前言
源码解读: utils/augmentations.py
1. random_perspective
这个函数是对mosaic整合后的图片进行随机旋转、缩放、平移、裁剪,透视变换,
并resize为输入大小img_size。
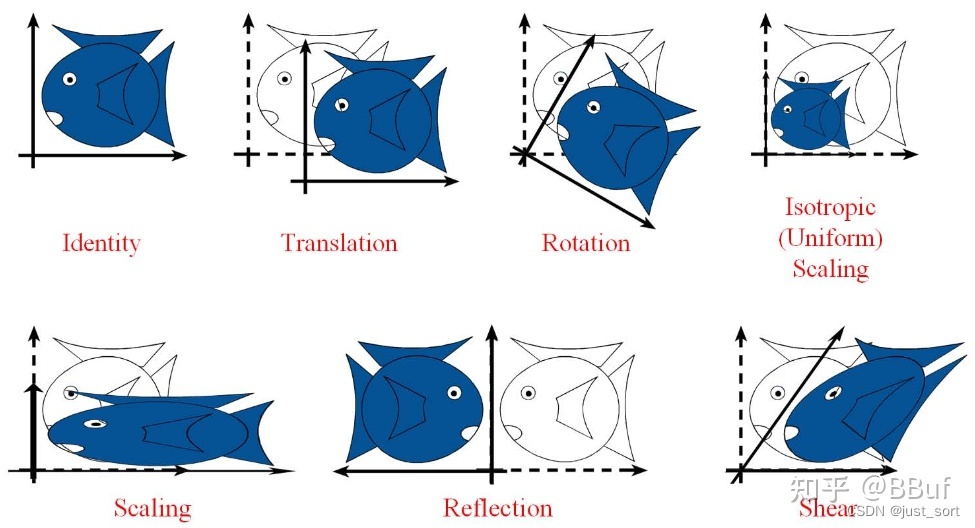
仿射变换包含:
平移、旋转、放缩、剪切、反射
仿射变换包括如下所有变换,以及这些变换任意次序次数的组合:
平移(translation)和 旋转(rotation)顾名思义,两者的组合称之为欧式变换(Euclidean transformation)或刚体变换(rigid transformation);
放缩(scaling)可进一步分为uniform scaling和non-uniform scaling,前者每个坐标轴放缩系数相同(各向同性),后者不同;如果放缩系数为负,则会叠加上反射(reflection)——reflection可以看成是特殊的scaling;
刚体变换+uniform scaling 称之为,相似变换(similarity transformation),即平移+旋转+各向同性的放缩;
剪切变换(shear mapping)将所有点沿某一指定方向成比例地平移,语言描述不如上面图示直观。
random_perspective函数代码:
def random_perspective(
img,
targets=(),
segments=(),
degrees=10,
translate=0.1,
scale=0.1,
shear=10,
perspective=0.0,
border=(0, 0),
):
"""这个函数会用于load_mosaic中用在mosaic操作之后
随机透视变换 对mosaic整合后的图片进行随机旋转、缩放、平移、裁剪,透视变换,并resize为输入大小img_size
:params img: mosaic整合后的图片img4 [2*img_size, 2*img_size]
如果mosaic后的图片没有一个多边形标签 segments为空
如果有一个多边形标签则 segments不为空。
:params targets: mosaic整合后图片的所有正常label标签labels4(不正常的会通过segments2boxes将多边形标签转化为正常标签) [N, cls+xyxy]
:params segments: mosaic整合后图片的所有不正常label信息(包含segments多边形也包含正常gt) [m, x1y1....]
