组件之间通信方案
| 序号 | 组件关系 | 数据通信 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 父子关系 | 子传父:props ; 父传子:$emit |
| 2 | 非父子关系 | eventBus: $on + $emit |
| 3 | 非父子关系 | vuex |
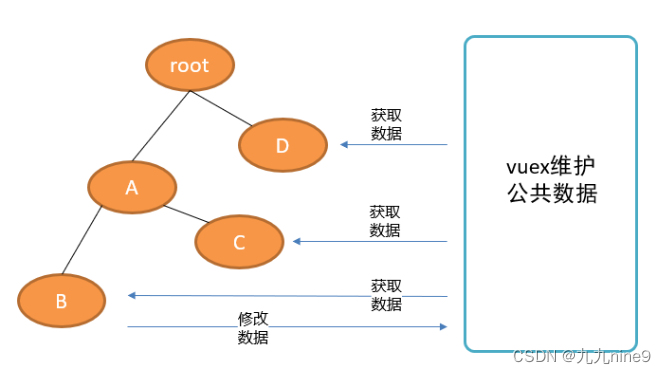
Vuex是什么
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式, 采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,解决多组件数据通信。
要点:
- vue官方搭配,专属使用 (类似于:vue-router),有专门的调试工具
- 集中式管理数据状态方案 (操作更简洁)
data() { return { 数据, 状态 }} - 数据变化是可预测的 (响应式)
vue官方提供的独立于组件体系之外的,管理公共数据的工具
使用场景:大型项目
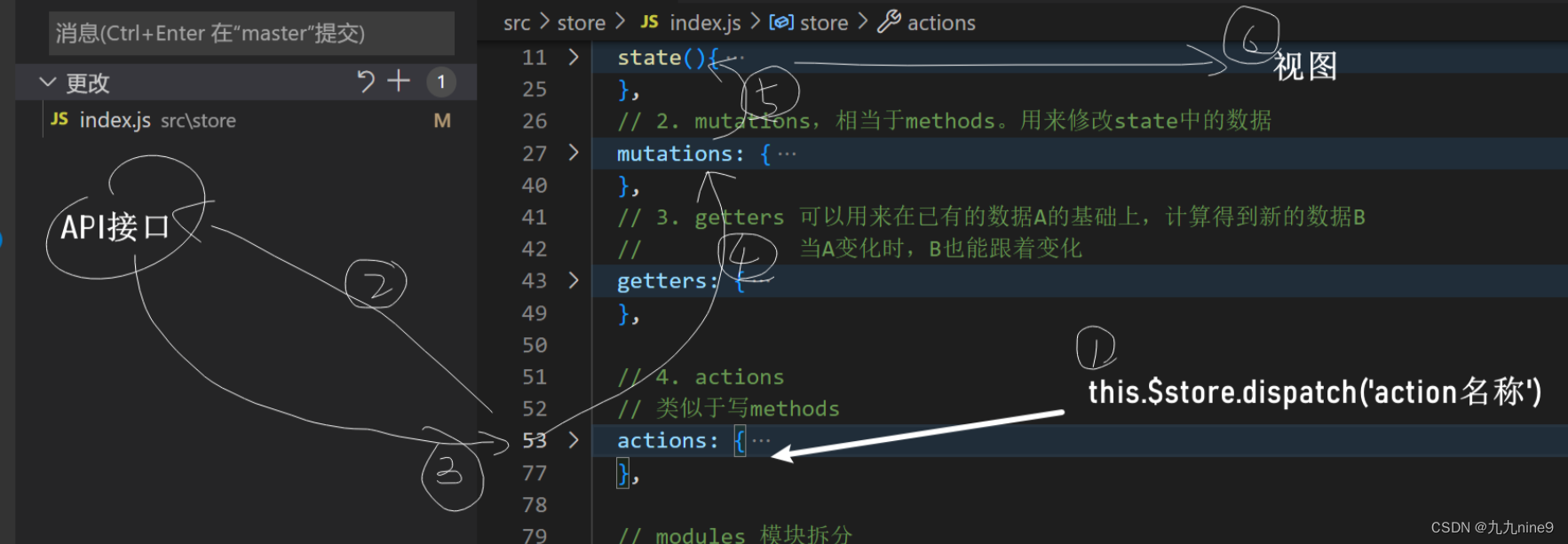
Vuex中的五个概念:
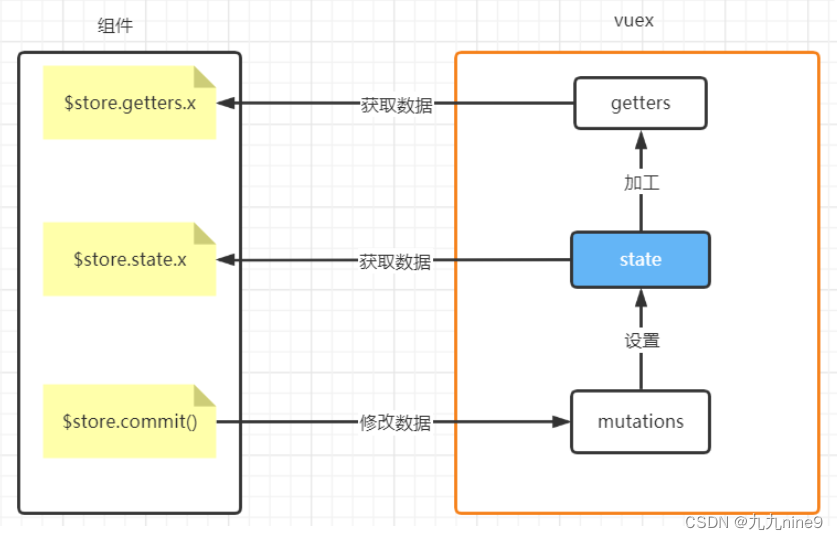
- state: 统一定义公共数据(类似于data(){return {a:1, b:2,xxxxxx}})
- mutations : 使用它来修改数据(类似于methods)
- getters: 类似于computed(计算属性,对现有的状态进行计算得到新的数据-------派生 )
- actions: 发起异步请求
- modules: 模块拆分
其中最为重要的内容是state和mutations
在Vue项目使用Vuex
两种情况
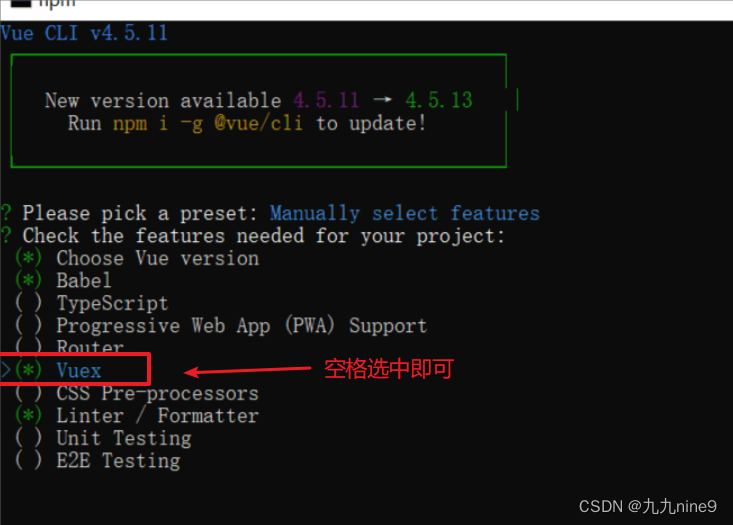
