Python解运筹学问题
PuLP
一般线性规划问题
例题:
from pulp import *
#构建问题
my_LpProblem = pulp.LpProblem("myProblem", LpMaximize)
# 设置变量
x1 = pulp.LpVariable("x1", 0, None)
x2 = pulp.LpVariable("x2", 0, None)
x3 = pulp.LpVariable("x3", 0, None)
# 最有函数
my_LpProblem += -x1+x2+x3
# 约束条件
my_LpProblem += x1 - x2 +2*x3 <= 10
my_LpProblem +=-x1 + x2 + x3 >= 4
my_LpProblem +=-x1 + x3 == 2
# 求解
status = my_LpProblem.solve()
print("Status:", LpStatus[my_LpProblem.status])
# 打印出最优解
for v in my_LpProblem.variables():
print(v.name, "=", v.varValue)
# 打印最优目标函数值
print("objective=", value(my_LpProblem.objective))
构造并求解混合0-1整数规划问题
例题:
from pulp import *
my_MipProblem = LpProblem("myproblem", LpMinimize)
solution = []
x1 = LpVariable("x1", lowBound=0, cat=LpInteger)# LpInteger:整数型
x2 = LpVariable("x2", cat=LpBinary)# LpBinary:0—1型
x3 = LpVariable("x3", lowBound=0)
my_MipProblem += 2 * x1 + 3 * x2 + x3, "obj"
my_MipProblem += 2 * x1 - x2 + 3 * x3 >= 6, "c1"
my_MipProblem += 4 * x1 + x2 + 5 * x3 == 24, "c2"
my_MipProblem.solve()
# 打印出已经求解问题的状态
print("Status:", LpStatus[my_MipProblem.status])
# 打印出最优解
for v in my_MipProblem.variables():
print(v.name, "=", v.varValue)
solution.append(v.varValue)
# 打印最优目标函数值
print("objective=", value(my_MipProblem.objective))
numpy和scipy
用scipy的linprog求解以下线性规划问题
标准问题(最小值,约束为<=)
例题:
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linprog
c = np.array([-6, -1, -2])
A_ub = np.array([[1, 3, 1], [2, 0, 1], [1, 1, 0]])
b_ub = np.array([12, 6, 2])
x1_bounds = [0, None]
x2_bounds = [0, None]
x3_bounds = [0, None]
my_linprog_result = linprog(c, A_ub, b_ub, A_eq=None, b_eq=None, bounds=(x1_bounds, x2_bounds, x3_bounds), callback=None)
my_solution = my_linprog_result.x
my_optimum_value = my_linprog_result.fun
print(my_solution)
print(my_optimum_value)
非标准形式
用linprog求解时,只能求解最小值且为小于约束的问题,如果要求解其他问题,则需先变换成规定的标准形式。
例题:
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linprog
c = np.array([-1,-1,2]) # 最大值变为最小值,取相反数
A_ub = np.array([[1,2,3],[-2,-1,2]]) # >=约束转换为<=约束,取相反数
b_ub = np.array([12,-8])
x1_bounds = [0,None]
x2_bounds = [0,None]
x3_bounds = [0,None]
my_linprog_result = linprog(c,A_ub,b_ub,A_eq=None,b_eq=None,bounds=(x1_bounds,x2_bounds,x3_bounds),method='simplex',callback=None)
my_solution = my_linprog_result.x
my_optimum_value = -my_linprog_result.fun # 将最优值转换为最大值
print(my_solution)
print(my_optimum_value)
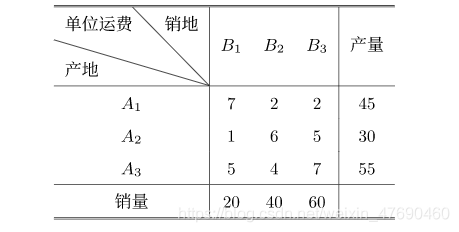
运输问题
例题:
from pulp import *
import numpy as np
from itertools import product
production = 3 #3个产地
sale = 4 #3个销地+1个虚拟销地
demand = [20, 40, 60, 10] # 销量
capacity = [45, 30, 55] # 产量
cost = np.array([[7, 2, 2, 0], [1, 6, 5, 0], [5, 4, 7, 0]])
# 建立模型
prob = LpProblem("Transportation", LpMinimize)
x = LpVariable.dicts("x", product(range(production), range(sale)), lowBound=0, upBound=None, cat=LpInteger) # product 作用未知
