下面我们来了解线程池的核心参数都有哪些?
- corePoolSize:表示核心线程池的大小。当提交一个任务时,如果当前核心线程池的线程个数没有达到 corePoolSize,则会创建新的线程来执行所提交的任务,即使当前核心线程池有空闲的线程。如果当前核心线程池的线程个数已经达到了 corePoolSize,则不再重新创建线程。如果调用了prestartCoreThread()或者 prestartAllCoreThreads(),线程池创建的时候所有的核心线程都会被创建并且启动。
- maximumPoolSize:表示线程池能创建线程的最大个数。如果当阻塞队列已满时,并且当前线程池线程个数没有超过 maximumPoolSize 的话,就会创建新的线程来执行任务
- keepAliveTime:空闲线程存活时间。如果当前线程池的线程个数已经超过了 corePoolSize,并且线程空闲时间超过了 keepAliveTime 的话,就会将这些空闲线程销毁,这样可以尽可能降低系统资源消耗
- unit:时间单位。为 keepAliveTime 指定时间单位
- workQueue:阻塞队列。用于保存任务的阻塞队列,可以使用ArrayBlockingQueue, LinkedBlockingQueue, SynchronousQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue
- threadFactory:创建线程的工程类。可以通过指定线程工厂为每个创建出来的线程设置更有意义的名字,如果出现并发问题,也方便查找问题原因
- handler:饱和策略。当线程池的阻塞队列已满和指定的线程都已经开启,说明当前线程池已经处于饱和状态了,那么就需要采用一种策略来处理这种情况。采用的策略有这几种:
- AbortPolicy: 直接拒绝所提交的任务,并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常
- CallerRunsPolicy:只用调用者所在的线程来执行任务
- DiscardPolicy:不处理直接丢弃掉任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃掉阻塞队列中存放时间最久的任务,执行当前任务
有兴趣的小伙伴可以看一下我这篇文章: 详述Java线程池实现原理
那么运行当中的线程池可以修改吗?接下来我们就用代码来验证一下是否可以。
int cpuSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
//创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,cpuSize * 4,30,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(200),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
System.out.println("修改之前的线程数:");
System.out.println("核心线程数:" + poolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());
poolExecutor.execute(() -> {
//这里面修改核心线程数
poolExecutor.setCorePoolSize(5);
});
//先休眠一会看打印的结果
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("修改之后线程数:");
System.out.println("核心线程数:" + poolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());
//关闭线程池
poolExecutor.shutdown();
从上面代码的结果可以知道,运行当中的线程可以修改核心线程数。
我们进去看一下 setCorePoolSize 源码是怎么实现的。
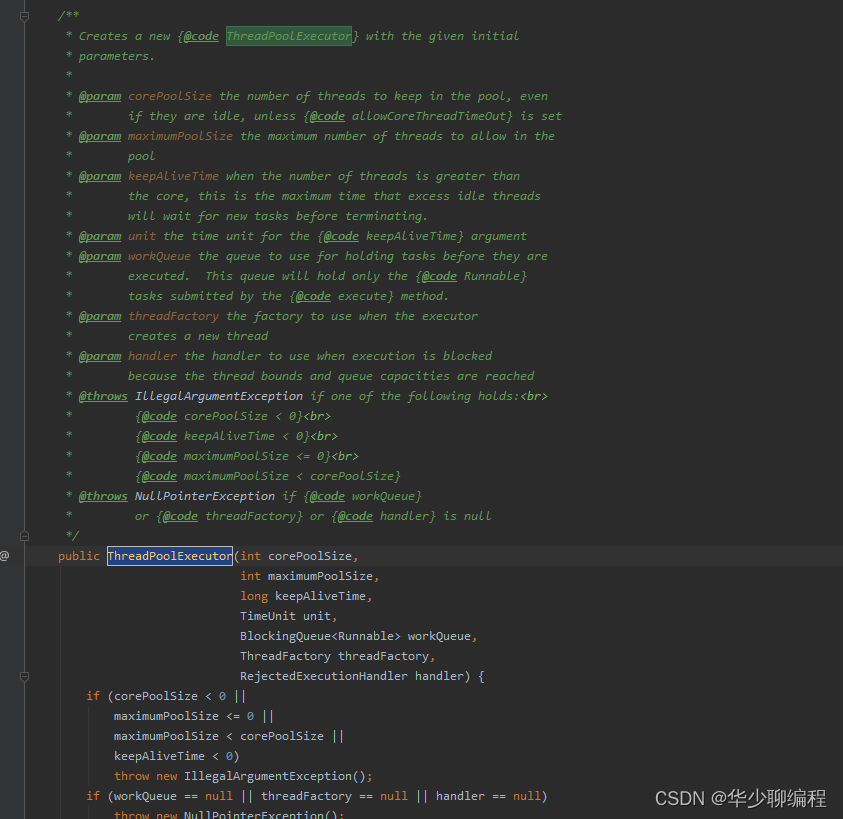
/**
* Sets the core number of threads. This overrides any value set
* in the constructor. If the new value is smaller than the
* current value, excess existing threads will be terminated when
* they next become idle. If larger, new threads will, if needed,
* be started to execute any queued tasks.
