将PointNet训练好的pth模型转换为ONNX模型,并基于C++的onnxruntime框架推理部署
1.pth模型转onnx模型
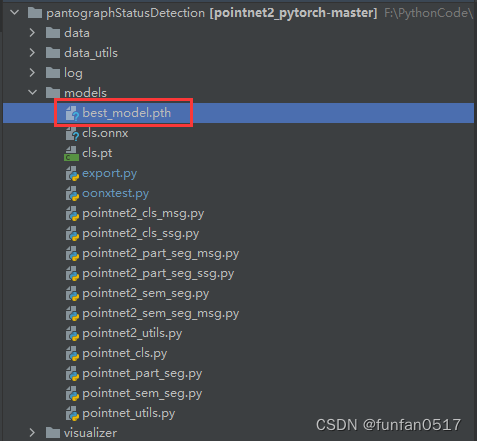
1.1将要转换的pth模型放到models目录下
1.2新建模型转换的脚本文件export.py
from models import pointnet2_cls_ssg
import os
import sys
import torch
import argparse
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = BASE_DIR
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'models', 'log'))
def parse_args():
'''PARAMETERS'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('Testing')
parser.add_argument('--use_cpu', action='store_true', default=True, help='use cpu mode')
parser.add_argument('--model', default='pointnet2_cls_ssg',help='model name [default: pointnet_cls]') # pointnet2_cls_ssg/pointnet_cls
parser.add_argument('--num_category', default=3, type=int, choices=[2, 3, 10, 40],help='training on ModelNet10/40')
parser.add_argument('--num_point', type=int, default=1024, help='Point Number')
parser.add_argument('--use_normals', action='store_true', default=False, help='use normals')
return parser.parse_args()
args = parse_args()
point_num = args.num_point
class_num = args.num_category
normal_channel = args.use_normals
model = pointnet2_cls_ssg.get_model(class_num, normal_channel)
if not args.use_cpu:
model = model.cuda()
model.eval()
if not args.use_cpu:
checkpoint = torch.load('best_model.pth')
else:
checkpoint = torch.load('best_model.pth', map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
x = (torch.rand(1, 6, point_num) if normal_channel else torch.rand(1, 3, point_num))
if not args.use_cpu:
x = x.cuda()
traced_script_module = torch.jit.trace(model, x)
export_onnx_file = "cls.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(traced_script_module, x, export_onnx_file, opset_version=11)
# traced_script_module.save("cls.pt")
1.3修改pointnet2_utils.py
为了torch.onnx.export(traced_script_module, x, export_onnx_file, opset_version=11)函数正常执行,需要对pointnet2_utils.py文件进行修改。修改后的代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from time import time
import numpy as np
def timeit(tag, t):
print("{}: {}s".format(tag, time() - t))
return time()
def pc_normalize(pc):
l = pc.shape[0]
centroid = np.mean(pc, axis=0)
pc = pc - centroid
m = np.max(np.sqrt(np.sum(pc ** 2, axis=1)))
pc = pc / m
return pc
def square_distance(src, dst):
"""
Calculate Euclid distance between each two points.
