文章目录
摘要
本文实现了Transformer模型中的关键组件,包括多头注意力机制、编码器层以及位置编码。首先 ,通过手写实现了多头注意力机制,利用多个注意力头并行计算,提升了信息的表达能力。然后,设计了自定义的编码器模块,结合了多头注意力、前馈神经网络和层归一化。最后,构建了完整的Transformer架构,为序列处理任务提供了一个基础框架。
Abstract
This paper implements key components of the Transformer model, including the multi-head attention mechanism, encoder layer, and positional encoding. First, the multi-head attention mechanism is manually implemented to enhance information representation by computing with multiple attention heads in parallel. Next, a custom encoder module is designed, integrating multi-head attention, feedforward neural networks, and layer normalization. Finally, a complete Transformer architecture is constructed, providing a foundational framework for sequence processing tasks.
1 手写多头注意力机制
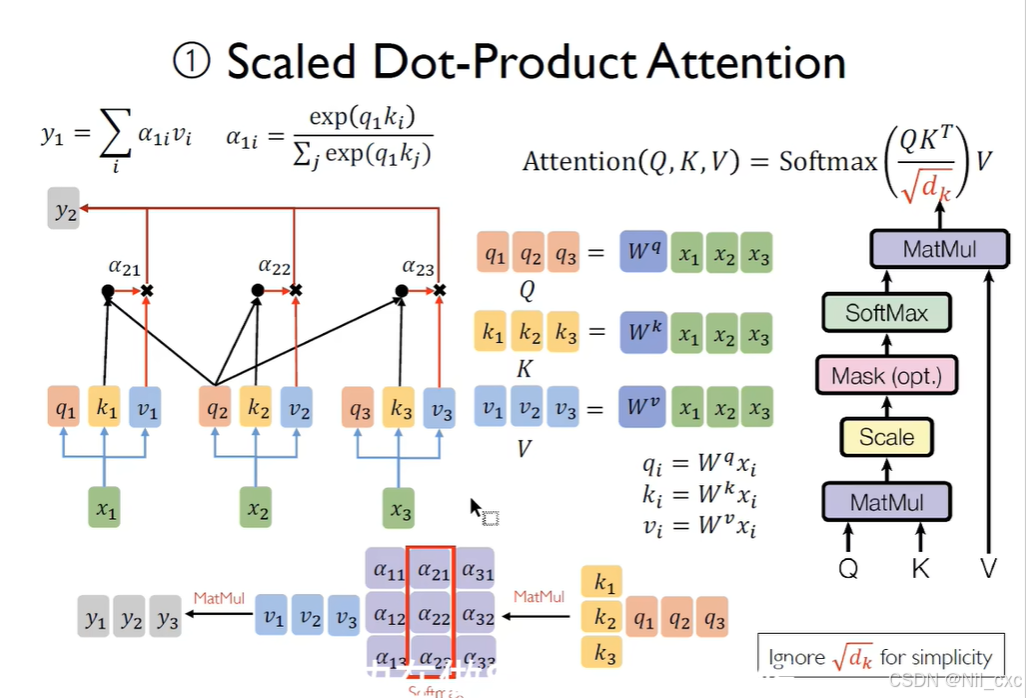
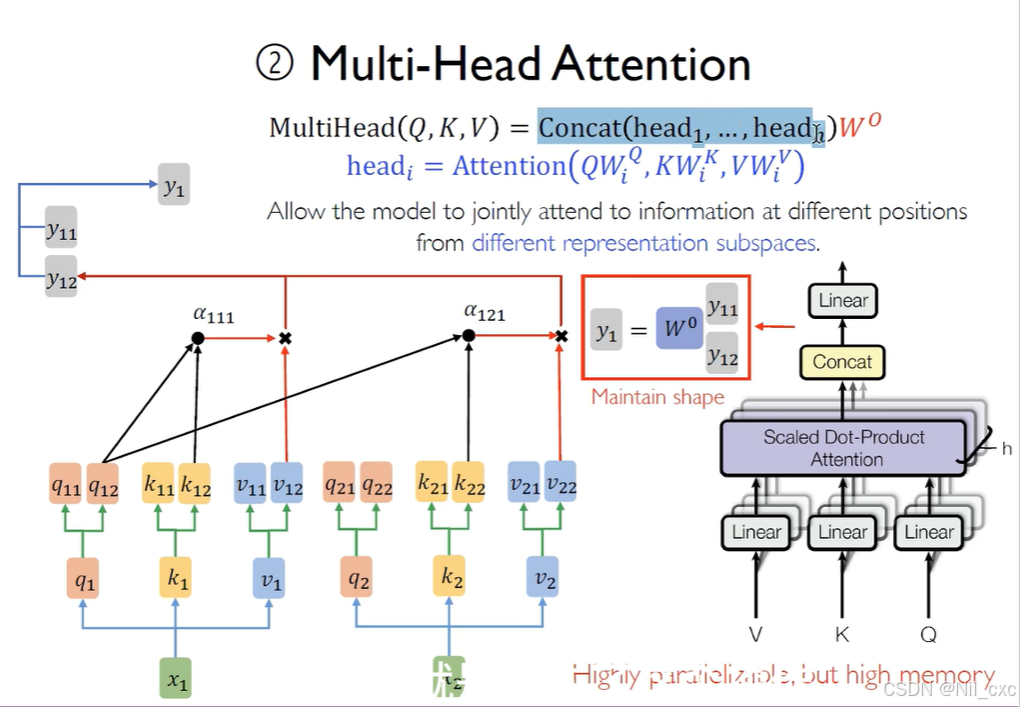
多头注意力机制原理:
多头注意力的核心思想是:通过多个注意力头并行计算,使得模型能够从不同的子空间学习到更多的信息。每个注意力头都会对输入的Query、Key、Value进行加权处理,最终的结果会被合并。具体来说,计算过程包括:
-
Q、K、V 变换: 首先,将输入的词向量通过线性变换分别映射到Query、Key、Value空间中。
-
Scaled Dot-Product Attention: 对于每个头,计算Q与K的点积,并除以 d k \sqrt{d_k} dk(即Key的维度的平方根)进行缩放,然后使用Softmax进行归一化,得到每个位置的权重。
-
头组合: 对每个头的结果加权平均,最终将所有头的结果拼接起来并通过一个线性变换生成最终输出。
通过该机制,我们能够通过多个注意力头并行地对输入序列进行处理,从而捕获不同的子空间信息。
代码部分
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.functional as f
import math
#%%
# 测试数据
X = torch.randn( 128, 64, 512) # Batch,Time,Dimension
print(X.shape)
#%%
# 设置multihead_attention基本参数
d_model = 512 # 映射到Q,K,V空间中有多少位
n_head = 8 # 有多少个头
#%%
class multi_head_attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model,n_head) -> None:
super(multi_head_attention,self).__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.d_model = d_model
self.w_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model) # 线性层映射函数,把初始向量映射到Q,K,V(query,key,value)
# 简单来说就是去寻找一些query去跟key,问他(key)哪些数据是跟我匹配的上的,匹配上之后,key所对应的value值进行加权组合,最终得到attention的输出
self.w_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_combine = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model) # 由于是多头注意力,所以要在最后做一个组合映射(多写一个w_combine的线性映射)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, q, k, v):
batch, time, dimension = q.shape
n_d = self.d_model // self.n_head # 得到新维度
q, k, v = self.w_q(q), self.w_k(k), self.w_v(v) # 把qkv分别丢到上面定义的三个线性映射层中,就可以得到qkv空间中的一个表示