:params degrees: 旋转和缩放矩阵参数
:params translate: 平移矩阵参数
:params scale: 缩放矩阵参数
:params shear: 剪切矩阵参数
:params perspective: 透视变换参数
:params border: 用于确定最后输出的图片大小
一般等于[-img_size//2, -img_size//2] 那么最后输出的图片大小为 [img_size, img_size]
:return img: 通过透视变换/仿射变换后的img [img_size, img_size]
:return targets: 通过透视变换/仿射变换后的img对应的标签 [n, cls+x1y1x2y2] (通过筛选后的)
OpenCV中的坐标系定义,如下图所示:
(0,0)o_________width______________x
| |
height |
| |
| |
| |
y____________________________o(w,h)
"""
# 设定输出图片的 H W
# border=-s // 2 所以最后图片的大小直接减半 [img_size, img_size, 3]
# 图片高宽(加上border边框)
height = img.shape[0] + border[0] * 2 # # 最终输出图像的H
width = img.shape[1] + border[1] * 2 # 最终输出图像的W
# ============================ 开始变换 =============================
# 需要注意的是,其实opencv是实现了仿射变换的, 不过我们要先生成仿射变换矩阵M
# Center 计算中心点
C = np.eye(3) # 生成3*3的对角为1的对角矩阵
# x 方向的中心
C[0, 2] = -img.shape[1] / 2 # x translation (pixels)
# y 方向的中心
C[1, 2] = -img.shape[0] / 2 # y translation (pixels)
# Perspective 设置透视变换矩阵
P = np.eye(3) # 生成3*3的对角为1的对角矩阵
# 随机生成x,y方向上的透视值
P[2, 0] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # x perspective (about y)
P[2, 1] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # y perspective (about x)
# Rotation and Scale
# 旋转和缩放
R = np.eye(3) # 初始化R = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]] (3, 3)
# a: 随机生成旋转角度 范围在(-degrees, degrees)
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
a = random.uniform(-degrees, degrees)
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
# s: 随机生成旋转后图像的缩放比例 范围在(1 - scale, 1 + scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
# 随机生成缩放比例
s = random.uniform(1 - scale, 1 + scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
# cv2.getRotationMatrix2D: 二维旋转缩放函数
# 参数 angle:旋转角度 center: 旋转中心(默认就是图像的中心) scale: 旋转后图像的缩放比例
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(0, 0), scale=s)
# Shear 设置剪切矩阵
# 弯曲角度
S = np.eye(3) # 初始化T = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]]
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# Translation 设置平移矩阵
T = np.eye(3) # 初始化T = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]] (3, 3)
T[0, 2] = (
random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * width
) # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = (
random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * height
) # y translation (pixels)
