【python图解】数据结构之字典和集合
在 Python 中,字典和集合是另外的两种重要数据结构,它们分别用于存储键值对和无序的唯一元素集合。下面我们将详细介绍字典和集合的定义、操作方法、使用场景及相关案例。
1. 字典(Dictionary)
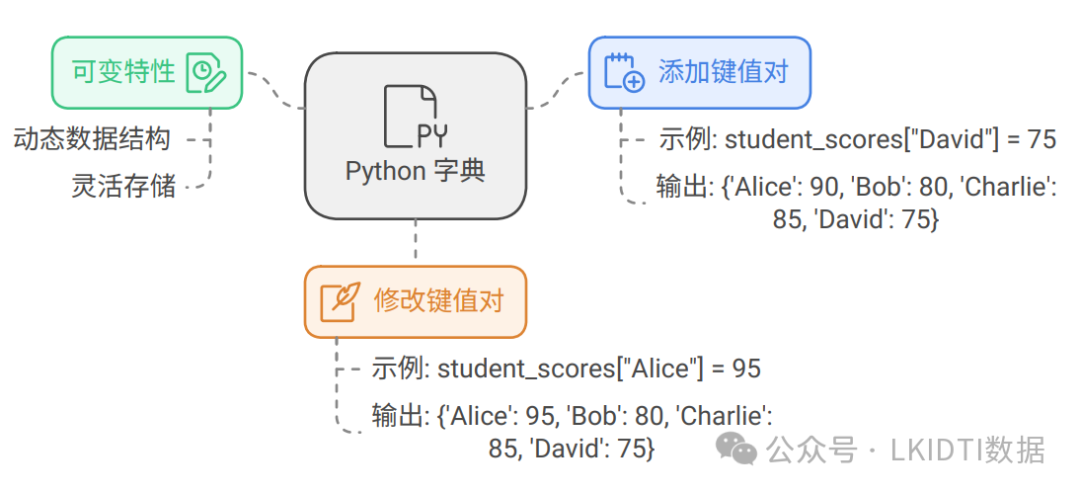
字典是一种存储键值对的可变数据类型,它使用大括号 {} 定义,通过键(key)来访问对应的值(value)。字典中的键必须是唯一且不可变的,通常是字符串或数字类型,值可以是任意数据类型。
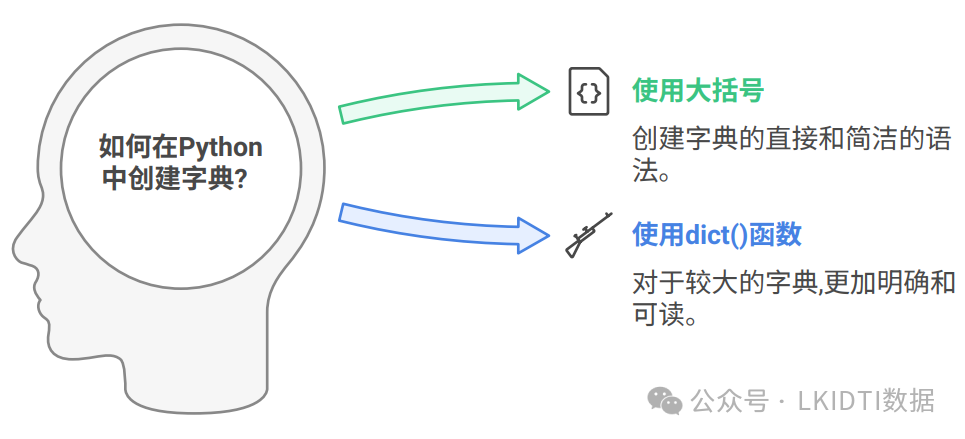
1.1 创建字典
字典的创建方式包括直接使用大括号或通过内置函数 dict()。
# 方式一:使用大括号创建字典
student_scores = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 80, "Charlie": 85}
# 方式二:使用 dict() 函数
employee_data = dict(name="John", age=30, department="HR")
print(student_scores) # 输出: {'Alice': 90, 'Bob': 80, 'Charlie': 85}
print(employee_data) # 输出: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'department': 'HR'}1.2 访问字典中的值
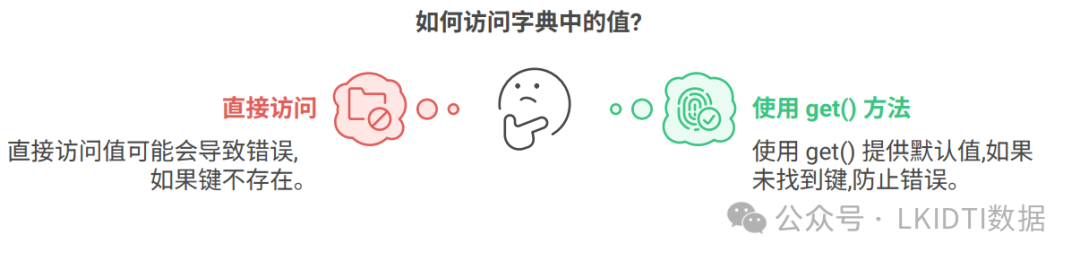
通过键来访问字典中的值。如果访问不存在的键会引发 KeyError,为此可以使用 get() 方法来安全访问值。
# 直接访问键的值
print(student_scores["Alice"]) # 输出: 90
# 使用 get() 方法
print(student_scores.get("David", "Not Found")) # 输出: Not Found1.3 增加和修改元素
字典是可变的数据类型,可以直接通过键进行增加或修改。
# 增加新键值对
student_scores["David"] = 75
print(student_scores) # 输出: {'Alice': 90, 'Bob': 80, 'Charlie': 85, 'David': 75}
# 修改现有键的值
student_scores["Alice"] = 95
print(student_scores) # 输出: {'Alice': 95, 'Bob': 80, 'Charlie': 85, 'David': 75}1.4 删除元素
