说明
本文主要介绍“依次取出一个整数的各位数字”及其 变种形式
本来的面貌
PS:废话少说,先贴代码,后面再举两个例子;
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
将正整数n,从最低位向最高位,依次取出每位数,并将取出的每位数压栈
void function(int n){
if(!n){//特殊情况特殊处理:当n=0时,直接输出,不执行后续代码
cout << "位数:" << 1 << endl;
cout << 0 << endl;
return;
}
stack<int>stack;//栈
int Count = 0;//统计该正整数,一共有几位数字
while (n%10 || n/10){//循环条件:(n%10)与(n/10)不同时为0即可;循环结束条件:(n%10)与(n/10)同时为0即结束循环
int Digit = n % 10;//取出正整数的最低位数字
n = n/10;//取出最低位数字后,剩余的
Count++;//个数加1
stack.push(Digit);//将取出的最低位数字,压栈
}//注意:循环结束后,n=0
输出
cout << "位数:" << Count << endl;//
cout << "位数:" << stack.size() << endl;//两种方式均可统计一共有几位数字
while(!stack.empty()){//出栈
int temp = stack.top();//取栈顶元素
stack.pop();//出栈,但是并不返回栈顶元素
cout << temp << " ";//显示结果为:依次从最高位到最低位输出每位数字
}
}
测试函数
int main(){
function(123);
return 0;
}
结果
///
下面是我的分析过程:
例子一:依次取出 3546 的各个数字
3546 % 10 = 6 //取出最低位
3546 / 10 = 354
354 % 10 = 4 //取出
354 / 10 = 35
35 % 10 = 5 //取出
35 / 10 = 3
3 % 10 = 3 //取出
3 / 10 = 0 //注:不同时为0,还要继续循环
0 % 10 = 0 //没进循环,不取
0 / 10 = 0 //注:同时为0,循环结束
例子二:依次取出 306 的各位数字
306 % 10 = 6 //取出
306 / 10 = 30
30 % 10 = 0 // 取出
30 / 10 = 3
3 % 10 = 3 //取出
3 / 10 = 0 //注:不同时为0,还要继续循环
0 % 10 = 0 //没进循环,不取
0 / 10 = 0 //注:同时为0,循环结束
PS:最后,方法有很多中,随便都能百度到,从大一到大四,前前后后也写过很多中版本,感觉这个还算比较简便吧,写在这里,记录一下,方便查看哈哈。第一次写博客,感觉好啰嗦哦!
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2022-3-31更新----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
变种一:计算一个正整数的各位数字之和
//计算一个正整数的各位数字之和
int function(int n){
int count = 0;//正整数n的位数
int sum = 0;
while(n%10 || n/10){