prob += pulp.lpSum(cost[l, c] * x[l, c] for l in range(production) for c in range(sale))
# 约束条件
for l in range(production):
prob += lpSum(x[l, c] for c in range(sale)) == capacity[l]
for c in range(sale):
prob += lpSum(x[l, c] for l in range(production)) == demand[c]
# 求解
prob.solve()
min_cost = value(prob.objective)
solution = []
for v in prob.variables():
solution.append(v.varValue)
solution = np.array(solution).reshape(3, 4)
print(solution)
print(min_cost)
指派问题(scipy的linear_sum_assignment)
学习阅读scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment
注意
- linear_sum_assignment只能求解目标函数为最小值的线性指派问题
- 可以直接求解任务数与人数不对等的指派问题
- 输入参数必须为一个2D的numpy.array实例
- 返回的结果为最优指派对应在此2D array上的index
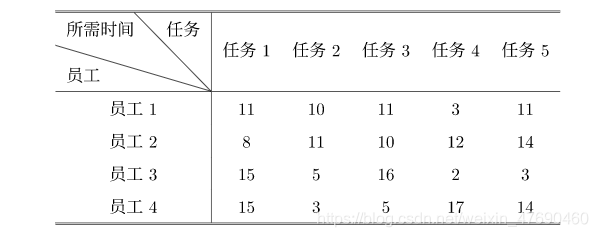
例题1:
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
s1 = [11, 10, 11, 3, 11]
s2 = [8, 11, 10, 12, 14]
s3 = [15, 5, 16, 2, 3]
s4 = [15, 3, 5, 17, 14]
time_array_standardized = np.vstack((s1, s2, s3, s4,s4))
row_ind, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(time_array_standardized)
print(row_ind)#开销矩阵对应的行索引
print(col_ind)#对应行索引的最优指派的列索引
print(time_array_standardized[row_ind,col_ind])#提取每个行索引的最优指派列索引所在的元素,形成数组
minimum_time = time_array_standardized[row_ind,col_ind].sum()#数组求和
print(minimum_time)
例题2:
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
s1 = [-320, -300, -440, -470, -450]
s2 = [-370, -490, -420, -550, -310]
s3 = [-360, -510, -440, -490, -300]
s4 = [-310, -420, -420, -450, -450]
s5 = [-340, -330, -400, -450, -510]
time_array_standardized = np.vstack((s1, s2, s3, s4, s5))
row_ind, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(time_array_standardized)
print(row_ind)#开销矩阵对应的行索引
print(col_ind)#对应行索引的最优指派的列索引
print(time_array_standardized[row_ind,col_ind])#提取每个行索引的最优指派列索引所在的元素,形成数组
maximum_sales = -time_array_standardized[row_ind,col_ind].sum()#数组求和
print(maximum_sales)
networkx 解图论问题
Python的Networkx包
NetworkX is a Python language software package for the creation, manipulation, and study of the structure, dynamics, and function of complex networks.
With NetworkX you can load and store networks in standard and nonstandard data formats, generate many types of random and classic networks, analyze network structure, build network models, design new network algorithms, draw networks, and much more.
预习内容:
- nx.Graph(无向图)和nx.DiGraph(有向图)的生成
- 用Networkx的minimum_spanning_tree和minimum_spanning_edges方法求解最小支撑树问题
用 - Networkx的最短路求解方法求解最短路问题
最小支撑树问题
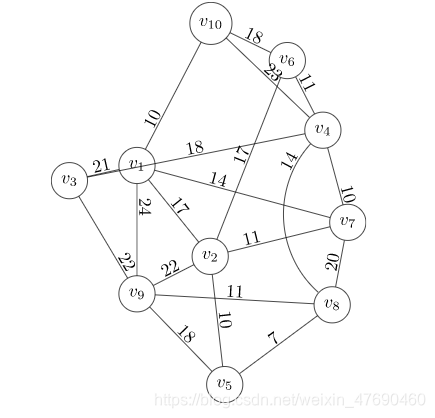
用Networkx的minimum_spanning_tree和minimum_spanning_edges方法求解以下最小支撑树问题,要求:
- 节点的编号从0开始
- 边的权重用weight表示
- 返回G,其为下图所对应的Graph.
- 返回T,为G对应的最小支撑树
- 返回T_edges,为T中的所有边,T_edges可以是一个list,或tuple,或generator.
- 返回T_weight,T的权重之和.
提示:使用Graph.size会有帮助.
