Taro + react 小程序分类菜单实现
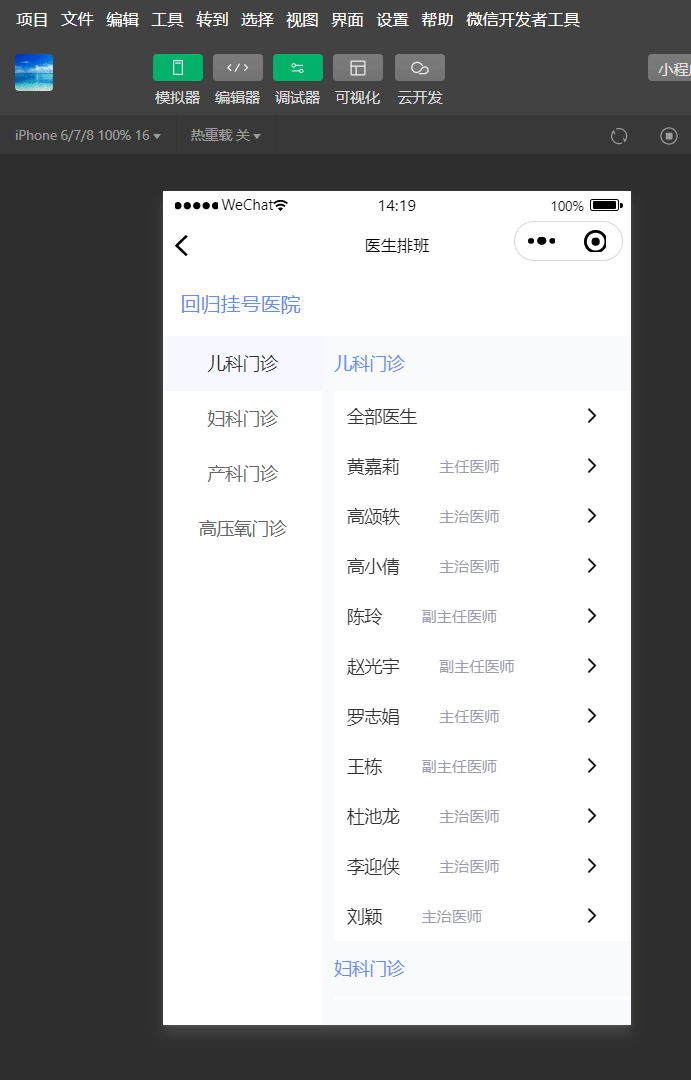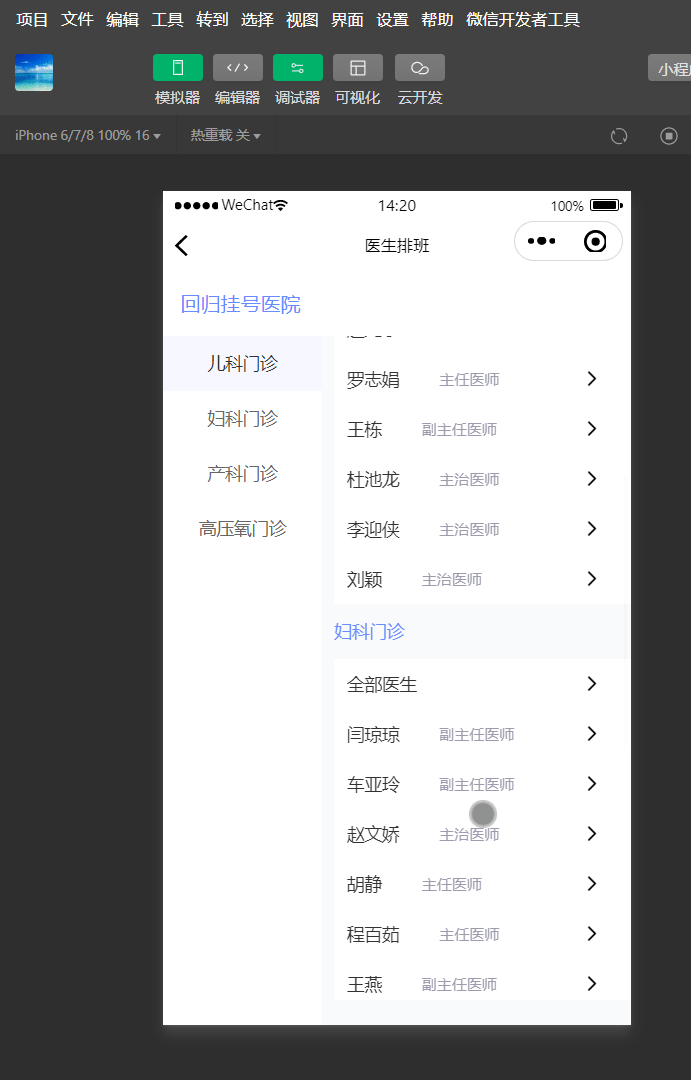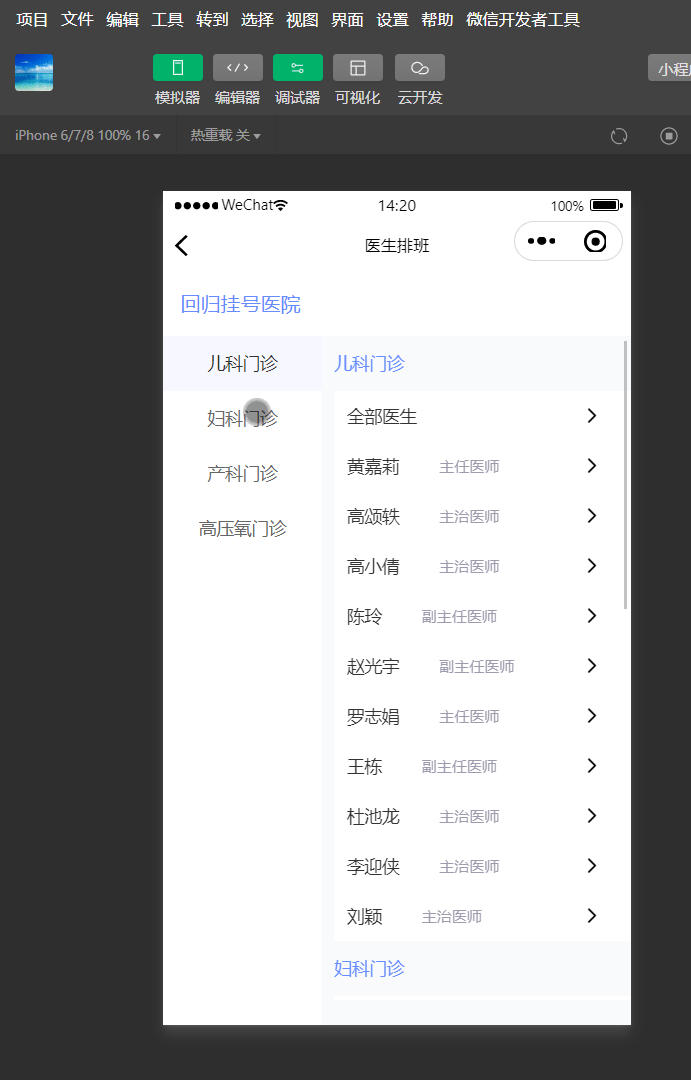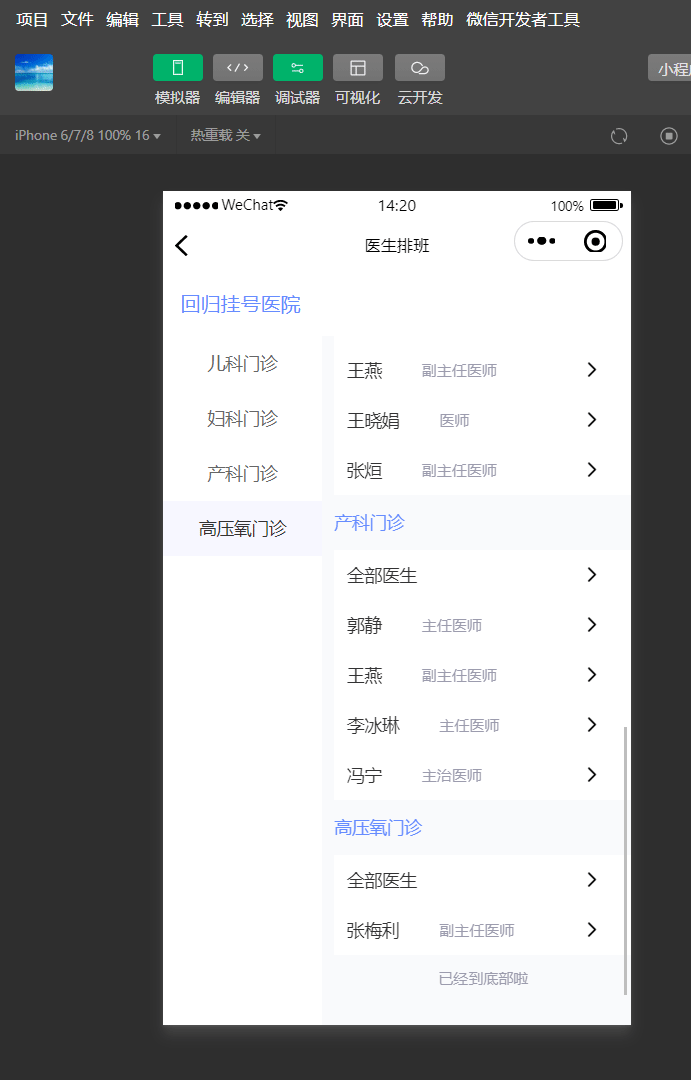
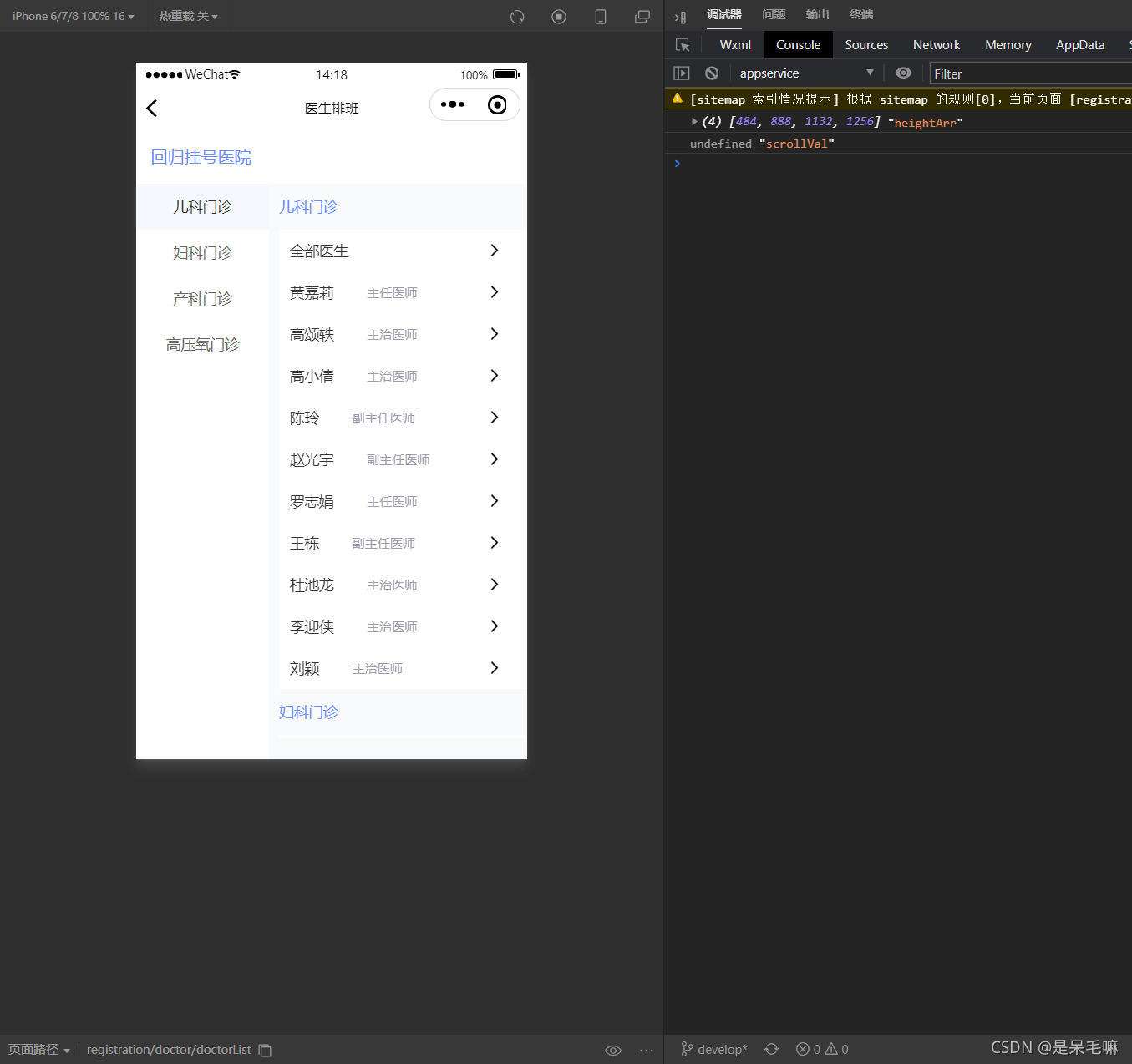
效果
滑动右侧内容区域,左侧菜单栏滑动对应分类位置。
点击左侧分类,右侧滑动到指定分类位置
思路
1.左右各位两个scroll-view,进行上下滚动。
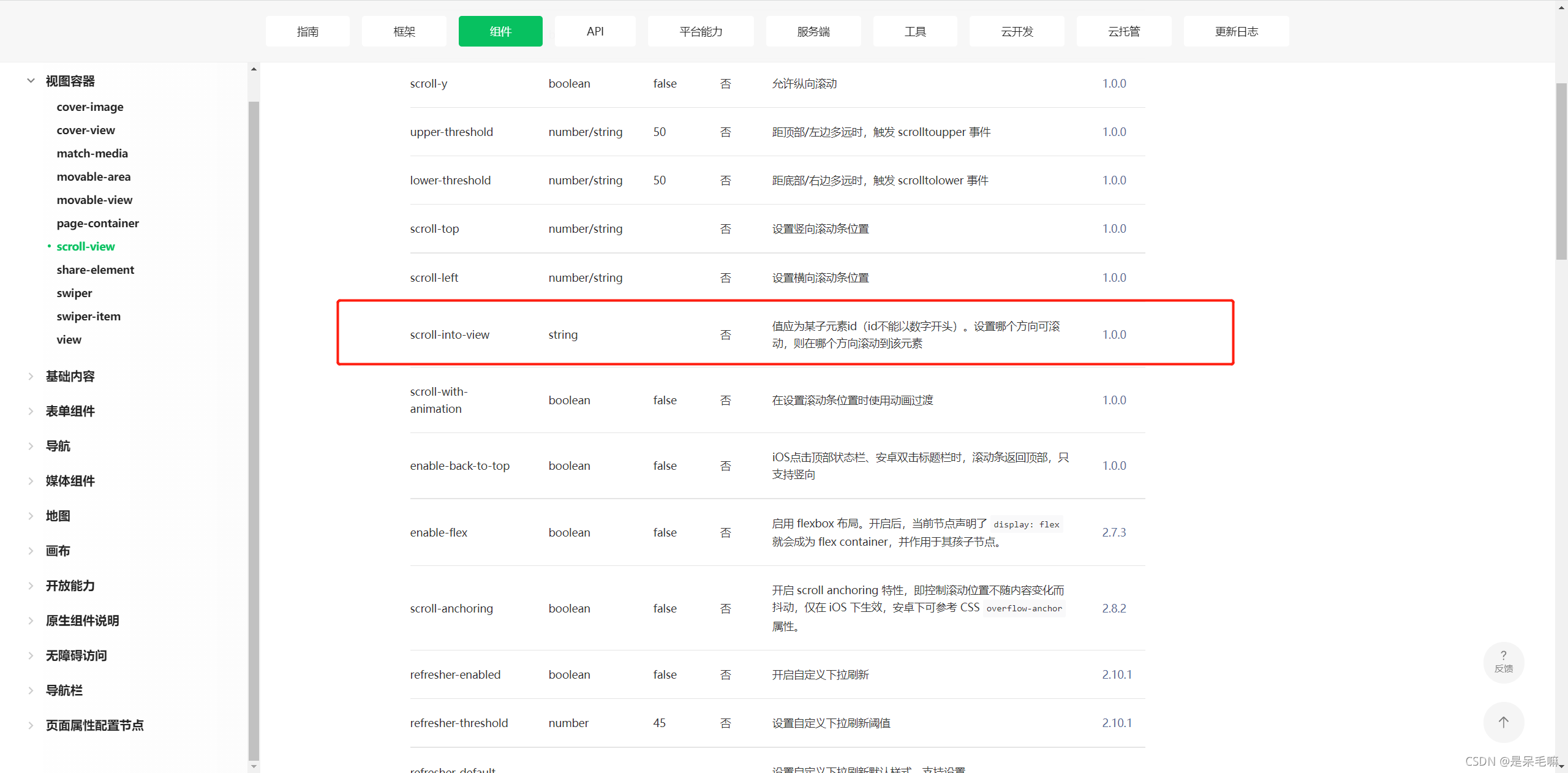
2.左侧菜单栏点击,右侧滑动指定位置,可用小程序自带的锚点 scroll-into-view
3.右侧内容区域获得对应每个模块高度,滚动判断左侧菜单栏位置。
技术
1.Taro 是一个开放式跨端跨框架解决方案,支持使用 React/Vue/Nerv 等框架来开发 微信 / 京东 / 百度 / 支付宝 / 字节跳动 / QQ 小程序 / H5 / RN 等应用。
2.小程序原生组件
3.react
实现
1.左侧菜单栏
相对而言简单些,代码如下
<View className="nav">
{/* 这是Taro的scrollView的写法,只需将其写成小程序对应的scroll-view即可 */}
<ScrollView scrollY style="height:100%">
{/* 这是Taro的scrollView的写法,只需将其写成小程序对应的for循环就好 */}
{serviceList.map((item, index) => {
return (
<View
key="item"
