分查找 : 非递归描述 3 * @param key 关键字 4 * @param arr 数组 5 * @return 若找到则返回true,否则返回false 6 */ 7 public static boolean BinaryLookup(int key, int[] arr) { 8 int low = 0; 9 int high = arr.length - 1; 10 while(low <= high) { 11 int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1); 12 if(key < arr[mid]) 13 high = mid - 1; 14 else if(key > arr[mid]) 15 low = mid + 1; 16 else 17 return true; 18 } 19 return false; 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 暴力查找 24 * @param key 25 * @param arr 26 * @return 在数组arr中找到key则返回true,否则返回false 27 */ 28 public static boolean bruteForceSearch(int key, int[] arr) { 29 for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i) 30 if(key == arr[i]) 31 return true; 32 return false; 33 } 34 35 public static void main(String[] args) { 36 int[] whiteList = new In(args[0]).readAllInts(); 37 long time0 = new Date().getTime(); 38 // Arrays.sort(whiteList); // 暴力破解无需排序 39 while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) { 40 int key = StdIn.readInt(); 41 boolean find = bruteForceSearch(key, whiteList); 42 if(!find) 43 StdOut.println(key); 44 } 45 long time1 = new Date().getTime(); 46 long elapsedTime = time1 - time0; 47 StdOut.println("用时: " + elapsedTime + " ms"); 48 }
测试命令:java xxx largeW.txt < largeT.txt > bruteForceSearch.txt
测试结果数据:http://files.cnblogs.com/files/gotodsp/TestResults.zip
1.1.39 随机匹配。编写一个使用BinarySearch 的程序,它从命令行接受一个整型参数T,并会分别针对N=10^3、10^4、10^5 和10^6 将以下实验运行 T 遍:生成两个大小为N 的随机6 位正整数数组并找出同时存在于两个数组中的整数的数量。打印一个表格,对于每个N,给出T 次实验中该数量的平均值。


1 /** 2 * 返回长度为length的随机6位正整数数组 3 * @param length 数组长度 4 * @return 随机6位正整数数组 5 */ 6 private static int[] randomArray(int length) { 7 int[] arr = new int[length]; 8 for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) 9 arr[i] = StdRandom.uniform(100000, 1000000); 10 return arr; 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * 递归查找关键词的索引 15 * @param key 关键字 16 * @param arr 数组 17 * @param low 当前查找段的起始索引 18 * @param high 当前查找段的最终索引 19 * @return 若查找到则返回关键字key的索引值,找不到则返回-1 20 */ 21 public static int rank(int key, int[] arr, int low, int high) { 22 if(low > high) 23 return -1; 24 int mid = low + ((high - low) >> 1); 25 if(key < arr[mid]) 26 return rank(key, arr, low, mid - 1); 27 else if(key > arr[mid]) 28 return rank(key, arr, mid + 1, high); 29 else 30 return mid; 31 } 32 33 /** 34 * 查找关键key是否在数组arr中 35 * @param key 关键字 36 * @param arr 数组 37 * @return 若找到则返回索引值,否则返回-1 38 */ 39 private static int binarySearch(int key, int[] arr) { 40 return rank(key, arr, 0, arr.length - 1); 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * 统计两个数组中的相同元素个数 45 * @param arr1 46 * @param arr2 47 * @return 48 */ 49 private static int countCommonElements(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) { 50 int cnt = 0; 51 for(int i = 0; i < arr1.length; ++i) { 52 int idx = binarySearch(arr1[i], arr2); 53 if(-1 != idx) 54 ++ cnt; 55 } 56 return cnt; 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * 随机匹配 61 * @param T 次数 62 */ 63 private static void randomMatch(int T) { 64 for(int N = 1000; N <= 1000000; N *= 10) { 65 int cnt = 0; 66 for(int i = 0; i < T; ++i) { 67 int[] arr1 = randomArray(N); 68 int[] arr2 = randomArray(N); 69 cnt += countCommonElements(arr1, arr2); 70 } 71 double avg = 1.0 * cnt / N; 72 StdOut.println(N + " " + avg); 73 } 74 } 75 76 public static void main(String[] args) { 77 randomMatch(10000); 78 }
本文原创,欢迎转载,请注明本站地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gotodsp/p/4319865.html,:)