Resnet
产生原因
介绍残差网络Resnet之前,先介绍一下卷积神经网络过程中会遇到的问题,分别有:
- 计算资源的消耗
- 模型容易过拟合
- 梯度消失/梯度爆炸问题的产生
问题1可以通过GPU集群来解决,对于一个企业资源并不是很大的问题;问题2的过拟合通过采集海量数据,并配合Dropout正则化等方法也可以有效避免;问题3通过Batch Normalization也可以避免。貌似我们只要无脑的增加网络的层数,我们就能从此获益,但实验数据给了我们当头一棒。事实上,随着网络层数的增加,网络发生了退化(degradation)的现象:随着网络层数的增多,训练集loss逐渐下降,然后趋于饱和,当你再增加网络深度的话,训练集loss反而会增大。注意这并不是过拟合,因为在过拟合中训练loss是一直减小的。
从信息论的角度讲,由于DPI(数据处理不等式)的存在,在前向传输的过程中,随着层数的加深,Feature Map包含的图像信息会逐层减少,而ResNet的直接映射的加入,保证了下一层的网络一定比上层包含更多的图像信息。基于这种使用直接映射来连接网络不同层直接的思想,残差网络应运而生。
理论介绍
本文以学习和应用为主,具体的公式推导不做过多的赘述,只是大概了解一下残差网络的原理即可。
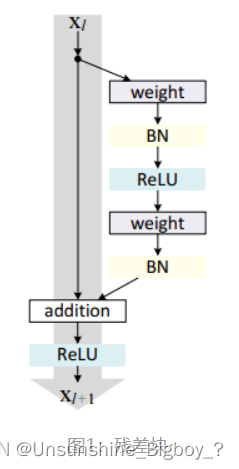
残差网络是由一系列残差块组成的(图1)。一个残差块可以用表示为:
残差块分成两部分直接映射部分和残差部分。 xl 是直接映射,反应在图1中是左边的曲线;F(xl,Wl) 是残差部分,一般由两个或者三个卷积操作构成,即图1中右侧包含卷积的部分。
简单来说,就是将上一层的输出,即本层的输入直接和通过本层网络后的网络参数值做一个叠加,从而保留了上层网络的信息,网络就不会出现退化的现象,也就是说随着层数的增加,网络一定会越来越优化。
但是实际上来说,当层数增加到一定程度上也会出现退化的现象,具体原因暂时还不理解。
详细网络推导参考:详解残差网络 - 知乎
前期准备
框架思路
整个过程大致分为四步,分别是:人脸检测——人脸截取——人脸矫正——人脸识别,用ResNet实现对一个人脸的编码,生成一个128维向量,然后通过计算两个向量之间的距离来实现识别。
环境搭建
需要用到的有:
- opencv(最好是用2.x.x版本,可以直接用参考文章的代码,但是我的是3.4.6导致原来的一些函数不能正常使用,出现了很多麻烦。)
- dlib深度学习库 安装教程链接:使用vs2017 + cmake 编译 dlib库的步骤以及遇到的问题_sihaiyinan的博客-CSDN博客
- VS2017
- Cmake
这里还得重点说明一下,由于opencv3以后的版本缺少contrib函数,所以不能用里面的Directory函数,这个函数本来是来得到文件夹目录中的所有特定类型的文件名,所以导致原来那个代码不能使用。为此,我去网上找了很多contrib库的安装教程,这个过程遇到的问题越来越多,最后成功了,但是因为文件地址的问题发现还是不能正常使用,于是找到了opencv3以后版本中的glob函数写了一个类,最后成功了。总之简单来说,如果要用参考里面的代码,就直接装opencv2,要是用我的代码,就不用管3以上的版本。
此外,还必须在dlib模型库中,下载链接为:http://dlib.net/files/ ,下载两个文件并解压,分别是为:
shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat
dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat
第一个是人脸特征点识别模型,可以识别68个特征点,第二个基于Resnet的人脸识别模型。
代码实现
代码基本都给出了非常详细的说明,我是在图片进行人脸识别之后修改的,然后调用摄像头进行动态是识别,FPS不高,但是整体效果还不错,建议大家先从图片识别开始入手,读取路径那些代码基本没动,只是注释掉了,最好还是参考一下这篇文章里面的代码。
文章链接:ResNet:用dlib实现人脸识别—C++,包括人脸检测和人脸矫正(附代码)_意疏的博客-CSDN博客_dlib resnet
完整代码(输入图片识别)
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
这是一个例子,说明使用DLIB C++的深度学习工具库。在这里,我们将展示如何进行人脸识别。此示例使用预先培训过的
DLib_人脸识别_resnet_model_v1模型,可从DLIB网站下载。该模型在标准LFW面上的精度为99.38%。识别基准,与其他
最先进的面部识别方法相比截至2017年2月的认可。
on_images_ex.cpp示例。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include "opencv\cv.h"
#include "opencv2\core.hpp"
#include "opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2\videoio.hpp"
//#include "contrib.hpp"
#include <dlib/dnn.h>
#include <dlib/gui_widgets.h>
#include <dlib/clustering.h>
#include <dlib/string.h>
#include <dlib/image_io.h>
#include <dlib/image_processing/frontal_face_detector.h>
#include <dlib\opencv.h>
