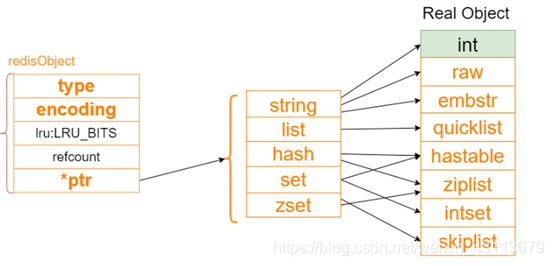
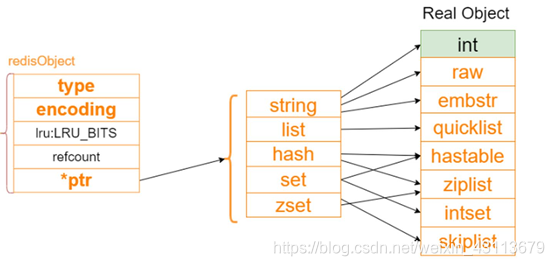
先放出一张图,来自Redis常用数据类型及其存储结构(源码篇),这张图描述了在redis中key和value存储的数据结构是什么样的
1、创建一个SDS的方法
/* Create an empty (zero length) sds string. Even in this case the string
* always has an implicit null term.
*创建一个空(零长度)sds字符串。即使在这种情况下,字符串也始终有一个隐式空项
*/
sds sdsempty(void) {
return sdsnewlen("",0);
}
/* Create a new sds string starting from a null terminated C string.
*从以null结尾的C字符串开始创建新的sds字符串
*/
sds sdsnew(const char *init) {
size_t initlen = (init == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(init);
return sdsnewlen(init, initlen);
}
//创建新的sds
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
return _sdsnewlen(init, initlen, 0);
}
//这是尝试创建sds
sds sdstrynewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
return _sdsnewlen(init, initlen, 1);
}
这里sdsnewlen和sdstrynewlen都是调用的_sdsnewlen,只是参数不一样,看下面的代码,区别可以看下面的trymalloc
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.使用“init”指针和“initlen”指定的内容创建一个新的sds字符串
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
* If SDS_NOINIT is used, the buffer is left uninitialized;
*如果“init”使用NULL,则字符串初始化为零字节。如果使用sds_NOINIT,则缓冲区未初始化
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*该字符串始终以null结尾(所有sds字符串都是,始终),因此即使您使用以下命令创建sds字符串
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header.
*您可以使用printf()打印字符串,因为字符串末尾有一个隐式\0 但是,字符串是二进制安全的,并且可以在中间包含0个字符,因为长度存储在SDS报头中。
*/
sds _sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen, int trymalloc) {
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
size_t usable;
assert(initlen + hdrlen + 1 > initlen); /* Catch size_t overflow */
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
usable = usable-hdrlen-1;
if (usable > sdsTypeMaxSize(type))
usable = sdsTypeMaxSize(type);
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}
上面有这么一段
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable);
相当于执行了不同的方法,1调用的是s_trymalloc_usable,0调用的是s_malloc_usable,下面是这两个方法的内部源码,通过注释知道s_trymalloc_usable 更加友好
#define s_malloc_usable zmalloc_usable
#define s_trymalloc_usable ztrymalloc_usable
/* Allocate memory or panic.
* '*usable' is set to the usable size if non NULL.
*分配内存或死机。如果非空,则将“可用”设置为可用大小
*/
void *zmalloc_usable(size_t size, size_t *usable) {
void *ptr = ztrymalloc_usable(size, usable);
if (!ptr) zmalloc_oom_handler(size);
return ptr;
}
/* Try allocating memory, and return NULL if failed.
* '*usable' is set to the usable size if non NULL.
