匿名函数
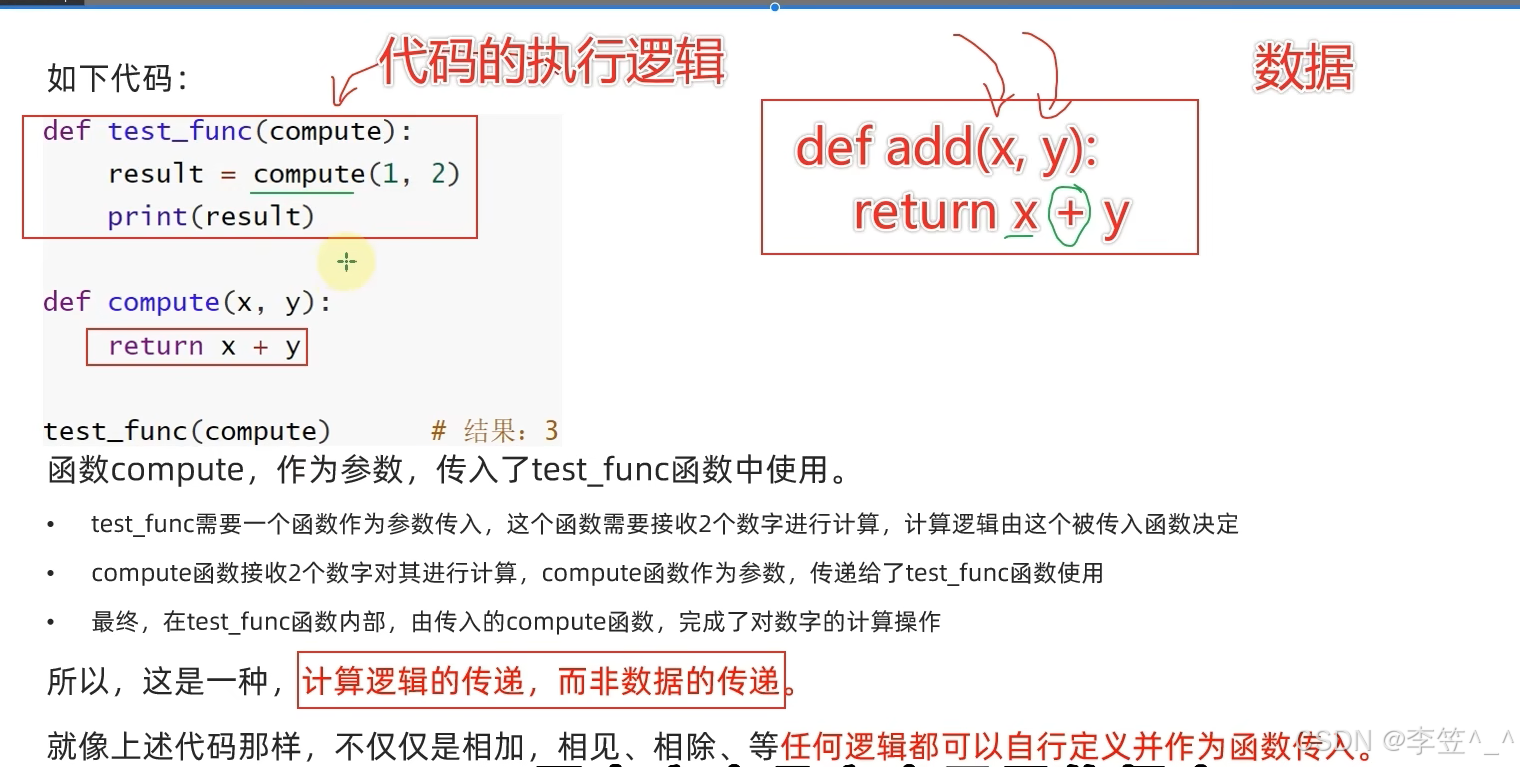
1.函数作为参数来传递
(函数的参数中调用另外一个函数)
#定义一个函数,接受另一个函数作为参数传入
#计算逻辑的传入
def test_func(compute):
result = compute(1,2)
print(result)
print(f"{type(result)}")
print(f"compute参数的类型是:{type(compute)}")
def compute (x,y):
return x * y
test_func(compute)
lambda匿名函数
def test_func(compute):
result = compute(1,2)
print(result)
print(f"{type(compute)}")
# 通过lambda匿名函数的形式,将匿名函数作为参数传入
#只能支持一行代码
test_func(lambda x,y:x+y)
test_func(lambda x,y:x*y)
test_func(lambda x,y:x/y)
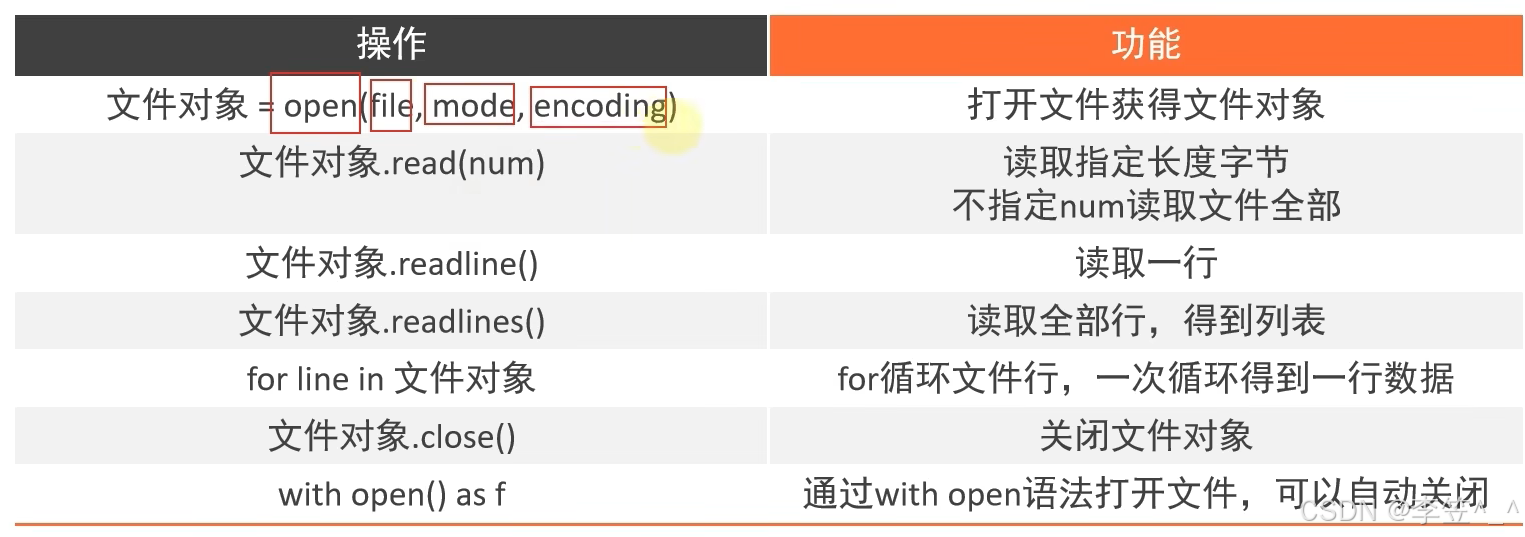