# 对空间表示进行切分,对我们需要得到几个头进行切分
q = q.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 把q进行维度划分,一维是batch,二维是time, 三维是n.head(分成几个头),四维是n.d(分完头之后的维度)
k = k.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 也可以说把最后一维拆成了n.head和n.d两个维度的乘积
v = v.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 做attention操作的时候head维是不能放在最后的,对最后两个维度进行处理,所以要用permute指令做一个维度变换
# 原先的维度是0,1,2,3现在则是0,2,1,3
score = q @ k.transpose(2, 3) / math.sqrt(n_d) # q乘以k的转置除以它的维度开根号(让方差变小) @是矩阵乘法
# torch.tril命令-生成下三角矩阵(左下角都是1,右上角都是0)
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(time, time, dtype=bool))
score = score.masked_fill(mask == 0, float("-inf")) # 把mask等于0的地方都填充为负无穷
# 填充为负无穷的原因:softmax操作时e^-inf就是0,就相当于我们不去care后面部分的信息
score = self.softmax(score) @ v
# 最后把得分的格式变回来(因为之前把time维和self.n_head维度进行了旋转,现在则是要旋转回来),然后再过一个连续性函数
score = score.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous().view(batch, time, dimension)
# contiguous()的作用是让整个矩阵序列在内存中都是连续的
output = self.w_combine(score)
return output
attention = multi_head_attention(d_model, n_head)
output = attention(X, X, X)
print(output, output.shape)
2 手写编码模块,encoder layer
2.1 参数初始化
首先,我们通过torch.randn生成测试数据,维度为 [Batch, Time, Dimension],用于模拟输入序列的嵌入表示。
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.functional as f
import math
#%%
# 测试数据
X = torch.randn( 128, 64, 512) # Batch,Time,Dimension
print(X.shape)
2.2 多头注意力完善(加入mask判断便于改为自注意力)
为了适应自注意力(self-attention)机制的需求,我们在多头注意力实现中加入了mask参数的支持。通过mask,我们可以控制在解码阶段避免信息泄露或遮挡padding部分。
# 设置multihead_attention基本参数
d_model = 512 # 映射到Q,K,V空间中有多少位
n_head = 8 # 有多少个头
#%%
# 对上次实现的multihead attention进行修复(因为之前都是默认生成了一个mask)
# 但是在encoder当中做的是self_attention,不需要mask
# 因此需要我们多新建一个参数,来告诉他你是否需要mask
class multi_head_attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model,n_head) -> None:
super(multi_head_attention,self).__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.d_model = d_model
self.w_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model) # 线性层映射函数,把初始向量映射到Q,K,V(query,key,value)
# 简单来说就是去寻找一些query去跟key,问他(key)哪些数据是跟我匹配的上的,匹配上之后,key所对应的value值进行加权组合,最终得到attention的输出
self.w_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_combine = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model) # 由于是多头注意力,所以要在最后做一个组合映射(多写一个w_combine的线性映射)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None):