*
* @param corePoolSize the new core size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code corePoolSize < 0}
* @see #getCorePoolSize
*/
public void setCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize) {
if (corePoolSize < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//新的核心线程数减去原核心线程数
int delta = corePoolSize - this.corePoolSize;
//新核心线程数赋值
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
//如果当前线程数大于新核心线程数
if (workerCountOf(ctl.get()) > corePoolSize)
//中断空闲线程
interruptIdleWorkers();
//如果需要新增线程则通过 addWorker 增加工作线程
else if (delta > 0) {
// We don't really know how many new threads are "needed".
// As a heuristic, prestart enough new workers (up to new
// core size) to handle the current number of tasks in
// queue, but stop if queue becomes empty while doing so.
int k = Math.min(delta, workQueue.size());
while (k-- > 0 && addWorker(null, true)) {
if (workQueue.isEmpty())
break;
}
}
}
在运行期线程池使用方调用此方法设置 corePoolSize 之后,线程池会直接覆盖原来的 corePoolSize 值,并且基于当前值和原始值的比较结果采取不同的处理策略。
这里有个问题是,每次修改必须重新发布才可以生效,那么有没有方法不用发布就可以动态调整线程池参数呢?当然有了。
我们可以使用 Apollo来实现动态配置 线程池参数。
Apollo 是携程框架部门研发的分布式配置中心,能够集中化管理应用不同环境、不同集群的配置,配置修改后能够实时推送到应用端,并且具备规范的权限、流程治理等特性,适用于微服务配置管理场景。
安装步骤请看这两篇文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34707456/article/details/103702828
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyjblogs/p/14163702.html#apollo搭建
动态配置线程池
现在我们把线程池和 Apollo 结合起来构建动态线程池,具备了上述知识编写起来并不复杂。首先我们用默认值构建一个线程池,然后线程池会监听 Apollo 关于相关配置项,如果相关配置有变化则刷新相关参数。
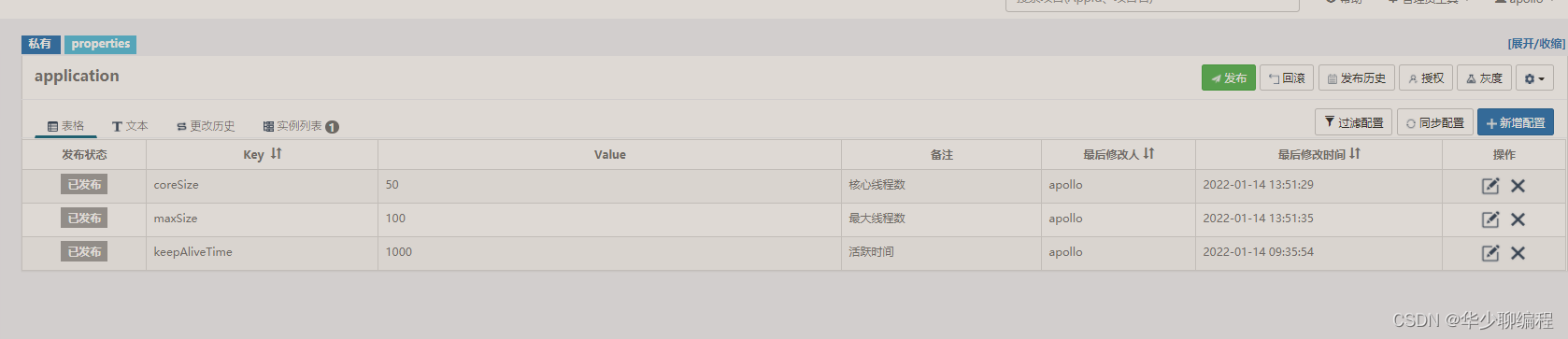
第一步我们先添加线程池对应的参数:
第二步我们编写核心的代码:
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ctrip.framework.apollo</groupId>
<artifactId>apollo-client</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
创建动态线程池执行器 ThreadExecutor 类:
@Configuration
public class ThreadExecutor {
@Resource
private ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory;
public void execute(String bizName, Runnable job) {
threadPoolFactory.getExecutor(bizName).execute(job);
}
public Future<?> sumbit(String bizName, Runnable job) {
