音量调节流程分析
- 按下音量键
音量键被按下后,按键事件会一路派发给Acitivity,如果无人拦截并处理,承载当前Activity的显示PhoneWindow类的onKeyDown()以及onKeyUp()函数将会被处理,从而开始通过音量键调整音量的处理流程;
按照输入事件的派发策略,Window对象在事件的派发队列中位于Acitivity的后面,所以应用程序可以重写自己的Activity.onKeyDown()函数以截获音量键的消息,并将其用作其他的功能。比如说,在一个相机应用中,按下音量键所执行的动作是拍照而不是调节音量;
Java层
PhoneWindow.Java
protected boolean onKeyDown(int featureId, int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
final KeyEvent.DispatcherState dispatcher =
mDecor != null ? mDecor.getKeyDispatcherState() : null;
//Log.i(TAG, "Key down: repeat=" + event.getRepeatCount()
// + " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(event.getFlags()));
switch (keyCode) {
//我们当前只要注重这三个音量键动作即可
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP://音量上键
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN://音量下键
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_MUTE: {//静音
// If we have a session send it the volume command, otherwise
// use the suggested stream.
if (mMediaController != null) {
getMediaSessionManager().dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService(event,
mMediaController.getSessionToken());
} else {
getMediaSessionManager().dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService(event,
mVolumeControlStreamType);
}
return true;
}
...
return false;
}
可以看到有两条条件逻辑进行接下来的音量调整,我们分别来看
MediaSessionManager.java
/**
* Dispatches the volume key event as system service to the session.
* <p>
* Should be only called by the {@link com.android.internal.policy.PhoneWindow} when the
* foreground activity didn't consume the key from the hardware devices.
*
* @param keyEvent the volume key event to send 要发送的音量键事件。
* @param sessionToken the session token to which the key event should be dispatched 指定的会话令牌,用于识别目标媒体会话。
* @hide
*/
//这个方法负责将音量键事件发送到指定的媒体会话,通常在前台活动未处理该事件时调用。
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService(@NonNull KeyEvent keyEvent,
@NonNull MediaSession.Token sessionToken) {
Objects.requireNonNull(sessionToken, "sessionToken shouldn't be null");
Objects.requireNonNull(keyEvent, "keyEvent shouldn't be null");
try {
//通过 mService 调用系统服务的相关方法,将音量键事件和会话令牌传递过去。
//mContext.getPackageName() 和 mContext.getOpPackageName() 提供了必要的上下文信息。
mService.dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService(mContext.getPackageName(),
mContext.getOpPackageName(), keyEvent, sessionToken);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Error calling dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService", e);
}
}
/**
* Dispatches the volume button event as system service to the session. This only effects the
* {@link MediaSession.Callback#getCurrentControllerInfo()} and doesn't bypass any permission
* check done by the system service.
* <p>
* Should be only called by the {@link com.android.internal.policy.PhoneWindow} or
* {@link android.view.FallbackEventHandler} when the foreground activity didn't consume the key
* from the hardware devices.
* <p>
* Valid stream types include {@link AudioManager.PublicStreamTypes} and
* {@link AudioManager#USE_DEFAULT_STREAM_TYPE}.
*
* @param keyEvent the volume key event to send 要发送的音量键事件。
* @param streamType type of stream 指定的音频流类型,可以是公开流类型或默认流类型。
* @hide
*/
//这个方法负责将音量键事件发送到与指定流类型相关的媒体会话。
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService(@NonNull KeyEvent keyEvent, int streamType) {
//这个方法实际上调用了一个内部方法 dispatchVolumeKeyEventInternal,并传递了音量事件、流类型以及两个布尔参数,指示是否仅限于音乐流和是否作为系统服务处理。
dispatchVolumeKeyEventInternal(keyEvent, streamType, /*musicOnly=*/false,
/*asSystemService=*/true);
}
这两个方法调用的场景有较大的区别:
dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService:
- 这个方法将音量键事件派发到特定的媒体会话,使用会话令牌。它主要用于处理与当前媒体会话相关的音量事件,适用于有活动的媒体控制。
dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService:
- 这个方法将音量键事件派发到与指定流类型相关的媒体会话。它不依赖于具体的媒体会话,而是根据流类型进行处理,适用于更广泛的音量事件派发场景。
简单举个例子就是:
假设你正在开发一个视频播放器应用,用户在观看视频时可以使用音量键来调整音量。我们将在不同情况下处理音量键事件。
- 使用
dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService
场景:用户正在播放视频并按下音量键。我们希望将音量事件发送到正在播放的媒体会话。
// 获取当前的媒体控制器和音量键事件
MediaController mediaController = getMediaController(); // 当前正在播放的视频的 MediaController
KeyEvent keyEvent = new KeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP);
if (mediaController != null) {
// 获取会话令牌
MediaSession.Token sessionToken = mediaController.getSessionToken();
// 将音量键事件派发到当前的媒体会话
getMediaSessionManager().dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService(keyEvent, sessionToken);
} else {
// 如果没有可用的媒体控制器,可以显示提示
Log.w("VideoPlayer", "No active media controller to handle volume event.");
}
- 使用
dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService
场景:用户在应用的设置页面按下音量键,但当前没有视频播放或媒体会话在活动。我们想根据流类型调整音量。
// 获取音量键事件
KeyEvent keyEvent = new KeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN);
int streamType = AudioManager.STREAM_MUSIC; // 选择音乐流类型
// 将音量键事件派发到系统服务
getMediaSessionManager().dispatchVolumeKeyEventAsSystemService(keyEvent, streamType);
我们在这篇文档中着重理解一下第二种情况,不依赖于具体的媒体会话,而是根据流类型进行处理,适用于更广泛的音量事件派发场景。
private void dispatchVolumeKeyEventInternal(@NonNull KeyEvent keyEvent, int stream,
boolean musicOnly, boolean asSystemService) {
Objects.requireNonNull(keyEvent, "keyEvent shouldn't be null");
try {
mService.dispatchVolumeKeyEvent(mContext.getPackageName(), mContext.getOpPackageName(),
asSystemService, keyEvent, stream, musicOnly);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to send volume key event.", e);
}
}
我们需要知道这个mService是指哪个类
private final ISessionManager mService;
ISessionManager是一个aidl文件,属于跨进程通信的一种机制,这种文件看上去就跟Java中的接口有一样,在编译后会生成Java文件。
mService = ISessionManager.Stub.asInterface(MediaFrameworkPlatformInitializer
.getMediaServiceManager()
.getMediaSessionServiceRegisterer()
.get());
通过推测mService应该是MediaSessionService
MediaSessionService.java
/**
* Dispatches volume key events. This is called when the foreground activity didn't handle
* the incoming volume key event.
* <p>
* Handles the dispatching of the volume button events to one of the
* registered listeners. If there's a volume key long-press listener and
* there's no active global priority session, long-presses will be sent to the
* long-press listener instead of adjusting volume.
*
* @param packageName The caller's package name, obtained by Context#getPackageName()
* @param opPackageName The caller's op package name, obtained by Context#getOpPackageName()
* @param asSystemService {@code true} if the event sent to the session as if it was come
* from the system service instead of the app process. This helps sessions to
* distinguish between the key injection by the app and key events from the
* hardware devices. Should be used only when the volume key events aren't handled
* by foreground activity. {@code false} otherwise to tell session about the real
* caller.
* @param keyEvent a non-null KeyEvent whose key code is one of the
* {@link KeyEvent#KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP},
* {@link KeyEvent#KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN},
* or {@link KeyEvent#KEYCODE_VOLUME_MUTE}.
* @param stream stream type to adjust volume.
* @param musicOnly true if both UI and haptic feedback aren't needed when adjusting volume.