- 情况1:在老项目中使用。 先额外安装vuex包,然后在配置。
- 情况2:在新项目中使用。 在配置vue-cli中创建项目时,就可以直接选中vuex项,这样就不用做任何配置了(脚手架会自动帮我们完成的)。具体如下图示:
在新项目中使用 vuex
在旧项目中使用vuex
整体步骤:
- 安装。它是一个独立的包,需要先安装。
- 配置
a. 创建Vuex.store实例
b. 向Vue实例注入store - 使用。在组件中使用store
安装包
进入项目目录,安装包
npm install [email protected]
vue2安装vuex3版本
vue3安装vuex4版本
实例化store
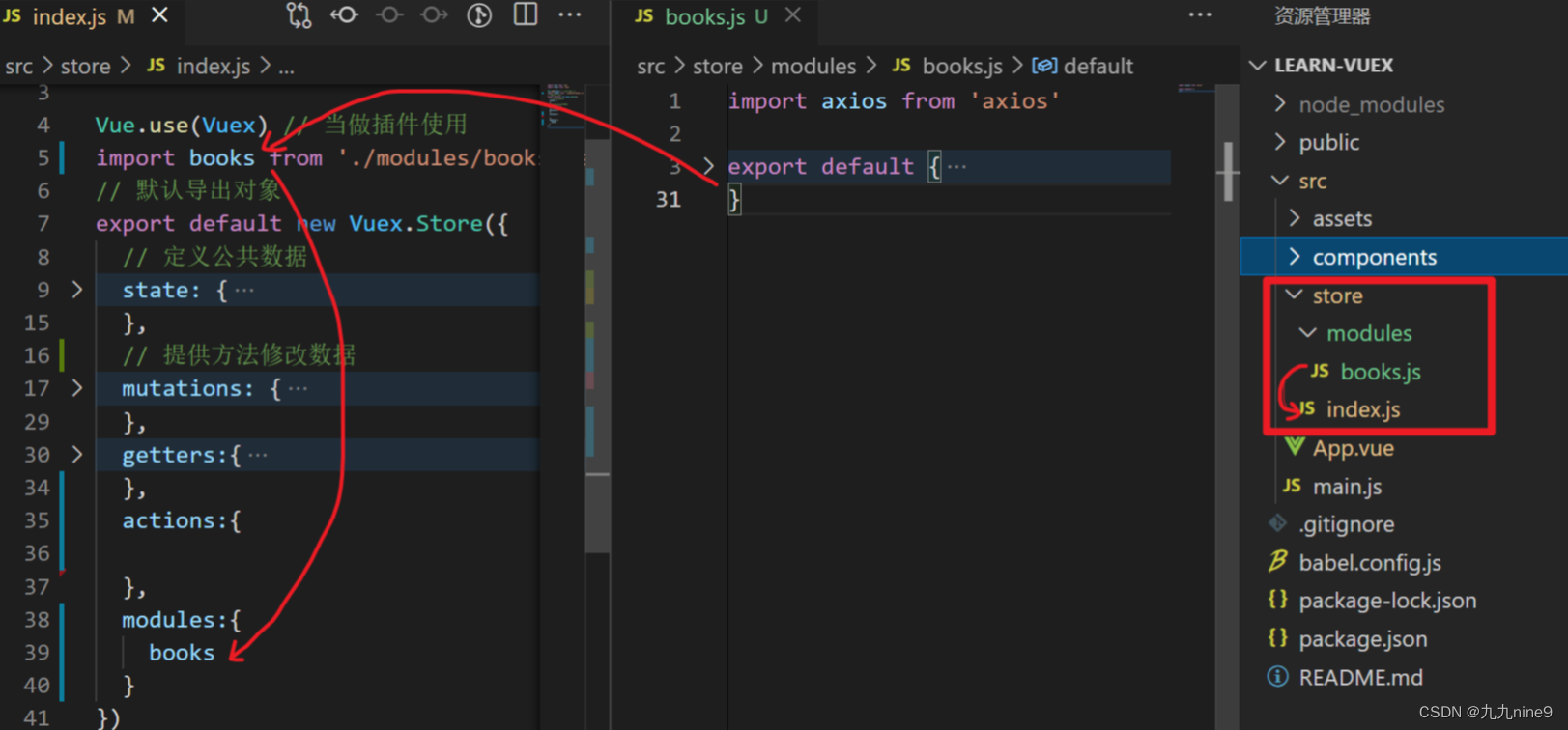
与router一样,当我们在项目中使用vuex之后,为了方便代码维护,我们一般需要做特殊的目录调整,约定的结构如下:
根组件
└── src
├── main.js
├── router
│ └── index.js # 路由
└── store
└── index.js # vuex
在store/index.js 中放置具体的代码,具体如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state(){
return {
// 就是公共的数据,所有的组件都可以直接使用
count: 100
}
}
})
export default store
向Vue实例注入store
在src/main.js中:
- 导入store
- 并注入Vue实例
// 省略其他
// 1. 导入store
import store from './store'
new Vue({
// 省略其他...
store // 2. 注入Vue实例
})
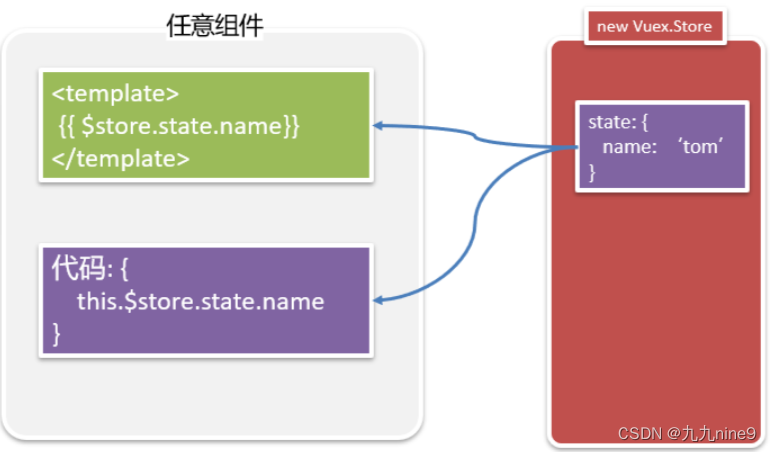