2、掌握文件编码的概念和常见编码
读操作
#打开文件
f = open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
print(type(f))
#读取文件
# print(f"读取10个字节的结果是:{f.read(10)}")
#多次调用read会在上一次调用read之后继续读取
# print(f"读取全部的结果是:{f.read()}")
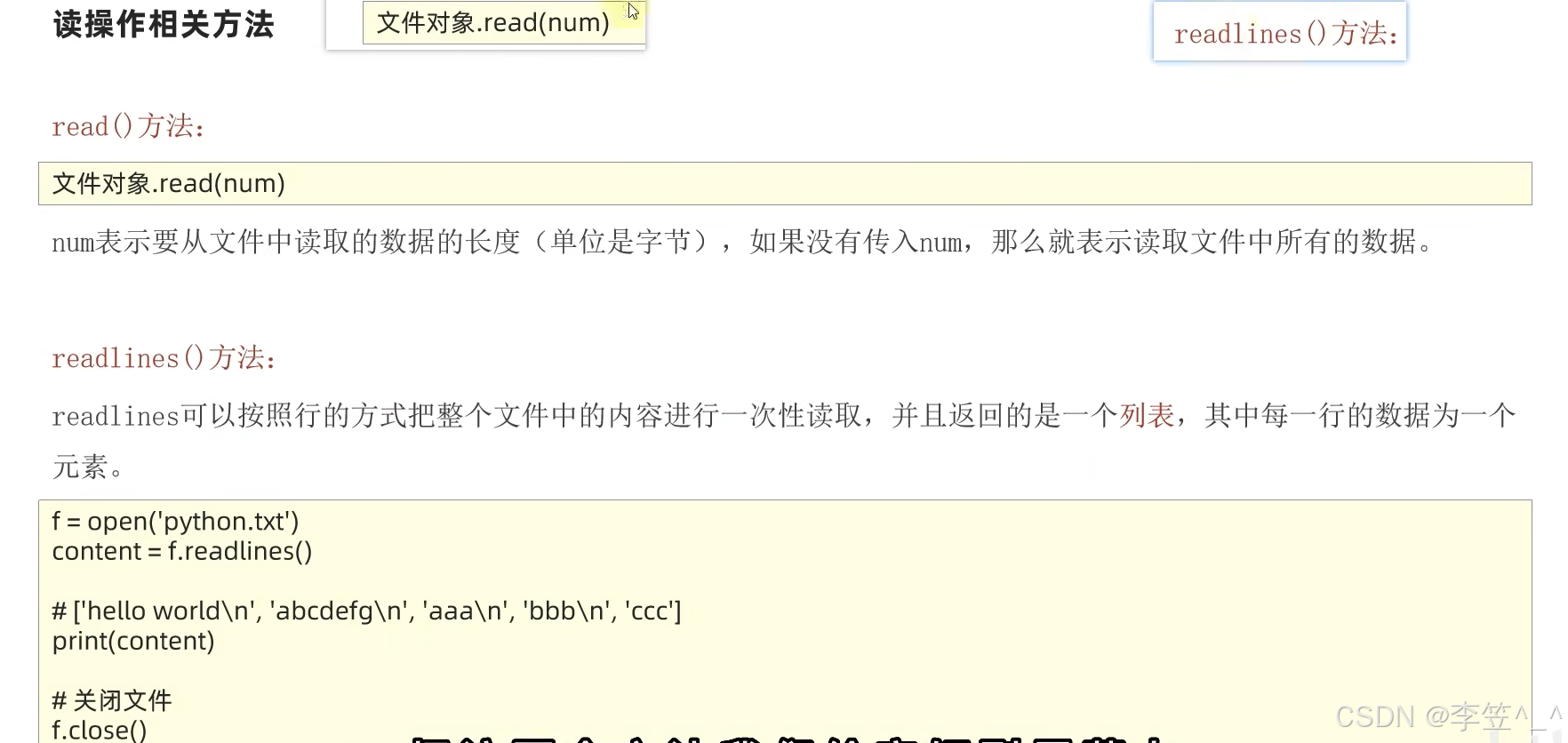
#读取文件---readLines()
#读取文件的全部行,封装到列表中
# lines = f.readlines()
# print(f"{lines}")
#readline()读取一行数据
line1 = f.readline()
line2 = f.readline()
line3 = f.readline()
print(line1)
print(line2)
print(line3)
#for循环读取文件行
f = open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
for line in f:
print(f"每一行的数据是{line}")