src^T * dst = xn * xm + yn * ym + zn * zm;
sum(src^2, dim=-1) = xn*xn + yn*yn + zn*zn;
sum(dst^2, dim=-1) = xm*xm + ym*ym + zm*zm;
dist = (xn - xm)^2 + (yn - ym)^2 + (zn - zm)^2
= sum(src**2,dim=-1)+sum(dst**2,dim=-1)-2*src^T*dst
Input:
src: source points, [B, N, C]
dst: target points, [B, M, C]
Output:
dist: per-point square distance, [B, N, M]
"""
B, N, _ = src.shape
_, M, _ = dst.shape
dist = -2 * torch.matmul(src, dst.permute(0, 2, 1))
dist += torch.sum(src ** 2, -1).view(B, N, 1)
dist += torch.sum(dst ** 2, -1).view(B, 1, M)
return dist
def index_points(points, idx):
"""
Input:
points: input points data, [B, N, C]
idx: sample index data, [B, S]
Return:
new_points:, indexed points data, [B, S, C]
"""
device = points.device
B = points.shape[0]
view_shape = list(idx.shape)
# view_shape[1:] = [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1)
new_view_shape = [view_shape[0]] + [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1)
view_shape = new_view_shape
repeat_shape = list(idx.shape)
repeat_shape[0] = 1
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(view_shape).repeat(repeat_shape)
new_points = points[batch_indices, idx, :]
return new_points
def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint: int):
"""
Input:
xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, 3]
npoint: number of samples
Return:
centroids: sampled pointcloud index, [B, npoint]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
centroids = torch.zeros(B, npoint, dtype=torch.long).to(device) # 采样点矩阵(B, npoint)
distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10 # 采样点到所有点距离(B, N)
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device) # 最远点,初试时随机选择一点点
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device) # batch_size 数组
for i in range(int(npoint)):
centroids[:, i] = farthest # 更新第i个最远点
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3) # 取出这个最远点的xyz坐标
dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1) # 计算点集中的所有点到这个最远点的欧式距离
mask = dist < distance
distance[mask] = dist[mask] # 更新distances,记录样本中每个点距离所有已出现的采样点的最小距离
farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1] # 返回最远点索引
return centroids
def query_ball_point(radius: float, nsample: int, xyz, new_xyz):
"""
Input:
radius: local region radius
nsample: max sample number in local region
xyz: all points, [B, N, 3]
new_xyz: query points, [B, S, 3]
Return:
group_idx: grouped points index, [B, S, nsample]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
_, S, _ = new_xyz.shape
group_idx = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(1, 1, N).repeat([B, S, 1])
sqrdists = square_distance(new_xyz, xyz)
group_idx[sqrdists > radius ** 2] = N
group_idx = group_idx.sort(dim=-1)[0][:, :, :nsample]
group_first = group_idx[:, :, 0].view(B, S, 1).repeat([1, 1, nsample])
mask = group_idx == N
group_idx[mask] = group_first[mask]
return group_idx
# def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, returnfps):
def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
npoint:
radius:
nsample:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3+D]
"""
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = npoint
fps_idx = farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint) # [B, npoint, C]
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, fps_idx)
idx = query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz)
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, idx) # [B, npoint, nsample, C]
