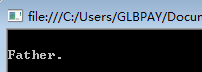
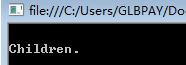
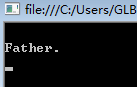
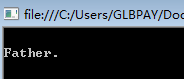
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } } class Children : Father { public new void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren."); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.Read(); } }
2. virtual override
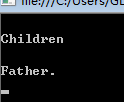
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father:IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } } class Children:Father { public override void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren."); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); } }
3. virtual
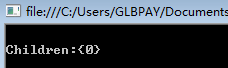
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } } class Children : Father { public void F(string arg) { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren:{0}", arg); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.Read(); } }
4.abstract
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } abstract class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } } class Children : Father { public void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren:{0}"); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
5.interface,class继承
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } } class Children : Father,IGrandFather //定义时类必须在接口前面 { public new void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren:{0}"); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children();//Children中的方法F实现了直接接口IGrandFather,该方法同时隐藏了从父类Father中继承的F()方法。 gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
6.ref
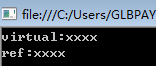
class A { public virtual void F(string p) { Console.WriteLine("virtual:"+p); } } class B : A { public void F(ref string p) //隐藏了父类的方法 { Console.WriteLine("ref:" + p); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { string s = "xxxx"; B b = new B(); b.F(s); //调用被隐藏的父类的方法 b.F(ref s); Console.Read(); } }
讲解:当一个父类被一个子类继承时,父类中的方法也被子类继承,
当子类中新建了一个同样的方法时,子类中的方法将覆盖父类中的方法,子类的实例将不能调用父类中的该方法(virtual,override)除外,
当实例化一个子类,并将其赋值给一个父类的实例时,父类的实例只接收了父类中的信息,没有接收子类本身的信息。
当父类中某方法声明为虚方法时,表示可以被子类中方法替换
当子类中某方法声明为重载时,表示在将一个子类对象赋值给一个父类对象时,该方法可以替换掉父类对象中的该方法。
当子类同时继承一个父类和接口时,必须先继承类,再继承接口,这是微软规定的写法,实际上不晓得继承的顺序
同上,子类对象赋值给接口对象时,接口对象只接收了接口中方法的部分。由于接口只规定了方法的定义,没法实例化,
所以这里的接口对象可以认为是子类对象剔除非接口方法元素的存在。
http://www.cnblogs.com/think/archive/2005/04/21/142460.html
扩展
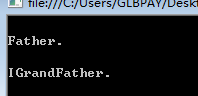
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather."); } } class Children : Father, IGrandFather { public new void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChildren"); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Father fa = new Children(); fa.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
隐式实现的话实现的方法属于实现的类的,可以直接通过类的对象访问,显式实现的话方法是属于接口的,可以看成是寄托在类中实现的,访问这些方法时要先把对象转换成接口对象,然后通过接口对象调用,
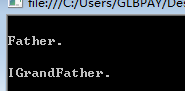
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather."); } } class Children : Father { } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { Father fa = new Children(); fa.F(); IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
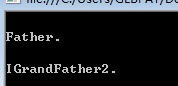
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather."); } } class Children : Father,IGrandFather { public new void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nChild."); } void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather2."); } } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { Father fa = new Children(); fa.F(); IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { public virtual void F() { Console.WriteLine("\nFather."); } void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather."); } } class Children : Father,IGrandFather { } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { Father fa = new Children(); fa.F(); IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }
当一个类实现一个接口,且是显示接口实现时,相当于把这个实现的方法寄存在类中,类本身对象调用不到,只有转换为接口对象才可以调用到
当该类被继承时,子类继承了父类的一切,包括显示实现接口的方法,也继续寄存在子类中,子类对象也调用不到,只有转换为接口对象才可以调用
当该子类同时继承父类实现的那个接口时,同时显示接口实现时,新的方法将覆盖旧的寄存方法。
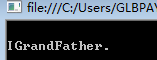
interface IGrandFather { void F(); } class Father : IGrandFather { void IGrandFather.F() { Console.WriteLine("\nIGrandFather."); } } class Children : Father,IGrandFather { } class Test { public static void Main(string[] args) { IGrandFather gf = new Children(); gf.F(); Console.ReadLine(); } }