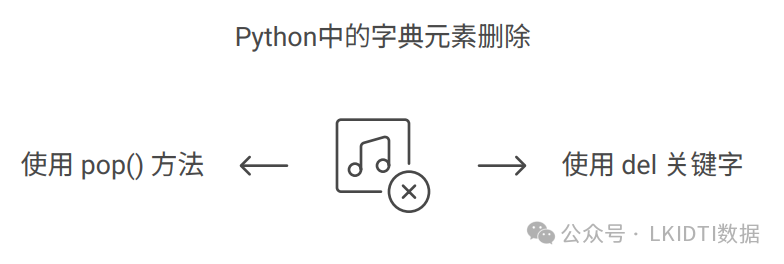
字典支持使用 del 关键字或 pop() 方法来删除元素。
# 使用 del 删除键值对
del student_scores["Bob"]
print(student_scores) # 输出: {'Alice': 95, 'Charlie': 85, 'David': 75}
# 使用 pop() 方法删除,并返回被删除的值
removed_score = student_scores.pop("Charlie")
print(removed_score) # 输出: 85
print(student_scores) # 输出: {'Alice': 95, 'David': 75}1.5 遍历字典
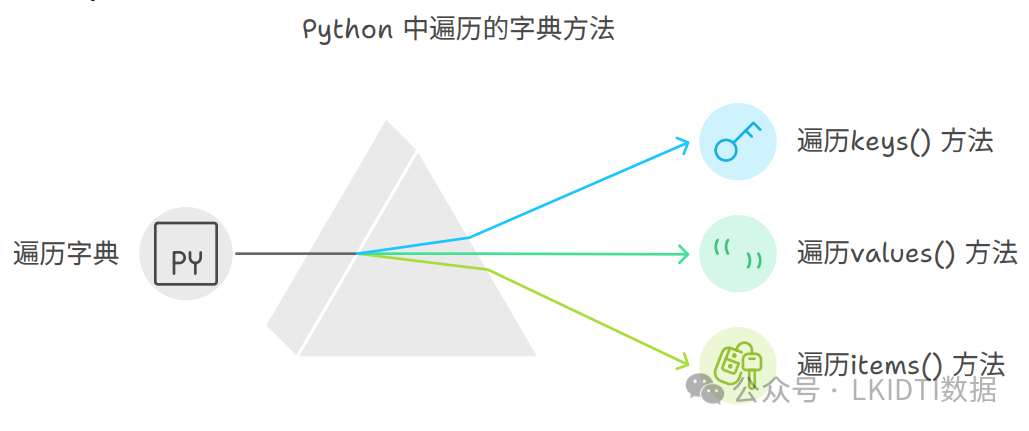
可以通过 keys()、values() 和 items() 方法来获取字典的键、值和键值对。
# 遍历字典的键
for key in student_scores.keys():
print(key)
# 遍历字典的值
for value in student_scores.values():
print(value)
# 遍历字典的键值对
for key, value in student_scores.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")1.6 字典常用方法
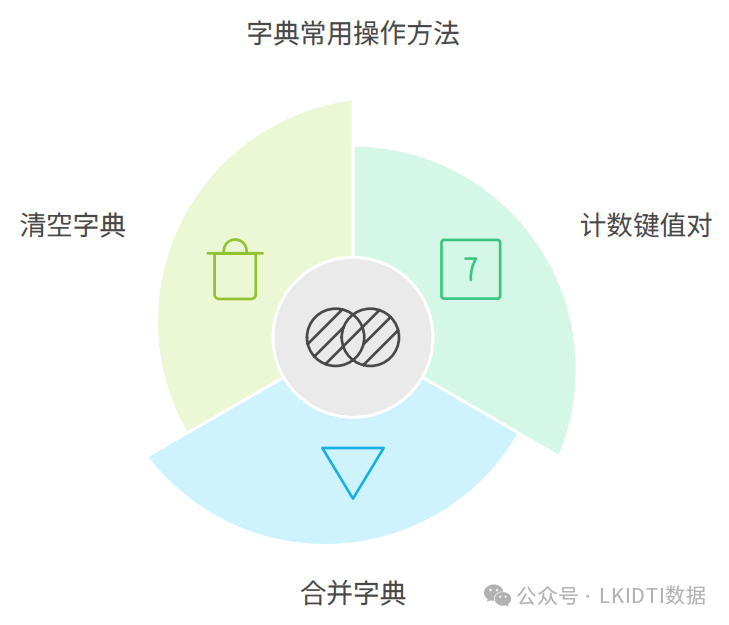
-
len(dict): 获取字典中键值对的数量。 -
dict.update(other_dict): 合并另一个字典中的键值对。 -
dict.clear(): 清空字典中的所有元素。
1.7 字典的应用场景
-
存储和管理配置信息。
-
快速查找和检索数据。
-
作为映射表或记录集合。
2. 集合(Set)
集合是一个无序且不重复的元素集合,使用大括号 {} 或 set() 函数创建。集合中的元素必须是不可变的,但集合本身是可变的。
2.1 创建集合
# 使用大括号创建集合
unique_numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5}
print(unique_numbers) # 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}(自动去重)
# 使用 set() 函数创建集合
empty_set = set() # 注意:{} 是空字典,不是集合2.2 添加和删除元素
集合支持 add()、remove() 和 discard() 方法。
my_set = {1,2,3}
# 添加元素
my_set.add(4)