return threadPoolFactory.getExecutor(bizName).submit(job);
}
}
配置线程动态类:
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolFactory {
private static final String NAME_SPACE = "Apollo-Test";
/** 线程执行器 **/
private volatile ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
/** 核心线程数 **/
private Integer CORE_SIZE = 10;
/** 最大值线程数 **/
private Integer MAX_SIZE = 20;
/** 等待队列长度 **/
private Integer QUEUE_SIZE = 2000;
/** 线程存活时间 **/
private Long KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 1000L;
public ThreadPoolFactory() {
Config config = ConfigService.getAppConfig();
init(config);
listen(config);
}
/**
* 初始化
*/
private void init(Config config) {
if (executor == null) {
synchronized (ThreadPoolFactory.class) {
if (executor == null) {
String coreSize = config.getProperty(KeysEnum.CORE_SIZE.getNodeKey(), CORE_SIZE.toString());
String maxSize = config.getProperty(KeysEnum.MAX_SIZE.getNodeKey(), MAX_SIZE.toString());
String keepAliveTIme = config.getProperty(KeysEnum.KEEP_ALIVE_TIME.getNodeKey(), KEEP_ALIVE_TIME.toString());
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queueToUse = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(QUEUE_SIZE);
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(Integer.valueOf(coreSize), Integer.valueOf(maxSize), Long.valueOf(keepAliveTIme), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, queueToUse);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 监听器
*/
private void listen(Config config) {
config.addChangeListener(new ConfigChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
System.out.println("命名空间发生变化={}"+changeEvent.getNamespace());
for (String key : changeEvent.changedKeys()) {
ConfigChange change = changeEvent.getChange(key);
String newValue = change.getNewValue();
refreshThreadPool(key, newValue);
System.out.println("发生变化key:"+ change.getPropertyName()+"oldValue:"+change.getOldValue()+"newValue:"+ change.getNewValue()+"changeType:"+ change.getChangeType());
}
}
});
}
/**
* 刷新线程池
*/