* @see #dispatchVolumeKeyEventToSessionAsSystemService
*/
@Override
public void dispatchVolumeKeyEvent(String packageName, String opPackageName,
boolean asSystemService, KeyEvent keyEvent, int stream, boolean musicOnly) {
if (keyEvent == null
|| (keyEvent.getKeyCode() != KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP
&& keyEvent.getKeyCode() != KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN
&& keyEvent.getKeyCode() != KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_MUTE)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to dispatch null or non-volume key event.");
return;
}
//获取调用者的进程 ID(PID)和用户 ID(UID),并清除调用身份,以确保后续的权限检查正确。
final int pid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (DEBUG_KEY_EVENT) {
Log.d(TAG, "dispatchVolumeKeyEvent, pkg=" + packageName
+ ", opPkg=" + opPackageName + ", pid=" + pid + ", uid=" + uid
+ ", asSystem=" + asSystemService + ", event=" + keyEvent
+ ", stream=" + stream + ", musicOnly=" + musicOnly);
}
try {
//重点在这
synchronized (mLock) {
//检查是否有全局优先级会话活动。如果有,则调用相应的方法派发音量事件;如果没有,则使用另一个处理器处理音量事件。
//全局优先例如语音助手、通话、紧急通知
if (isGlobalPriorityActiveLocked()) {
dispatchVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, keyEvent, stream, musicOnly);
} else {
// TODO: Consider the case when both volume up and down keys are pressed
// at the same time.
mVolumeKeyEventHandler.handleVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, keyEvent, opPackageName, stream, musicOnly);
}
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
}
大部分情况,我们会执行**mVolumeKeyEventHandler.handleVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid,asSystemService, keyEvent, opPackageName, stream, musicOnly);**我们接着进行跟踪handleVolumeKeyEventLocked方法
void handleVolumeKeyEventLocked(String packageName, int pid, int uid,
boolean asSystemService, KeyEvent keyEvent, String opPackageName, int stream,
boolean musicOnly) {
handleKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService, keyEvent, false,
opPackageName, stream, musicOnly);
}
void handleKeyEventLocked(String packageName, int pid, int uid,
boolean asSystemService, KeyEvent keyEvent, boolean needWakeLock,
String opPackageName, int stream, boolean musicOnly) {
if (keyEvent.isCanceled()) {
return;
}
int overriddenKeyEvents = 0;
if (mCustomMediaKeyDispatcher != null
&& mCustomMediaKeyDispatcher.getOverriddenKeyEvents() != null) {
overriddenKeyEvents = mCustomMediaKeyDispatcher.getOverriddenKeyEvents()
.get(keyEvent.getKeyCode());
}
cancelTrackingIfNeeded(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService, keyEvent,
needWakeLock, opPackageName, stream, musicOnly, overriddenKeyEvents);
if (!needTracking(keyEvent, overriddenKeyEvents)) {
if (mKeyType == KEY_TYPE_VOLUME) {
dispatchVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, keyEvent, stream, musicOnly);
} else {
dispatchMediaKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService,
keyEvent, needWakeLock);
}
return;
}
if (isFirstDownKeyEvent(keyEvent)) {
mTrackingFirstDownKeyEvent = keyEvent;
mIsLongPressing = false;
return;
}
//处理长按
// Long press is always overridden here, otherwise the key event would have been
// already handled
if (isFirstLongPressKeyEvent(keyEvent)) {
mIsLongPressing = true;
}
if (mIsLongPressing) {
handleLongPressLocked(keyEvent, needWakeLock, overriddenKeyEvents);
return;
}
if (keyEvent.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
mTrackingFirstDownKeyEvent = null;
if (shouldTrackForMultipleTapsLocked(overriddenKeyEvents)) {
if (mMultiTapCount == 0) {
mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable = createSingleTapRunnable(packageName, pid,
uid, asSystemService, keyEvent, needWakeLock,
opPackageName, stream, musicOnly,
isSingleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents));
if (isSingleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents)
&& !isDoubleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents)
&& !isTripleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents)) {
mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable.run();
} else {
mHandler.postDelayed(mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable,
MULTI_TAP_TIMEOUT);
mMultiTapCount = 1;
mMultiTapKeyCode = keyEvent.getKeyCode();
}
} else if (mMultiTapCount == 1) {
mHandler.removeCallbacks(mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable);
mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable = createDoubleTapRunnable(packageName, pid,
uid, asSystemService, keyEvent, needWakeLock, opPackageName,
stream, musicOnly, isSingleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents),
isDoubleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents));
if (isTripleTapOverridden(overriddenKeyEvents)) {
mHandler.postDelayed(mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable, MULTI_TAP_TIMEOUT);
mMultiTapCount = 2;
} else {
mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable.run();
}
} else if (mMultiTapCount == 2) {
mHandler.removeCallbacks(mMultiTapTimeoutRunnable);
onTripleTap(keyEvent);
}
} else {
dispatchDownAndUpKeyEventsLocked(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService,
keyEvent, needWakeLock, opPackageName, stream, musicOnly);
}
}
}
可以看到上面分出了很多个点击次数分支,单击的时候走什么逻辑,双击的时候走什么逻辑,三击的时候走什么逻辑,但是随着逻辑的往下跟,发现他们最后都会指定到*dispatchDownAndUpKeyEventsLocked*,我们着重看一下这个方法的实现。
private void dispatchDownAndUpKeyEventsLocked(String packageName, int pid, int uid,
boolean asSystemService, KeyEvent keyEvent, boolean needWakeLock,
String opPackageName, int stream, boolean musicOnly) {
KeyEvent downEvent = KeyEvent.changeAction(keyEvent, KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN);
if (mKeyType == KEY_TYPE_VOLUME) {
//调节音量走这
dispatchVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, downEvent, stream, musicOnly);
dispatchVolumeKeyEventLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, keyEvent, stream, musicOnly);
} else {
dispatchMediaKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService, downEvent,
needWakeLock);
dispatchMediaKeyEventLocked(packageName, pid, uid, asSystemService, keyEvent,
needWakeLock);
}
}
private void dispatchVolumeKeyEventLocked(String packageName, String opPackageName, int pid,
int uid, boolean asSystemService, KeyEvent keyEvent, int stream,
boolean musicOnly) {
boolean down = keyEvent.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN;
boolean up = keyEvent.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP;
int direction = 0;
boolean isMute = false;
//根据不同的keycode设置相对应的direction
switch (keyEvent.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP:
direction = AudioManager.ADJUST_RAISE;
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN:
direction = AudioManager.ADJUST_LOWER;
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_MUTE:
isMute = true;
break;
}
if (down || up) {
//根据事件类型(按下或抬起),设置不同的标志。
int flags = AudioManager.FLAG_FROM_KEY;
if (!musicOnly) {
// These flags are consistent with the home screen
if (up) {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND | AudioManager.FLAG_VIBRATE;
} else {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_UI | AudioManager.FLAG_VIBRATE;
}
}
if (direction != 0) {
// If this is action up we want to send a beep for non-music events
if (up) {
direction = 0;// 在抬起事件时重置方向
}
//音量调整
dispatchAdjustVolumeLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, stream, direction, flags, musicOnly);
} else if (isMute) {
if (down && keyEvent.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
//切换静音
dispatchAdjustVolumeLocked(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid,
asSystemService, stream, AudioManager.ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE, flags,
musicOnly);
}
}
}
}
可以发现无论是音量调整跟设置静音,其实都是调用的*dispatchAdjustVolumeLocked*。
private void dispatchAdjustVolumeLocked(String packageName, String opPackageName, int pid,
int uid, boolean asSystemService, int suggestedStream, int direction, int flags,
boolean musicOnly) {
//根据是否存在全局优先会话来获取当前的音频会话。
MediaSessionRecordImpl session = isGlobalPriorityActiveLocked() ? mGlobalPrioritySession
: mCurrentFullUserRecord.mPriorityStack.getDefaultVolumeSession();
//检查建议的音频流类型是否有效且当前是否正在活动。
boolean preferSuggestedStream = false;
if (isValidLocalStreamType(suggestedStream)
&& AudioSystem.isStreamActive(suggestedStream, 0)) {
preferSuggestedStream = true;
}
if (session == null || preferSuggestedStream) {
//如果没有有效的会话或建议的流被优先考虑,使用 mHandler 来异步执行音量调整,避免潜在的死锁。
if (DEBUG_KEY_EVENT) {
Log.d(TAG, "Adjusting suggestedStream=" + suggestedStream + " by " + direction
+ ". flags=" + flags + ", preferSuggestedStream="
+ preferSuggestedStream + ", session=" + session);
}
if (musicOnly && !AudioSystem.isStreamActive(AudioManager.STREAM_MUSIC, 0)) {
if (DEBUG_KEY_EVENT) {
Log.d(TAG, "Nothing is playing on the music stream. Skipping volume event,"
+ " flags=" + flags);
}
return;
}
// Execute mAudioService.adjustSuggestedStreamVolume() on
// handler thread of MediaSessionService.
// This will release the MediaSessionService.mLock sooner and avoid
// a potential deadlock between MediaSessionService.mLock and
// ActivityManagerService lock.