# Combined rotation matrix @ 表示矩阵乘法 生成仿射变换矩阵M
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C # order of operations (right to left) is IMPORTANT
# 将仿射变换矩阵M作用在图片上
if (border[0] != 0) or (border[1] != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
if perspective:
# 透视变换函数 实现旋转平移缩放变换后的平行线不再平行
# 参数和下面warpAffine类似
img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img, M, dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114)
)
else:
# 仿射变换函数 实现旋转平移缩放变换后的平行线依旧平行
# image changed img [1472, 1472, 3] => [736, 736, 3]
# cv2.warpAffine: opencv实现的仿射变换函数
# 参数: img: 需要变化的图像 M: 变换矩阵 dsize: 输出图像的大小 flags: 插值方法的组合(int 类型!)
# borderValue: (重点!)边界填充值 默认情况下,它为0。
img = cv2.warpAffine(
img, M[:2], dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114)
)
# Visualize 可视化
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 6))[1].ravel()
# ax[0].imshow(img[:, :, ::-1]) # base
# ax[1].imshow(img2[:, :, ::-1]) # warped
# Transform label coordinates
# 同样需要调整标签信息
n = len(targets)
if n:
# 判断是否可以使用segment标签: 只有segments不为空时即数据集中有多边形gt也有正常gt时才能使用segment标签 use_segments=True
# 否则如果只有正常gt时segments为空 use_segments=False
use_segments = any(x.any() for x in segments)
new = np.zeros((n, 4)) # [n, 0+0+0+0]
# 如果使用的是segments标签(标签中含有多边形gt)
if use_segments: # warp segments
# 先对segment标签进行重采样
# 比如说segment坐标只有100个,通过interp函数将其采样为n个(默认1000)
# [n, x1y2...x99y100] 扩增坐标-> [n, 500, 2]
# 由于有旋转,透视变换等操作,所以需要对多边形所有角点都进行变换
segments = resample_segments(segments)
for i, segment in enumerate(segments): # segment: [500, 2] 多边形的500个点坐标xy
xy = np.ones((len(segment), 3)) # [1, 1+1+1]
xy[:, :2] = segment # [500, 2]
# 对该标签多边形的所有顶点坐标进行透视变换 或 仿射变换
xy = xy @ M.T # transform @表示矩阵乘法运算
xy = (
xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3] if perspective else xy[:, :2]
) # perspective rescale or affine
# 根据segment的坐标,取xy坐标的最大最小值,得到边框的坐标 clip
new[i] = segment2box(xy, width, height) # xy [500, 2]
# 不使用segments标签 使用正常的矩形的标签targets
else: # warp boxes
# 直接对box透视变换 或 仿射变换
# 由于有旋转,透视变换等操作,所以需要对四个角点都进行变换
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3))
xy[:, :2] = targets[:, [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 4, 3, 2]].reshape(
n * 4, 2
) # x1y1, x2y2, x1y2, x2y1
xy = xy @ M.T # transform 每个角点的坐标
xy = (xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3] if perspective else xy[:, :2]).reshape(
n, 8
) # perspective rescale or affine
# create new boxes
x = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]]
y = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]]
new = (
np.concatenate((x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1))).reshape(4, n).T
)
# clip 去除太小的target(target大部分跑到图外去了)
new[:, [0, 2]] = new[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, width)
new[:, [1, 3]] = new[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, height)
# filter candidates 过滤target 筛选box
# 计算候选框并返回
# 长和宽必须大于wh_thr个像素 裁剪过小的框(面积小于裁剪前的area_thr) 长宽比范围在(1/ar_thr, ar_thr)之间的限制
# 筛选结果 [n] 全是True或False 使用比如: box1[i]即可得到i中所有等于True的矩形框 False的矩形框全部删除
i = box_candidates(
box1=targets[:, 1:5].T * s,
box2=new.T,
area_thr=0.01 if use_segments else 0.10,
)
# 得到所有满足条件的targets
targets = targets[i]
targets[:, 1:5] = new[i]
return img, targets
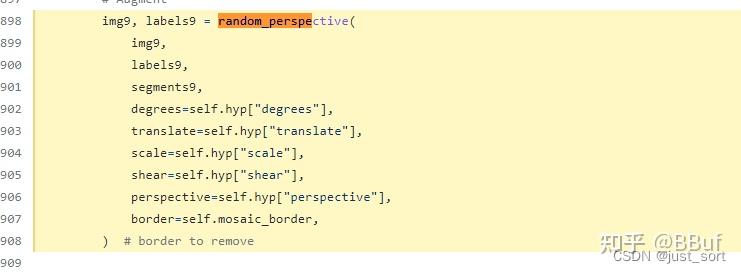
这个函数会用于load_mosaic中的mosaic操作之后进行透视变换 或 仿射变换:
在这里插入图片描述
这个函数的参数来自 hyp.yaml 中的下面5个参数:
在这里插入图片描述
2. box_candidates
官方作者介绍**Question about function box_candidates() in datasets.py**
这个函数用在random_perspective中,是对透视变换后的图片label进行筛选,去除被裁剪过小的框(面积小于裁剪前的area_thr) 并且保留下来的框的长宽必须大于wh_thr个像素,且长宽比范围在(1/ar_thr, ar_thr)之间。
box_candidates 函数代码:
def box_candidates(box1, box2, wh_thr=2, ar_thr=20, area_thr=0.1, eps=1e-16):
"""box_candidates() is used to filter the labels and reject poor label candidates:
用在random_perspective中 对透视变换后的图片label进行筛选
去除被裁剪过小的框(面积小于裁剪前的area_thr) 还有长和宽必须大于wh_thr个像素,且长宽比范围在(1/ar_thr, ar_thr)之间的限制
Compute candidate boxes: box1 before augment, box2 after augment, wh_thr (pixels), aspect_ratio_thr, area_ratio
:params box1: [4, n]
:params box2: [4, n]
:params wh_thr: 筛选条件 宽高阈值
:params ar_thr: 筛选条件 宽高比、高宽比最大值阈值
:params area_thr: 筛选条件 面积阈值
:params eps: 1e-16 接近0的数 防止分母为0
:return i: 筛选结果 [n] 全是True或False 使用比如: box1[i]即可得到i中所有等于True的矩形框 False的矩形框全部删除
"""
w1, h1 = box1[2] - box1[0], box1[3] - box1[1] # 求出所有box1矩形框的宽和高 [n] [n]
w2, h2 = box2[2] - box2[0], box2[3] - box2[1] # 求出所有box2矩形框的宽和高 [n] [n]
ar = np.maximum(w2 / (h2 + eps), h2 / (w2 + eps)) # 求出所有box2矩形框的宽高比和高宽比的较大者 [n, 1]
# 筛选条件: 增强后w、h要大于2 增强后图像与增强前图像面积比值大于area_thr 宽高比大于ar_thr
return (
(w2 > wh_thr)
& (h2 > wh_thr)
& (w2 * h2 / (w1 * h1 + eps) > area_thr)
& (ar < ar_thr)
) # candidates
3. replicate
这个函数是随机偏移标签中心,生成新的标签与原标签结合。可以用在load_mosaic里的mosaic操作之后 以及random_perspective操作之前, 作者默认是关闭的, 自己可以实验一下效果。
replicate模块代码:
def replicate(img, labels):
"""可以用在load_mosaic里在mosaic操作之后 random_perspective操作之前 作者默认是关闭的 自己可以实验一下效果
随机偏移标签中心,生成新的标签与原标签结合 Replicate labels