using namespace dlib;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//下一位代码定义Resnet网络。基本上是复制的
//并从dnn_imagenet_ex.cpp示例粘贴,但我们替换了损失
//使用损耗度量进行分层,使网络变得更小。去读导论吧
//dlib dnn示例了解所有这些内容的含义。
//另外,dnn_metric_learning_on_images_ex.cpp示例显示了如何训练此网络。
//本例使用的dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1模型是使用
//基本上是dnn_metric_learning_on_images_ex.cpp中显示的代码,除了
//小批量大(35x15而不是5x5),迭代没有进展
//设置为10000,训练数据集由大约300万个图像组成,而不是
//55。此外,输入层被锁定为150大小的图像。
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
template <template <int, template<typename>class, int, typename> class block, int N, template<typename>class BN, typename SUBNET>
using residual = add_prev1<block<N, BN, 1, tag1<SUBNET>>>;
template <template <int, template<typename>class, int, typename> class block, int N, template<typename>class BN, typename SUBNET>
using residual_down = add_prev2<avg_pool<2, 2, 2, 2, skip1<tag2<block<N, BN, 2, tag1<SUBNET>>>>>>;
template <int N, template <typename> class BN, int stride, typename SUBNET>
using block = BN<con<N, 3, 3, 1, 1, relu<BN<con<N, 3, 3, stride, stride, SUBNET>>>>>;
template <int N, typename SUBNET> using ares = relu<residual<block, N, affine, SUBNET>>;
template <int N, typename SUBNET> using ares_down = relu<residual_down<block, N, affine, SUBNET>>;
template <typename SUBNET> using alevel0 = ares_down<256, SUBNET>;
template <typename SUBNET> using alevel1 = ares<256, ares<256, ares_down<256, SUBNET>>>;
template <typename SUBNET> using alevel2 = ares<128, ares<128, ares_down<128, SUBNET>>>;
template <typename SUBNET> using alevel3 = ares<64, ares<64, ares<64, ares_down<64, SUBNET>>>>;
template <typename SUBNET> using alevel4 = ares<32, ares<32, ares<32, SUBNET>>>;
using anet_type = loss_metric<fc_no_bias<128, avg_pool_everything<
alevel0<
alevel1<
alevel2<
alevel3<
alevel4<
max_pool<3, 3, 2, 2, relu<affine<con<32, 7, 7, 2, 2,
input_rgb_image_sized<150>
>>>>>>>>>>>>;
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//截取文件名函数
String Getfilename(String &Orgfolder, String &Orgfilenames)
{
char a[20];//保存字符
int i = 0;
int n = Orgfilenames.size() - Orgfolder.size()-1;//文件名长度
for (i; i < n-4; i++)
{
a[i] = Orgfilenames[Orgfolder.size() + i+1];
}
a[i] = '\0';//结束标志
String filename = a;//构造String类型数据
return filename;
}
int main()
{
VideoCapture capture(0); // 打开摄像头
if (!capture.isOpened()) // 判断是否打开成功
{
cout << "open camera failed. " << endl;
return -1;
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
cv::Mat II, III; //定义Mat矩阵存放摄像头图片