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
final String callingOpPackageName;
final int callingUid;
final int callingPid;
if (asSystemService) {
callingOpPackageName = mContext.getOpPackageName();
callingUid = Process.myUid();
callingPid = Process.myPid();
} else {
callingOpPackageName = opPackageName;
callingUid = uid;
callingPid = pid;
}
try {
mAudioManager.adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(suggestedStream,
direction, flags, callingOpPackageName, callingUid, callingPid,
getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
} catch (SecurityException | IllegalArgumentException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot adjust volume: direction=" + direction
+ ", suggestedStream=" + suggestedStream + ", flags=" + flags
+ ", packageName=" + packageName + ", uid=" + uid
+ ", asSystemService=" + asSystemService, e);
}
}
});
} else {
//如果会话有效,直接调用会话的 adjustVolume 方法。
if (DEBUG_KEY_EVENT) {
Log.d(TAG, "Adjusting " + session + " by " + direction + ". flags="
+ flags + ", suggestedStream=" + suggestedStream
+ ", preferSuggestedStream=" + preferSuggestedStream);
}
session.adjustVolume(packageName, opPackageName, pid, uid, asSystemService,
direction, flags, true);
}
}
我们这篇文档主要讲述的是没有有效会话的情况,我们来仔细看看其中的核心语句*mAudioManager.adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid*
private AudioManager mAudioManager;
接下来我们进入到AudioManager进行跟踪。
AudioManager.java
/**
* Adjusts the volume of the most relevant stream, or the given fallback
* stream.
* <p>
* This method should only be used by applications that replace the
* platform-wide management of audio settings or the main telephony
* application.
* <p>
* This method has no effect if the device implements a fixed volume policy
* as indicated by {@link #isVolumeFixed()}.
* <p>This API checks if the caller has the necessary permissions based on the provided
* component name, uid, and pid values.
* See {@link #adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int, int, int)}.
*
* @param suggestedStreamType The stream type that will be used if there
* isn't a relevant stream. {@link #USE_DEFAULT_STREAM_TYPE} is
* valid here.
* @param direction The direction to adjust the volume. One of
* {@link #ADJUST_LOWER}, {@link #ADJUST_RAISE},
* {@link #ADJUST_SAME}, {@link #ADJUST_MUTE},
* {@link #ADJUST_UNMUTE}, or {@link #ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE}.
* @param flags One or more flags.
* @param packageName the package name of client application
* @param uid the uid of client application
* @param pid the pid of client application
* @param targetSdkVersion the target sdk version of client application
* @see #adjustVolume(int, int)
* @see #adjustStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #setStreamVolume(int, int, int)
* @see #isVolumeFixed()
*
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi(client = SystemApi.Client.MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public void adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int suggestedStreamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, int targetSdkVersion) {
try {
//核心语句
getService().adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(suggestedStreamType, direction, flags,
packageName, uid, pid, UserHandle.getUserHandleForUid(uid), targetSdkVersion);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
这个方法很简单,核心语句就是执行了*getService().adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid*,我们需要搞懂这个getService获取的是什么服务才能接着梳理流程。
private static IAudioService getService()
{
if (sService != null) {
return sService;
}
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
sService = IAudioService.Stub.asInterface(b);
return sService;
}
可以看到service是获取的AudioService。
AudioService
/** @see AudioManager#adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int, int, int, String, int, int, int) */
@Override
public void adjustSuggestedStreamVolumeForUid(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
@NonNull String packageName, int uid, int pid, UserHandle userHandle,
int targetSdkVersion) {
if (Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
throw new SecurityException("Should only be called from system process");
}
// direction and stream type swap here because the public
// adjustSuggested has a different order than the other methods.
adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(direction, streamType, flags, packageName, packageName, uid,
hasAudioSettingsPermission(uid, pid), VOL_ADJUST_NORMAL);
}
private void adjustSuggestedStreamVolume(int direction, int suggestedStreamType, int flags,
String callingPackage, String caller, int uid, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings,
int keyEventMode) {
if (DEBUG_VOL) Log.d(TAG, "adjustSuggestedStreamVolume() stream=" + suggestedStreamType
+ ", flags=" + flags + ", caller=" + caller
+ ", volControlStream=" + mVolumeControlStream
+ ", userSelect=" + mUserSelectedVolumeControlStream);
if (direction != AudioManager.ADJUST_SAME) {
sVolumeLogger.log(new VolumeEvent(VolumeEvent.VOL_ADJUST_SUGG_VOL, suggestedStreamType,
direction/*val1*/, flags/*val2*/, new StringBuilder(callingPackage)
.append("/").append(caller).append(" uid:").append(uid).toString()));
}
boolean hasExternalVolumeController = notifyExternalVolumeController(direction);
new MediaMetrics.Item(mMetricsId + "adjustSuggestedStreamVolume")
.setUid(Binder.getCallingUid())
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.CALLING_PACKAGE, callingPackage)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.CLIENT_NAME, caller)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.DIRECTION, direction > 0
? MediaMetrics.Value.UP : MediaMetrics.Value.DOWN)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.EXTERNAL, hasExternalVolumeController
? MediaMetrics.Value.YES : MediaMetrics.Value.NO)
.set(MediaMetrics.Property.FLAGS, flags)
.record();
if (hasExternalVolumeController) {
return;
}
final int streamType;
//使用锁定机制确保在多线程环境中安全地获取当前的音频流类型。根据用户选择和活动流类型来确定最终的流类型。
synchronized (mForceControlStreamLock) {
// Request lock in case mVolumeControlStream is changed by other thread.
if (mUserSelectedVolumeControlStream) { // implies mVolumeControlStream != -1
streamType = mVolumeControlStream;
} else {
final int maybeActiveStreamType = getActiveStreamType(suggestedStreamType);
final boolean activeForReal;
if (maybeActiveStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_RING
|| maybeActiveStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_NOTIFICATION) {
activeForReal = wasStreamActiveRecently(maybeActiveStreamType, 0);
} else {
activeForReal = mAudioSystem.isStreamActive(maybeActiveStreamType, 0);
}
if (activeForReal || mVolumeControlStream == -1) {
streamType = maybeActiveStreamType;
} else {
streamType = mVolumeControlStream;
}
}
}
//确定当前调整是否为静音。
final boolean isMute = isMuteAdjust(direction);
ensureValidStreamType(streamType);
final int resolvedStream = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
/* 播放声音的限制:
场景:用户正在用手机听音乐,同时想要调整音量。用户按下音量加按钮。
代码执行:在调整音量的过程中,代码检查 flags 是否包含 AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND,并且确认当前的流类型是否为 STREAM_RING。
因为用户正在听音乐,所以 resolvedStream 会是 STREAM_MUSIC。
结果:由于 resolvedStream 不是 STREAM_RING,代码将 flags 中的 FLAG_PLAY_SOUND 去除。这意味着用户不会听到音量调整的声音提示,
从而避免在享受音乐时产生不必要的干扰。
*/
// Play sounds on STREAM_RING only.
