目录
迷宫中离入口最近的出口
题目
思路
使用宽度优先遍历解决这道题,需要一个二维数组标记是否被遍历过,也需要一个队列辅助完成宽度优先遍历,类似于水波纹一样,一层一层的往外扩,如果扩到了矩阵边缘行,则返回步数,就是离入口最近的距离。
代码
class Solution {
int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1};
int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0};
public:
int nearestExit(vector<vector<char>>& maze, vector<int>& entrance) {
int m=maze.size(),n=maze[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m,vector<bool>(n,false));
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
int step=0;
q.push({entrance[0],entrance[1]});
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]]=true;
while(!q.empty()){
int sz=q.size();
step++;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++){
int a=q.front().first;
int b=q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=a+dx[k],y=b+dy[k];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 &&y<n && !vis[x][y] && maze[x][y]=='.'){
if(x==0 || x==m-1 || y==0 || y==n-1)
return step;
q.push({x,y});
vis[x][y]=true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};最小基因变化
题目
思路
其实仔细分析这道题后可以发现,也可以用宽度优先遍历来解决这道题,每一次某位置变化一个字母,就相当于以某位置为起点往外扩了一层,为了便于快速地判断变换后的基因序列是否在基因库中,将基因库中的基因序列存储到哈希表中,同时也需要一个哈希表来标记某些基因序列是否已经变换过,另外也需要一个队列来完成宽度优先遍历的辅助操作。
需要注意的是,在对基因序列的某位置变换前,需保存一下变换前的基因序列,便于变换后再进行恢复还原。
代码
class Solution {
public:
int minMutation(string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank) {
unordered_set<string> vis;
unordered_set<string> hash(bank.begin(),bank.end());
string s="ACGT";
if(startGene==endGene) return 0;
if(!hash.count(endGene)) return -1;
queue<string> q;
q.push(startGene);
vis.insert(startGene);
int ret=0;
while(!q.empty()){
int sz=q.size();
ret++;
for(int k=0;k<sz;k++){
string top=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
string str=top;
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
top[i]=s[j];
if(top==endGene) return ret;
if(!vis.count(top) && hash.count(top))
q.push(top),vis.insert(top);
}
top=str;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};单词接龙
题目
思路
其实这道题和前一道题是类似的,只不过这道题的单词变化范围不再是'A','C','G','T',而是26个英文小写字母,为了快速判断单词是否是字典中的单词,首先将字典中的单词存放到哈希表中,同时也需要一个哈希表标记已经访问过的单词和一个队列来完成宽度优先遍历的辅助操作。
这道题同上一道题一样,进行单词的某位置前需要先保存原始单词,以便变换完单词某位置后进行恢复和还原。
代码
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> vis;
unordered_set<string> hash(wordList.begin(),wordList.end());
if(!hash.count(endWord)) return 0;
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
vis.insert(beginWord);
int ret=1;
while(!q.empty()){
int sz=q.size();
ret++;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++){
string top=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=0;j<beginWord.size();j++){
string str=top;
for(char ch='a';ch<='z';ch++){
top[j]=ch;
if(top==endWord) return ret;
if(!vis.count(top) && hash.count(top))
q.push(top),vis.insert(top);
}
top=str;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};为高尔夫比赛砍树
题目
思路
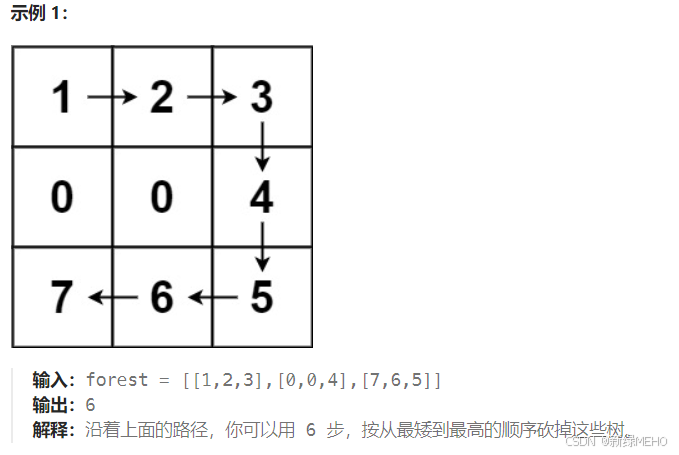
解决这道题也是使用宽度优先遍历来解决,但是题目要求按高度从低到高砍完所有的树,因此需要对砍树的顺序进行排序,然后求出被砍顺序挨着的两个树的最短距离,分别求出这样的被砍顺序挨着的两个树的最短距离,然后加起来,就是按高度从低到高砍完所有树的最短步数,如果某一步不能正常进行,说明无法完成砍树,直接返回-1.
代码
class Solution {
int m,n;
int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0};
int dy[4]={0,0,1,-1};
public:
int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {
m=forest.size(),n=forest[0].size();
vector<pair<int,int>> order;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(forest[i][j]>1)
order.push_back({i,j});
sort(order.begin(),order.end(),[&](const pair<int,int>& p1,const pair<int,int>& p2){
return forest[p1.first][p1.second]<forest[p2.first][p2.second];
});
int bx=0,by=0;
int ret=0;
for(auto& [a,b]:order){
int step=bfs(forest,bx,by,a,b);
if(step==-1) return -1;
ret+=step;
bx=a,by=b;
}
return ret;
}
int bfs(vector<vector<int>>& forest,int bx,int by,int ex,int ey){
if(bx==ex && by==ey) return 0;
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
bool vis[51][51];
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
q.push({bx,by});
vis[bx][by]=true;
int step=0;
while(!q.empty()){
int sz=q.size();
step++;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++){
auto [a,b]=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
int x=a+dx[j],y=b+dy[j];
if(x==ex && y==ey) return step;
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && forest[x][y] && !vis[x][y])
q.push({x,y}),vis[x][y]=true;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};