batch, time, dimension = q.shape
n_d = self.d_model // self.n_head # 得到新维度
q, k, v = self.w_q(q), self.w_k(k), self.w_v(v) # 把qkv分别丢到上面定义的三个线性映射层中,就可以得到qkv空间中的一个表示
# 对空间表示进行切分,对我们需要得到几个头进行切分
q = q.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 把q进行维度划分,一维是batch,二维是time, 三维是n.head(分成几个头),四维是n.d(分完头之后的维度)
k = k.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 也可以说把最后一维拆成了n.head和n.d两个维度的乘积
v = v.view(batch, time, self.n_head, n_d).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # 做attention操作的时候head维是不能放在最后的,对最后两个维度进行处理,所以要用permute指令做一个维度变换
# 原先的维度是0,1,2,3现在则是0,2,1,3
score = q @ k.transpose(2, 3) / math.sqrt(n_d) # q乘以k的转置除以它的维度开根号(让方差变小) @是矩阵乘法
# torch.tril命令-生成下三角矩阵(左下角都是1,右上角都是0)
if mask is not None:
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(time, time, dtype=bool))
score = score.masked_fill(mask == 0, float("-inf")) # 把mask等于0的地方都填充为负无穷
# 填充为负无穷的原因:softmax操作时e^-inf就是0,就相当于我们不去care后面部分的信息
score = self.softmax(score) @ v
# 最后把得分的格式变回来(因为之前把time维和self.n_head维度进行了旋转,现在则是要旋转回来),然后再过一个连续性函数
score = score.permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous().view(batch, time, dimension)
# contiguous()的作用是让整个矩阵序列在内存中都是连续的
output = self.w_combine(score)
return output
attention = multi_head_attention(d_model, n_head)
output = attention(X, X, X)
print(output, output.shape)
2.3 Embedding
Token Embedding: 通过nn.Embedding层将输入的token映射到固定维度的向量空间
1. Token Embedding
class TokenEmbedding(nn.Embedding):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model):
super(TokenEmbedding,self).__init__(vocab_size, d_model, padding_idx=1)
2. Position Embedding
Position Embedding: 为了引入序列顺序信息,我们使用了位置编码。具体方法是通过正弦与余弦函数生成固定的周期性编码。
class PositionalEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, maxlen, device):
super(PositionalEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.encoding = torch.zeros(maxlen, d_model, device) # 初始化编码(长度是maxlen)
self.encoding.requires_grad_(False) # 告诉模型不用梯度
pos = torch.arange(0, maxlen, device)
pos = pos.float().unsqueeze(1) # 增加一个维度
_2i = torch.arange(0, d_model, 2, device)
self.encoding[:,0::2] = torch.sin(pos / (10000 ** (_2i / d_model)))
self.encoding[:,1::2] = torch.cos(pos / (10000 ** (_2i / d_model)))
def forward(self, x):