grouped_xyz_norm = grouped_xyz - new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C)
if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, idx)
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz_norm, grouped_points], dim=-1) # [B, npoint, nsample, C+D]
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz_norm
# if returnfps:
# return new_xyz, new_points, grouped_xyz, fps_idx
# else:
return new_xyz, new_points
def sample_and_group_all(xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, 1, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, 1, N, 3+D]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
new_xyz = torch.zeros(B, 1, C).to(device)
grouped_xyz = xyz.view(B, 1, N, C)
if points is not None:
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz, points.view(B, 1, N, -1)], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz
return new_xyz, new_points
class PointNetSetAbstraction(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, npoint, radius, nsample, in_channel, mlp, group_all):
super(PointNetSetAbstraction, self).__init__()
self.npoint = npoint
self.radius = radius
self.nsample = nsample
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
self.group_all = group_all
def forward(self, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N]
points: input points data, [B, D, N]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S]
new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S]
"""
xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
if points is not None:
points = points.permute(0, 2, 1)
if self.group_all:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points)
else:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points)
# new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group(self.npoint, self.radius, self.nsample, xyz, points)
# new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, C]
# new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, C+D]
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1) # [B, C+D, nsample,npoint]
for i, (conv, bn) in enumerate(zip(self.mlp_convs, self.mlp_bns)):
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
new_points = torch.max(new_points, 2)[0]
new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
return new_xyz, new_points
class PointNetSetAbstractionMsg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, npoint, radius_list, nsample_list, in_channel, mlp_list):
super(PointNetSetAbstractionMsg, self).__init__()
self.npoint = npoint
self.radius_list = radius_list
self.nsample_list = nsample_list
self.conv_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
self.bn_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(mlp_list)):
convs = nn.ModuleList()
bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel + 3
for out_channel in mlp_list[i]:
convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
self.conv_blocks.append(convs)
self.bn_blocks.append(bns)
def forward(self, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N]
points: input points data, [B, D, N]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S]
new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S]
"""
xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
if points is not None:
points = points.permute(0, 2, 1)
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = self.npoint
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, farthest_point_sample(xyz, S))
