目录
1.栈
1. 什么是栈?如何理解栈?
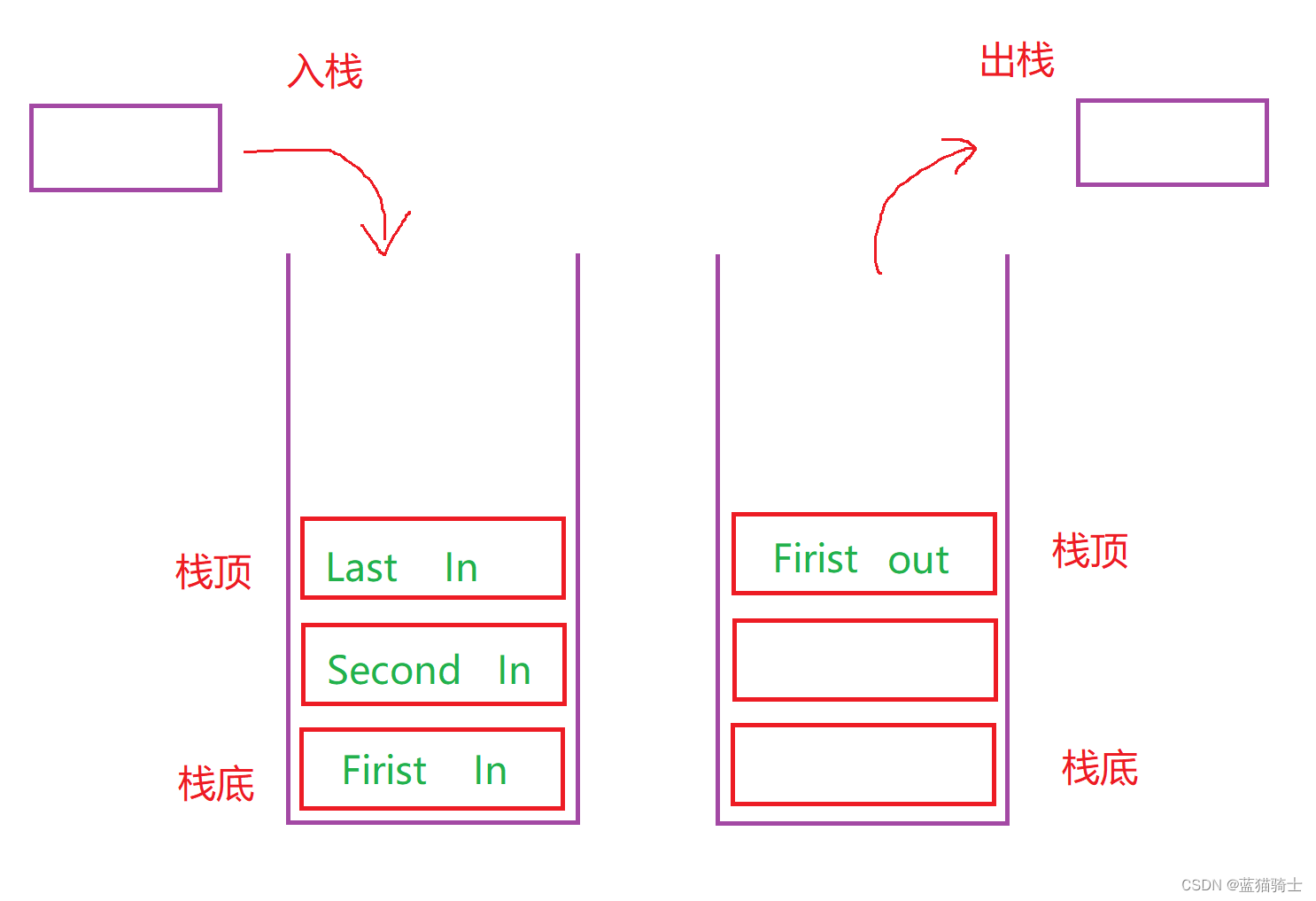
栈作为一种数据结构,是一种只能在一端进行插入和删除操作的特殊线性表。它按照后进先出的原则存储数据,先进入的数据被压入栈底,最后的数据在栈顶,需要读数据的时候从栈顶开始弹出数据(最后一个数据被第一个读出来),。栈具有记忆作用,对栈的插入与删除操作中,不需要改变栈底指针。
按图示来理解就是:
2.栈的实现;
一. 创建结构体变量;初始化栈
typedef struct Stack
{
int* a;
int top; // 栈顶
int capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* SL)
{
assert(SL);
SL->a =NULL;
SL->capacity = 0;
SL->top = 0;
}二. 出栈 入栈 显示栈顶元素 等函数的实现;
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* SL,int x);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* SL);
// 打印
void StackPrintf(Stack SL);
//获取栈顶元素
int StackFront(Stack SL);
//获取栈中有效元素的个数
int StackSize(Stack SL);
//检查栈是否为空 为空 返回 1 不为空 返回 0
int StackEmpty(Stack SL);
void StackPush(Stack* SL,int x)
{
assert(SL);
if(SL->top == SL->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = SL->capacity == 0 ? 4 : (SL->capacity) * 2;
int* newnode = (int*)realloc(SL->a, sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
SL->a = newnode;
SL->capacity = newcapacity;
}
SL->a[SL->top] = x;
SL->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* SL)
{
assert(SL);
if (SL->top <= 0)
{
return;
}
else
SL->top--;
}
void StackPrintf(Stack SL)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SL.top; i++)
{
printf("%d ", SL.a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int StackFront(Stack SL)
{
return SL.a[SL.top - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack SL)
{
int i = 0;
int n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SL.top; i++)
{
n++;
}
return n;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack SL)
{
return SL.top == 0;
}三. 销毁栈;
void StackDestory(Stack* SL)
{
assert(SL);
free(SL->a);
SL->a = NULL;
SL->capacity = SL->top = 0;
}四. 检验案例
#include"标头.h"
test()
{
Stack SL;
StackInit(&SL);
StackPush(&SL, 2);
StackPush(&SL, 3);
StackPush(&SL, 5);
StackPush(&SL, 4);
StackPrintf(SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPush(&SL, 5);
StackPush(&SL, 9);
StackPrintf(SL);
int a = StackFront(SL);
printf("%d\n", a);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
StackPop(&SL);
int b = StackEmpty(SL);
printf("%d\n", b);
StackPush(&SL, 2);
StackPush(&SL, 3);
StackPush(&SL, 5);
StackPush(&SL, 4);
StackPrintf(SL);
int c = StackSize(SL);
printf("%d\n", c);
StackDestory(&SL);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
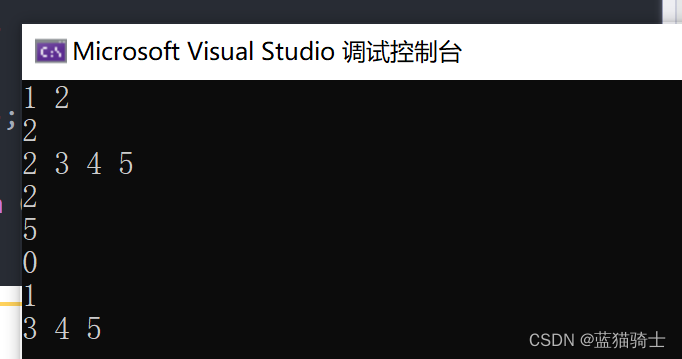
}运行结果如下:
2.队列
1.什么是队列?如何理解队列?
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)(头删头插)入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
2.队列的实现
针对于队列的实现,也可以有两种实现的方法——数组和链表;那么哪种方法更为方便呢?
答案是:使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
一. 创建结构体变量,初始化队列;