seq_len = x.shape[1]
return self.encoding[:seq_len,:]
3. Total Embedding (综合前两者)
class TransformerEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model, max_len, drop_prob, device):
super(TransformerEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.tok_emb = TokenEmbedding(vocab_size, d_model)
self.pos_emb = PositionalEmbedding(d_model, max_len, device)
self.drop_out = nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
def forward(self, x):
tok_emb = self.tok_emb(x)
pos_emb = self.pos_emb(x)
return self.drop_out(tok_emb + pos_emb)
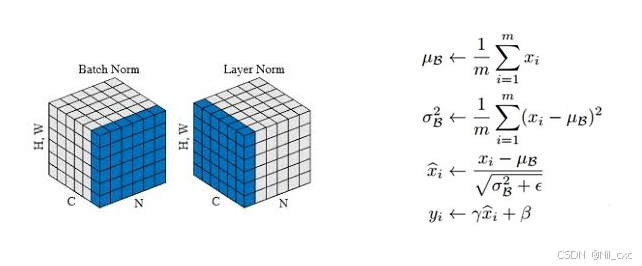
2.4 LayerNorm (归一化)
使用LayerNorm对每一层的输入进行标准化,减少训练中的不稳定性,并加速收敛。
# 归一化————学习两个参数-减均值除方差
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, eps = 1e-10):
super(LayerNorm, self).__init__()
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(d_model))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(d_model))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
mean = x.mean(-1, keepdim=True)
var = x.var(-1, unbiased=False, keepdim=True)
out = (x - mean) / torch.sqrt(var + self.eps)
out = self.gamma * out + self.beta
return out
2.5 FFN
FFN——feedforward层,本质上是一个两层的MLP,第一层会将输入的向量升维,第二层将向量重新降维,这样就可以学习到更加抽象的特征
前馈神经网络(Feedforward Neural Network, FFN)由两层全连接层组成,通常用于特征转换和非线性映射。
class PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, hidden, dropout=0.1):
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(d_model, hidden)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden, d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
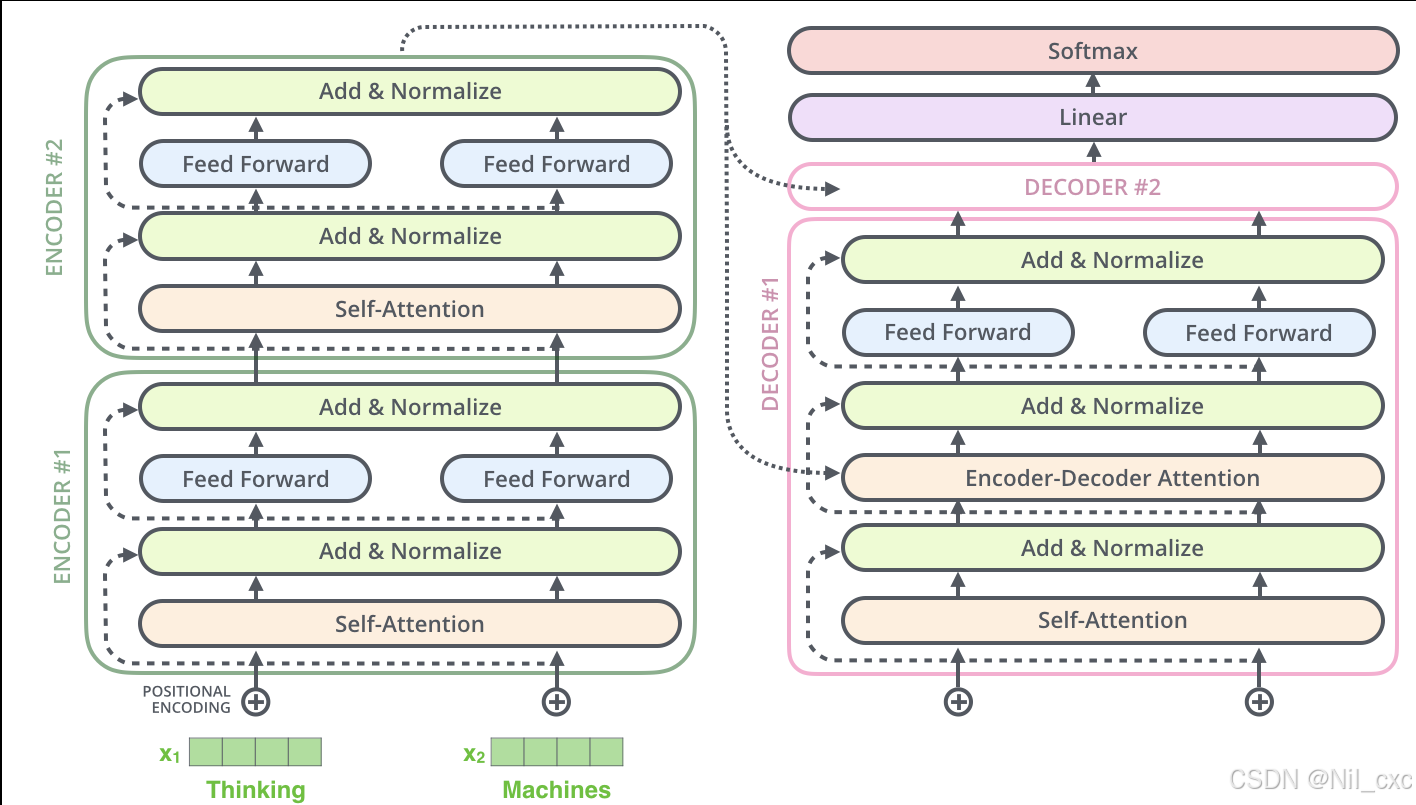
2.6 Encoder layer
Encoder Layer通过多头注意力和FFN两部分组成,其中包含了残差连接与归一化步骤,以提高模型的学习能力。
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
# ffn_hidden为隐藏层维度,drop_prob为dropout的概率
def __init__(self, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob) -> None:
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.attention = multi_head_attention(d_model, n_head)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop_prob)
self.ffn = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, ffn_hidden, drop_prob)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop_prob)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
# 因为等会要用到残差连接,所以要先生成一个备份
_x = x
x = self.attention(x, x, x, mask)