if ((flags & AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND) != 0 &&
resolvedStream != AudioSystem.STREAM_RING) {
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND;
}
/*
调整抑制逻辑:
场景:用户在进行电话会议,当前音频流是 STREAM_VOICE_CALL,而且用户的设备只有一个音量控制(例如,手机只在一个音量级别下工作)。
代码执行:在执行音量调整时,代码调用 mVolumeController.suppressAdjustment() 方法,这个方法会检查当前流是否允许调整。
如果返回 true,表示当前的环境不适合进行音量调整,比如用户正在专注于通话。
结果:如果 suppressAdjustment 返回 true,代码将 direction 设置为 0(即不进行任何音量调整),
并且去除 FLAG_PLAY_SOUND 和 FLAG_VIBRATE。这样,用户按下音量键时不会听到声音提示或震动反馈,从而确保通话不被打断。
*/
// For notifications/ring, show the ui before making any adjustments
// Don't suppress mute/unmute requests
// Don't suppress adjustments for single volume device
if (mVolumeController.suppressAdjustment(resolvedStream, flags, isMute)
&& !mIsSingleVolume) {
direction = 0;
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_PLAY_SOUND;
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_VIBRATE;
if (DEBUG_VOL) Log.d(TAG, "Volume controller suppressed adjustment");
}
adjustStreamVolume(streamType, direction, flags, callingPackage, caller, uid,
hasModifyAudioSettings, keyEventMode);
}
protected void adjustStreamVolume(int streamType, int direction, int flags,
String callingPackage, String caller, int uid, boolean hasModifyAudioSettings,
int keyEventMode) {
// 检查是否使用固定音量
mUseFixedVolume = mContext.getResources().getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_useFixedVolume);
// 连接蓝牙音箱时,控制音量的逻辑
if (NesuseFixedVolume) {
int mfixvolumestreamTypeAlias = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
final int mfixvolumedevice = getDeviceForStream(mfixvolumestreamTypeAlias);
// 如果是音乐流且连接了A2DP设备
if (mfixvolumestreamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC &&
AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(mfixvolumedevice) &&
(flags & AudioManager.FLAG_BLUETOOTH_ABS_VOLUME) == 0) {
DeviceConnectBTSpk = true; // 设定为连接了蓝牙音箱
} else {
DeviceConnectBTSpk = false; // 没有连接蓝牙音箱
}
} else {
DeviceConnectBTSpk = false; // 不使用固定音量
}
// 如果使用固定音量且没有连接蓝牙音箱,则直接返回
if (mUseFixedVolume && !DeviceConnectBTSpk) {
return;
}
// 检查是否允许通过 HDMI CEC 控制音量
boolean isControlVolume = SystemProperties.getBoolean("persist.sys.nes.smartir", false);
boolean isControlTv = SystemProperties.getBoolean("persist.sys.nes.is.tv", false);
if (isControlTv || (isControlVolume && !isMuteAdjust(direction))) {
return; // 不调整音量
}
// 调试信息,记录音量调整的流类型、方向和调用者信息
if (DEBUG_VOL) Log.d(TAG, "adjustStreamVolume() stream=" + streamType + ", dir=" + direction
+ ", flags=" + flags + ", caller=" + caller);
// 确保方向和流类型有效
ensureValidDirection(direction);
ensureValidStreamType(streamType);
boolean isMuteAdjust = isMuteAdjust(direction);
// 检查是否需要进行静音调整
if (isMuteAdjust && !isStreamAffectedByMute(streamType)) {
return; // 如果流类型不受静音影响,直接返回
}
// 对于静音调整,确保调用者具有必要权限
if (isMuteAdjust && (streamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_VOICE_CALL ||
streamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO) &&
mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_PHONE_STATE)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
Log.w(TAG, "MODIFY_PHONE_STATE Permission Denial: adjustStreamVolume from pid="
+ Binder.getCallingPid() + ", uid=" + Binder.getCallingUid());
return; // 权限不足,返回
}
// 检查 STREAM_ASSISTANT 类型是否有 MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING 权限
if (streamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_ASSISTANT &&
mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
Log.w(TAG, "MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING Permission Denial: adjustStreamVolume from pid="
+ Binder.getCallingPid() + ", uid=" + Binder.getCallingUid());
return; // 权限不足,返回
}
// 使用流类型别名进行音量调整,以便相同别名的流具有相同的行为
int streamTypeAlias = mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType];
VolumeStreamState streamState = mStreamStates[streamTypeAlias]; // 获取流状态
final int device = getDeviceForStream(streamTypeAlias); // 获取当前设备类型
int aliasIndex = streamState.getIndex(device); // 获取当前设备的索引
boolean adjustVolume = true; // 标志,指示是否可以调整音量
int step;
// 跳过非A2DP设备的绝对音量控制请求
if (!AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device) &&
(flags & AudioManager.FLAG_BLUETOOTH_ABS_VOLUME) != 0) {
return; // 不是A2DP设备,返回
}
// 检查当前用户
if (uid == android.os.Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
uid = UserHandle.getUid(getCurrentUserId(), UserHandle.getAppId(uid));
}
// 检查应用操作是否被允许
if (mAppOps.noteOp(STREAM_VOLUME_OPS[streamTypeAlias], uid, callingPackage)
!= AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED) {
return; // 不允许操作,返回
}
// 重置任何待处理的音量命令
synchronized (mSafeMediaVolumeStateLock) {
mPendingVolumeCommand = null;
}
// 清除固定音量标志
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_FIXED_VOLUME;
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC && isFixedVolumeDevice(device)) {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_FIXED_VOLUME; // 设定为固定音量
// 对于固定音量设备,调整到最大安全音量或0
if (mSafeMediaVolumeState == SAFE_MEDIA_VOLUME_ACTIVE &&
mSafeMediaVolumeDevices.contains(device)) {
step = safeMediaVolumeIndex(device); // 安全音量索引
} else {
step = streamState.getMaxIndex(); // 最大音量索引
}
if (aliasIndex != 0) {
aliasIndex = step; // 更新别名索引
}
} else {
// 将 UI 步长转换为内部单位
step = rescaleStep(10, streamType, streamTypeAlias);
}
// 检查铃声模式调整的情况
if (((flags & AudioManager.FLAG_ALLOW_RINGER_MODES) != 0) ||
(isUiSoundsStreamType(streamTypeAlias))) {
int ringerMode = getRingerModeInternal();
if (ringerMode == AudioManager.RINGER_MODE_VIBRATE) {
flags &= ~AudioManager.FLAG_VIBRATE; // 在振动模式下不振动
}
// 检查铃声模式是否处理此调整
final int result = checkForRingerModeChange(aliasIndex, direction, step,
streamState.mIsMuted, callingPackage, flags);
adjustVolume = (result & FLAG_ADJUST_VOLUME) != 0; // 更新调整音量标志
// 根据结果决定是否显示静音或振动提示
if ((result & AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_SILENT_HINT) != 0) {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_SILENT_HINT;
}
if ((result & AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_VIBRATE_HINT) != 0) {
flags |= AudioManager.FLAG_SHOW_VIBRATE_HINT;
}
}
// 检查静音或勿扰模式
if (!volumeAdjustmentAllowedByDnd(streamTypeAlias, flags)) {
adjustVolume = false; // 不允许调整
}
int oldIndex = mStreamStates[streamType].getIndex(device); // 获取当前设备的旧音量索引
if (adjustVolume && (direction != AudioManager.ADJUST_SAME) && (keyEventMode != VOL_ADJUST_END)) {
mAudioHandler.removeMessages(MSG_UNMUTE_STREAM); // 移除未静音消息
if (isMuteAdjust && !mFullVolumeDevices.contains(device)) { // 处理静音调整
boolean state;
if (direction == AudioManager.ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE) {
state = !streamState.mIsMuted; // 切换静音状态
} else {
state = direction == AudioManager.ADJUST_MUTE; // 设置为静音
}
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC) {
setSystemAudioMute(state); // 设置系统音频静音状态
}
for (int stream = 0; stream < mStreamStates.length; stream++) {
if (streamTypeAlias == mStreamVolumeAlias[stream]) {
if (!(readCameraSoundForced() && (mStreamStates[stream].getStreamType() == AudioSystem.STREAM_SYSTEM_ENFORCED))) {
mStreamStates[stream].mute(state); // 执行静音操作
}
}
}
} else if ((direction == AudioManager.ADJUST_RAISE) &&