尝试分配内存,如果失败,则返回NULL。如果非空,则将“可用”设置为可用大小
*/
void *ztrymalloc_usable(size_t size, size_t *usable) {
ASSERT_NO_SIZE_OVERFLOW(size);
void *ptr = malloc(MALLOC_MIN_SIZE(size)+PREFIX_SIZE);
if (!ptr) return NULL;
#ifdef HAVE_MALLOC_SIZE
size = zmalloc_size(ptr);
update_zmalloc_stat_alloc(size);
if (usable) *usable = size;
return ptr;
#else
*((size_t*)ptr) = size;
update_zmalloc_stat_alloc(size+PREFIX_SIZE);
if (usable) *usable = size;
return (char*)ptr+PREFIX_SIZE;
#endif
}
2、SDS的的字符串存储空间有五种类型
SDS旧版本只有一种,但是新版本已经根据key的长度让SDS的字符串存储空间大小不同,可以节省资源,因为字符串底层存储的是用char数组来存的,这样对于key短的可以节省很多空间
下面是根据字符串的长度返回SDS的类型
static inline char sdsReqType(size_t string_size) {
if (string_size < 1<<5)
return SDS_TYPE_5;
if (string_size < 1<<8)
return SDS_TYPE_8;
if (string_size < 1<<16)
return SDS_TYPE_16;
#if (LONG_MAX == LLONG_MAX)
if (string_size < 1ll<<32)
return SDS_TYPE_32;
return SDS_TYPE_64;
#else
return SDS_TYPE_32;
#endif
}
下面是根据SDS的类型返回不同的字符串存储空间
static inline int sdsHdrSize(char type) {
switch(type&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return sizeof(struct sdshdr5);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return sizeof(struct sdshdr8);
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return sizeof(struct sdshdr16);
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return sizeof(struct sdshdr32);
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return sizeof(struct sdshdr64);
}
return 0;
}
下面是五种字符串的存储空间
typedef char *sds;
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings.
注意:sdshdr5从未使用过,我们只是直接访问标志字节。但是这里是为了记录类型5 SDS字符串的布局
*/
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
3、其他real Object
redis中有string list zset hash set,但是底层到底是用什么存储?
答:redis的对象的实际编码方式由encoding参数指定,也就是*ptr指针指向的数据以何种底层实现存放,再看一下第一张图
/* The actual Redis Object
这里不要误会,这里只是代表存储的类型,实际的存储是有区别的,可以看上图,
像通过API set 一个key-value 的String,type就是OBJ_STRING,但是实际存储的可能是raw也有可能是embstr*/
#define OBJ_STRING 0 /* String object. */
#define OBJ_LIST 1 /* List object. */
#define OBJ_SET 2 /* Set object. */
#define OBJ_ZSET 3 /* Sorted set object. */
#define OBJ_HASH 4 /* Hash object. */
类型是上面这五种类型,但是实际上存储的是下面这些,再细分的
/* Objects encoding. Some kind of objects like Strings and Hashes can be
* internally represented in multiple ways. The 'encoding' field of the object
* is set to one of this fields for this object.
*对象编码。某些类型的对象(如字符串和哈希)可以通过多种方式在内部表示。对象的“编码”字段设置为此对象的此字段之一
*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_RAW 0 /* Raw representation 简单动态字符串*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INT 1 /* Encoded as integer 整数*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_HT 2 /* Encoded as hash table 哈希表*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPMAP 3 /* Encoded as zipmap 是一个连续的key value集合*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST 4 /* No longer used: old list encoding. 不再使用:旧列表编码*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST 5 /* Encoded as ziplist ziplist是由一系列特殊编码的连续内存块组成的顺序存储结构,
类似于数组,ziplist在内存中是连续存储的,但是不同于数组,为了节省内存 ziplist的每个元素所占的内存大小可以不同*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET 6 /* Encoded as intset intset是一个由整数组成的有序集合,从而便于在上面进行二分查找,用于快速地判断一个元素是否属于这个集合*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST 7 /* Encoded as skiplist 跳跃表(skiplist)是一种随机化的数据*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR 8 /* Embedded sds string encoding embstr编码的简单动态字符串*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST 9 /* Encoded as linked list of ziplists 编码为 ziplists 的链表*/
#define OBJ_ENCODING_STREAM 10 /* Encoded as a radix tree of listpacks */
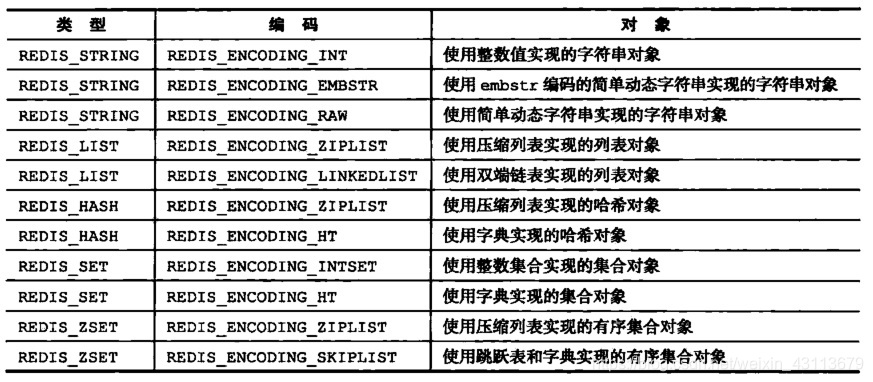
再用一张表格解释一下