std::vector<matrix<float, 0, 1>> vec; //定义一个向量组,用于存放每一个人脸的编码;
float vec_error[30]; //定义一个浮点型的数组,用于存放一个人脸编码与人脸库的每一个人脸编码的差值;
String dir_path = "C:\\Users\\18xlt\\Desktop\\Learning\\Photo\\train";//定义人脸库路径
//cout << "Enter the path of picture set:"; //也可以输入人脸库文件夹路径
//std::cin >> dir_path;
string test_path; //定义测试集图片路径
std::vector<cv::String> fileFullNames; //将人脸库中每张图片创建路径列表
std::vector<string> fileNames; //将人脸库中每张图片名字列表
cv::glob(dir_path, fileFullNames, false); //统计文件夹里jpg格式文件的个数,并将每个文件的名字保存
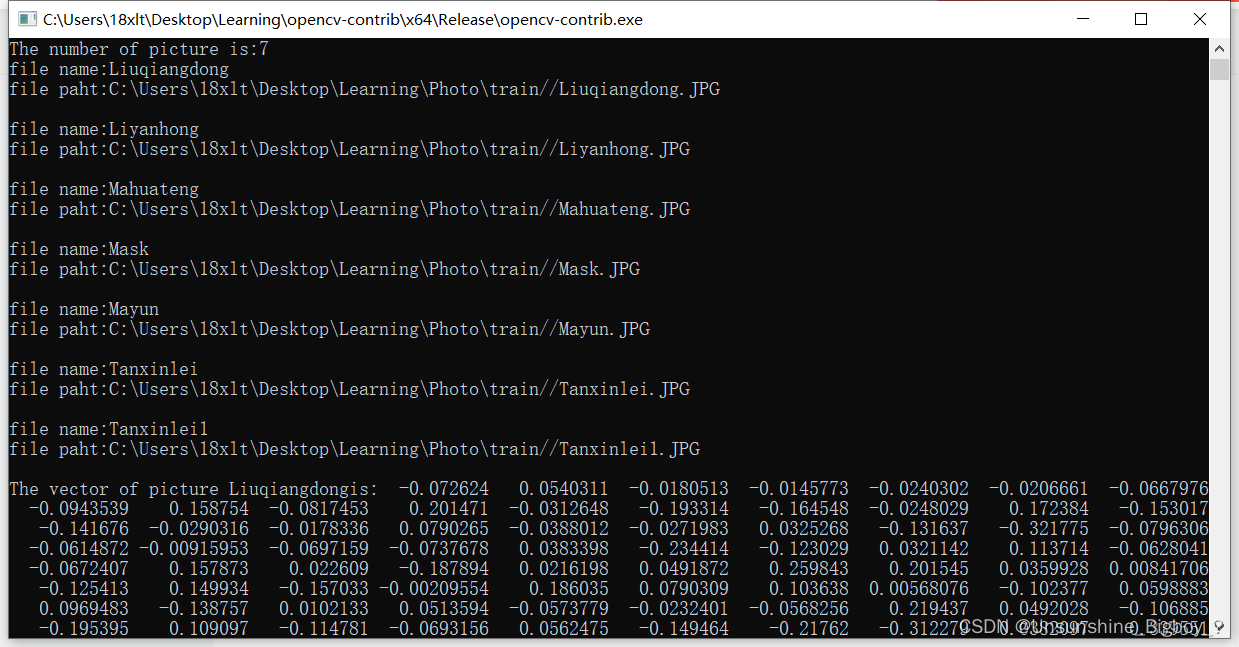
cout << "The number of picture is:" << fileFullNames.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < fileFullNames.size(); i++) //输出人脸库每张图片的绝对路径和对应姓名
{
string fileName = Getfilename(dir_path, fileFullNames[i]);
fileNames.push_back(fileName);
string fileFullName = dir_path + "//" + fileName + ".JPG";
cout << "file name:" << fileName << endl;
cout << "file paht:" << fileFullName << endl << endl;
}
//加载所有模型。首先,因为我们需要在图像中查找人脸我们需要人脸检测器:
frontal_face_detector detector = get_frontal_face_detector();
//我们还将使用人脸标记模型将人脸与标准姿势对齐:(有关介绍,请参见Face_Landmark_Detection_ex.cpp)
shape_predictor sp;
deserialize("D:/WorkSoftware/dlib/model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") >> sp;
//终于我们加载Resnet模型进行人脸识别
anet_type net;
deserialize("D:/WorkSoftware/dlib/model/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat") >> net;
matrix<rgb_pixel> img, img1, img3; //定义dlib型图片,彩色
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//此下为建立人脸编码库代码
for (int k = 0; k < fileNames.size(); k++) //依次加载完图片库里的文件
{
string fileFullName = dir_path + "/" + fileNames[k] + ".JPG";//图片地址+文件名
load_image(img, fileFullName);//加载图片
std::vector<dlib::rectangle> dets = detector(img); //用dlib自带的人脸检测器检测人脸,然后将人脸位置大小信息存放到dets中
img1 = img;
cv::Mat I = dlib::toMat(img1); //dlib转成opencv
std::vector<full_object_detection> shapes;
if (dets.size() < 1) //判断是否单人脸图片
cout << "There is no face" << endl;
else if (dets.size() > 1)
cout << "There is to many face" << endl;
else
{
shapes.push_back(sp(img, dets[0])); //画人脸轮廓,68点
if (!shapes.empty()) {
for (int j = 0; j < 68; j++) {
circle(I, cvPoint(shapes[0].part(j).x(), shapes[0].part(j).y()), 3, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), -1);
// shapes[0].part(i).x();//68¸ö
}
}
dlib::cv_image<rgb_pixel> dlib_img(I);//dlib<-opencv
// Run the face detector on the image of our action heroes, and for each face extract a
// copy that has been normalized to 150x150 pixels in size and appropriately rotated
// and centered.