new_points_list = []
for i, (convs, bns) in enumerate(zip(self.conv_blocks, self.bn_blocks)):
K = self.nsample_list[i]
radius = self.radius_list[i]
group_idx = query_ball_point(radius, K, xyz, new_xyz)
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, group_idx)
grouped_xyz -= new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C)
if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, group_idx)
grouped_points = torch.cat([grouped_points, grouped_xyz], dim=-1)
else:
grouped_points = grouped_xyz
grouped_points = grouped_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1) # [B, D, K, S]
# for j in range(len(self.conv_blocks[i])):
# conv = self.conv_blocks[i][j]
# bn = self.bn_blocks[i][j]
# grouped_points = F.relu(bn(conv(grouped_points)))
for j, (conv, bn) in enumerate(zip(convs, bns)):
grouped_points = F.relu(bn(conv(grouped_points)))
new_points = torch.max(grouped_points, 2)[0] # [B, D', S]
new_points_list.append(new_points)
new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
new_points_concat = torch.cat(new_points_list, dim=1)
return new_xyz, new_points_concat
class PointNetFeaturePropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, mlp):
super(PointNetFeaturePropagation, self).__init__()
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv1d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
def forward(self, xyz1, xyz2, points1, points2):
"""
Input:
xyz1: input points position data, [B, C, N]
xyz2: sampled input points position data, [B, C, S]
points1: input points data, [B, D, N]
points2: input points data, [B, D, S]
Return:
new_points: upsampled points data, [B, D', N]
"""
xyz1 = xyz1.permute(0, 2, 1)
xyz2 = xyz2.permute(0, 2, 1)
points2 = points2.permute(0, 2, 1)
B, N, C = xyz1.shape
_, S, _ = xyz2.shape
if S == 1:
interpolated_points = points2.repeat(1, N, 1)
else:
dists = square_distance(xyz1, xyz2)
dists, idx = dists.sort(dim=-1)
dists, idx = dists[:, :, :3], idx[:, :, :3] # [B, N, 3]
dist_recip = 1.0 / (dists + 1e-8)
norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=2, keepdim=True)
weight = dist_recip / norm
interpolated_points = torch.sum(index_points(points2, idx) * weight.view(B, N, 3, 1), dim=2)
if points1 is not None:
points1 = points1.permute(0, 2, 1)
new_points = torch.cat([points1, interpolated_points], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = interpolated_points
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 2, 1)
for i, (conv, bn) in enumerate(zip(self.mlp_convs, self.mlp_bns)):
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
return new_points
1.4测试导出的onnx模型
在models目录中新建oonxtest.py,代码如下:
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import onnx
model = onnx.load('cls.onnx')
#输入层
input_nodes = model.graph.input
for input_node in input_nodes:
print(input_node.name)
#输出层
output_nodes = model.graph.output
for output_node in output_nodes:
print(output_node.name)
#测试onnx模型
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
# ort_session = ort.InferenceSession('cls.onnx')
# outputs = ort_session.run(None, {'xyz.1': np.random.randn(10, 20), 'input_mask': np.random.randn(1, 20, 5)})
# 由于设置了dynamic_axes,支持对应维度的变化
# outputs = ort_session.run(None, {'input': np.random.randn(10, 5), 'input_mask': np.random.randn(1, 26, 2)})
# outputs 为 包含'output'和'output_mask'的list
程序没报错就是onnx模型可用,记录下输入层和输出层的名称,后续C++加载推理模型会用到
参考文章:
pointnet C++推理部署–onnxruntime框架
Pointnet++在Pytorch下模型(.pth)转Libtorch下模型(.pt)
