1、初识 Node.js
1.1 Node.js 简介
- Node.js 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境
- Node.js 的官网地址: https://nodejs.org/zh-cn/
1.2 Node.js 中的 JavaScript 运行环境
- 浏览器是 JavaScript 的前端运行环境
- Node.js 是 JavaScript 的后端运行环境
- Node.js 中无法调用 DOM 和 BOM 等 浏览器内置 API
1.3 Node.js 可以做什么
- Node.js 作为一个 JavaScript 的运行环境,仅仅提供了基础的功能和 API
- 基于 Node.js 提供的这些基础能,很多强大 的工具和框架
1.4 Node.js 怎么学
- JavaScript 基础语法
- Node.js 内置 API 模块(fs、path、http等)
- 第三方 API 模块(express、mysql 等)
2 fs 文件系统模块
2.1 使用readFile方法读取文件的内容
// 1. 导入 fs 模块,来操作文件
const fs = require('fs')
// 2. 调用 fs.readFile() 方法读取文件
// 参数1:读取文件的存放路径
// 参数2:读取文件时候采用的编码格式,一般默认指定 utf8
// 参数3:回调函数,拿到读取失败和成功的结果 err dataStr
fs.readFile('./files/11.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
// 2.1 打印失败的结果
// 如果读取成功,则 err 的值为 null
// 如果读取失败,则 err 的值为 错误对象,dataStr 的值为 undefined
console.log(err)
console.log('-------')
// 2.2 打印成功的结果
console.log(dataStr)// 111
})
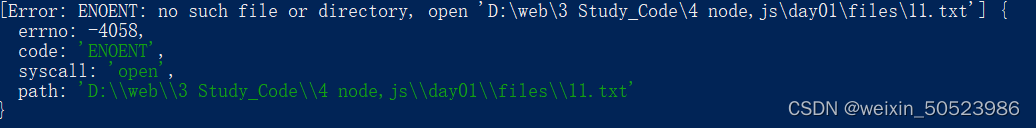
- 读取失败输出的err:
2.2 判断文件是否读取成功
const fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('./files/11.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('读取文件成功!' + dataStr)
})
读取文件失败!Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, open ‘D:\web\3 Study_Code\4 node,js\day01\files\11.txt’
2.3 写入文件内容
// 1. 导入 fs 文件系统模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 2. 调用 fs.writeFile() 方法,写入文件的内容
// 参数1:表示文件的存放路径
// 参数2:表示要写入的内容
// 参数3:回调函数
fs.writeFile('./files/3.txt', 'ok123', function(err) {
// 2.1 如果文件写入成功,则 err 的值等于 null
// 2.2 如果文件写入失败,则 err 的值等于一个 错误对象
// console.log(err)
if (err) {
return console.log('文件写入失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('文件写入成功!')
})
2.4 案例-整理成绩
// 1. 导入 fs 模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 2. 调用 fs.readFile() 读取文件的内容
fs.readFile('../素材/成绩.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
// 3. 判断是否读取成功
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('读取文件成功!' + dataStr)
// 4.1 先把成绩的数据,按照空格进行分割
const arrOld = dataStr.split(' ')
// 4.2 循环分割后的数组,对每一项数据,进行字符串的替换操作
const arrNew = []
arrOld.forEach(item => {
// 用冒号替换等号
arrNew.push(item.replace('=', ':'))
})
// 4.3 把新数组中的每一项,进行合并,得到一个新的字符串
const newStr = arrNew.join('\r\n')
// 5. 调用 fs.writeFile() 方法,把处理完毕的成绩,写入到新文件中
fs.writeFile('./files/成绩-ok.txt', newStr, function(err) {
if (err) {
return console.log('写入文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('成绩写入成功!')