:params img: img4 因为是用在mosaic操作之后 所以size=[2*img_size, 2*img_size]
:params labels: mosaic整合后图片的所有正常label标签labels4(不正常的会通过segments2boxes将多边形标签转化为正常标签) [N, cls+xyxy]
:return img: img4 size=[2*img_size, 2*img_size] 不过图片中多了一半的较小gt个数
:params labels: labels4 不过另外增加了一半的较小label [3/2N, cls+xyxy]
"""
h, w = img.shape[:2] # 得到图片的高和宽
boxes = labels[:, 1:].astype(int) # 得到所有gt框的矩形坐标 xyxy [N, xyxy]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes.T # 左上角: x1 y1 右下角: x2 y2 [N]
s = (
(x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1)
) / 2 # side length (pixels) [N] 得到N个gt的 (w+h)/2 用来衡量gt框的大小
# 生成原标签个数一半的新标签 s.size返回ndarray的元素数量
for i in s.argsort()[: round(s.size * 0.5)]: # 返回较小(s较小)的一半gt框的index信息
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = boxes[i] # 得到这一半较小gt框的坐标信息 左上角x1b y1b 右下角x2b y2b
bh, bw = y2b - y1b, x2b - x1b # 得到这一般较小gt框的高宽信息
# 随机偏移标签中心点 y范围在[0, 图片高-gt框高] x范围在[0, 图片宽-gt框宽]
yc, xc = int(random.uniform(0, h - bh)), int(
random.uniform(0, w - bw)
) # offset x, y
# 重新生成这一半的gt框坐标信息(偏移后)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = [xc, yc, xc + bw, yc + bh]
# 将图片中真实的gt框偏移到对应生成的坐标(一半较小的偏移 较大的不偏移)
img[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# append 原来的labels标签 + 偏移了的标签
labels = np.append(labels, [[labels[i, 0], x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a]], axis=0)
return img, labels
会用在load_mosaicload_mosaic里在mosaic操作之后 random_perspective操作之前(一般会关闭 具体还要看个人实验)
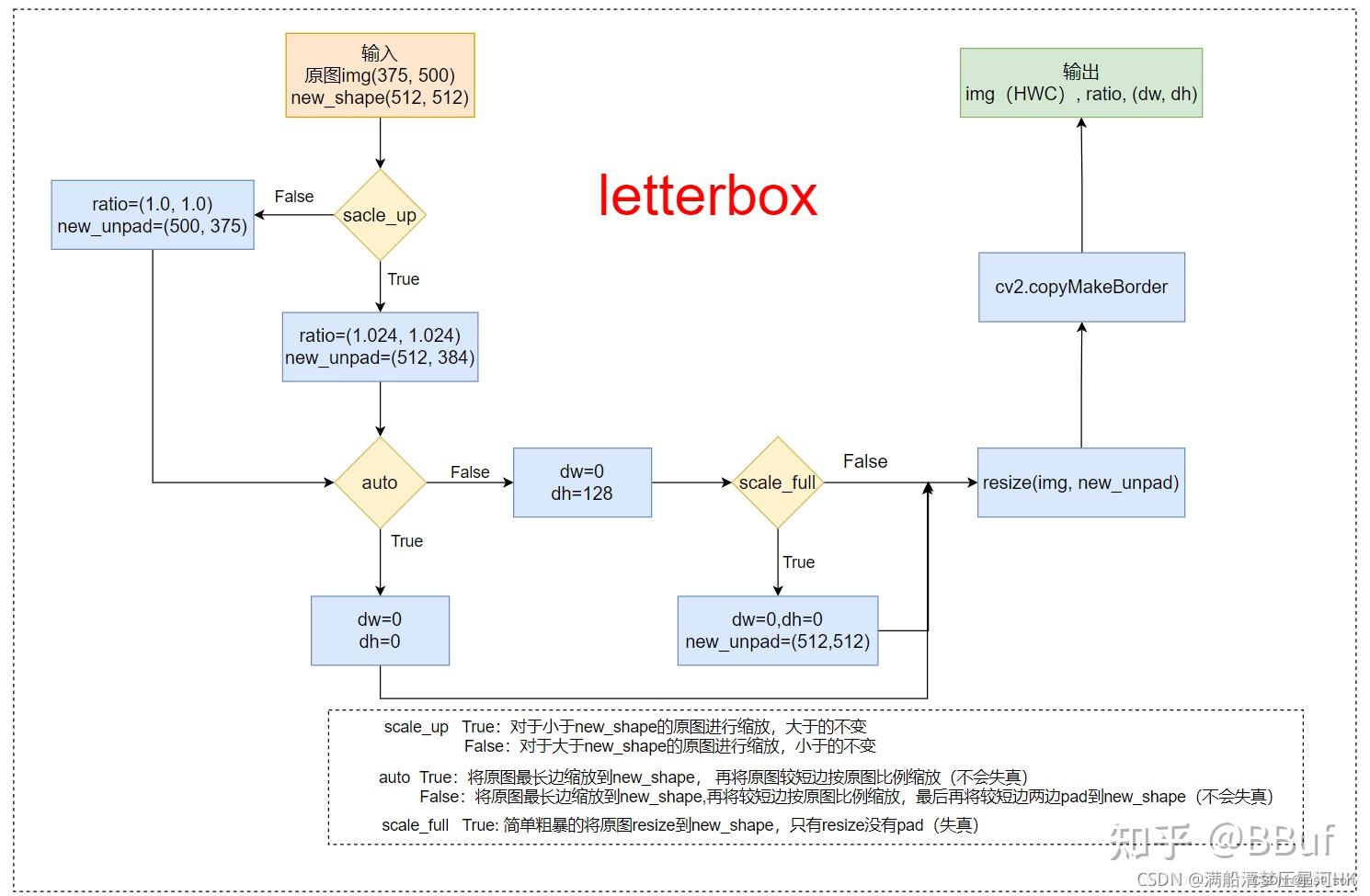
4. letterbox
YOLOV5中的自适应图片缩放**letterbox** 保持图片的宽高比例,剩下的部分用灰色填充。
letterbox 的img转换部分
此时:auto=False(需要pad), scale_fill=False, scale_up=False。
显然,这部分需要缩放,因为在这之前的load_image部分已经缩放过了(最长边等于指定大小,较短边等比例缩放),
那么在letterbox只需要计算出较小边需要填充的pad, 再将较小边两边pad到相应大小(每个batch需要每张图片的大小,这个
大小是不相同的)即可。
也可以结合下面画的流程图来理解下面的letterbox代码:
<br>图片来源于: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38253797/article/details/119904518
def letterbox(
img,
new_shape=(640, 640),
color=(114, 114, 114),
auto=True,
scaleFill=False,
scaleup=True,
stride=32,
):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块的__getitem__函数 只在val时才会使用
将图片缩放调整到指定大小
Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/232
:param img: 原图 hwc (形状是 (h,w,c) 高、宽、通道(RGB) 像素值范围是0-255 )
:param new_shape: 缩放后的最长边大小
:param color: pad的颜色
:param auto: True 保证缩放后的图片保持原图的比例 即 将原图最长边缩放到指定大小,再将原图较短边按原图比例缩放(不会失真)
False 将原图最长边缩放到指定大小,再将原图较短边按原图比例缩放,最后将较短边两边pad操作缩放到最长边大小(不会失真)
