系列文章目录
文章目录
Spring容器
IOC容器是具有依赖注入功能的容器,负责对象的实例化、对象的初始化,对象和对象之间依赖关系配置、对象的销毁、对外提供对象的查找等操作,对象的整个生命周期都是由容器来控制。我们需要使用的对象都由ioc容器进行管理,不需要我们再去手动通过new的方式去创建对象,由ioc容器直接帮我们组装好,当我们需要使用的时候直接从ioc容器中直接获取就可以了。
spring ioc容器是如何知道需要管理哪些对象呢?
需要我们给ioc容器提供一个配置清单,这个配置支持xml格式和java注解的方式,在配置文件中列出需要让ioc容器管理的对象,以及可以指定让ioc容器如何构建这些对象,当spring容器启动的时候,就会去加载这个配置文件,然后将这些对象给组装好以供外部访问者使用。
IOC容器也叫spring容器。
Spring自带了哪些容器实现?
- bean 工厂是最简单的容器,提供基本的 DI 支持
- 应用上下文基于 BeanFactory 构建,并提供应用框架级别的服务。
因为 bean 工厂对大多数应用来说往往太低级了,因此,应用上下文要比 bean 工厂更受欢迎。
创建Spring容器
// 创建一个Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 是比较常见的两种创建Spring容器的方式。但是用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext其实已经过时了,在新版的Spring MVC和Spring Boot的底层主要用的都是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的用法和ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是非常类似的,只不过需要传入的是一个class,而不是一个xml文件。
手写Spring容器
传入一个Java配置类
public class MyApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass){
this.configClass = configClass;
}
}
这个时候,就可以通过MyApplicationContext构造方法传入AppConfig.class,然后再通过Java配置类上的 @ComponentScan 注解得到扫描路径
@ComponentScan注解类
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
这样AppConfig.class即可通过@ComponentScan 注解添加扫描包路径
@ComponentScan("org.example.my.service")
public class AppConfig {
}
Spring容器通过AppConfig配置类获取扫描包路径
public class MyApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
public MyApplicationContext(Class configClass){
this.configClass = configClass;
scan();
}
public void scan(){
if(this.configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value();
}
}
}
通过包路径加载所有class获取bean信息
这时候要去target目录下找到路径下的class文件而不是src下面的java文件,可以通过ClassLoader的getResource()方法
public void scan(){
if(this.configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value();
path = path.replace(".","/");
ClassLoader classLoader = MyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println(resource); //file:/C:/Users/ZPJX/IdeaProjects/MySpring/target/classes/org/example/my/service
}
}
这里已经取得了扫描包的绝对路径了,然后再通过绝对路径获得扫描包的目录,再通过目录遍历扫描包下面的class文件。获得class文件后要想获得class文件里面是否含有@Component注解,Spring用的是AMS技术,而现在最简单的方式就是用应用程序类加载器加载这个class文件。
public void scan(){
if(this.configClass.isAnnotationPresent(ComponentScan.class)){
ComponentScan componentScanAnnotation = (ComponentScan)configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScanAnnotation.value();
path = path.replace(".","/");
ClassLoader classLoader = MyApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println(resource); //file:/C:/Users/ZPJX/IdeaProjects/MySpring/target/classes/org/example/my/service
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
for (File f : file.listFiles()) {
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("classes")+"classes".length()+1,absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\",".");
try {
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
//
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
获取到文件的class对象以后,如果class文件有@Component注解,再将这个bean的定义,也就是beanDefinition保存到一个Map中。
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
//取出beanName
Component componentAnnotation = (Component)clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
if("".equals(beanName)){
beanName = Introspector.decapitalize(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
//创建beanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(clazz);
beanDefinition.setBeanName(beanName);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)){