!checkSafeMediaVolume(streamTypeAlias, aliasIndex + step, device)) {
Log.e(TAG, "adjustStreamVolume() safe volume index = " + oldIndex);
mVolumeController.postDisplaySafeVolumeWarning(flags); // 显示安全音量警告
} else if (!isFullVolumeDevice(device) &&
(streamState.adjustIndex(direction * step, device, caller, hasModifyAudioSettings) || streamState.mIsMuted)) {
// 如果音量调整被允许,发送系统音量设置消息
if (streamState.mIsMuted) {
// 如果之前被静音,则立即解除静音
if (direction == AudioManager.ADJUST_RAISE) {
for (int stream = 0; stream < mStreamStates.length; stream++) {
if (streamTypeAlias == mStreamVolumeAlias[stream]) {
mStreamStates[stream].mute(false); // 解除静音
}
streamState.mute(false); // 解除当前流的静音
}
} else if (direction == AudioManager.ADJUST_LOWER) {
if (mIsSingleVolume) {
sendMsg(mAudioHandler, MSG_UNMUTE_STREAM, SENDMSG_QUEUE, streamTypeAlias, flags, null, UNMUTE_STREAM_DELAY); // 延迟未静音消息
}
}
}
sendMsg(mAudioHandler, MSG_SET_DEVICE_VOLUME, SENDMSG_QUEUE, device, 0, streamState, 0); // 发送音量设置消息
}
int newIndex = mStreamStates[streamType].getIndex(device); // 获取新的音量索引
// 检查是否需要发送音量更新到 AVRCP
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC &&
AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device) &&
(flags & AudioManager.FLAG_BLUETOOTH_ABS_VOLUME) == 0) {
if (mStreamStates[streamType].mIsMuted) {
newIndex = 0; // 如果静音,则设置索引为0
}
if (DEBUG_VOL) {
Log.d(TAG, "adjustStreamVolume: postSetAvrcpAbsoluteVolumeIndex index=" + newIndex + " stream=" + streamType);
}
mDeviceBroker.postSetAvrcpAbsoluteVolumeIndex(newIndex / 10); // 发送 AVRCP 音量索引
}
// 检查是否需要发送音量更新到助听器
if (device == AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HEARING_AID) {
if (streamType == getHearingAidStreamType()) { // 确保流类型与助听器预期一致
if (DEBUG_VOL) {
Log.d(TAG, "adjustStreamVolume postSetHearingAidVolumeIndex index=" + newIndex + " stream=" + streamType);
}
mDeviceBroker.postSetHearingAidVolumeIndex(newIndex, streamType); // 发送助听器音量更新
}
}
// 检查是否需要发送音量更新到 HDMI 系统音频
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC) {
setSystemAudioVolume(oldIndex, newIndex, getStreamMaxVolume(streamType), flags); // 更新系统音量
}
}
final int newIndex = mStreamStates[streamType].getIndex(device); // 重新获取新的音量索引
if (adjustVolume) {
synchronized (mHdmiClientLock) {
if (mHdmiManager != null) {
if (mHdmiPlaybackClient != null && mHdmiCecVolumeControlEnabled &&
streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC &&
mFullVolumeDevices.contains(device)) {
int keyCode = KeyEvent.KEYCODE_UNKNOWN; // 初始化按键代码
switch (direction) {
case AudioManager.ADJUST_RAISE:
keyCode = KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_UP; // 增加音量
break;
case AudioManager.ADJUST_LOWER:
keyCode = KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_DOWN; // 降低音量
break;
case AudioManager.ADJUST_TOGGLE_MUTE:
case AudioManager.ADJUST_MUTE:
case AudioManager.ADJUST_UNMUTE:
keyCode = KeyEvent.KEYCODE_VOLUME_MUTE; // 静音
break;
default:
break;
}
if (keyCode != KeyEvent.KEYCODE_UNKNOWN) {
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); // 清除调用身份
try {
switch (keyEventMode) {
case VOL_ADJUST_NORMAL:
mHdmiPlaybackClient.sendVolumeKeyEvent(keyCode, true); // 发送按键按下事件
mHdmiPlaybackClient.sendVolumeKeyEvent(keyCode, false); // 发送按键释放事件
break;
case VOL_ADJUST_START:
mHdmiPlaybackClient.sendVolumeKeyEvent(keyCode, true); // 发送按键按下事件
break;
case VOL_ADJUST_END:
mHdmiPlaybackClient.sendVolumeKeyEvent(keyCode, false); // 发送按键释放事件
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Invalid keyEventMode " + keyEventMode); // 错误处理
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident); // 恢复调用身份
}
}
}
if (mHdmiPlaybackClient != null &&
(streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC) &&
isVolumePassthrough()) {
showPassthroughWarning(); // 显示直通警告
}
if (streamTypeAlias == AudioSystem.STREAM_MUSIC &&
(oldIndex != newIndex || isMuteAdjust)) {
maybeSendSystemAudioStatusCommand(isMuteAdjust); // 可能发送系统音频状态命令
}
}
}
}
sendVolumeUpdate(streamType, oldIndex, newIndex, flags, device); // 发送音量更新信息
}
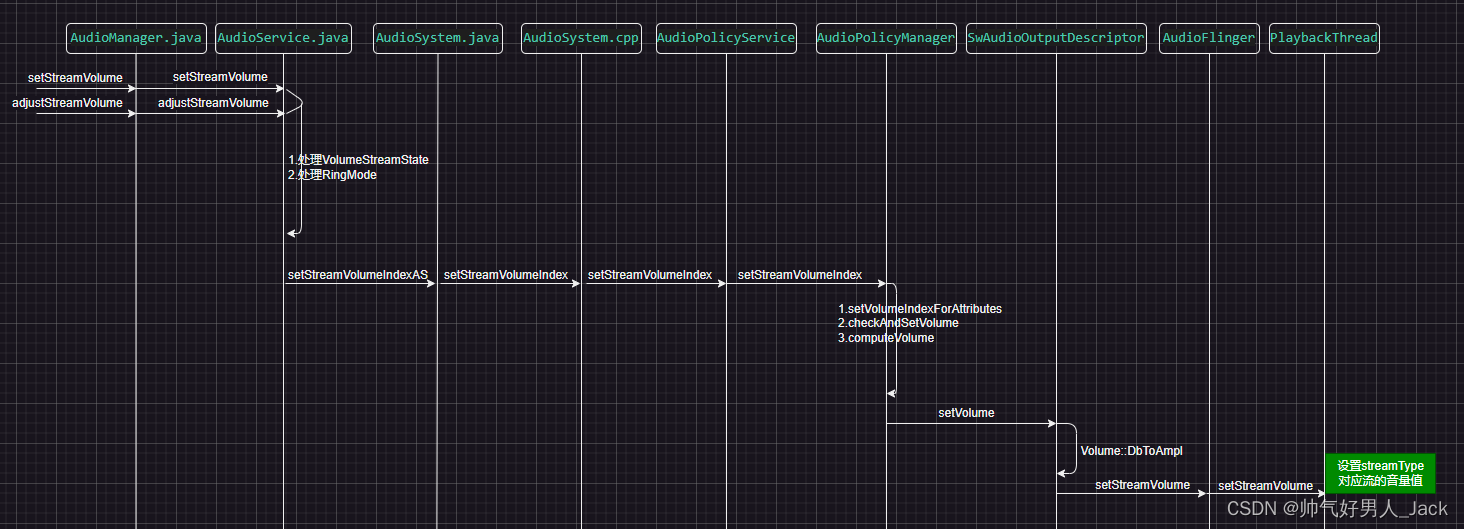
这个方法代码很长,注释也算详细,我们主要来关注他的核心逻辑
sendMsg(mAudioHandler,
MSG_SET_DEVICE_VOLUME,
SENDMSG_QUEUE,
device,
0,
streamState,
0);
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SET_DEVICE_VOLUME:
setDeviceVolume((VolumeStreamState) msg.obj, msg.arg1);
break;
...
}
}
/*package*/ void setDeviceVolume(VolumeStreamState streamState, int device) {
synchronized (VolumeStreamState.class) {
// Apply volume
streamState.applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(device);
// Apply change to all streams using this one as alias
int numStreamTypes = AudioSystem.getNumStreamTypes();
for (int streamType = numStreamTypes - 1; streamType >= 0; streamType--) {
if (streamType != streamState.mStreamType &&
mStreamVolumeAlias[streamType] == streamState.mStreamType) {
// Make sure volume is also maxed out on A2DP device for aliased stream
// that may have a different device selected
int streamDevice = getDeviceForStream(streamType);
if ((device != streamDevice) && mAvrcpAbsVolSupported
&& AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)) {
mStreamStates[streamType].applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(device);
}
mStreamStates[streamType].applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(streamDevice);
}
}
}
// Post a persist volume msg
sendMsg(mAudioHandler,
MSG_PERSIST_VOLUME,
SENDMSG_QUEUE,
device,
0,
streamState,
PERSIST_DELAY);
}
看注释我们就可以知道,*streamState.applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(device);*作为核心语句进行音量的调节。
// must be called while synchronized VolumeStreamState.class
/*package*/ void applyDeviceVolume_syncVSS(int device) {
int index;
//检查设备是否处于完全静音状态
if (isFullyMuted()) {
index = 0;//静音状态将index设置成0
} else if (AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_ALL_A2DP_SET.contains(device)
&& mAvrcpAbsVolSupported) {
//如果设备属于 A2DP 输出集合并且支持 AVRCP 绝对音量协议(用于蓝牙设备的音量同步),
//则使用 getAbsoluteVolumeIndex 方法计算适用于 AVRCP 的绝对音量索引。
index = getAbsoluteVolumeIndex((getIndex(device) + 5)/10);
} else if (isFullVolumeDevice(device) && isHdmiFullVolumeEnabled()) {
//如果设备属于完全音量设备(如 HDMI 输出),并且启用了 HDMI 完全音量,音量索引设置为音量最大值
index = (mIndexMax + 5)/10;
} else if (device == AudioSystem.DEVICE_OUT_HEARING_AID) {
//如果设备是助听器音频输出设备,设置为最大音量,以确保听力设备音量优化。
index = (mIndexMax + 5)/10;
} else {
//对于非完全音量设备,计算出设备的常规音量索引。
index = (getIndex(device) + 5)/10;
}
setStreamVolumeIndex(index, device);
}
这里我们得清楚一个概念,为啥需要先把index+5再除10。代码 index = (getIndex(device) + 5) / 10 是一种四舍五入的操作,将设备的音量索引从内部的线性表示转换为 AVRCP 或其他设备可以理解的音量范围。
- 线性音量表示:
- Android 内部音量索引通常是一个较大的整数值(比如 0 到 100),以便提供更细粒度的控制。
- 而设备通常使用一个较小范围的音量刻度(如 0 到 10)来表示音量。
- 四舍五入计算:
+5表示在进行整数除法之前,将数值增加一半,以实现四舍五入的效果。- 这样,当
getIndex(device)为 45 到 54 之间的值时,(getIndex(device) + 5) / 10就会取到 5。 - 如果不加 5,直接除以 10,结果将向下取整,从而失去精度。
假设 getIndex(device) 返回的是 47:
- 如果直接
47 / 10,结果会是 4(向下取整)。 - 使用
(47 + 5) / 10变为52 / 10,得到 5,这样在音量缩小后的范围内会更准确。
总结
通过 +5 实现四舍五入,确保在不同设备和协议要求下都能尽可能准确地映射到合适的音量值。
理解这个概念之后,我们接着来跟进一下流程。
private void setStreamVolumeIndex(int index, int device) {
// Only set audio policy BT SCO stream volume to 0 when the stream is actually muted.