className={`nav_title ${index === navActive ? 'nav_active' : ''}`}
onClick={() => navClick(index)}
>
{item.name}
</View>
)
})}
</ScrollView>
</View>
{/* 注意此处的点击事件的赋值*/}
const [selectId, setSelectId] = useState('' as string) //这个是对应锚点的值
const [navActive, setAavActive] = useState(0 as number) //这个是左侧点击选中的菜单栏下标
// 左边菜单栏点击
const navClick = index => {
setAavActive(index)
setSelectId('item' + index)
}
此处要注意的是,因为scroll-into-view是不能以数字开头,倘若用后台返回的id值也会有以id开头的,就会报错,所以此处使用了item字符串拼接index,'item’随意任何字符串都可以
2.右侧内容区
<View className="content">
<ScrollView
className="content_scroll"
style={{ height: winHeight - 72 + 'px' }}
scrollY
scrollWithAnimation
//此处对应的锚点就是左侧菜单栏选中时,拼接的锚点id
scrollIntoView={selectId}
enhanced
bounces={false}
onScroll={e => onscroll(e)}
scrollTop={scrollVal}
>
//此处都为Taro的写法,对应的是小程序的循环
{serviceList.map((item, index) => {
return (
<View key="item" id={'item' + index} className="content_box">
<View className="content_title">{item.name}</View>
<View className="content_center_box">
{item.doctors.map(it => {
return (
<View key="it" className="content_center" onClick={() => contentClick(it)}>
<View className="content_doctor">
{it.type === 'all' ? (
<View className="doctor_name" style="font-weight: 500;">
{it.name}
</View>
) : (
<View className="doctor_name"> {it.name}</View>
)}
<View className="doctor_level">{it.level}</View>
</View>
<View className="iconfont iconmy_btn_arrow_black_big2x"></View>
</View>
)
})}
</View>
</View>
)
})}
{serviceList.length > 0 && <View className="content_footer">已经到底部啦</View>}
</ScrollView>
</View>
//页面加载时执行的方法
const [scrollVal, setScrollVal] = useState(0 as number)