})
})
2.6 fs 模块 - 路径动态拼接的问题
- 使用./或者是…/的写法
const fs = require('fs')
// 出现路径拼接错误的问题,是因为提供了 ./ 或 ../ 开头的相对路径
// 如果要解决这个问题,可以直接提供一个完整的文件存放路径就行
fs.readFile('./files/1.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('读取文件成功!' + dataStr)
})
- 使用完整路径写法
// 移植性非常差、不利于维护
const fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('C:\\Users\\escook\\Desktop\\Node.js基础\\day1\\code\\files\\1.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('读取文件成功!' + dataStr)
})
- __dirname写法
fs.readFile(__dirname + '/files/1.txt', 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
if (err) {
return console.log('读取文件失败!' + err.message)
}
console.log('读取文件成功!' + dataStr)
})
3 path 路径模块
path 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的、用来处理路径的模块
它提供了一系列的方法和属性,用来满足用户对路径的处理需求
3.1 path.join方法的使用
使用 path.join() 方法,可以把多个路径片段拼接为完整的路径字符串
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
// 注意: ../ 会抵消前面的路径
const pathStr = path.join('/a', '/b/c', '../../', './d', 'e')
console.log(pathStr) // \a\d\e
fs.readFile(__dirname + '/files/1.txt')
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, './files/1.txt'), 'utf8', function(err, dataStr) {
if (err) {
return console.log(err.message)
}
console.log(dataStr)// 111
})
3.2 获取路径中的文件名
使用 path.basename() 方法,可以获取路径中的最后一部分,经常通过这个方法获取路径中的文件名
const path = require('path')
// 定义文件的存放路径
const fpath = '/a/b/c/index.html'
// 文件名+文件后缀
const fullName = path.basename(fpath)
console.log(fullName) // index.html
// 文件名(没有后缀)
const nameWithoutExt = path.basename(fpath, '.html')
console.log(nameWithoutExt) // index
3.3 获取路径中的文件扩展名(文件后缀)
const path = require('path')
// 这是文件的存放路径
const fpath = '/a/b/c/index.html'
const fext = path.extname(fpath)
console.log(fext) // .html
3.4 综合案例 - 时钟案例
4 http 模块
什么是客户端、什么是服务器?
- 在网络节点中,负责消费资源的电脑,叫做客户端
- 负责对外提供网络资源的电脑,叫做服务器
什么是 http 模块
- http 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的、用来创建 web 服务器的模块
- 能方便的把一台普通的电脑,变成一台 Web 服务器,从而对外提供 Web 资源服务
4.1 服务器相关的概念
4.1.1 IP 地址
- IP 地址就是互联网上每台计算机的唯一地址 IP 地址的格式
- 通常用“点分十进制”表示成(a.b.c.d)的形式
- a,b,c,d 都是0~255 之间的十进制整数
- 用点分十进表示的 IP地址(192.168.1.1)
4.1.2 域名和域名服务器
- IP地址和域名是一一对应的关系,存放在域名服务器的电脑中
- 域名服务器就是提供 IP 地址和域名之间的转换服务的服务器
- 在开发测试,127.0.0.1 对应的域名是 localhost,代表自己的这台电脑
4.1.3 端口号
- 在一台电脑中,可以运行成百上千个 web 服务
- 每个 web 服务都对应一个唯一的端口号
注意:
- 每个端口号不能同时被多个 web 服务占用
- 在实际应用中,URL 中的 80 端口可以被省略
4.2 创建最基本的 web 服务器
// 1. 导入 http 模块
const http = require('http')
// 2. 创建 web 服务器实例
const server = http.createServer()
// 3. 为服务器实例绑定 request 事件,监听客户端的请求
server.on('request', function (req, res) {
console.log('Someone visit our web server.')