例题:
import networkx as nx
G = nx.Graph()
# 设置节点
v = {}
for i in range(10):
v[i] = f'v{i}'
G.add_nodes_from(v)
# 设置无向边
weight = [(0,1,17), (0,2,21), (0,6,14), (0,8,24), (0,9,10),
(1,4,10), (1,5,17), (1,6,11), (1,8,22),
(2,3,18), (2,8,22),
(3,5,11), (3,6,10), (3,7,14), (3,9,23),
(4,7,7), (4,8,18),
(5,9,18),
(6,7,20),
(7,8,11)]
# 生成无向图
for (start,end,flow) in weight:
G.add_edge(start,end,weight=flow)
# 求最小树和最小树的边
T = nx.minimum_spanning_tree(G)
T_edges = list(nx.minimum_spanning_edges(G))
# 计算T_weight(从tuple中取出dict,再从dict中取出值)
T_weight = 0 # 初始化
for (start, end, weight) in T_edges:
T_weight = T_weight + weight.get('weight') # dict没有value方法(T_weight = T_weight + weight.value())
print(sorted(T.edges(data=True)))
print(T_weight)
最短路问题
用Networkx的最短路求解方法求解以下最短路问题,要求:
- 节点的编号从0开始
- 返回G,其为下图所对应的DiGraph.
- 返回all_shortest_paths,为G中source和target之间的所有最短路径,例如如果v1到v8的最短路径有两条:v1→v2→v8和v1→v3→v4→v8,则返回一个list或generator,其格式为[[0,1,7], [0,2,3,7]].
- 返回shortest_path_length,为最短路的长度.
例题1:求解下图中从v1至v8的最短路径及最短距离.
import networkx as nx
# 生成有向图
G = nx.DiGraph()
edge = [(0, 1, 1), (0, 2, 4), (0, 3, 3),
(1, 2, 3), (1, 4, 8),
(2, 4, 5), (2, 5, 3), (2, 6, 6),
(3, 2, 4), (3, 6, 5),
(4, 5, 4), (4, 7, 3),
(5, 7, 4),
(6, 5, 2), (6, 7, 5)] #可以是list,也可以是tuple
for (start, end, flow) in edge:
G.add_edge(start, end, weight=flow)# 设置属性
# 求解最短路径
all_shortest_paths = list(nx.all_shortest_paths(G, source=0, target=7, weight='weight')) #默认算法是dijkstra,调出属性
shortest_path_length = nx.shortest_path_length(G,source=0,target=7,weight='weight')
print(all_shortest_paths)
print(shortest_path_length)
例题2:
import networkx as nx
# 生成有向图
G = nx.DiGraph()
edge = [(0, 1, 3), (0, 2, 2), (0, 4, 3),
(1, 3, -2), (1, 4, 7),
(2, 4, 4), (2, 5, 1),
(3, 4, 5), (3, 6, 4),
(4, 5, 1), (4, 6, 4),
(5, 6, 2), (5, 7, 5),
(6, 7, 6), (6, 8, 4),
(7, 8, 6)] #可以是list,也可以是tuple
for (start, end, flow) in edge:
G.add_edge(start, end, weight=flow)# 设置属性
# 求解最短路径
all_shortest_paths = list(nx.all_shortest_paths(G, source=0, target=8, weight='weight')) #默认算法是dijkstra,调出属性
shortest_path_length = nx.shortest_path_length(G,source=0,target=8, weight='weight')
print(all_shortest_paths)
print(shortest_path_length)
最大流问题
用Networkx的Maximum Flow算法方法求解以下网络最大流问题。
例题要求:
-
节点的编号从0开始
-
返回G,其为下图所对应的DiGraph,其中弧上的权重用capacity表示.
-
返回max_flow_value,为最大流的流量(数值).
-
返回cut_set,为最小割集,可以是一个list或set.
-
求解下图中从v1至v11的最大流及最小割,并思考最小割集是什么。图中弧上的数字表示其容量.
import networkx as nx
G = nx.DiGraph()
edge = [(0, 1, 155), (0, 2, 180), (0, 3, 30),
(1, 4, 155), (1, 5, 185),
(2, 4, 105), (2, 5, 65), (2, 6, 60),
(3, 5, 120), (3, 6, 160),
(4, 7, 110), (4, 8, 60),
(5, 7, 180), (5, 8, 155), (5, 9, 60),
(6, 8, 135), (6, 9, 135),
(7, 10, 85),
(8, 10, 85),
(9, 10, 155)]
for (start, end, flow) in edge:
G.add_edge(start, end, capacity=flow)# 设置属性
# 计算最大流的值
max_flow_value = nx.maximum_flow_value(G, 0, 10, capacity="capacity")
# 计算最小割
cut_value, partition = nx.minimum_cut(G, 0, 10,capacity="capacity")# partition (u,v)
reachable, non_reachable = partition
# 设置弧
cut_set = set()
for u, nbrs in ((n, G[n]) for n in reachable):
cut_set.update((u, v) for v in nbrs if v in non_reachable)