:param scale_fill: True 简单粗暴的将原图resize到指定的大小 相当于就是resize 没有pad操作(失真)
:param scale_up: True 对于小于new_shape的原图进行缩放,大于的不变
False 对于大于new_shape的原图进行缩放,小于的不变
:return: img: letterbox后的图片 hwc
ratio: wh ratios
(dw, dh): w和h的pad
"""
shape = img.shape[:2] # 第一层resize后图片大小[h, w] = [343, 512]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape) # (512, 512)
# scale ratio (new / old) 1.024 new_shape=(384, 512)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1]) # r=1
# 只进行下采样 因为上采样会让图片模糊
# (for better test mAP) scale_up = False 对于大于new_shape(r<1)的原图进行缩放,小于new_shape(r>1)的不变
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios (1, 1)
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(
round(shape[0] * r)
) # wh(512, 343) 保证缩放后图像比例不变
dw, dh = (
new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0],
new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1],
) # wh padding dw=0 dh=41
if auto: # minimum rectangle 保证原图比例不变,将图像最大边缩放到指定大小
# 这里的取余操作可以保证padding后的图片是32的整数倍(416x416),如果是(512x512)可以保证是64的整数倍
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding dw=0 dh=0
elif scaleFill: # stretch 简单粗暴的将图片缩放到指定尺寸
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
# 在较小边的两侧进行pad, 而不是在一侧pad
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides 将padding分到上下,左右两侧 dw=0
dh /= 2 # dh=20.5
# shape:[h, w] new_unpad:[w, h]
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize 将原图resize到new_unpad(长边相同,比例相同的新图)
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(
round(dh + 0.1)
) # 计算上下两侧的padding # top=20 bottom=21
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(
round(dw + 0.1)
) # 计算左右两侧的padding # left=0 right=0
# add border/pad
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color
) # add border
# img: (384, 512, 3) ratio=(1.0,1.0) 这里没有缩放操作 (dw,dh)=(0.0, 20.5)
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
总结下在val.py数据加载部分主要是做了三件事:
- load_image将图片从文件中加载出来,并resize到相应的尺寸(最长边等于我们需要的尺寸,最短边等比例缩放);
- letterbox将之前resize后的图片再pad到我们所需要的放到dataloader中(collate_fn函数)的尺寸(矩形训练要求同一个 batch中的图片的尺寸必须保持一致);
- 将label从相对原图尺寸(原文件中图片尺寸)缩放到相对letterbox pad后的图片尺寸。因为前两部分的图片尺寸发生了变化,同样的我们的label也需要发生相应的变化。
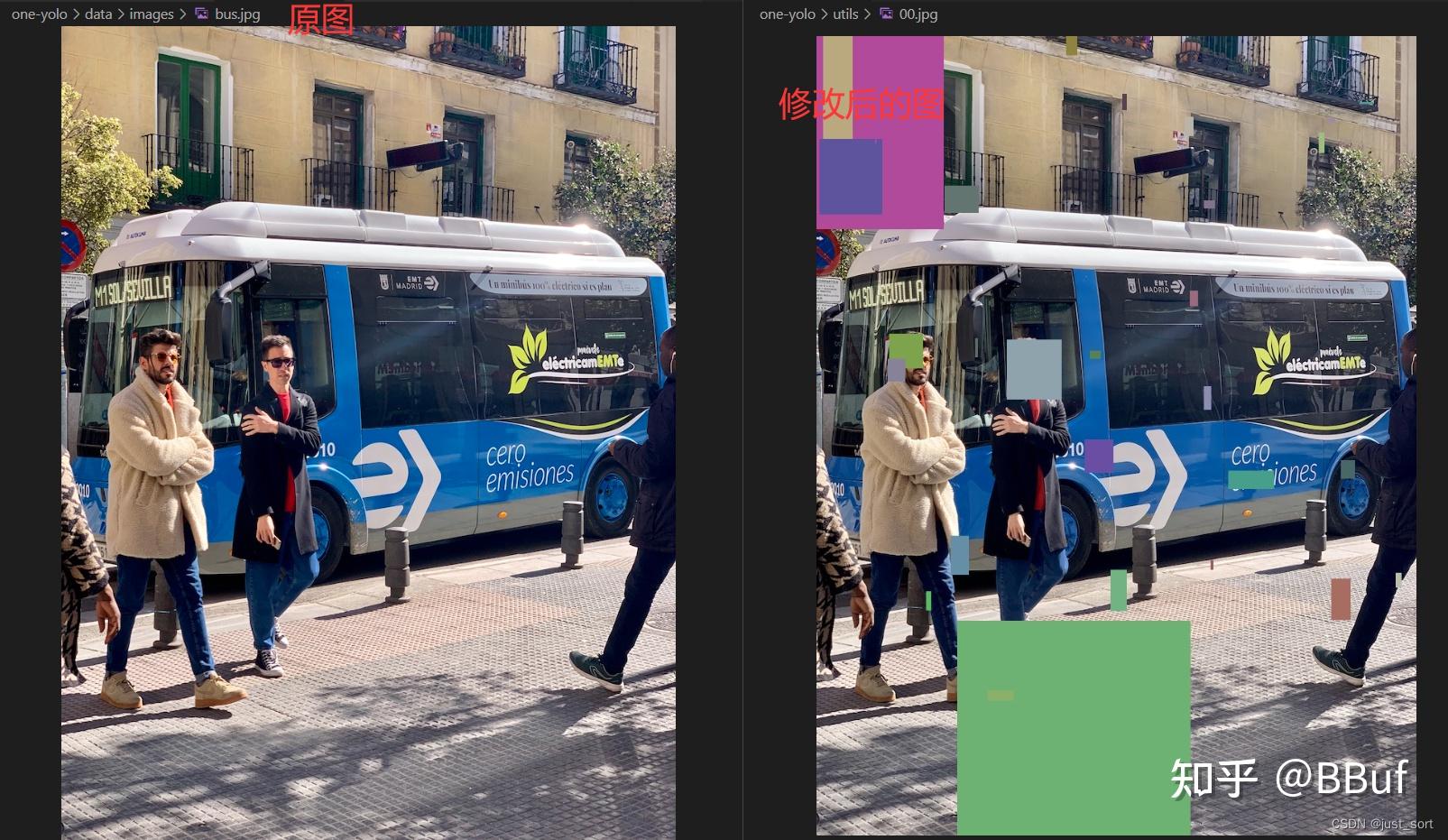
5. cutout
图片上的随机裁剪像素块
cutout数据增强,给图片随机添加随机大小的方块噪声 ,目的是提高泛化能力和鲁棒性。源自论文: Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout 。
示例:
image_path = "one-yolo/data/images/bus.jpg"
img = cv2.imread(str(image_path))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