在组件中使用store
在任意组件中,通过this.$store.state 来获取公共数据。
小结
在老项目中使用vuex的步骤
- 安装。它是一个独立的包,需要先安装。注意版本号,vue2,安装版本号 [email protected] , vue3,安装版本号 [email protected]。
- 配置
a. 创建Vuex.store实例(有固定代码,类似于vue-router;不需要记忆)
b. 向Vue实例注入store - 使用。在组件中使用store。
a. 代码:this.$store.state
b. template:{{$store.state}}
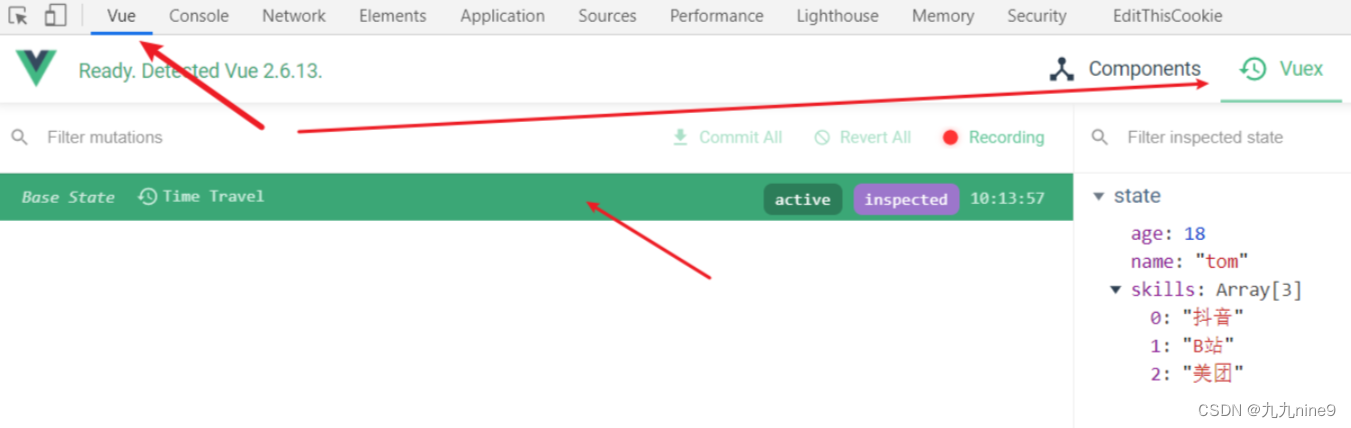
vue-devtool调试工具
Vuex-state定义公共数据并在组件中使用
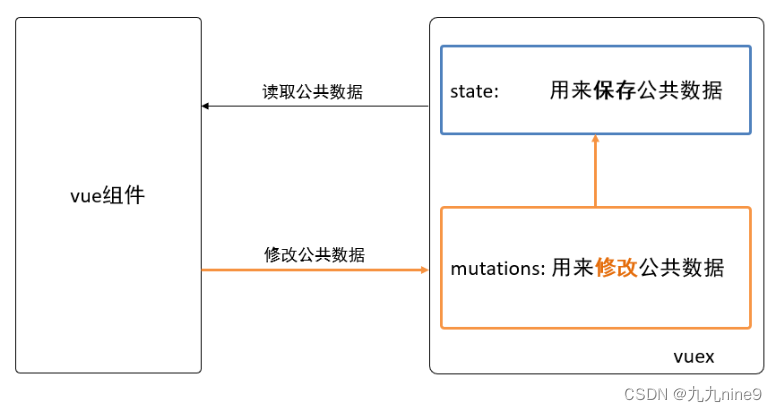
state的作用
vuex用它来保存公共数据
格式
new Vuex.store({
state() {
return {
属性名: 属性值
}
}
// state:{}
})
示例
new Vuex.store({
state(){
return {
userInfo: {
name: 'tom',
skills: ['抖音', 'B站', '美团'],
address: '武汉',
logo: 'https://vuejs.org/images/logo.svg'
// https://www.runoob.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/react.png
}
}
}
})
使用公共数据
格式:
在组件中,通过this.$store.state.属性名来访问。
在模板中,则可以省略this而直接写成: {{$store.state.属性名}}
小结