x = self.drop1(x)
self.norm1(x + _x)
_x = x
x = self.ffn(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
x = self.norm2(x + _x)
return x
3 手写Decoderlayer
3.1 Decoderlayer部分
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.attention1 = multi_head_attention(d_model, n_head)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(drop_prob)
# cross attention
self.cross_attention = multi_head_attention(d_model, n_head)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(drop_prob)
self.ffn = PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, ffn_hidden, drop_prob)
self.norm3 = LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(drop_prob)
# dec:解码器需要的输入信息 enc:从编码器当中传过来的信息
# 最后两个参数是两个掩码块,一个是用来对padding的掩码(用来统一句子长度),第二个掩码是对未来信息的掩码(在解码的时候肯定不能看到真实的答案再去解码)
# t_mask 是因果掩码,不希望在做attention的时候看到未来的信息 s_mask 是位置掩码,不需要关注到padding的信息
def forward(self, dec, enc, t_mask, s_mask):
_x = dec
x = self.attention1(dec, dec, dec, t_mask) # 下三角掩码
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = self.norm1(x + _x)
if enc is not None:
_x = x
x = self.cross_attention(x, enc, enc, s_mask) # 用s_mask掩码,不需要关注padding信息
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.norm2(x + _x)
_x = x
x = self.ffn(x)
x = self.dropout3(x)
x = self.norm3(x + _x)
3.2 Decoder和Encoder做个集成
Encoder部分
# 做集成(把encoder和decoder都拼到一起)
class Encoder(nn.Module):
# env_voc_size:需要编码的vocabulary的size大小 max_len:最大给他的长度
# n_layer: 搭几层 device:把数据存到哪里
def __init__(self, env_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, n_layer, drop_prob, device):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = TransformerEmbedding(d_model, max_len, env_voc_size, drop_prob, device)
self.layers = nn.Modulelist(
[EncoderLayer(d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob) for _ in range(n_layer)]
)
def forward(self, x, s_mask):
x = self.embedding(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, s_mask)
return x
Decoder部分
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dec_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, n_layer, drop_prob, device):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = TransformerEmbedding(d_model, max_len, dec_voc_size, drop_prob, device)
self.layers = nn.Modulelist(
[DecoderLayer(d_model, ffn_hidden, n_head, drop_prob) for _ in range(n_layer)]