Scope scopeAnnotation = (Scope)clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String scope = scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScopeType(scope);
}else {
//默认为单例bean
beanDefinition.setScopeType("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
通过beanDefinitionMap创建单例bean
扫描包完成以后,要通过beanDefinitionMap遍历创建单例bean
//创建单例bean
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : beanDefinitionMap.entrySet()) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
if(beanDefinition.getScopeType().equals("singleton")){
Object o = createBean(beanDefinition);
singletonMap.put(entry.getKey(),o);
}
}
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition){
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
Object instance = null;
try {
instance = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return instance;
}
再写getBean(String beanName)方法
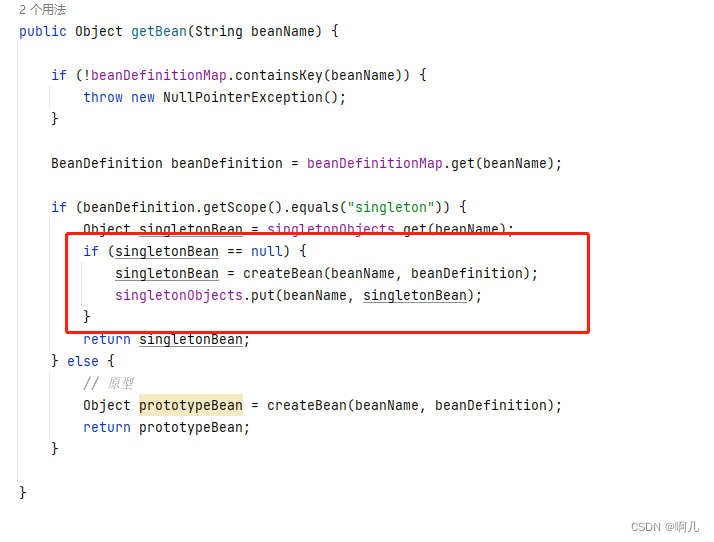
public Object getBean(String beanName){
if(!beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
String scope = beanDefinition.getScopeType();
if("singleton".equals(scope)){
Object singletonBean = singletonMap.get(beanName);
return singletonBean;
}else{
Object prototypeBean = createBean(beanDefinition);
return prototypeBean;
}
}
@Autowired注解类(这里不考虑循环依赖)
再添加@Autowired注解,在createBean中创建一个实例的时候,需要遍历class中的所有字段,判断是否含有@Autowired注解,如果有,则给instance中的该字段注入bean对象。先通过字段类型找bean,如果找到多个,再通过字段名称找bean。
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition){
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
Object instance = null;
try {
instance = clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
Class type = field.getType();
List<String> beanNames = beanDefinitionMap.entrySet().stream().filter(new Predicate<Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition>>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry) {
BeanDefinition bean = entry.getValue();
if(bean.getBeanClass().equals(type)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}).map(e->e.getKey()).collect(Collectors.toList());
if(beanNames.size()==1){
field.set(instance,getBean(beanNames.get(0)));
}else {
String name = field.getName();
field.set(instance,getBean(name));
}
}
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return instance;
}
在给instance注入bean对象的时候,bean对象可能还没创建,当bean为单例的时候,在singletonMap中还找不到,需要创建。
实现初始化、初始化前、初始化后
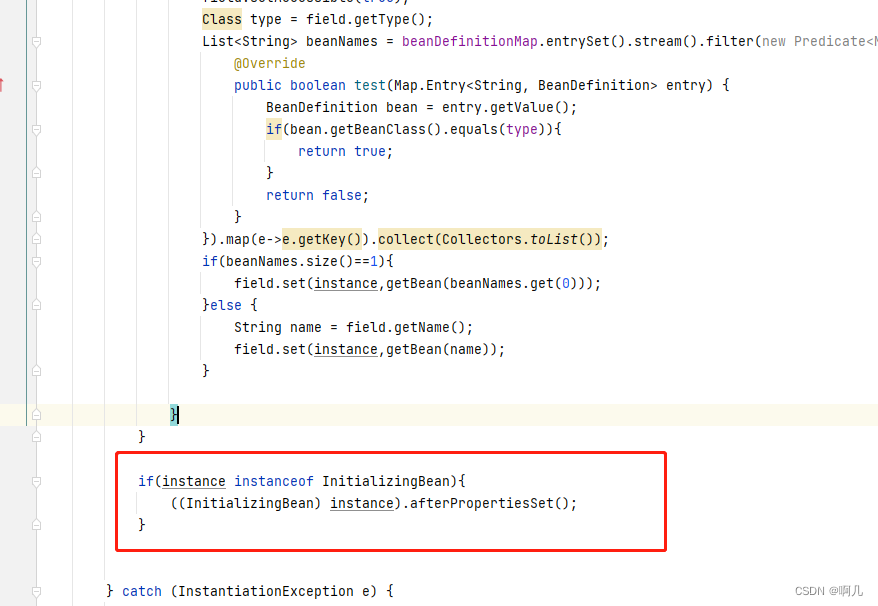
注入完成以后,就开始 初始化前、初始化、初始化后等动作了
初始化比较简单,实现一个InitializingBean接口,让bean实现afterPropertiesSet()方法
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
if(instance instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
}
初始化前和初始化后都和BeanPostProcessor有关,可以自定义一个类去实现该接口,同时给类加上@Component注解
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
}
在扫描包的时候扫到BeanPostProcessor后放到List
if(BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)){
BeanPostProcessor instance = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(instance);
continue;
}
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance,beanName);
}
if(instance instanceof InitializingBean){
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance,beanName);
}
beanPostProcessor可以实现动态代理各种操作,就是AOP的实现方法,通过beanPostProcessor实现切面逻辑。
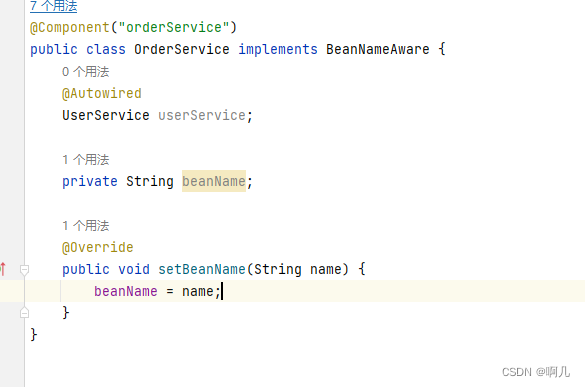
Aware机制
还可以实现各种Aware接口,比如BeanNameAware接口。
if (instance instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) instance).setBeanName(beanName);
}
一个基本的Spring底层实现就完成啦!