// This allows RX path muting by the audio HAL only when explicitly muted but not when
// index is just set to 0 to repect BT requirements、
/*
Bluetooth SCO 特殊处理:
Bluetooth SCO 的音量控制有一些特殊要求。某些蓝牙设备在音量为 0 时会执行不同的操作,比如切断音频路径(即停止传输)。
为避免意外切断音频路径,如果流并没有被完全静音(!isFullyMuted()),即便用户将音量索引设置为 0,也会将 index 改为 1,以防止音频完全中断。
这意味着只有在流已被明确静音时,index 才会设置为 0,确保音频路径正常。
*/
if (mStreamType == AudioSystem.STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO && index == 0
&& !isFullyMuted()) {
index = 1;
}
AudioSystem.setStreamVolumeIndexAS(mStreamType, index, device);
}
/** @hide Wrapper for native methods called from AudioService */
public static int setStreamVolumeIndexAS(int stream, int index, int device) {
if (DEBUG_VOLUME) {
Log.i(TAG, "setStreamVolumeIndex: " + STREAM_NAMES[stream]
+ " dev=" + Integer.toHexString(device) + " idx=" + index);
}
return setStreamVolumeIndex(stream, index, device);
}
可以看到,我们到这就准备开始调用Native层的方法了,*setStreamVolumeIndex*是native方法
private static native int setStreamVolumeIndex(int stream, int index, int device);
Native层
AudioSystem.cpp
status_t AudioSystem::setStreamVolumeIndex(audio_stream_type_t stream,
int index,
audio_devices_t device) {
//获取音频策略服务:IAudioPolicyService
const sp<IAudioPolicyService>& aps = AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service();
//如果获取失败,则代表权限不足或者服务不可用
if (aps == 0) return PERMISSION_DENIED;
//将stream、index、device转换成c++中的格式
media::AudioStreamType streamAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(
legacy2aidl_audio_stream_type_t_AudioStreamType(stream));
int32_t indexAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(convertIntegral<int32_t>(index));
int32_t deviceAidl = VALUE_OR_RETURN_STATUS(legacy2aidl_audio_devices_t_int32_t(device));
return statusTFromBinderStatus(
aps->setStreamVolumeIndex(streamAidl, deviceAidl, indexAidl));
}
const sp<IAudioPolicyService> AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service() {
sp<IAudioPolicyService> ap;
sp<AudioPolicyServiceClient> apc;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gLockAPS);
if (gAudioPolicyService == 0) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder;
do {
binder = sm->getService(String16("media.audio_policy"));
if (binder != 0)
break;
ALOGW("AudioPolicyService not published, waiting...");
usleep(500000); // 0.5 s
} while (true);
if (gAudioPolicyServiceClient == NULL) {
gAudioPolicyServiceClient = new AudioPolicyServiceClient();
}
binder->linkToDeath(gAudioPolicyServiceClient);
gAudioPolicyService = interface_cast<IAudioPolicyService>(binder);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(gAudioPolicyService == 0);
apc = gAudioPolicyServiceClient;
// Make sure callbacks can be received by gAudioPolicyServiceClient
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
}
ap = gAudioPolicyService;
}
if (apc != 0) {
int64_t token = IPCThreadState::self()->clearCallingIdentity();
ap->registerClient(apc);
ap->setAudioPortCallbacksEnabled(apc->isAudioPortCbEnabled());
ap->setAudioVolumeGroupCallbacksEnabled(apc->isAudioVolumeGroupCbEnabled());
IPCThreadState::self()->restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
return ap;
}
*statusTFromBinderStatus*返回设置音量的状态(成功or失败)
static inline status_t statusTFromBinderStatus(const ::android::binder::Status &status) {
return status.isOk() ? OK // check OK,
: status.serviceSpecificErrorCode() // service-side error, not standard Java exception
// (fromServiceSpecificError)
?: status.transactionError() // a native binder transaction error (fromStatusT)
?: statusTFromExceptionCode(status.exceptionCode()); // a service-side error with a
// standard Java exception (fromExceptionCode)
}
我们需要着重看一下真正调节音量的核心语句*aps->setStreamVolumeIndex(streamAidl, deviceAidl, indexAidl));*
AudioPolicyManager.cpp
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setStreamVolumeIndex(audio_stream_type_t stream,
int index,
audio_devices_t device)
{
// 获取与给定音频流类型相关联的音频属性。
// 这个属性通常包含音频流的特性,如音质、用途等。
auto attributes = mEngine->getAttributesForStreamType(stream);
// 检查获取的音频属性是否有效。
// 如果没有为该音频流类型找到任何属性,则记录警告信息并退出。
if (attributes == AUDIO_ATTRIBUTES_INITIALIZER) {
ALOGW("%s: no group for stream %s, bailing out", __func__, toString(stream).c_str());
return NO_ERROR;
}
ALOGV("%s: stream %s attributes=%s", __func__,
toString(stream).c_str(), toString(attributes).c_str());
// 调用 setVolumeIndexForAttributes 方法,根据音频属性设置音量索引。
// 该方法将处理具体的音量调整逻辑。
return setVolumeIndexForAttributes(attributes, index, device);
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setVolumeIndexForAttributes(const audio_attributes_t &attributes,
int index,
audio_devices_t device)
{
// Get Volume group matching the Audio Attributes
// 获取与音频属性匹配的音量组。
auto group = mEngine->getVolumeGroupForAttributes(attributes);
if (group == VOLUME_GROUP_NONE) {
ALOGD("%s: no group matching with %s", __FUNCTION__, toString(attributes).c_str());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
ALOGV("%s: group %d matching with %s", __FUNCTION__, group, toString(attributes).c_str());
status_t status = NO_ERROR;
IVolumeCurves &curves = getVolumeCurves(attributes);// 获取与属性相关的音量曲线。
VolumeSource vs = toVolumeSource(group);// 将音量组转换为音量源。
product_strategy_t strategy = mEngine->getProductStrategyForAttributes(attributes);// 获取策略。
status = setVolumeCurveIndex(index, device, curves);// 根据音量曲线设置音量索引。
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("%s failed to set curve index for group %d device 0x%X", __func__, group, device);
return status;
}
DeviceTypeSet curSrcDevices;// 当前源设备集合。
auto curCurvAttrs = curves.getAttributes();// 获取当前音量曲线的属性。
if (!curCurvAttrs.empty() && curCurvAttrs.front() != defaultAttr) {
auto attr = curCurvAttrs.front();
curSrcDevices = mEngine->getOutputDevicesForAttributes(attr, nullptr, false).types();
} else if (!curves.getStreamTypes().empty()) {
// 如果没有有效的属性,则根据流类型获取输出设备。
auto stream = curves.getStreamTypes().front();
curSrcDevices = mEngine->getOutputDevicesForStream(stream, false).types();
} else {
ALOGE("%s: Invalid src %d: no valid attributes nor stream",__func__, vs);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
// 获取当前源设备类型。
audio_devices_t curSrcDevice = Volume::getDeviceForVolume(curSrcDevices);
resetDeviceTypes(curSrcDevices, curSrcDevice);
// 遍历所有输出设备,更新音量。
// update volume on all outputs and streams matching the following:
// - The requested stream (or a stream matching for volume control) is active on the output
// - The device (or devices) selected by the engine for this stream includes
// the requested device
// - For non default requested device, currently selected device on the output is either the
// requested device or one of the devices selected by the engine for this stream
// - For default requested device (AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME), apply volume only if
// no specific device volume value exists for currently selected device.