labels = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 800, 800]])
print("原图宽高:\nw1={}\nh1={}".format(w, h)) # 810, 1800
lb = cutout(im=img, labels=labels, p=1000.0)
cv2.imwrite("./00.jpg",img)
在这里插入图片描述
cutout模块代码:
def cutout(image, labels):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块中的__getitem__函数进行cutout增强 v5源码作者默认是没用用这个的 感兴趣的可以测试一下
cutout数据增强, 给图片随机添加随机大小的方块噪声 目的是提高泛化能力和鲁棒性
实现:随机选择一个固定大小的正方形区域,然后采用全0填充就OK了,当然为了避免填充0值对训练的影响,应该要对数据进行中心归一化操作,norm到0。
论文: https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552
:params image: 一张图片 [640, 640, 3] numpy
:params labels: 这张图片的标签 [N, 5]=[N, cls+x1y1x2y2]
:return labels: 筛选后的这张图片的标签 [M, 5]=[M, cls+x1y1x2y2] M<N
筛选: 如果随机生成的噪声和原始F的gt框相交区域占gt框太大 就筛出这个gt框label
"""
h, w = image.shape[:2] # 获取图片高和宽
def bbox_ioa(box1, box2):
"""用在cutout中
计算box1和box2相交面积与box2面积的比例
Returns the intersection over box2 area given box1, box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4. boxes are x1y1x2y2
:params box1: 传入随机生成噪声 box [4] = [x1y1x2y2]
:params box2: 传入图片原始的label信息 [n, 4] = [n, x1y1x2y2]
:return [n, 1] 返回一个生成的噪声box与n个原始label的相交面积与b原始label的比值
"""
box2 = box2.transpose()
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
# 求box1和box2的相交面积
inter_area = (np.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2) - np.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clip(0) * \
(np.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2) - np.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clip(0)
# box面积
box2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1) + 1e-16
# 返回box1和box2相交面积 与 box2面积之比
return inter_area / box2_area
# 设置cutout添加噪声的scale create random masks
scales = [0.5] * 1 + [0.25] * 2 + [0.125] * 4 + [0.0625] * 8 + [0.03125] * 16 # image size fraction
for s in scales:
# 随机生成噪声 宽高
mask_h = random.randint(1, int(h * s))
mask_w = random.randint(1, int(w * s))
# 随机生成噪声 box
xmin = max(0, random.randint(0, w) - mask_w // 2)
ymin = max(0, random.randint(0, h) - mask_h // 2)
xmax = min(w, xmin + mask_w)
ymax = min(h, ymin + mask_h)
# 添加随机颜色的噪声 apply random color mask
image[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax] = [random.randint(64, 191) for _ in range(3)]
# 返回没有噪声的label return unobscured labels
if len(labels) and s > 0.03:
box = np.array([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], dtype=np.float32) # 随机生成的噪声box