2.下载搭建onnxruntime框架
2.1onnx模型介绍
ONNX(Open Neural Network Exchange)是由微软、Facebook和亚马逊等公司合作推出的用于机器学习模型的开放式框架。它的目的是让不同的深度学习框架之间可以无缝地交换模型。
ONNX从模型的角度出发,提供了通用的表示方法,使得不同深度学习框架可以将自己的模型导出到ONNX格式,而其他深度学习框架则可以将ONNX格式的模型导入,并在自己的框架中运行。
ONNX支持的深度学习框架包括PyTorch、TensorFlow、Caffe2、MXNet等。通过使用ONNX,深度学习从业者可以更加灵活地选择使用不同的框架,同时也可以更加方便地将模型部署到不同的硬件设备上。
2.2下载解压
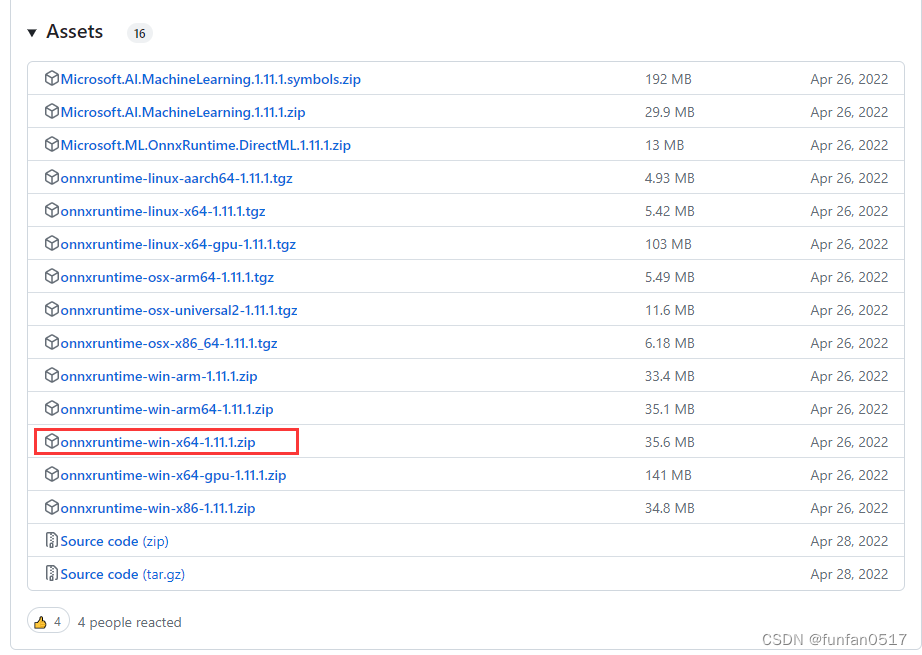
根据Windows或Linux系统、是否使用显卡、以及导出的onnx版本选择要下载的onnxruntime版本
onnxruntime官方下载地址:https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime/releases
本次实验在无显卡的Windows系统上进行的,选择对应版本进行下载
参考文章:ONNX:C++通过onnxruntime使用.onnx模型进行前向计算【下载的onnxruntime是编译好的库文件,可直接使用】
3.C++推理onnx模型
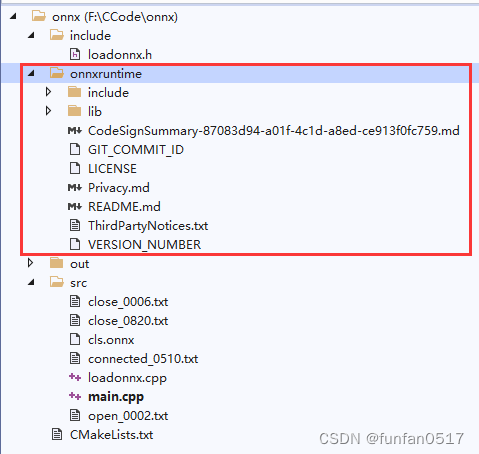
3.1创建项目
将下载的onnxruntime放到项目目录中,新建include和src目录,将所需模型和点云文件放到src目录下
3.2新建loadonnx.h
loadonnx.h代码如下:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
void pc_normalize(std::vector<float>& points);
int classfier(std::vector<float>& points);
const int point_num = 1024;
const int class_num = 3;
可以根据自己项目更改类别数目
3.3新建loadonnx.cpp
loadonnx.cpp代码如下:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include "loadonnx.h"
//const int point_num = 1024;
//const int class_num = 3;
void pc_normalize(std::vector<float>& points)
{
float mean_x = 0, mean_y = 0, mean_z = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; ++i)
{
mean_x += points[3 * i];
mean_y += points[3 * i + 1];
mean_z += points[3 * i + 2];
}
mean_x /= point_num;
mean_y /= point_num;
mean_z /= point_num;
for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; ++i)
{
points[3 * i] -= mean_x;
points[3 * i + 1] -= mean_y;
points[3 * i + 2] -= mean_z;
}
float m = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; ++i)
{
if (sqrt(pow(points[3 * i], 2) + pow(points[3 * i + 1], 2) + pow(points[3 * i + 2], 2)) > m)
m = sqrt(pow(points[3 * i], 2) + pow(points[3 * i + 1], 2) + pow(points[3 * i + 2], 2));
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; ++i)
{
points[3 * i] /= m;
points[3 * i + 1] /= m;
points[3 * i + 2] /= m;
}
}
int classfier(std::vector<float>& points)
{
Ort::Env env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "cls");
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
session_options.SetIntraOpNumThreads(1);
session_options.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_EXTENDED);
//OrtCUDAProviderOptions cuda_option;
//cuda_option.device_id = 0;
//cuda_option.arena_extend_strategy = 0;
//cuda_option.cudnn_conv_algo_search = OrtCudnnConvAlgoSearchExhaustive;
//cuda_option.gpu_mem_limit = SIZE_MAX;
//cuda_option.do_copy_in_default_stream = 1;
//session_options.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_ALL);
//session_options.AppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(cuda_option);
const wchar_t* model_path = L"cls.onnx";
Ort::Session session(env, model_path, session_options);
Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
size_t num_input_nodes = session.GetInputCount();
std::vector<const char*> input_node_names = { "xyz.1" };
std::vector<const char*> output_node_names = { "163","l3_points" };
const size_t input_tensor_size = 1 * 3 * point_num;
std::vector<float> input_tensor_values(input_tensor_size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < point_num; j++)
{
input_tensor_values[point_num * i + j] = points[3 * j + i];
}
}
std::vector<int64_t> input_node_dims = { 1, 3, point_num };
auto memory_info = Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtArenaAllocator, OrtMemTypeDefault);