for (size_t i = 0; i < mOutputs.size(); i++) {
sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor> desc = mOutputs.valueAt(i);
DeviceTypeSet curDevices = desc->devices().types();
/*
假设在某个情况下,用户的扬声器被标识为安全扬声器(例如,因音量过高被系统保护)。
在音频播放逻辑中,如果不进行处理,可能会导致音频无法正常输出或输出音量过低。
通过将其替换为标准扬声器,系统可以更好地控制音量,确保用户获得预期的音频体验。
*/
if (curDevices.erase(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER_SAFE)) {
curDevices.insert(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER);
}
/*
音量应用: 只有在正在活动的音频流(如播放音乐)或通话中的输出描述符上,系统才会进行音量调整。
这确保了音量调整不会在无效或不需要的设备上进行,从而提升用户体验。
通话优先: 如果用户正在通话,系统将优先保持通话音量,而不会意外改变其他音频流的音量。
*/
if (!(desc->isActive(vs) || isInCall())) {
continue;
}
/*
假设我们在处理音量调节的逻辑,当前系统中有多个音频设备可供选择,如扬声器、耳机和蓝牙设备。
场景描述:
当前音频设备是耳机(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HEADSET),用户希望调节耳机的音量。
系统中还有一个默认的音频输出设备,例如扬声器(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME)。
代码逻辑解释:
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME && curDevices.find(device) == curDevices.end()):
这个条件检查当前调节的设备是否是默认音频输出设备。
如果不是默认设备,接着检查curDevices中是否存在该设备(即,当前活跃的设备集合中是否有耳机)。
逻辑结果:
如果当前设备是耳机,但curDevices中并不包含耳机,那么音量调节将被跳过(continue),意味着不会对耳机进行音量调整。
这种情况下,可能是因为耳机当前没有处于活动状态(例如用户拔掉了耳机)。
*/
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME &&
curDevices.find(device) == curDevices.end()) {
continue;
}
bool applyVolume = false;
if (device != AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_DEFAULT_FOR_VOLUME) {
curSrcDevices.insert(device);
applyVolume = (curSrcDevices.find(
Volume::getDeviceForVolume(curDevices)) != curSrcDevices.end());
} else {
applyVolume = !curves.hasVolumeIndexForDevice(curSrcDevice);
}
if (!applyVolume) {
continue; // next output
}
// Inter / intra volume group priority management: Loop on strategies arranged by priority
// If a higher priority strategy is active, and the output is routed to a device with a
// HW Gain management, do not change the volume
//涉及音量控制时的优先级管理
if (desc->useHwGain()) {
//如果当前设备(desc)支持硬件增益,则初始化applyVolume为false,因为我们可能不想改变音量。
applyVolume = false;
for (const auto &productStrategy : mEngine->getOrderedProductStrategies()) {
auto activeClients = desc->clientsList(true /*activeOnly*/, productStrategy,
false /*preferredDevice*/);
//遍历按优先级排序的音频策略。如果该策略下没有活动客户端,跳过此策略。
if (activeClients.empty()) {
continue;
}
bool isPreempted = false;
bool isHigherPriority = productStrategy < strategy;
for (const auto &client : activeClients) {
//如果发现当前活动客户端的优先级高于正在处理的音频源(vs),则不改变音量。
//记录相关信息以便于调试。
if (isHigherPriority && (client->volumeSource() != vs)) {
ALOGV("%s: Strategy=%d (\nrequester:\n"
" group %d, volumeGroup=%d attributes=%s)\n"
" higher priority source active:\n"
" volumeGroup=%d attributes=%s) \n"
" on output %zu, bailing out", __func__, productStrategy,
group, group, toString(attributes).c_str(),
client->volumeSource(), toString(client->attributes()).c_str(), i);
applyVolume = false;
isPreempted = true;
break;
}
// However, continue for loop to ensure no higher prio clients running on output
//如果当前活动客户端是与正在处理的音频源相同,则可以调整音量。
if (client->volumeSource() == vs) {
applyVolume = true;
}
}
if (isPreempted || applyVolume) {
break;
}
}
//如果applyVolume仍然为false,则跳过当前输出设备,继续处理下一个设备。
if (!applyVolume) {
continue; // next output
}
}
//FIXME: workaround for truncated touch sounds
// delayed volume change for system stream to be removed when the problem is
// handled by system UI
/*
这里标记了一个“FIXME”注释,表示该部分代码是一个临时解决方案,目的是处理触摸声音被截断的问题。
注释中提到,一旦系统用户界面解决了这个问题,相关的延迟音量更改将被移除。
*/
//调用checkAndSetVolume函数来检查并设置音量。
//传入参数包括音量曲线(curves)、音量源(vs)、音量索引(index)、音频输出描述(desc)和当前设备(curDevices)。
//如果当前音频源是系统音频流(AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM),则使用固定的延迟(TOUCH_SOUND_FIXED_DELAY_MS)来设置音量;否则,延迟为0。
status_t volStatus = checkAndSetVolume(
curves, vs, index, desc, curDevices,
((vs == toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM))?
TOUCH_SOUND_FIXED_DELAY_MS : 0));
if (volStatus != NO_ERROR) {
status = volStatus;
}
}
//回调函数,表示Audio的音量组已经修改
mpClientInterface->onAudioVolumeGroupChanged(group, 0 /*flags*/);
return status;
}
这个方法主要的调节音量的方法为*checkAndSetVolume*,我们接着跟踪这个方法
status_t AudioPolicyManager::checkAndSetVolume(IVolumeCurves &curves,
VolumeSource volumeSource,
int index,
const sp<AudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc,
DeviceTypeSet deviceTypes,
int delayMs,
bool force)
{
// do not change actual attributes volume if the attributes is muted
if (outputDesc->isMuted(volumeSource)) {
ALOGVV("%s: volume source %d muted count %d active=%d", __func__, volumeSource,
outputDesc->getMuteCount(volumeSource), outputDesc->isActive(volumeSource));
return NO_ERROR;
}
//这里定义了两个音频流类型:通话音频流(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL)和蓝牙 SCO 音频流(AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO)。
//isVoiceVolSrc和isBtScoVolSrc用于检查当前音频源是否为通话流或蓝牙 SCO 流。
VolumeSource callVolSrc = toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL);
VolumeSource btScoVolSrc = toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO);
bool isVoiceVolSrc = callVolSrc == volumeSource;
bool isBtScoVolSrc = btScoVolSrc == volumeSource;
//判断是否有SOC请求
bool isScoRequested = isScoRequestedForComm();
// do not change in call volume if bluetooth is connected and vice versa
// if sco and call follow same curves, bypass forceUseForComm
if ((callVolSrc != btScoVolSrc) &&
((isVoiceVolSrc && isScoRequested) ||
(isBtScoVolSrc && !isScoRequested))) {
ALOGV("%s cannot set volume group %d volume when is%srequested for comm", __func__,
volumeSource, isScoRequested ? " " : "n ot ");
// Do not return an error here as AudioService will always set both voice call
// and bluetooth SCO volumes due to stream aliasing.
return NO_ERROR;
}
if (deviceTypes.empty()) {
deviceTypes = outputDesc->devices().types();
}
float volumeDb = computeVolume(curves, volumeSource, index, deviceTypes);
if (std::isnan(volumeDb)
&& (volumeSource == toVolumeSource(AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM))
&& !curves.hasVolumeIndexForDevice(*(outputDesc->devices().types().begin()))) {
if (*(outputDesc->devices().types().begin()) == AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER) {//扬声器
//设置默认音量
volumeDb = -18.937500f;
}
}
if (outputDesc->isFixedVolume(deviceTypes) ||
// Force VoIP volume to max for bluetooth SCO device except if muted
(index != 0 && (isVoiceVolSrc || isBtScoVolSrc) &&
isSingleDeviceType(deviceTypes, audio_is_bluetooth_out_sco_device))) {
//音量值将被设置为 0.0 dB,这通常表示音量为最大。
volumeDb = 0.0f;
}
/*[Amlogic start]+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*/
/* Change-Id: Ia4120848f02c700d9b03a48e0b7122415eb63799 */
/* Need adjust audio hal volume when television platform. */
bool soundbarMode = property_get_int32("persist.vendor.media.audio.soundbar.mode", 0) == 1;
bool tvProduct = property_get_bool("ro.vendor.platform.has.tvuimode", false /* default_value */);
if (tvProduct || soundbarMode) {
DeviceTypeSet curSrcDevicesVector = deviceTypesFromBitMask(getDevicesForStream(AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC));
audio_devices_t curDevice = Volume::getDeviceForVolume(curSrcDevicesVector);
DeviceTypeSet curDeviceVector = deviceTypesFromBitMask(curDevice);
bool speakerGainApplied = false;
bool bootVideoRunning = property_get_int32("service.bootvideo.exit", 0) == 1;
if (curDevice == AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER &&
(outputDesc->isStrategyActive(streamToStrategy(AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC)) || bootVideoRunning)) {
//ignoring the "index" passed as argument and always use MUSIC stream index
//for all stream types works on TV because all stream types are aliases of MUSIC.