)
self.fc = nn.Linear(d_model, dec_voc_size)
def forward(self, dec, enc, t_mask, s_mask):
dec = self.embedding(dec)
for layer in self.layers:
dec = layer(dec, enc, t_mask, s_mask)
dec = self.fc(dec)
return dec
4 Transformer部分
class Transformer(nn.Module):
# 首先是两个pad,就是对输入的pad和decoder pad的一个标识符的一个记录
# 然后告诉大家encoder vocabulary size和decoder vocabulary size 分辨是多大
# max_len最大长度,d_model的大小,头的大小
# 前向传播隐藏层的大小,总层数,dropout,最后还有device
def __init__(self, src_pad_idx, trg_pad_idx, enc_voc_size, dec_voc_size, max_len, d_model, n_heads, ffn_hidden, n_layers, drop_prob, device):
super(Transformer,self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(enc_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_heads, n_layers, drop_prob, device)
self.decoder = Decoder(dec_voc_size, max_len, d_model, ffn_hidden, n_heads, n_layers, drop_prob, device)
# 生成两个padding的index标识符
self.src_pad_idx = src_pad_idx
self.trg_pad_idx = trg_pad_idx
self.device = device
def make_pad_mask(self, q, k, pad_idx_q, pad_idx_k):
len_q, len_k = q.size(1), k.size(1)
# (Batch, Time, len_q, len_k) 第三维和第四维是QK相乘之后得到的2*2矩阵,所以后面两个就是矩阵的一个维度
q = q.ne(pad_idx_q).unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(3) # 本来q的维度是batch和len_q两维,现在为了统一格式,因此需要增加两个维度到四维
q = q.repeat(1, 1, 1, len_k) # 需要把len_k补全(因为每一个q都有一个对应的k)
k = k.ne(pad_idx_k).unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
k = k.repeat(1, 1, len_q, 1)
# 生成Q,K之后,需要进行暗位取余的操作(全一出一,只要有零则出零)
mask = q & k
return mask
def make_casual_mask(self, q, k):
len_q, len_k = q.size(1), k.size(1)
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(len_q, len_k)).type(torch.BoolTensor).to(self.device)
return mask
def forward (self, src, trg):
# 构建mask
# 首先构建encoder当中自己的padding mask
src_mask = self.make_pad_mask(src, src, self.src_pad_idx, self.src_pad_idx)
# 然后是decoder自己的因果mask
trg_mask = self.make_pad_mask(trg, trg, self.trg_pad_idx, self.trg_pad_idx) * self.make_casual_mask(trg, trg)
# 交叉注意力机制的mask, q来自query(target),k来自encoder(source),
src_trg_mask = self.make_pad_mask(trg, src, self.trg_pad_idx, self.src_pad_idx)
enc = self.encoder(src, src_mask)
output = self.decoder(trg, enc, trg_mask, src_trg_mask)
return output
总结
通过手写实现了Transformer的核心组件,详细理解了多头注意力机制、编码器层,解码器层和前馈神经网络等模块的设计与实现。