})
// 4. 启动服务器
server.listen(8080, function () {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080')
})
4.3 了解req请求对象
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
// req 是请求对象,包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// req.url 是客户端请求的 URL 地址
const url = req.url
// req.method 是客户端请求的 method 类型
const method = req.method
const str = `Your request url is ${url}, and request method is ${method}`
console.log(str)
// 调用 res.end() 向客户端发送指定的内容,并结束这次请求过程
res.end(str)
})
server.listen(80, () => {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
4.4 解决中文乱码问题
当调用 res.end() 方法,向客户端发送中文内容的时候,会出现乱码问题,此时,需要手动设置内容的编码格式
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 定义一个字符串,包含中文的内容
const str = `您请求的 URL 地址是 ${req.url},请求的 method 类型为 ${req.method}`
// 调用 res.setHeader() 方法,设置 Content-Type 响应头,解决中文乱码的问题
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
// res.end() 将内容响应给客户端
res.end(str)
})
server.listen(80, () => {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
4.5 根据不同的 url 响应不同的 html 内容
① 获取请求的 url 地址
② 设置默认的响应内容为 404 Not found
③ 判断用户请求的是否为 / 或 /index.html 首页
④ 判断用户请求的是否为 /about.html 关于页面
⑤ 设置 Content-Type 响应头,防止中文乱码
⑥ 使用 res.end() 把内容响应给客户端
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 1. 获取请求的 url 地址
const url = req.url
// 2. 设置默认的响应内容为 404 Not found
let content = '<h1>404 Not found!</h1>'
// 3. 判断用户请求的是否为 / 或 /index.html 首页
// 4. 判断用户请求的是否为 /about.html 关于页面
if (url === '/' || url === '/index.html') {
content = '<h1>首页</h1>'
} else if (url === '/about.html') {
content = '<h1>关于页面</h1>'
}
// 5. 设置 Content-Type 响应头,防止中文乱码
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8')
// 6. 使用 res.end() 把内容响应给客户端
res.end(content)
})
server.listen(80, () => {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
4.6 案例 - 实现 clock 时钟的 web 服务器
5 模块化
5.1 模块化的基本概念
5.1.1 什么是模块化
编程领域中的模块化,就是遵守固定的规则,把一个大文件拆成独立并互相依赖的多个小模块
5.1.2 模块化规范
模块化规范就是对代码进行模块化的拆分与组合时,需要遵守的那些规则
例如:
- 使用什么样的语法格式来引用模块
- 在模块中使用什么样的语法格式向外暴露成员
5.2 Node.js 中模块化
5.2.1 Node.js 中模块的分类
- 内置模块(内置模块是由 Node.js 官方提供的,例如 fs、path、http 等)
- 自定义模块(用户创建的每个 .js 文件,都是自定义模块)
- 第三方模块(由第三方开发出来的模块使用前需要先下载)
5.2.2 加载模块
// 1 加载内置的 fs 模块
const fs = require('fs')
// 2 加载用户自定义模块
const custom = require('./custom.js')
// 3 加载第三方模块(后面会详细说)
const moment = require('moment')
5.2.3 Node.js 中的模块作用域
和函数作用域类似,在自定义模块中定义的变量、方法等成员,只能在当前模块内被访问
好处:
- 防止了全局变量污染的问题
5.2.4 向外共享模块作用域中的成员
5.2.4.1. module 对象
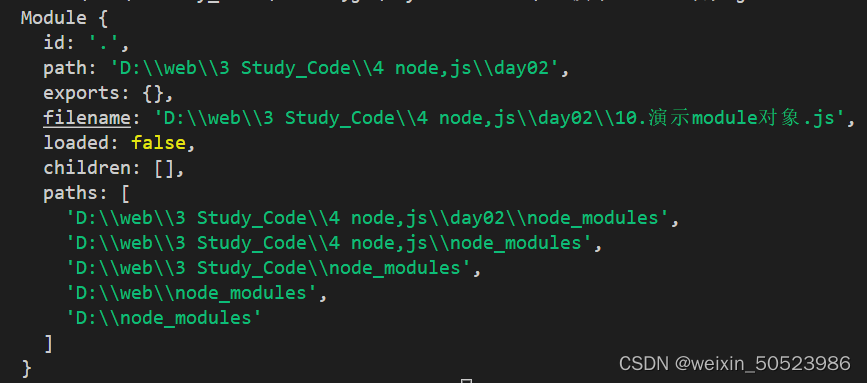
在每个 .js 自定义模块中都有一个 module 对象,它里面存储了和当前模块有关的信息
console.log(module)
5.2.4.2 module.exports 对象
- 使用 module.exports 对象,将模块内的成员共享出去,供外界使用
- 外界用 require() 方法导入自定义模块时,得到的就是 module.exports 所指向的对象
- 使用 require() 方法导入模块时,导入的结果,永远以 module.exports 指向的对象为准
自己定义的模块:
// 在一个自定义模块中,默认情况下, module.exports = {}
const age = 20
// 向 module.exports 对象上挂载 username 属性
module.exports.username = 'zs'
// 向 module.exports 对象上挂载 sayHello 方法
module.exports.sayHello = function() {
console.log('Hello!')
}
module.exports.age = age
// 让 module.exports 指向一个全新的对象
module.exports = {
nickname: '小黑',
sayHi() {
console.log('Hi!')