device_category devCategory = Volume::getDeviceCategory(curDeviceVector);
auto &volCurves = getVolumeCurves(AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC);
int volumeIndex = volCurves.getVolumeIndex(curDeviceVector);
int volumeMaxIndex = volCurves.getVolumeIndexMax();
int volumeMinIndex = volCurves.getVolumeIndexMin();
float musicVolumeDb = volCurves.volIndexToDb(devCategory, volumeIndex);
float maxMusicVolumeDb = volCurves.volIndexToDb(devCategory, volumeMaxIndex);
float minMusicVolumeDb = volCurves.volIndexToDb(devCategory, volumeMinIndex);
ALOGV("[%s:%d] volumeIndex:%d, volumeMinIndex:%d, volumeMaxIndex:%d, curDevice:%#x, devCategory:%d",
__func__, __LINE__, volumeIndex, volumeMinIndex, volumeMaxIndex, curDevice, devCategory);
ALOGV("[%s:%d] musicVolumeDb:%f, minMusicVolumeDb:%f, maxMusicVolumeDb:%f, bootVideoRunning:%d",
__func__, __LINE__, musicVolumeDb, minMusicVolumeDb, maxMusicVolumeDb, bootVideoRunning);
if (bootVideoRunning) {
maxMusicVolumeDb = 0.0f;
minMusicVolumeDb = -10000.0f;
musicVolumeDb = -1837.0f;
}
speakerGainApplied = outputDesc->updateGain(curDevice,
musicVolumeDb, minMusicVolumeDb, maxMusicVolumeDb);
}
if (curDevice == AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC || curDevice == AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE ||
(speakerGainApplied && (curDevice & AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER) != 0)) {
volumeDb = 0.0f;
}
}
/*[Amlogic end]-----------------------------------------------------------*/
//设置音量
outputDesc->setVolume(
volumeDb, volumeSource, curves.getStreamTypes(), deviceTypes, delayMs, force);
if (isVoiceVolSrc || isBtScoVolSrc) {
float voiceVolume;
// Force voice volume to max or mute for Bluetooth SCO as other attenuations are managed by the headset
if (isVoiceVolSrc) {
voiceVolume = (float)index/(float)curves.getVolumeIndexMax();
} else {
voiceVolume = index == 0 ? 0.0 : 1.0;
}
if (voiceVolume != mLastVoiceVolume) {
mpClientInterface->setVoiceVolume(voiceVolume, delayMs);
mLastVoiceVolume = voiceVolume;
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
可以看到核心的设置音量方法*outputDesc->setVolume*,outputDesc这个对象的类是AudioOutputDescriptor。我们接着跟踪下去。
AudioOutputDescriptor.cpp
bool AudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume(float volumeDb,
VolumeSource volumeSource,
const StreamTypeVector &/*streams*/,
audio_devices_t /*device*/,
uint32_t delayMs,
bool force)
{
// We actually change the volume if:
// - the float value returned by computeVolume() changed 与之前的音量不同
// - the force flag is set 强制标记
if (volumeDb != getCurVolume(volumeSource) || force) {
ALOGV("%s for volumeSrc %d, volume %f, delay %d", __func__, volumeSource, volumeDb, delayMs);
//设置到VolumeActivities的db成员中,本类中会getCurVolume获取当前音量,并向AudioFlinger设置到回播线程中,根据streamType设置到对应的stream上去
setCurVolume(volumeSource, volumeDb);
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool SwAudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume(float volumeDb,
VolumeSource vs, const StreamTypeVector &streamTypes,
audio_devices_t device,
uint32_t delayMs,
bool force)
{
StreamTypeVector streams = streamTypes;
if (!AudioOutputDescriptor::setVolume(volumeDb, vs, streamTypes, device, delayMs, force)) {
return false;
}
if (streams.empty()) {
streams.push_back(AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC);
}
for (const auto& devicePort : devices()) {
// 设备相等,且支持gain硬件调整音量的去设置
if (device == devicePort->type() &&
devicePort->hasGainController(true) && isActive(vs)) {
ALOGV("%s: device %s has gain controller", __func__, devicePort->toString().c_str());
//将0dB转换为功率值
float volumeAmpl = Volume::DbToAmpl(0);
//为此类型的软件音量值设置0就是不发声,
for (const auto &stream : streams) {
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
//硬件音量更新
AudioGains gains = devicePort->getGains();
int gainMinValueInMb = gains[0]->getMinValueInMb();
int gainMaxValueInMb = gains[0]->getMaxValueInMb();
int gainStepValueInMb = gains[0]->getStepValueInMb();
int gainValueMb = ((volumeDb * 100)/ gainStepValueInMb) * gainStepValueInMb;
gainValueMb = std::max(gainMinValueInMb, std::min(gainValueMb, gainMaxValueInMb));
audio_port_config config = {};
devicePort->toAudioPortConfig(&config);
config.config_mask = AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_GAIN;
config.gain.values[0] = gainValueMb;
//硬件音量设置
return mClientInterface->setAudioPortConfig(&config, 0) == NO_ERROR;
}
}
//上述走过硬件音量后,下面的都是软件音量,获取当前音量并转换为功率值ampl
float volumeAmpl = Volume::DbToAmpl(getCurVolume(vs));
if (hasStream(streams, AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO)) {
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
//设置功率值
for (const auto &stream : streams) {
ALOGV("%s output %d for volumeSource %d, volume %f, delay %d stream=%s", __func__,
mIoHandle, vs, volumeDb, delayMs, toString(stream).c_str());
mClientInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, volumeAmpl, mIoHandle, delayMs);
}
return true;
}
这个device支持gain硬件方式设置音量,就使用硬件音量调整setAudioPortConfig,此方法会调用到hal的set_audio_port_config指针函数;否则就是软件音量调整设置setStreamVolume,我们后续先看一下不支持gain硬件的设置音量流程
需要先把Db分贝转换为功率值ampl。
static inline float DbToAmpl(float decibels)
{
if (decibels <= VOLUME_MIN_DB) {
return 0.0f;
}
return exp( decibels * 0.115129f); // exp( dB * ln(10) / 20 )
}
AudioPolicyClientInterface * const mClientInterface;
AudioPolicyInterface.h
virtual status_t setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float volume, audio_io_handle_t output, int delayMs = 0) = 0;
AudioPolicyClientImpl.cpp
status_t AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream,
float volume, audio_io_handle_t output,
int delay_ms)
{
return mAudioPolicyService->setStreamVolume(stream, volume, output,
delay_ms);
}
AudioPolicyService.h
virtual status_t setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream,
float volume,
audio_io_handle_t output,
int delayMs = 0);
AudioPolicyService.cpp
int AudioPolicyService::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream,
float volume,
audio_io_handle_t output,
int delayMs)
{
return (int)mAudioCommandThread->volumeCommand(stream, volume,
output, delayMs);
}
AudioFlinger.cpp
status_t AudioFlinger::setStreamVolume(audio_stream_type_t stream, float value,
audio_io_handle_t output)
{
// check calling permissions
if (!settingsAllowed()) {
return PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
status_t status = checkStreamType(stream);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
return status;
}
if (output == AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(stream == AUDIO_STREAM_PATCH && value != 1.0f,
"AUDIO_STREAM_PATCH must have full scale volume");
AutoMutex lock(mLock);
//从mPlaybackThreads集合中拿到一个回播线程实例
VolumeInterface *volumeInterface = getVolumeInterface_l(output);
if (volumeInterface == NULL) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
//设置音量对应功率值到playbackthread中的stream对应的音量值去
volumeInterface->setStreamVolume(stream, value);
return NO_ERROR;
}