print(my_set)# 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4}
# 删除元素
my_set.remove(2)# 如果元素不存在会引发 KeyError
my_set.discard(3)# 如果元素不存在不会引发错误
print(my_set) # 输出: {1, 4}2.3 集合的常用操作
-
联合(Union):
set1 | set2或set1.union(set2) -
交集(Intersection):
set1 & set2或set1.intersection(set2) -
差集(Difference):
set1 - set2或set1.difference(set2) -
对称差集(Symmetric Difference):
set1 ^ set2或set1.symmetric_difference(set -

set1 = {1,2,3}
set2 ={3,4,5}
# 联合
print(set1 | set2)# 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# 交集
print(set1 & set2)# 输出: {3}
# 差集
print(set1 - set2)# 输出: {1, 2}
# 对称差集
print(set1 ^ set2) # 输出: {1, 2, 4, 5}2.4 集合的应用场景
-
数据去重。
-
进行集合运算(交集、差集等)。
-
快速判断某元素是否存在于集合中。
3. 综合案例:使用字典和集合管理学生成绩
假设我们需要管理学生成绩并统计考试分数的唯一值集合。可以使用字典存储每个学生的成绩,用集合计算不同的成绩值。
# 字典存储学生成绩
grades ={
"Alice":[85,90,95],
"Bob":[70,80,90],
"Charlie":[90,85,80]
}
# 计算所有成绩的集合
unique_scores =set()
for scores in grades.values():
unique_scores.update(scores)
print("学生成绩记录:", grades)
print("所有唯一成绩:", unique_scores)
# 统计每个学生的平均成绩
average_grades ={name: sum(scores)/ len(scores)for name, scores in grades.items()}
print("平均成绩:", average_grades)总结
-
字典用于存储键值对,适合快速查找、更新和存储结构化数据。
-
集合是无序的且元素唯一,适合数据去重和集合操作。
-
合理使用字典和集合可以提升程序的性能和数据管理能力
-