const [heightArr, setHeightArr] = useState([] as Array<any>)
const [distance, setDistance] = useState(0 as number)
const selectHeight = () => {
let arr = [] as any
let h = 0
const query = Taro.createSelectorQuery()
query.selectAll('.content_box').boundingClientRect()
query.exec(function (res) {
res[0].forEach(item => {
h += item.height
arr.push(h)
})
//获取每一块儿content_box的高度值存储起来
setHeightArr(arr)
//内容区滚动的高度,首次加载获取第一项
setScrollVal(arr[navActive - 1])
})
}
//右侧滚动时方法
const onscroll = e => {
//内容区域不会超出滚动就返回
if (heightArr.length === 0) return
//滚动的高度
let scrollTop = e.detail.scrollTop
// 到达底部
if (scrollTop + winHeight + 1 >= heightArr[heightArr.length - 1]) {
//到达底部要把锚点id清除,否则锚点id选中不到第一项item1,因为item1此时已经变成了默认值,无法通过锚点跳转
setSelectId('')
}
// 向下滚动,如果向下滚动的值大于了存储的distance值,distance默认为0,每次滚动都会把滚动值存储为distance
if (scrollTop >= distance) {
if (navActive + 1 < heightArr.length && scrollTop >= heightArr[navActive]) {
//对应的左侧菜单栏的选中项进行加1
setAavActive(navActive + 1)
}
//向上滚动
} else {
if (navActive - 1 >= 0 && scrollTop < heightArr[navActive - 1]) {
//对应的左侧菜单栏的选中项进行减1
setAavActive(navActive - 1)
}
}
//存储了滚动的值
setDistance(scrollTop)
}
存储的高度值与滚动值首次渲染如下
此处需要注意一个点是,要先获取后台返回的list数据,再进行右侧content_box高度内容渲染,否则拿到是空数组,无法进行向上向下滚动逻辑处理,左侧分类就不会跟随改变。
3.css样式
//在最外层,我用View包裹起来,felx变成左右布局;
.center {
display: flex;
height: 100%;
.nav {
flex-basis: 255px;
width: 255px;
overflow-y: scroll;
background-color: #fff;
color: #666666;
font-size: 28px;
font-weight: 400;
line-height: 40px;
.nav_title {
padding: 24px 42px;
overflow: hidden;
text-align: center;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
white-space: nowrap;
}
.nav_active {
background: #f7f7ff;
color: #333333;
font-weight: 500;
}
}
.content {
flex: 1;
margin-left: 20px;
overflow-y: scroll;
.content_scroll {
height: 100%;
overflow-y: scroll;
}
.content_title {
height: 40px;
padding: 24px 0px;
color: #668cff;
font-size: 28px;
font-weight: 500;
line-height: 40px;
}
.content_center_box {
background: #ffffff;
.content_center {
display: flex;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 20px 40px 20px 20px;
font-weight: 400;
line-height: 40px;
.content_doctor {
display: flex;
flex: 1;
.doctor_name {
margin-right: 12px;
color: #333333;
font-size: 28px;
}
.doctor_level {
margin-left: 28px;
color: #9c9cae;
font-size: 24px;
}
}
}
}
.content_footer {
padding: 20px 0px;
color: #9c9cae;
font-size: 24px;
text-align: center;
}
}
}