state的作用是:保存公共数据(多组件中共用的数据)
state是响应式的: 如果修改了数据,相应的在视图上的值也会变化。
Vuex-用mutations修改公共数据
作用
通过调用mutations来修改定义在state中的公共数据。
格式
分两个格式: 定义格式,调用格式
定义格式:
new Vue.store({
// 省略其他...
mutations:{
// 每一项都是一个函数,可以声明两个形参
mutation名1:function(state [, 载荷]) {
},
mutation名2:function(state [, 载荷]) {
}
}
})
每一项都是一个函数,可以声明两个形参:
● 第一个参数是必须的,表示当前的state。在使用时不需要传入
● 第二个参数是可选的,表示载荷,是可选的。在使用时要传入的数据
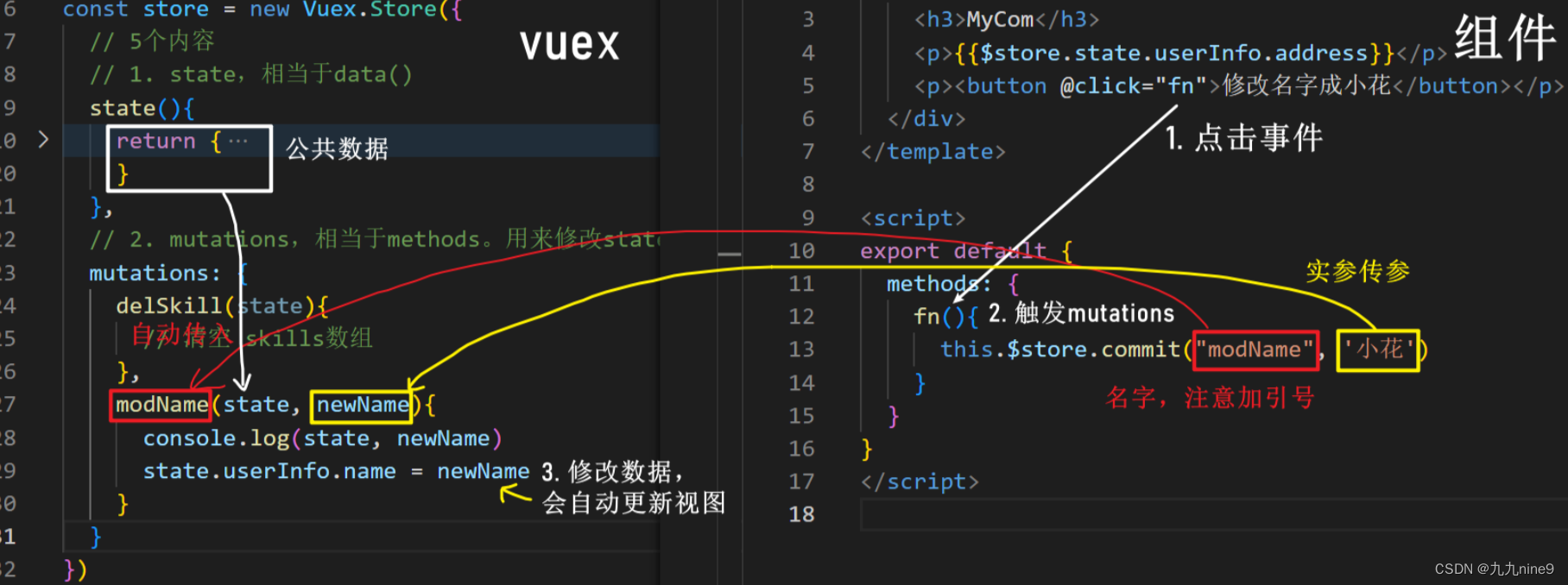
使用格式
this.$store.commit('mutation名', 实参)
这里的commit是固定的方法
示例
在store/index.js中,补充:
数据项
更新数据项url的mutations
export default new Vuex.Store({
// state: 用来保存所有的公共数据
state: {
userInfo: {
name: 'tom',
skills: ['抖音', 'B站', '美团'],
address: '武汉黑马',
logo: 'https://vuejs.org/images/logo.svg'
// https://www.runoob.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/react.png
}
},
// mutations: 用它提供修改数据的方法
// 中文是:变化,异动。
