前言
普通的二叉树是不适合用数组来存储的,因为这样会存在大量的空间浪费,但是完全二叉树却更适合用顺序结构存储。
堆
堆的概念以及结构
堆的概念
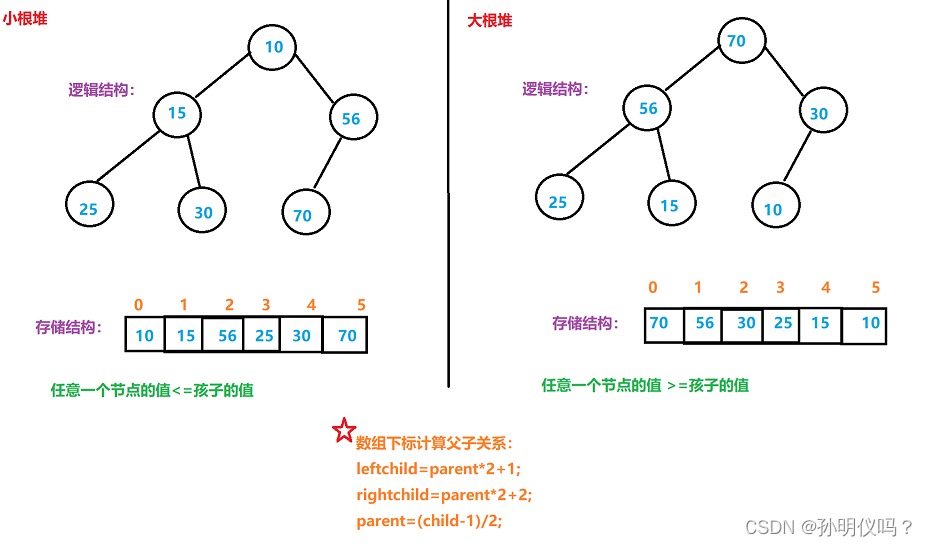
堆是一种二叉树,可以用顺序结构的数组来存储。(这里的堆和操作系统的虚拟进程地址空间的堆不一样,一个是数据结构一个是操作系统的管理内存的一块区域分段)
把所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储在一个一维数组中。
堆的性质
1.堆的某个节点的值总是不大于或者不小于其父节点的值;
2.堆是一棵完全二叉树;
根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或者大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或者小根堆。
堆的结构
堆的搭建
1.向上调整创建堆
void AdjustUp(HPdatatype *a,int child)//小堆
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[parent] > a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Heapbuild1(int *a,int n)//直接就是对a数组进行建堆打印
{ //向上建堆
for (int i = 1;i < n;i++)//一开始让第0个成为堆
{
AdjustUp(a, i);//每给一个下标数,就相当于后接的数,依次向上调整成堆
}//建堆
}
2.向下调整建堆
向下调整有个前提:左右子树必须是一个堆
void AdjustDown(HPdatatype* a,int parent,int n)//小堆
{
HPdatatype minchild = parent * 2 + 1;
while (minchild < n)//最小孩子没超出范围时
{
if (minchild+1<n&&(a[minchild + 1] < a[minchild]))
{
minchild++;
}
if (a[parent] > a[minchild])
{
Swap(&a[minchild], &a[parent]);
parent = minchild;
minchild = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Heapbuild2(int* a, int n)//向下调整建堆
{
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2;i >= 0;i--)//从最后一个节点的父亲开始,再去减减 调整
{
AdjustDown(a, i, n);
}
}
注意:,一开始要从最后一个节点的父亲开始,以它为父节点,左右子树满足堆,然后向下调整,让这个小子树为堆,最后对当前的parent减减,在去不断让子树成堆,parent不断向上,最后整体也就建成了堆。
比较两种建堆的时间复杂度
1.向上调整建堆
时间复杂度 O(N*logN)
节点越多,调整越多。
有N个数,每次向上调整时间复杂度为 O(logN)(大概为2k=N)
2.向下调整建堆
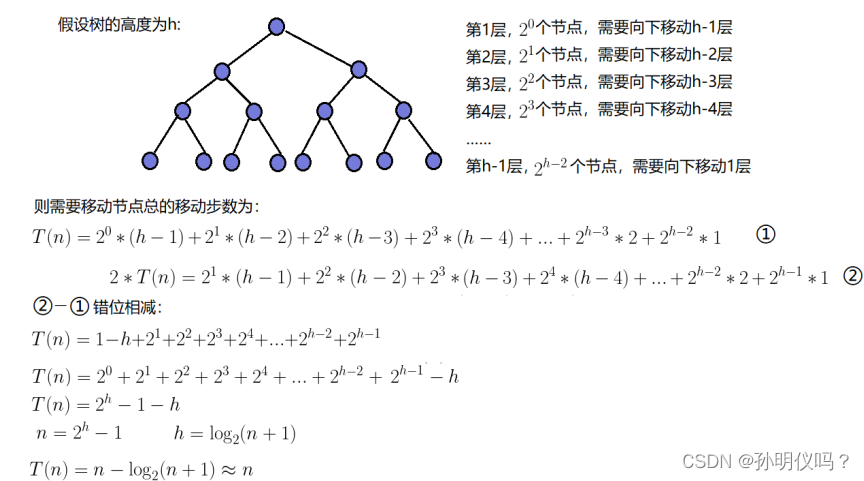
时间复杂读 O(N)
节点越多,调整的越少
(最后一层节点数量2k-1(假设是满的),都快等于总节点数量了2k-1几乎一半了,然而向下调整建堆却不从最后一层开始)
证明:
利用错位相减得,时间复杂度为O(N).
综上,建堆最好用向下建堆法!
堆的实现
头文件
typedef int HPdatatype;
typedef struct
{
HPdatatype* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}Heap;
void HeapInit(Heap*hp);
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp);
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPdatatype x);
void HeapPop(Heap* hp);
HPdatatype HeapTop(Heap* hp);
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
void AdjustUp(HPdatatype* a, int child);
void AdjustDown(HPdatatype* a, int parent, int n);
void Swap(HPdatatype* a, HPdatatype* b);
void HeapPrint(Heap* hp);
函数定义
初始化
与顺序表的类似
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)//初始化
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)//销毁