//复制已规格化为150x150像素并适当旋转的
//居中。
std::vector<matrix<rgb_pixel>> faces;//定义存放截取人脸数据组
auto shape = sp(img, dets[0]);
matrix<rgb_pixel> face_chip;
extract_image_chip(img, get_face_chip_details(shape, 150, 0.25), face_chip);//截取人脸部分,并将大小调为150*150
faces.push_back(move(face_chip));
image_window win1(img); //显示原图
win1.add_overlay(dets[0]);//在原图上框出人脸
image_window win2(dlib_img); //显示68点图
image_window win3(faces[0]);//显示截取的人脸图像
// Also put some boxes on the faces so we can see that the detector is finding
// them.
//同时在表面放置一些盒子,这样我们可以看到探测器正在寻找他们。
// This call asks the DNN to convert each face image in faces into a 128D vector.
// In this 128D vector space, images from the same person will be close to each other
// but vectors from different people will be far apart. So we can use these vectors to
// identify if a pair of images are from the same person or from different people.
//此调用要求dnn将面中的每个面图像转换为128d矢量。
//在这个128d向量空间中,同一个人的图像会彼此靠近
//但是来自不同人群的向量会相差很远。所以我们可以用这些向量
//标识一对图像是来自同一个人还是来自不同的人。
std::vector<matrix<float, 0, 1>> face_descriptors = net(faces);//将150*150人脸图像载入Resnet残差网络,返回128D人脸特征存于face_descriptors
//sprintf(vec, "%f", (double)length(face_descriptors[0]);
//printf("%f\n", length(face_descriptors[0]));
//vec[0] = face_descriptors[0];
vec.push_back(face_descriptors[0]); //保存这一个人脸的特征向量到vec向量的对应位置
cout << "The vector of picture " << fileNames[k] << "is:" << trans(face_descriptors[0]) << endl;//打印该人脸的标签和特征向量
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
}
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//此下为识别部分代码
while (1)
{
cout << "input the path of test picture:";
cin >> test_path;
cout << test_path << endl;
//capture.read(III); // 读取图像帧至III
//flip(III, II, 1); //镜像翻转
load_image(img3, test_path);
//dlib::cv_image<rgb_pixel> img3(II);
//image_window win4(img4);
std::vector<matrix<rgb_pixel>> faces_test;
for (auto face_test : detector(img3))
{
auto shape_test = sp(img3, face_test);
matrix<rgb_pixel> face_chip_test;
extract_image_chip(img3, get_face_chip_details(shape_test, 150, 0.25), face_chip_test);
faces_test.push_back(move(face_chip_test));
// Also put some boxes on the faces so we can see that the detector is finding
// them.
}
std::vector<dlib::rectangle> dets_test = detector(img3);
std::vector<matrix<float, 0, 1>> face_test_descriptors = net(faces_test);
// In particular, one simple thing we can do is face clustering. This next bit of code
// creates a graph of connected faces and then uses the Chinese whispers graph clustering
// algorithm to identify how many people there are and which faces belong to whom.
std::vector<sample_pair> edges;
for (size_t i = 0; i < face_test_descriptors.size(); ++i) //比对,识别
{
size_t m = 100;
float error_min = 100.0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < vec.size(); ++j)
{
// Faces are connected in the graph if they are close enough. Here we check if
// the distance between two face descriptors is less than 0.6, which is the
// decision threshold the network was trained to use. Although you can
// certainly use any other threshold you find useful.