# 计算生成的一个噪声box与这张图片中所有gt的box做计算 inter_area/label_area [n, 1]
ioa = bbox_ioa(box, labels[:, 1:5])
# remove>60% obscured labels 不能切的太大 ioa < 0.60 保留cutout噪声遮挡小于60%的标签
labels = labels[ioa < 0.60]
return labels
注意:
- 在LoadImagesAndLabels模块中的__getitem__函数进行cutout增强:
6. mixup
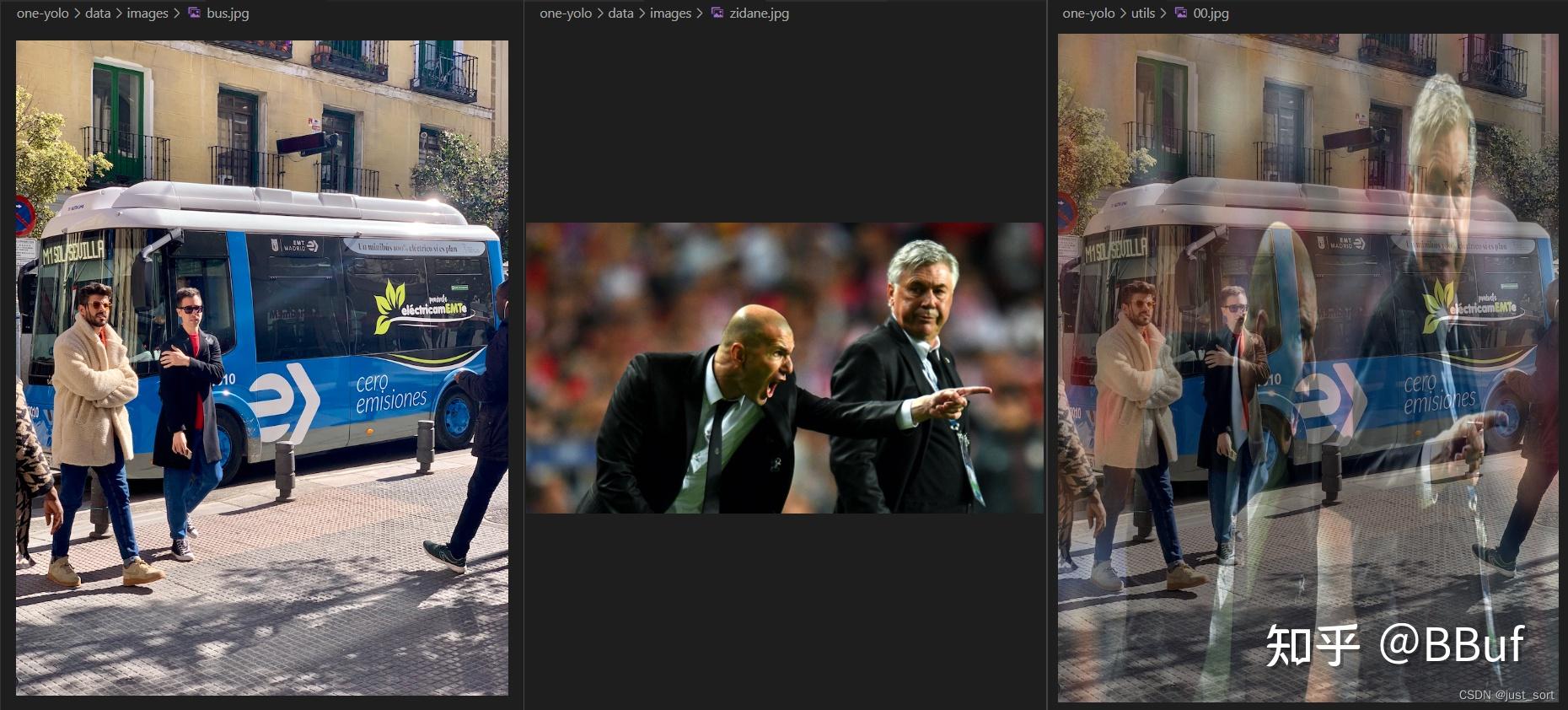
这个函数是进行mixup数据增强:按比例融合两张图片。论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf。
示例:
img1 = cv2.imread("one-yolo/data/images/bus.jpg")
img2 = cv2.imread("one-yolo/data/images/zidane.jpg")
img2 = cv2.resize(img2,(810,1080))
labels1 = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 800, 800]])
labels2 = np.array([[0, 800, 800, 1080, 810]])
img, labels = mixup(img1, labels1, img2, labels2)
cv2.imwrite("./00.jpg", img)
在这里插入图片描述
mixup模块代码:
def mixup(im, labels, im2, labels2):
"""用在LoadImagesAndLabels模块中的__getitem__函数进行mixup增强
mixup数据增强, 按比例融合两张图片 Applies MixUp augmentation
论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf
:params im:图片1 numpy (640, 640, 3)
:params labels:[N, 5]=[N, cls+x1y1x2y2]
:params im2:图片2 (640, 640, 3)
:params labels2:[M, 5]=[M, cls+x1y1x2y2]
:return img: 两张图片mixup增强后的图片 (640, 640, 3)
:return labels: 两张图片mixup增强后的label标签 [M+N, cls+x1y1x2y2]
"""
# 随机从beta分布中获取比例,range[0, 1]
r = np.random.beta(32.0, 32.0) # mixup ratio, alpha=beta=32.0
# 按照比例融合两张图片
im = (im * r + im2 * (1 - r)).astype(np.uint8)
# 将两张图片标签拼接到一起
labels = np.concatenate((labels, labels2), 0)
return im, labels
注意:
- 在LoadImagesAndLabels模块中的__getitem__函数进行mixup增强。
- mixup增强由超参hyp[‘mixup’]控制,0则关闭 默认为1(表示100%打开)。
7. hist_equalize
这个函数是用于对图片进行直方图均衡化处理,但是在yolov5中并没有用到这个函数,学习了解下就好,不是重点。
hist_equalize模块代码:
def hist_equalize(img, clahe=True, bgr=False):
"""yolov5并没有使用直方图均衡化的增强操作 可以自己试试
直方图均衡化增强操作 Equalize histogram on BGR image 'img' with img.shape(n,m,3) and range 0-255
:params img: 要进行直方图均衡化的原图
:params clahe: 是否要生成自适应均衡化图片 默认True 如果是False就生成全局均衡化图片
:params bgr: 传入的img图像是否是bgr图片 默认False
:return img: 均衡化之后的图片 大小不变 格式RGB
"""
# 图片BGR/RGB格式 -> YUV格式
yuv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV if bgr else cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
if clahe:
# cv2.createCLAHE生成自适应均衡化图像
c = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8))
yuv[:, :, 0] = c.apply(yuv[:, :, 0])
else:
# 全局均衡化
yuv[:, :, 0] = cv2.equalizeHist(yuv[:, :, 0]) # equalize Y channel histogram
return cv2.cvtColor(
yuv, cv2.COLOR_YUV2BGR if bgr else cv2.COLOR_YUV2RGB
) # convert YUV image to RGB