Ort::Value input_tensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, input_tensor_values.data(), input_tensor_size, input_node_dims.data(), input_node_dims.size());
std::vector<Ort::Value> ort_inputs;
ort_inputs.push_back(std::move(input_tensor));
std::vector<Ort::Value> output_tensors = session.Run(Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr }, input_node_names.data(), ort_inputs.data(), input_node_names.size(), output_node_names.data(), output_node_names.size());
const float* rawOutput = output_tensors[0].GetTensorData<float>();
std::vector<int64_t> outputShape = output_tensors[0].GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetShape();
size_t count = output_tensors[0].GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo().GetElementCount();
std::vector<float> output(rawOutput, rawOutput + count);
int predict_label = std::max_element(output.begin(), output.end()) - output.begin();
//std::cout << predict_label << std::endl;
return predict_label;
}
//int main()
//{
// std::vector<float> points;
// float x, y, z, nx, ny, nz;
// char ch;
// std::ifstream infile("close_0006.txt");
// for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; i++)
// {
// infile >> x >> ch >> y >> ch >> z >> ch >> nx >> ch >> ny >> ch >> nz;
// points.push_back(x);
// points.push_back(y);
// points.push_back(z);
// }
// infile.close();
// pc_normalize(points);
// classfier(points);
// return 0;
//}
可以根据自己项目修改输入层名称和输出层名称
3.4新建main.cpp
main.cpp代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include "loadonnx.h"
int main()
{
std::vector<float> points;
float x, y, z, nx, ny, nz;
char ch;
int res;
std::ifstream infile("close_0006.txt");
for (size_t i = 0; i < point_num; i++)
{
infile >> x >> ch >> y >> ch >> z >> ch >> nx >> ch >> ny >> ch >> nz;
points.push_back(x);
points.push_back(y);
points.push_back(z);
}
infile.close();
pc_normalize(points);
res=classfier(points);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}
可以根据自己项目调整输入的点云文件
3.5新建CMakeLists.txt
CMakeLists.txt内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
project(loadonnx)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
if(NOT ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR)
if(WIN32)
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/onnxruntime")
else()
set(ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR "/usr/local")
endif()
endif()
# 添加ONNX Runtime库头文件的包含路径
include_directories("${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR}/include")
include_directories("${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include")
# 添加ONNX Runtime库的链接路径
link_directories("${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR}/lib")
# 添加ONNX Runtime库的链接库
LINK_LIBRARIES("${ONNXRUNTIME_ROOTDIR}/lib/onnxruntime.lib")
# 添加可执行文件
add_executable(loadonnx "src/loadonnx.cpp" "src/main.cpp")
# 将以.dll结尾的文件复制到生成的debug目录下
file(GLOB DLLS_FILES "onnxruntime/lib/*.dll")
file(COPY ${DLLS_FILES} DESTINATION ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR})
# 将以.onnx结尾的文件复制到生成的debug目录下
file(GLOB ONNX_FILES "src/*.onnx")
file(COPY ${ONNX_FILES} DESTINATION ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR})
3.6运行项目
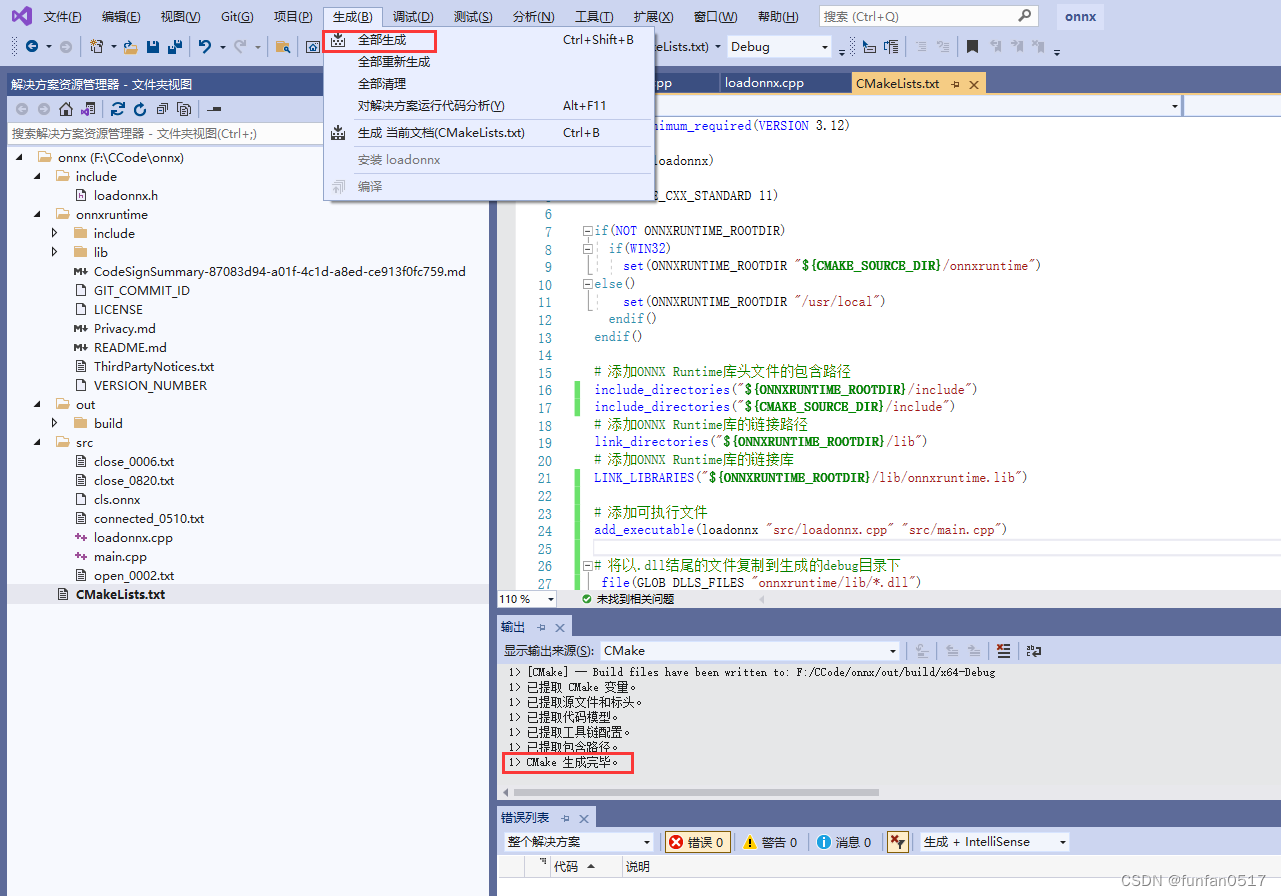
(1)点击CMakeLists.txt,按ctrl+s保存文件,同时会构建项目,生成out\build\x64-Debug目录
(2)构建成功后,点击生成exe可执行文件
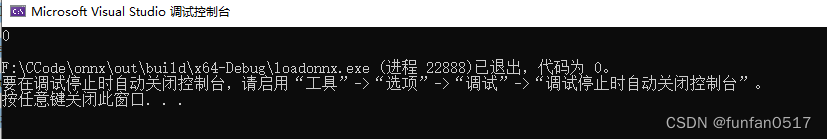
(3)运行main.cpp程序,输出点云文件所属类别
参考文章:
pointnet C++推理部署–onnxruntime框架
c++动态库之一 安装onnx