// 数据不应该在组件内部直接修改,必须在组件内调用mutations来修改
mutations: {
setLogo(state, newUrl) {
state.userInfo.logo = newUrl
}
}
}
在组件中,调用
const url = 'http://s02.mifile.cn/assets/static/image/logo-mi2.png'
this.$store.commit('changeUrl', url)
小结
mutations的中文含义是:变异。 它是Vuex中用来修改公共数据的唯一入口。
在定义时:它的第一个参数是state,第二个参数是载荷
在调用时:用 this.$store.commit(‘mutation名’, 载荷) 来调用
Vuex-mutaions拓展理解
问:为啥是 s t o r e . c o m m i t ( ′ m u t a t i o n s 的 名 字 ′ ) 而 不 是 store.commit('mutations的名字')而不是 store.commit(′mutations的名字′)而不是store.mutations的名字()?
答:Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数。
问:数据不可以该在组件内部直接修改吗?
答:不能。虽然语法上不报错,也有响应式的特点。但是不推荐。特别是在严格模式下会报错。若将vue创建 store 的时候传入 strict: true, 开启严格模式,那么任何修改state的操作,只要不经过 mutation的函数,vue就会报错
问:可以传递多个数据吗?
答:参数只能有一个:下面的写法是不对的:
this.$store.commit('setUrl', url, host) // host这个参数将无法被接收到
如果希望传递复杂的数据,第二个参数可以是对象,例如下面的写法
this.$store.commit('setUrl', { url, host} )
问:等价写法 this.$store.commit({type: ‘mutations的名字’})
Vuex-用getters的派生状态
作用
在state中的数据的基础上,进一步对数据进行加工得到新数据。(与组件中computed一样)
定义格式
new Vuex.store({
// 省略其他...
getters: {
// state 就是上边定义的公共数据state
getter的名字1: function(state) {
return 要返回的值
}
}
})
使用格式
在组件中通过:$store.getters.getter的名字 来访问
Vuex-state-mutation-getters 小结
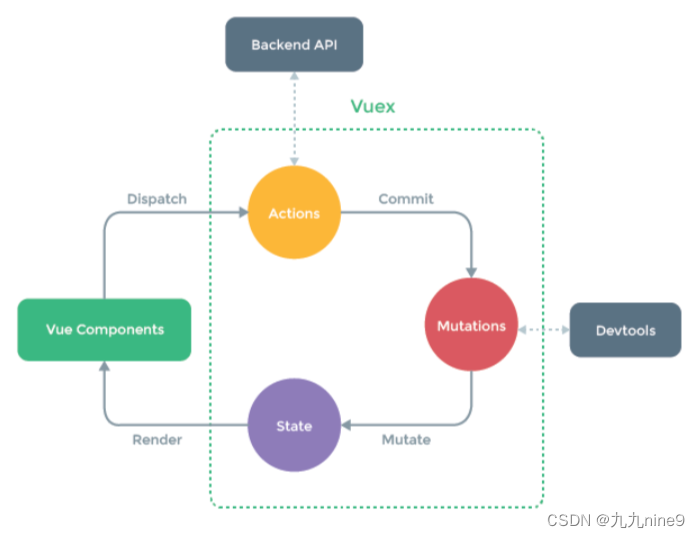
vuex维护公共数据,主要有两个动作:
- 定义数据:
- 提供获取/修改数据的方法
Vuex-actions-发异步请求
导入
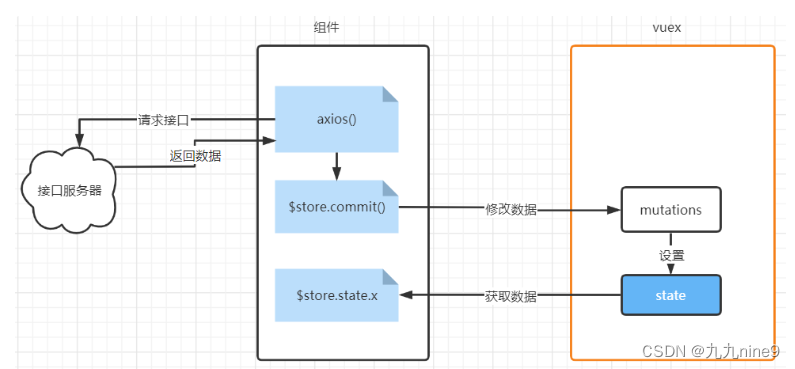
以前获取图书信息的方式是:
- 组件内部发ajax
- ajax回来之后,去调用mutations来保存到vuex中
这种方式有一个问题:代码不好重用
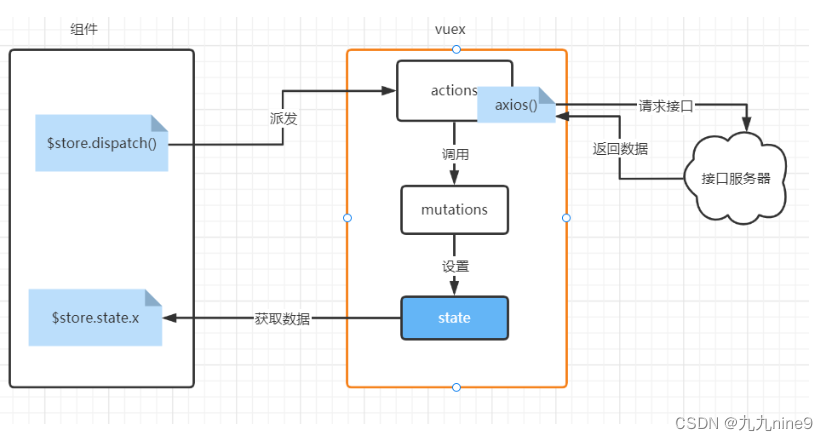
actions介绍
● actions是vuex的一个配置项
● 作用:发异步请求获取数据,调用mutations来保存数据,将整个ajax操作封装到Vuex的内部
● 要点:
○ action 内部可以发异步请求操作
○ action是间接修改state的:是通过调用 mutation来修改state
○ 减少了代码复用
定义格式
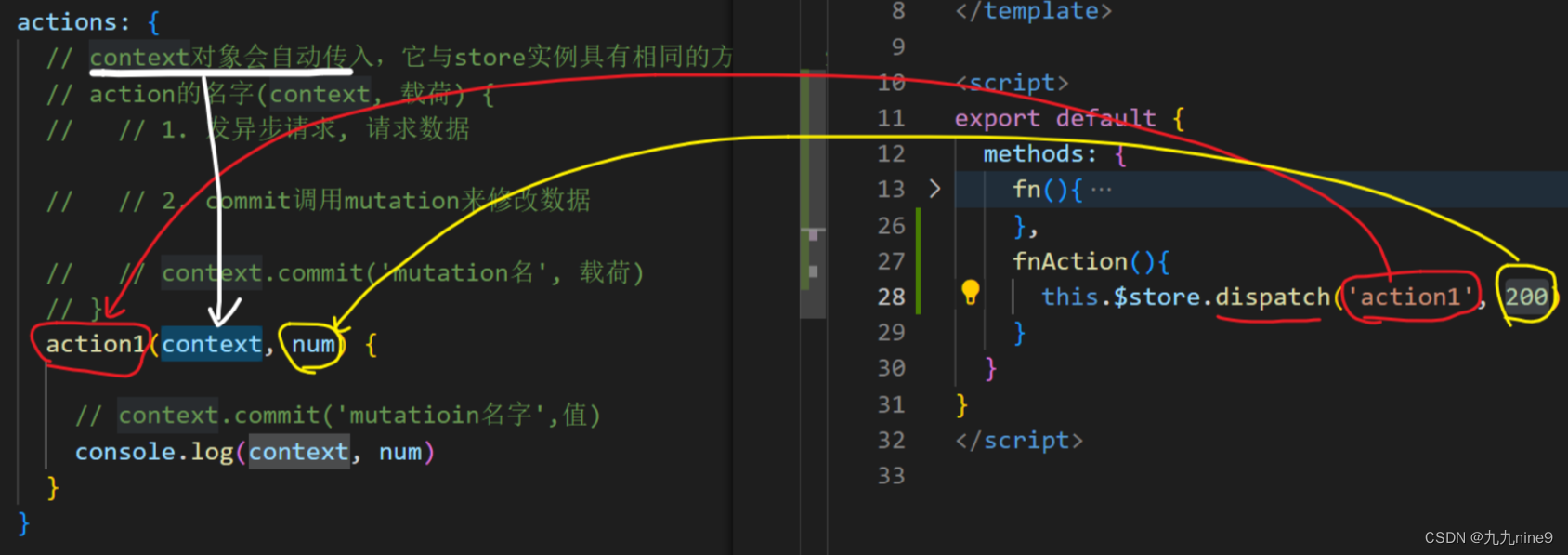
new Vuex.store({
// 省略其他...
actions: {
// context对象会自动传入,它与store实例具有相同的方法和属性
action的名字: function(context, 载荷) {
// 1. 发异步请求, 请求数据
// 2. commit调用mutation来修改数据
// context.commit('mutation名', 载荷)
}
}
})
// 发ajax请求,从后端获取数据,再来去修改state中的数据
actions: {
getBooks (context) {
// 1. 发异步请求
axios({
url: 'https://www.fastmock.site/mock/37d3b9f13a48d528a9339fbed1b81bd5/book/api/books',
method: 'GET'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
// 2. 调用mutation
context.commit('setBooks', res.data.data)
})
}
},
context.commit('setBooks', res.data.data)调用 mutation来修改state
调用格式
在组件中通过this.$store.dispatch('actions的名字', 参数)来调用action
小结
action一般用来发异步请求,数据回来之后,在去调用mutations来保存数据
将ajax请求放在actions中有两个好处:
- 代码得到了进一步封装。将发ajax和保存数据到vuex绑定在一起。
- 逻辑更通顺。如果数据需要保存在Vuex的state中,那从接口处获取数据的操作就定义在Vuex的actions中。
Vuex-用modules来拆分复杂业务
modules的作用
拆分模块,把复杂的场景按模块来拆开
格式
export default new Vuex.Store({
// state: 用来保存所有的公共数据
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
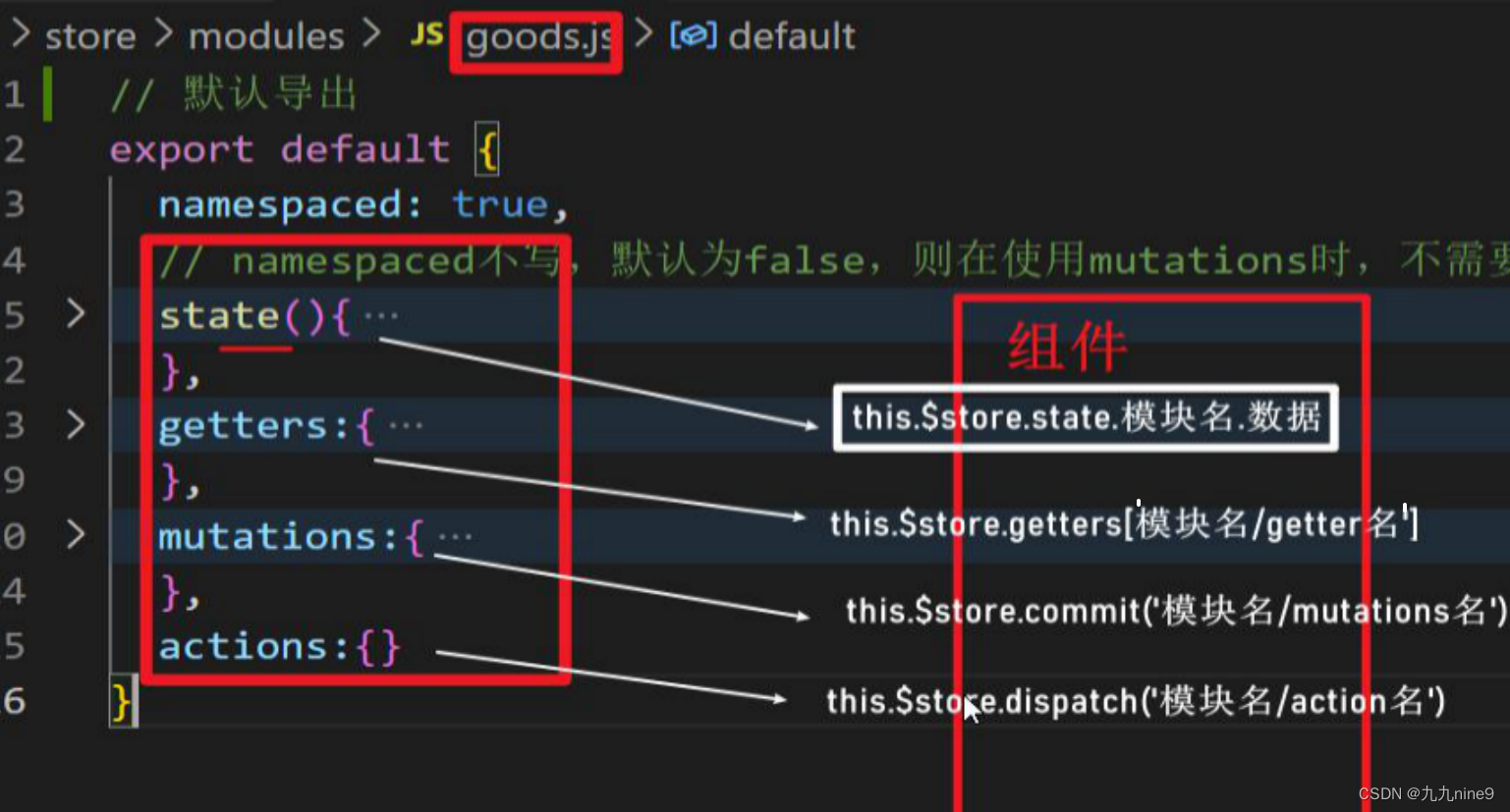
modules: {
模块名1: {
// namespaced为true,则在使用mutations时,就必须要加上模块名
namespaced: true,
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
},
模块名2: {
// namespaced不写,默认为false,则在使用mutations时,不需要加模块名
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
}
}
})
也可以更进一步对文件进行拆分。
|–store /
|------- index.js # 引入模块
|------- modules
|-------------- / mod1.js # 模块1
|-------------- / mod2.js # 模块2
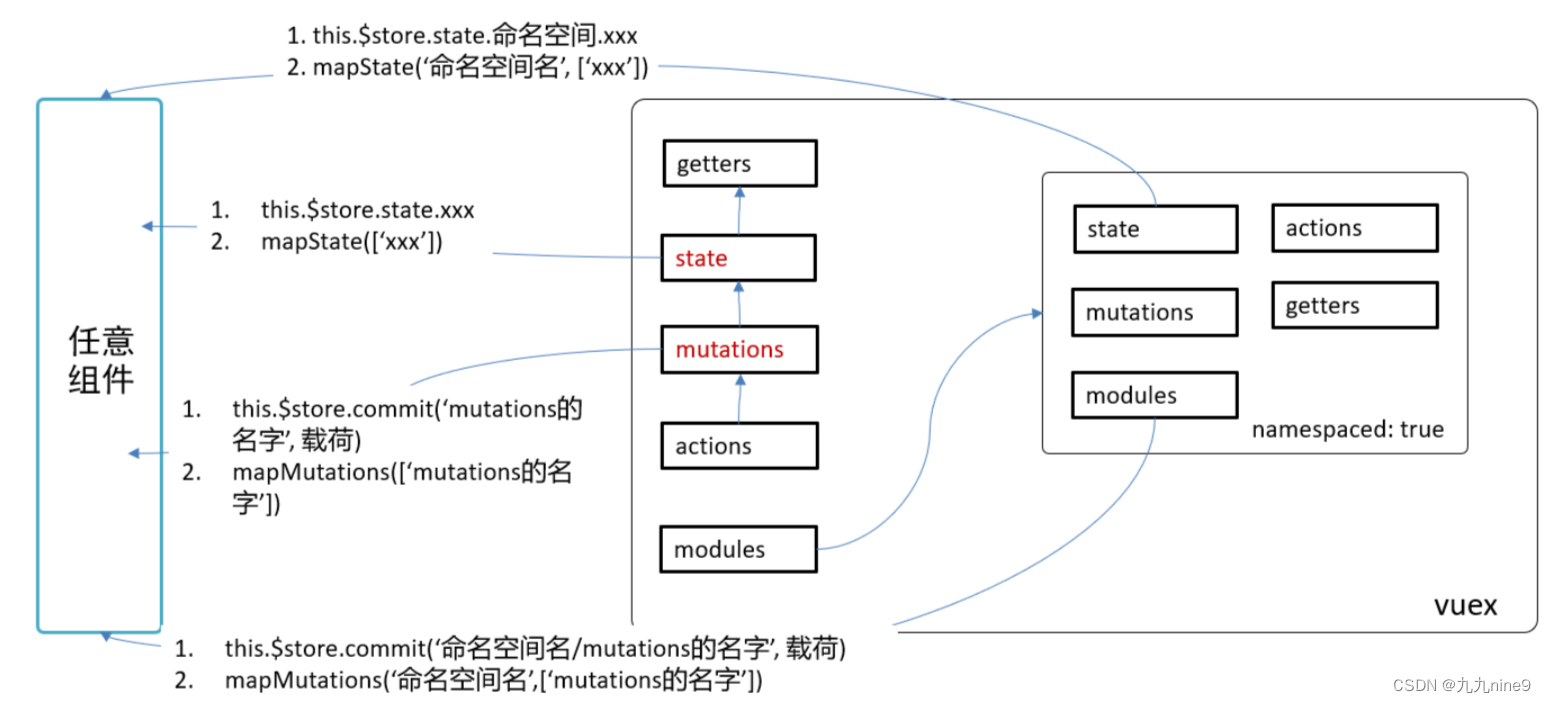
访问数据和修改数据的调整
● 访问模块中的数据,要加上模块名
获取数据项: {{$store.state.模块名.数据项名}}
获取getters: {{$store.getters['模块名/getters名']}}
● 访问模块中的mutations/actions:
○ 如果namespaced为true,则需要额外去补充模块名,一般都要设置namespaced为true
○ 如果namespaced为false,则不需要额外补充模块名
$store.commit('mutations名') // namespaced为false
$store.commit('模块名/mutations名') // namespaced为true
$store.dispatch('actions名') // namespaced为false
$store.dispatch('模块名/actions名') // namespaced为true
小结
使用了modules之后,在访问数据时就要额外添加modules的名字了。
结论: 在使用modules时,建议都给加上namespaced
vuex-用modules之后代码结构优化