int digit = n % 10;//取最低位
n = n/10;//更新
count++;
//
sum = sum + digit;
}
return sum;
}
变种二:判断水仙花数
//编写判断水仙花数的函数;
//PS:水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和等于它本身。
// 例如:因为1^3 + 5^3+ 3^3 = 153,所以153是水仙花数
bool function(int n){
int temp = n;//暂存,非常容易错
int count = 0;//
int sum = 0;
while(n%10 || n/10){
int digit = n%10;//取最低位
n = n/10;
count++;
//
sum = sum + digit*digit*digit;
}//循环结束,n=0
if(sum == temp)
return true;
else
return false;
}
变种三:判断是否是 对称数
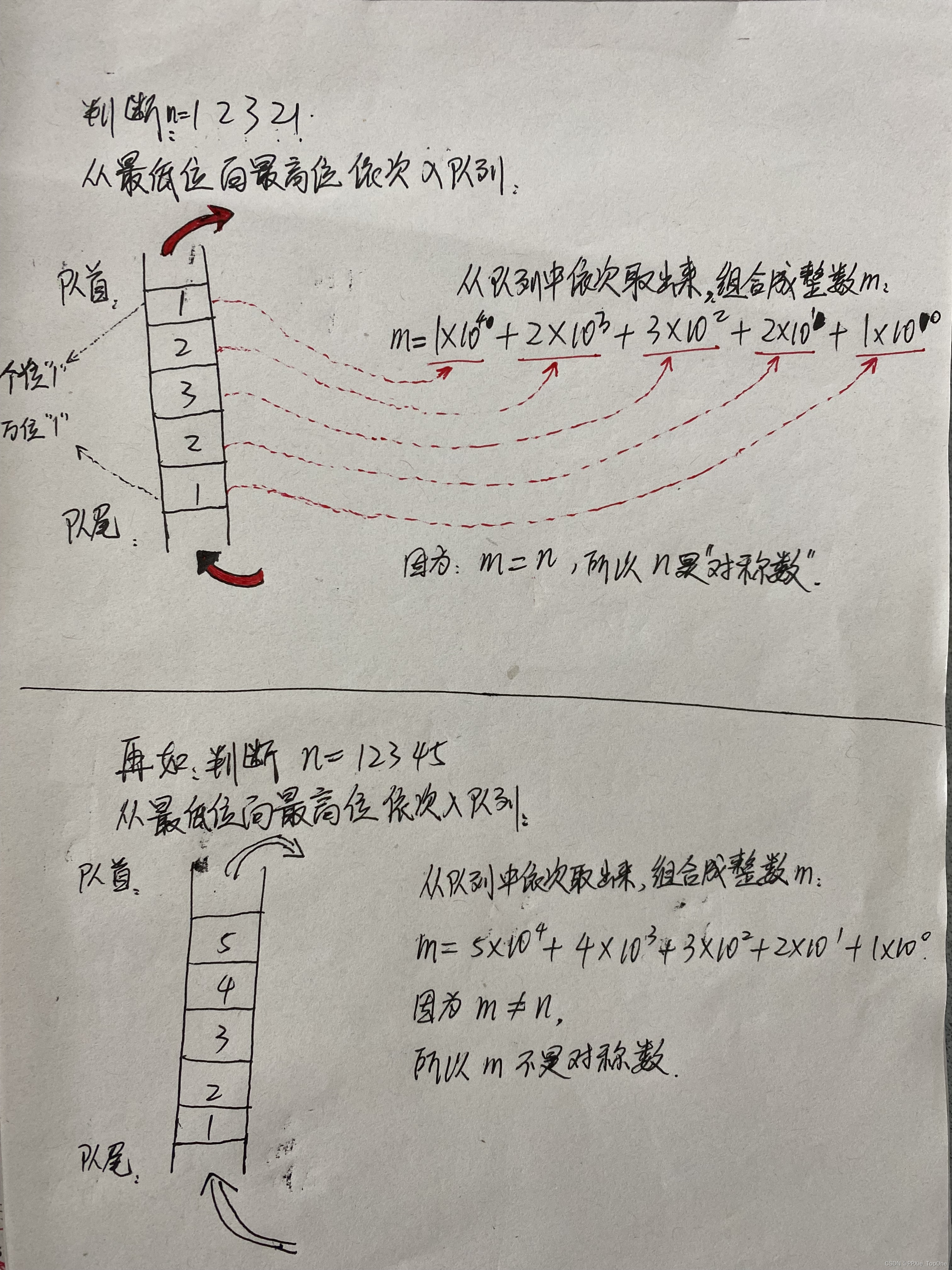
对称数 定义:一个整数,正序和倒序都对称的数,如11、22、12321、123321等都是对称数,而123不是对称数;
处理方式一
分析
先从最低位向最高位取出整数n的每一位数,存放在队列中;
然后出队列重新组合成一个新的整数m,最后与整数n进行比较,若m==n则说明是对称数,如下图:
代码
//homework.h文件
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
bool function(int n){
int count = 0;//
queue<int>Queue;
int temp = n;//暂存
while(n%10 || n/10){
int digit = n%10;
n = n/10;
count++;
//
Queue.push(digit);//入队
}//结束n=0
int sum = 0;
int i = count-1;
while(!Queue.empty()){
sum = sum + Queue.front()*pow(10,i);//返回队首元素
Queue.pop();//只删不返回
i--;
}
//
if(sum == temp)
return true;
else
return false;
}
处理方式二
分析
先从最低位向最高位取出整数n的每一位数,放在数组中;
然后再统计 i、j 指向元素相等的个数是否等于原整数位数的一半:用两个指针 i、j 分别指向数组第一个和最后一个元素位置,若i、j 指向的元素相等则 i++、j–
代码
bool function(int n){
int temp = n;//暂存
int test[10];//正整数n最多不超过10位
int count = 0;
while(n%10 || n/10){
int digit = n%10;//取出最低位
n = n/10;//更新
count++;
//
test[count-1] = digit;
}//执行后n=0
int i = 0,j = count-1;//指针
int m = 0;
while(test[i] == test[j] && i<j){
i++;
j--;
m++;
}
if(m == count/2)
return true;
else
return false;
}