1. 基本查询
#查询所有记录
select * from 表名;
#查询指定字段
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名;2. DISTINCT查询
查询时可以剔除重复记录,重复的定义是指选取的查询字段对应的记录全部一样,如果只是某一个字段相同不算重复记录。
#剔除重复选项
select distinct * from 表名;
select distinct 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名;3. IN查询
查询时可以通过IN关键字,限定查询的某一字段的记录取值范围。
#in查询
select * from 表名 where 列名 in (值1, 值2, ...);
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n in (值1, 值2, ...);
#not in
#in查询
select * from 表名 where 列名 not in (值1, 值2, ...);
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n not in (值1, 值2, ...);- 使用IN查询时,如果 in(),括号中有NULL,并不会返回值为NULL的记录
- 使用not in 查询时,如果not in(),括号中有NULL,一条记录都查不出来
4. between and
IN查询可以限定多个离散的取值点,between and可以限定一个取值范围,但是只能用于数值和时间类型。
between n1 and n2,限定的范围是[n1, n2]
#between and
select * from 表名 where 列名 between n1 and n2;
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n between n1 and n2;
#not between and
select * from 表名 where 列名 not between n1 and n2;
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n not between n1 and n2; 5. like
MySQL中支持使用关键字like和通配符进行模糊查询。
| 通配符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| _ | 匹配单个字符 |
| % | 匹配任意长度字符 |
- 模糊查询不仅适用于字符串,数值同样可以模糊查询
- 不管是数值还是字符串,模糊查询时like后面的限定条件都要是字符串形式,以''或""包括
#like
select * from 表名 where 列名 like '包含通配符的字符串';
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n like '包含通配符的字符串';
#not like
select * from 表名 where 列名 not like '包含通配符的字符串';
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 where 列名n not like '包含通配符的字符串';6. order by
使用关键字 order by 可以对查询结果排序。
- order by后面一般只带一个列名
- 排序时,记录值为NULL的看作最小值
- ASC:升序 ;DESC:降序
#order by
select * from 表名 order by 列名 ASC/DESC;
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名 order by 列名n ASC/DESC;7. group by
使用关键字group by可以进行分组查询。
#group by
select 函数名(列名n), group_concat(列名1), group_concat(列名2), ... from 表名 where 条件 group by 列名m; - 分组查询常常和统计函数一起使用
| 统计函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sum(列名) | 求和 |
| avg(列名) | 统计平均值 |
| count(列名) | 统计记录条数,不包括NULL |
| count(*) | 统计记录条数, 包括NULL |
| max(列名) | 统计最大值 |
| min(列名) | 统计最小值 |
- 分组后,如果查询字段除了统计函数,还有其他字段,查询出的内容只显示分组中第一条记录
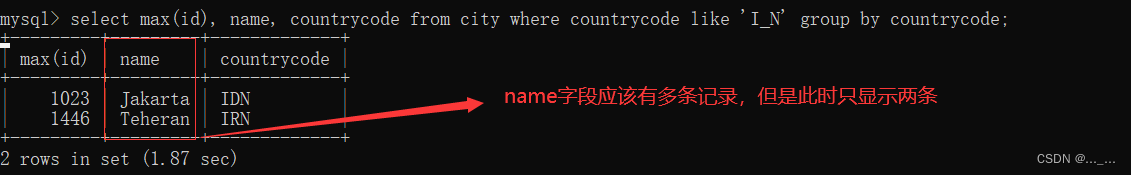
- 使用group_concat可以显示分组中的多条记录

8. 判断NULL
MySQL的判断逻辑有三种结果:true、false和unknow。当判断中有NULL时,一定会形成unknow逻辑,即使两个NULL做相等比较。
在条件判断时,如果相对值为NULL做判断,可以使用is null或is not null
#判断为NULL
select * from 表名 where 列名 is null;
#判断不为NULL
select * from 表名 where 列名 is not null;9. inner join
使用inner join关键字可以实现多表的联合查询 ---- 内连接查询。
#inner join
select * from 表名1 inner join 表名2 on 联合条件;
#使用别名
select 表别名1.列名1 as 列别名1_1, ... 表别名2.列名1 as 列别名2_1, ... from 表名1 as 表别名1 inner join 表名2 as 表别名2 on 联合条件; - 内连接查询必须带上联合条件
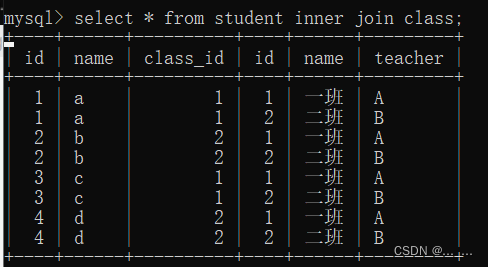
- 内连接查询是将一个表(表a)的每一条记录,对应另一张表(表2)的所有记录,根据联合条件剔除不符合条件的记录,最终得到查询结果
举例:
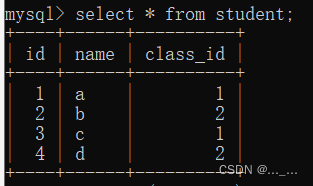
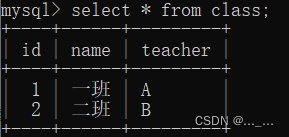
class表:两个班级,分别有两个老师
student表:4个学生,分别属于两个班级
不使用联合条件:
联合条件效果:
- 自连接
- 内连接有一种特殊情况,连接的表是自己本身,称为自连接。
10. outer join
使用outer join可以实现外连接查询,使用上和内连接类似。
#outer join
select * from 表名1 left/right outer join 表名2 on 联合条件;
#使用别名
select 表别名1.列名1 as 列别名1_1, ... 表别名2.列名1 as 列别名2_1, ... from 表名1 as 表别名1 left/right outer join 表名2 as 表别名2 on 联合条件; - 外连接相比内连接多了参考表的概念,被选为参考的表,所有记录都要显示
- left outer join选择关键字左边的表为参考表,right outer join相反
举例:
class表:两个班级,分别有两个老师
student表:5个学生,学生e的班级不在班级表中
左外连接:
右外连接:
11. union
union关键字可以将多个select查询的结果合并在一起。
#union
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名1 union select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名2;
#union all
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名1 union select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名2; - 使用union时,多个select查询的列名数量必须一致
- union会将合并的结果去重,union all不会去重
12. 子查询
可以在查询中嵌套查询,以一个查询的结果作为另一个查询的查询范围,称为子查询。
#子查询
select 列名1, 列名2, ... from 表名1 where 列名 运算符|IN|ANY|ALL|EXISTS (select 列名 from 表名2);- ANY:满足子查询中任意一条结果即可
- ALL:要满足子查询的所有结果
- EXISTS:子查询结果为空返回false,不空返回true
————————————————
转载于:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39281599/article/details/126096682