vec_error[j] = (double)length(face_test_descriptors[i] - vec[j]);
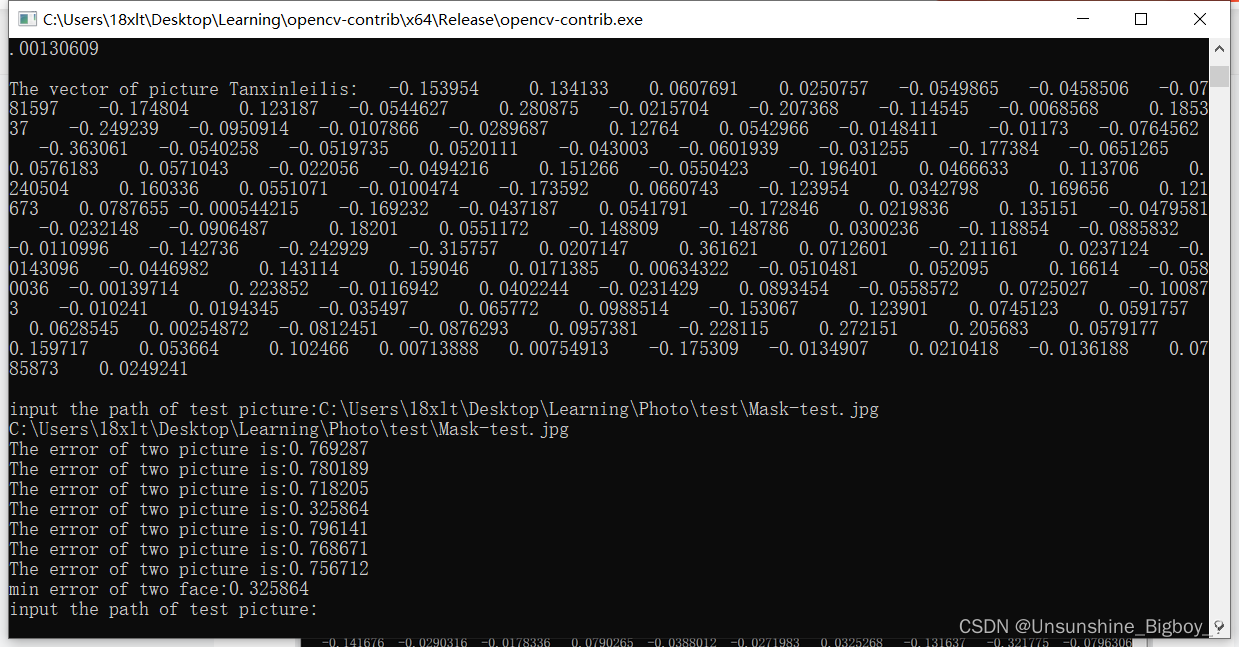
cout << "The error of two picture is:" << vec_error[j] << endl;
//if (length(face_descriptors[i] - face_descriptors[j]) < 0.6)
if (vec_error[j] < error_min)
{
error_min = vec_error[j];
m = j;
}
}
cout << "min error of two face:" << error_min << endl;
II = dlib::toMat(img3);//dlib图片转成opencv的MAT
std::string text = "Other face";
if ((error_min < 0.5) && (m <= 27))
text = fileNames[m]; //通过m定位文件,得到文件名
int font_face = cv::FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX;
double font_scale = 1;
int thickness = 2;
int baseline;
//获取文本框的长宽
cv::Size text_size = cv::getTextSize(text, font_face, font_scale, thickness, &baseline);
//将文本框居中绘制
cv::Point origin;
cv::rectangle(II, cv::Rect(dets_test[i].left(), dets_test[i].top(), dets_test[i].width(), dets_test[i].width()), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 1, 0);//画矩形框
origin.x = dets_test[i].left();
origin.y = dets_test[i].top();
cv::putText(II, text, origin, font_face, font_scale, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), thickness, 2, 0);//给图片加文字
}
dlib::cv_image<rgb_pixel> img4(II);
image_window win4(img4);
if (!II.empty()) // 判断是否为空
{
imshow("人脸识别", II);
}
//system("pause");
if (cv::waitKey(50) == 27) { break; };
}
}结果
- 先读取文件夹中图片数量和每张图片的绝对路径和名字,方便调试而已,可以注释掉。
- 输入测试图片的绝对路径(加文件名),打印特征向量以及找到和测试图片误差最小的训练图片。
- 最后识别结果。
总结
个人觉得这种方法做出来的效果确实非常不错,默认的是误差小于0.4就认为是同一个人,但是在我实际用摄像头进行调节的过程中发现在头转动一定角度之后或者场景的光强等因素变化的时候会出现有时候不能识别的情况,于是微调了一下阈值,小于0.5就认为是同一个人,效果就非常不错了。但是可能出现相似的人识别错误的问题,暂时还未发现。