}
}
导入模块:
// 在外界使用 require 导入一个自定义模块的时候,得到的成员,
// 就是 那个模块中,通过 module.exports 指向的那个对象
const m = require('./11.自定义模块')
// 输出的结果是:{ nickname: '小黑', sayHi: [Function: sayHi] }
console.log(m)
5.2.4.3 exports 对象
- 默认情况下,exports 和 module.exports 指向同一个对象
- 最终共享的结果,还是以 module.exports 指向的对象为准
const username = 'zs'
module.exports.username = username
exports.age = 20
exports.sayHello = function() {
console.log('大家好!')
}
// 最终,向外共享的结果,永远都是 module.exports 所指向的对象
const m = require('./13.exports对象')
// { username: 'zs', age: 20, sayHello: [Function (anonymous)] }
console.log(m)
注意: 不要在同一个模块中同时使用 exports 和 module.exports
5.2.5 Node.js 中的模块化规范
- 每个模块内部,module 变量代表当前模块
- module 变量是一个对象,它的 exports 属性是对外的接口
- 加载某个模块,其实是加载该模块的 module.exports 属性。require() 方法用于加载模块
5.3 npm与包
- Node.js 中的第三方模块又叫做包
5.3.1 npm 初体验
格式化时间的高级做法:
- 使用 npm 包管理工具,在项目中安装格式化时间的包 moment
- 使用 require() 导入格式化时间的包
- 参考 moment 的官方 API 文档对时间进行格式化
// 1. 导入需要的包
// 注意:导入的名称,就是装包时候的名称
const moment = require('moment')
const dt = moment().format('YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss')
console.log(dt) // 2023-04-03 23:27:02
5.4 模块的加载机制
6 Express
6.1 初识 Express
6.1.1 Express 简介
- Express 是基于 Node.js 平台,快速、开放、极简的 Web 开发框架
- Express 的作用和 Node.js 内置的 http 模块类似,是专门用来创建 Web 服务器的
- 一个 npm 上的第三方包,提供了快速创建 Web 服务器的便捷方法
- Expess是基于http 内置模块进一步封装出来的
6.1.2 Express 的基本使用
- 安装
npm i expess@4.17.1
- 创建基本的 Web 服务器
- 监听 GET 请求
- 监听 POST 请求
- 把内容响应给客户端
- 获取 URL 中携带的查询参数
- 获取 URL 中的动态参数
// 1. 导入 express
const express = require('express')
// 2. 创建 web 服务器
const app = express()
// 4. 监听客户端的 GET 和 POST 请求,并向客户端响应具体的内容
app.get('/user', (req, res) => {
// 调用 express 提供的 res.send() 方法,向客户端响应一个 JSON 对象
res.send({ name: 'zs', age: 20, gender: '男' })
})
app.post('/user', (req, res) => {
// 调用 express 提供的 res.send() 方法,向客户端响应一个 文本字符串
res.send('请求成功')
})
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
// 通过 req.query 可以获取到客户端发送过来的 查询参数
// 注意:默认情况下,req.query 是一个空对象
console.log(req.query)
res.send(req.query)
})
// 注意:这里的 :id 是一个动态的参数
app.get('/user/:ids/:username', (req, res) => {
// req.params 是动态匹配到的 URL 参数,默认也是一个空对象
console.log(req.params)
res.send(req.params)
})
// 3. 启动 web 服务器
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
6.1.3 托管静态资源
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// 在这里,调用 express.static() 方法,快速的对外提供静态资源
// 1 对外提供一个静态资源
app.use(express.static('./public'))
// 2 托管多个静态资源目录
app.use(express.static('./public'))
app.use(express.static('./files'))
// 3 挂载路径前缀
app.use('/files', express.static('./public'))
app.listen(80, () => {
console.log('express server running at http://127.0.0.1')
})
- 对外提供一个静态资源:可以访问 public 目录中的所有文件
http://localhost:3000/images/bg.jpg
http://localhost:3000/css/style.css
http://localhost:3000/js/login.js
注意:存放静态文件的目录名不会出现在 URL 中 - 挂载路径前缀:通过带有 /public 前缀地址来访问 public 目录中的文件
http://localhost:3000/public/images/kitten.jpg
http://localhost:3000/public/css/style.css
http://localhost:3000/public/js/app.js
6.1.4 nodemon
- 监听项目文件的变动,当代码被修改后,nodemon 会自动帮我们重启项目
- 安装 nodemon
npm install -g nodemon
- 使用 nodemon
nodemn app.js