// 链式结构表示队列
typedef struct Queue
{
struct Queue* next;
int x;
}Queue;
// 队列的结构
typedef struct QueueNode
{
Queue* head;
Queue* tail;
}QueueNode;
void QueueInit(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
SL->head = SL->tail = NULL;
}二. 头删 头插 头查 尾查 等函数的实现;
//初始化
void QueueInit(QueueNode* SL);
//头插
void QueuePush(QueueNode* SL, int x);
//打印
void QueuePrintf(QueueNode* SL);
//头删
void QueuePop(QueueNode* SL);
//获取队头元素
int QueueFront(QueueNode* SL);
//获取队尾元素
int QueueBack(QueueNode* SL);
// 检查是否尾空 为空返回 1 不为空返回 0
int QueueEmpty(QueueNode* SL);
void QueuePush(QueueNode* SL, int x)
{
assert(SL);
Queue* newnode = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
}
newnode->x = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (SL->tail == NULL)
{
SL->head = SL->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
SL->tail ->next = newnode;
SL->tail = SL->tail->next;
}
}
void QueuePrintf(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
Queue* cur = SL->head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->x);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void QueuePop(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
if (SL->head == NULL)
{
return ;
}
if (SL->head->next == NULL)
{
free(SL->head);
SL->head = SL->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
Queue* del = SL->head;
SL->head = SL->head->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
}
int QueueFront(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
return SL->head->x;
}
int QueueBack(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
return SL->tail->x;
}
int QueueEmpty(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
return (SL->tail == NULL)&&(SL->head == NULL);
}
三 . 队列的销毁;
void QueueDestory(QueueNode* SL)
{
assert(SL);
/*Queue* del = SL->head;
while (del)
{
Queue* next = del->next;
free(del);
del = next;
}*/
Queue* cur = SL->head;
while (cur)
{
Queue* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
SL->head = SL->tail = NULL;
}四. 测试案例;
#include"标头.h"
test()
{
QueueNode SL;
QueueInit(&SL);
QueuePush(&SL, 1);
QueuePush(&SL, 2);
QueuePrintf(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePrintf(&SL);
QueuePush(&SL, 3);
QueuePush(&SL, 4);
QueuePush(&SL, 5);
QueuePrintf(&SL);
int a = QueueFront(&SL);
printf("%d\n", a);
int b = QueueBack(&SL);
printf("%d\n", b);
int c = QueueEmpty(&SL);
printf("%d\n", c);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
QueuePop(&SL);
c = QueueEmpty(&SL);
printf("%d\n", c);
QueuePush(&SL, 3);
QueuePush(&SL, 4);
QueuePush(&SL, 5);
QueuePrintf(&SL);
QueueDestory(&SL);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}运行结果如下: