决策树原理及实现
一,原理
树模型:
- 决策树:从根节点开始一步步走到叶子节点(决策)
- 所有数据最终都会落到叶子节点,即可以做分类也可以做回归
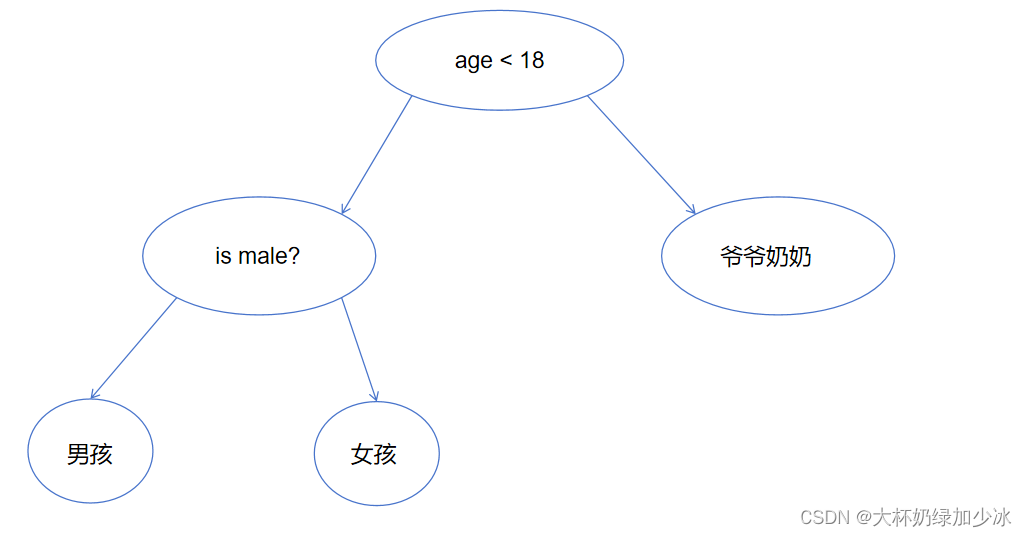
例如:在一个家族当中,我们都有着爸爸妈妈,爷爷奶奶,还有自己的兄弟姐妹,而将这个投射到决策树中,我们能够选取到的特征就有年龄,性别等特征,那我在初始时候,是不是得选择特征值最强的一个作为根节点,然后再向下选择节点。
树的组成:
- 根节点:第一个选择点
- 非叶子节点与分支:中间过程
- 叶子节点:最终的决策结果
决策树的训练与测试:
- 训练阶段:从给定的训练集构造出来一颗树(从根节点开始选取特征)
- 测试阶段:根据构造出来的树模型从上到下去测试一遍
- 一旦构造好了决策树,那么分类或者预测任务就很简单了,只需要走一遍 就可以了,那么难点就在于如何构造出来一颗树,这就没那么容易了,需 要考虑的问题还有很多的!
对节点的切分:
- 对于根节点的选取,最常见的选取特征值最强的作为根节点(一把手),在下面的自然就是二把手,三把手,依次顺延。
衡量标准—熵
首先,我们来了解一下熵的定义:熵是表示随机变量不确定性的度量(解释:说白了就是物体内部的混乱程度,比如杂货市场里面什么都有,那肯定就混乱,例如:去华为专卖店里面是不是就都是买的华为,此时是不是就是趋于稳定,而如果去华强北店,里面是不是啥牌子手机都有呢)
因此,我们可以得出不确定性越大,得到的熵值也就越大。
公式表达就是:
H(X) = - ∑ pi * log pi, i = 1, 2, 3, ...., n
如:A集合[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,2,2], B集合[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,1]
显然我们可以看出A集合的熵值要低,因为A里面只有两种类别,相对稳定一些,而B中类别太多了,熵值就会大很多
如:
数据:14天打球情况
特征:4种环境变化
目标:构造决策树
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sunny | hot | high | FALSE | no |
| sunny | hot | high | TRUE | yes |
| sunny | hot | high | FALSE | no |
| rainy | mild | normal | TRUE | no |
| rainy | mild | high | FALSE | no |
| rainy | mild | normal | TRUE | yes |
| rainy | hot | normal | FALSE | no |
| overcast | hot | normal | FALSE | no |
| overcast | cool | normal | FALSE | yes |
| overcast | cool | high | FALSE | yes |
| sunny | hot | high | TRUE | no |
| sunny | cool | high | TRUE | yes |
| sunny | mild | high | TRUE | no |
| rainy | cool | normal | TRUE | yes |
- 划分方式:4种
- 基于天气的划分
- 基于温度的划分
- 基于湿度的划分
- 基于有风的划分
- 问题:谁当根节点
- 依据:信息增益(表示特征X使得类Y的不确定性减少的程度,分类后的专一性,希望分类后的结果是同类在一起)
如在历史数据中将打球天数和不打球天数计算出一个熵值,在将特征逐一分析该特征下的熵值,最后得出信息增益。
二,代码
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from math import log
import operator
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
def createDataSet():
# 创建数据集
dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']]
labels = ['F1-AGE', 'F2-WORK', 'F3-HOME', 'F4-LOAN']
return dataSet, labels
def createTree(dataset, labels, featLabels):
# 创建决策树
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataset]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
if len(dataset[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel)
myTree = {bestFeatLabel: {}}
del labels[bestFeat]
featValue = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataset]
uniqueVals = set(featValue)
for val in uniqueVals:
sublabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][val] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataset, bestFeat, val), sublabels, featLabels)
return myTree
def majorityCnt(classList):
# 计算多数类
classCount = {}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedclassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedclassCount[0][0]
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset):
# 选择最佳特征进行划分
numFeatures = len(dataset[0]) - 1
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataset)
bestInfoGain = 0
bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [example[i] for example in dataset]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0
for val in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataset, i, val)
prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataset))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature
def splitDataSet(dataset, axis, val):
# 根据特征划分数据集
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataset:
if featVec[axis] == val:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis + 1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
def calcShannonEnt(dataset):
# 计算香农熵
numExamples = len(dataset)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataset:
currentlabel = featVec[-1]
if currentlabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentlabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentlabel] += 1
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prop = float(labelCounts[key]) / numExamples
shannonEnt -= prop * log(prop, 2)
return shannonEnt
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
# 获取叶子节点数
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
# 获取树的深度
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
# 绘制节点
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
# font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:/windows/fonts/simsunb.ttf", size=14)
# font = {'family': 'SimHei', 'size': 12}
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
# 绘制中间文本
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
# 绘制树
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
# 创建绘图窗口
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset, labels = createDataSet()
featLabels = []
myTree = createTree(dataset, labels, featLabels)
createPlot(myTree)