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
插入数据
与顺序表一样,先判断是否要扩容,然后把插入的数据放在数组的最后,再去向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPdatatype *a,int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[parent] > a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Swap(HPdatatype* a, HPdatatype* b)
{
HPdatatype c = 0;
c = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = c;
}
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPdatatype x)//插入数据
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->capacity == hp->size)
{
int newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 :hp-> capacity * 2;
HPdatatype* new = (HPdatatype*)realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPdatatype) * newCapacity);
if (new == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = new;
hp->capacity = newCapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size-1);
}
删除数据
在顺序表里,删除就是size–;但是在堆里,删除的是堆顶的元素。
这里的算法是,1.先将堆顶元素和最后一个元素互转,2.然后size–,3.最后把堆顶那个数向下调整。
void AdjustDown(HPdatatype* a,int parent,int n)
{
HPdatatype minchild = parent * 2 + 1;
while (minchild < n)//最小孩子没超出范围时
{
if (minchild+1<n&&(a[minchild + 1] < a[minchild]))
{
minchild++;
}
if (a[parent] > a[minchild])
{
Swap(&a[minchild], &a[parent]);
parent = minchild;
minchild = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HeapPop(Heap* hp)// 删除堆顶元素
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a,0,hp->size);
}
返回堆顶元素
HPdatatype HeapTop(Heap* hp)//返回堆顶元素
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
}
返回堆的数量
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size - 1;
}
判断堆是否为空
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
打印
void HeapPrint(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
for (int i = 0;i < hp->size;i++)
{
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
主函数
int main()
{
Heap hp;
HeapInit(&hp);//创建结构体变量再去初始化,把数组a的值一个个传过去malloc建堆
int a[] = { 18,15,17,56,28,1,65,38,27,37 };
for (int i = 0;i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);i++)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPush(&hp, 10);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
//打印也可以
while (!HeapEmpty(&hp))
{
printf("%d ", HeapTop(&hp));
HeapPop(&hp);
}
return 0;
}
但是调用print函数和不断top返回数据,打印出来是不一样的。
不断的top 会不断返回完后再去调整成新堆,顺序和之间print的不一样。