实现代码:
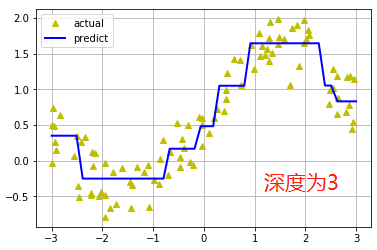
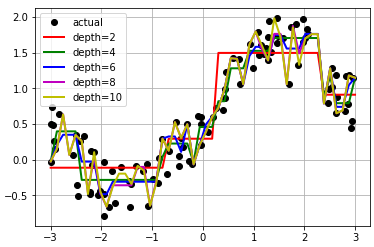
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Wed Aug 29 14:52:09 2018 4 5 @author: zhen 6 """ 7 import numpy as np 8 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 n = 100 11 x = np.random.rand(n) * 6 - 3 # 生成100个范围在-3~3的数据 12 x.sort() #排序 13 14 y = np.sin(x) + np.random.rand(n) + 0.05 15 x = x.reshape(-1, 1) #把数据转成任意行一列类型 16 y = y.reshape(-1, 1) 17 18 decision_tree_regressor = DecisionTreeRegressor(criterion='mse', max_depth=3) 19 decision_tree_regressor.fit(x, y) 20 21 x_test = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50).reshape(-1, 1) # 创建等差数列 22 y_hat = decision_tree_regressor.predict(x_test) 23 24 plt.plot(x, y, "y^", label="actual") 25 plt.plot(x_test, y_hat, "b-", linewidth=2, label="predict") 26 27 plt.legend(loc="upper left") 28 plt.grid() 29 plt.show() 30 31 # 比较不同深度的决策树 32 depth = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] 33 color = 'rgbmy' 34 dec_tree_reg = DecisionTreeRegressor() 35 36 plt.plot(x, y, "ko", label="actual") 37 x_test = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50).reshape(-1, 1) 38 for d, c in zip(depth, color): 39 dec_tree_reg.set_params(max_depth=d) 40 dec_tree_reg.fit(x, y) 41 y_hat = dec_tree_reg.predict(x_test) 42 plt.plot(x_test, y_hat, '-', color=c, linewidth=2, label="depth=%d" % d) 43 44 plt.legend(loc="upper left") 45 plt.grid(b=True) 46 plt.show()
结果:
不同深度对预测的影响:
总结:
决策树分量算法有构造速度快、结构明显、分类精度高等优点。
决策树是以实例(Instance)为核心的归纳分类方法。
它从一组无序的、无特殊领域知识的数据集中提取出决策树表现形式的分类规则,
包含了分支节点、叶子节点和分支结构。它采用自顶向下的递归方式构造树状结构,
在决策时分支节点进行基于属性值的分类选择,分支节点覆盖了可能的分类结果,
最终分支节点连接了代表分类结果的叶子节点。
分类过程中经过的连接节点代表了一条分类模式,而这些分类模式的集合就组成了决策树的框架。