#文件的关闭 #把文件的占用停掉 # f.close()
import time
#文件自动的被close
f = open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
with open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8") as f:
for line in f:
print(f"每一行数据是:{line}")
time.sleep(60000)
#方式1
#读取全部内容,通过字符串count统计itheima单词数量
f = open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
test = f.read()
count = test.count("itheima")
print(count)
f.close()
"""
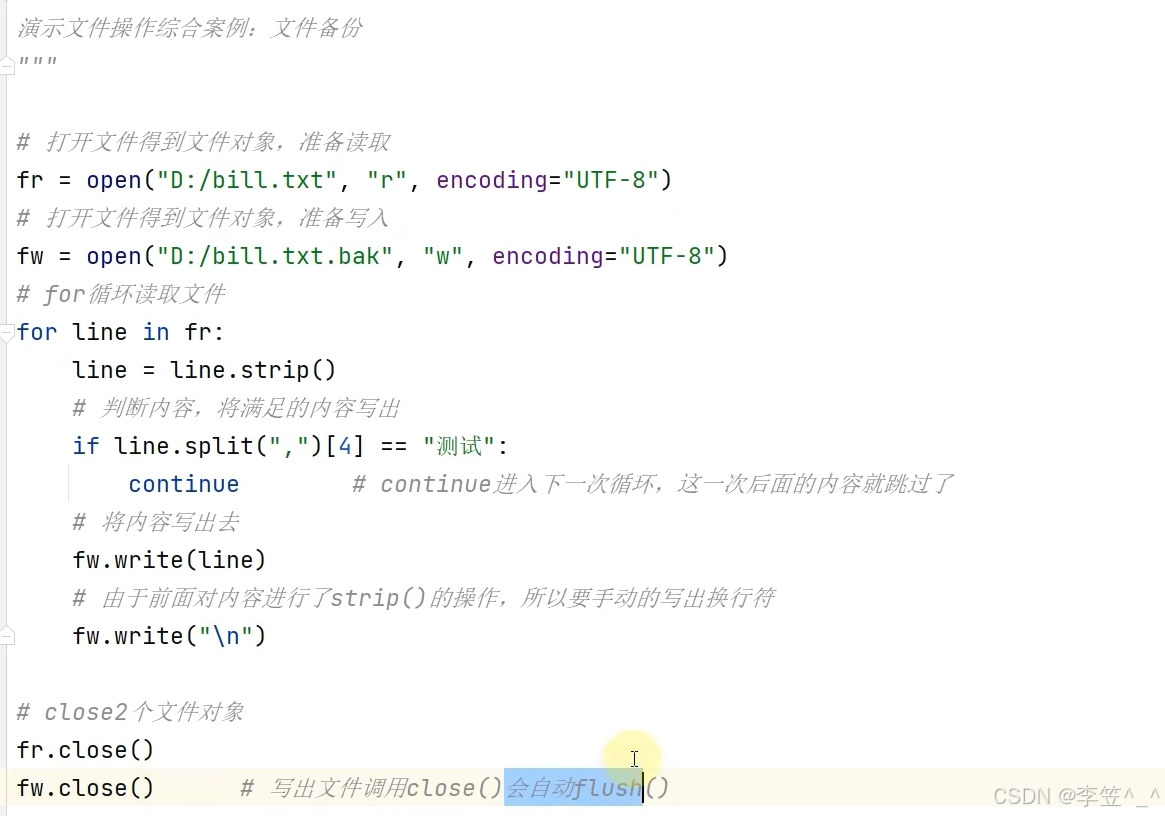
#方式2 读取内容,一行一行读取
f = open("D:/hello.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
count = 0
for line in f:
#剔除反斜杠n
line = line.strip()#去除换行符以及开头和结尾的空格
words = line.split(" ")
for word in words:
if word == 'itheima':
count+=1
print(count)
f.close()
写入操作

#文件的写入操作
#打开文件
f = open("D:/test.txt","w",encoding="UTF-8")
#写入操作 write
f.write("hello world!!!")
#flush刷新
f.flush()
f.close()#close 内置了flush功能的
#打开文件,不存在的文件
# f = open("D:/test.txt","a",encoding="UTF-8")
#write写入
# f.write("黑马程序员")
#flush刷新
# f.flush()
#close关闭
# f.close()
#打开一个存在的文件
f = open("D:/test.txt","a",encoding="UTF-8")
f.write("\n月薪过万")
f.close()