private void refreshThreadPool(String key, String newValue) {
if (executor == null) {
return;
}
if (KeysEnum.CORE_SIZE.getNodeKey().equals(key)) {
executor.setCorePoolSize(Integer.valueOf(newValue));
System.out.println("修改核心线程数key:"+key+"value:"+newValue);
}
if (KeysEnum.MAX_SIZE.getNodeKey().equals(key)) {
executor.setMaximumPoolSize(Integer.valueOf(newValue));
System.out.println("修改最大线程数key:"+key+"value:"+newValue);
}
if (KeysEnum.KEEP_ALIVE_TIME.getNodeKey().equals(key)) {
executor.setKeepAliveTime(Integer.valueOf(newValue), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("修改活跃时间key:"+key+"value:"+newValue);
}
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor getExecutor(String threadName) {
return executor;
}
enum KeysEnum {
CORE_SIZE("coreSize", "核心线程数"),
MAX_SIZE("maxSize", "最大线程数"),
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME("keepAliveTime", "线程活跃时间")
;
private String nodeKey;
private String desc;
KeysEnum(String nodeKey, String desc) {
this.nodeKey = nodeKey;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getNodeKey() {
return nodeKey;
}
public void setNodeKey(String nodeKey) {
this.nodeKey = nodeKey;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
}
}
创建 yml 配置
#服务器配置
server:
port: 8083
# apollo配置
app:
id: Apollo-Test
apollo:
bootstrap:
enabled: true
namespaces: application
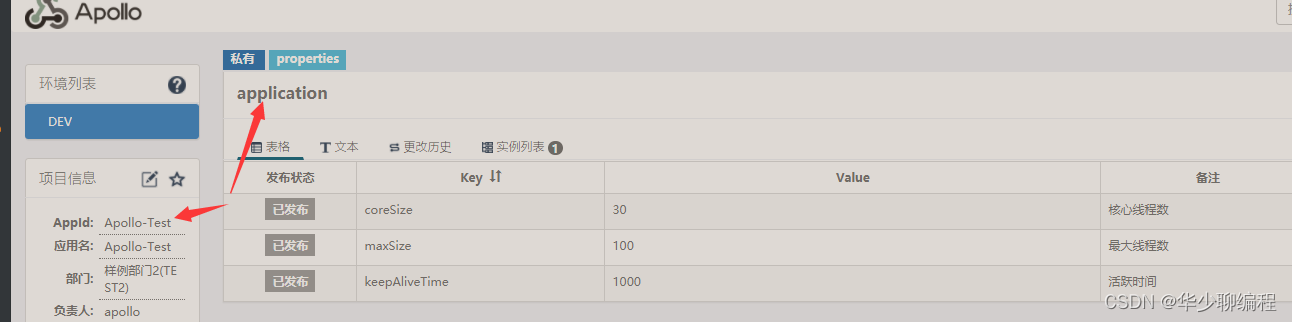
appid 和 namespaces 如下所示:
最后启动线程执行
@SpringBootTest
@EnableApolloConfig
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
private ThreadExecutor threadExecutor;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
threadExecutor.execute("bizName", new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程在执行!");
}
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
}
}
下面我们启动看一下效果:
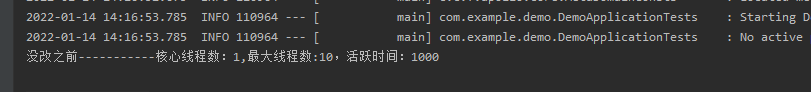
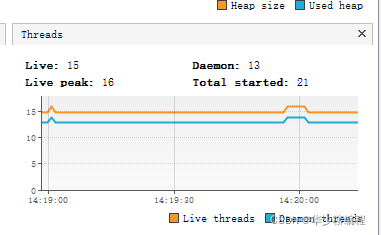
这是没改之前监听到的数据,而且通过 VisualVM 可以观察到线程数如下:
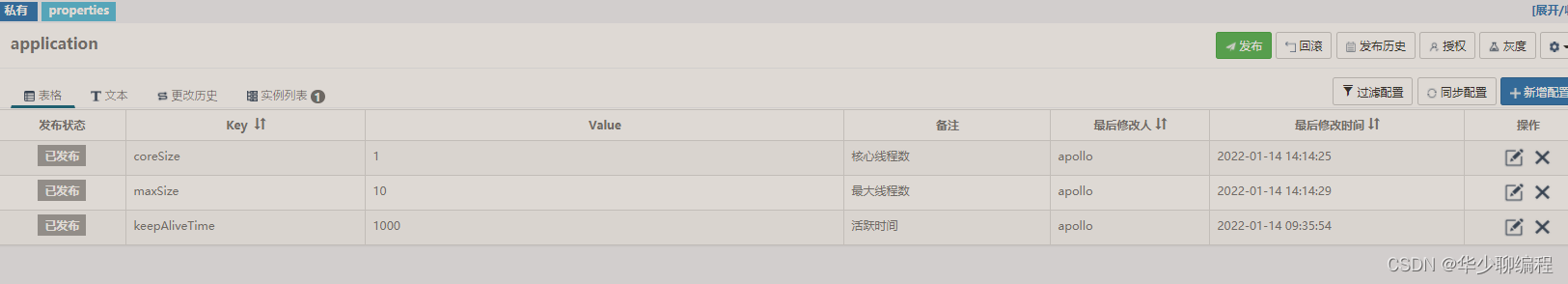
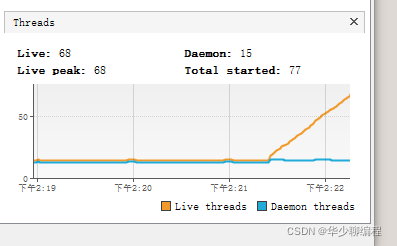
我们在配置中心修改配置项把核心线程数设置为100,最大线程数设置为500:
通过 VisualVM 可以观察到线程数在上升。
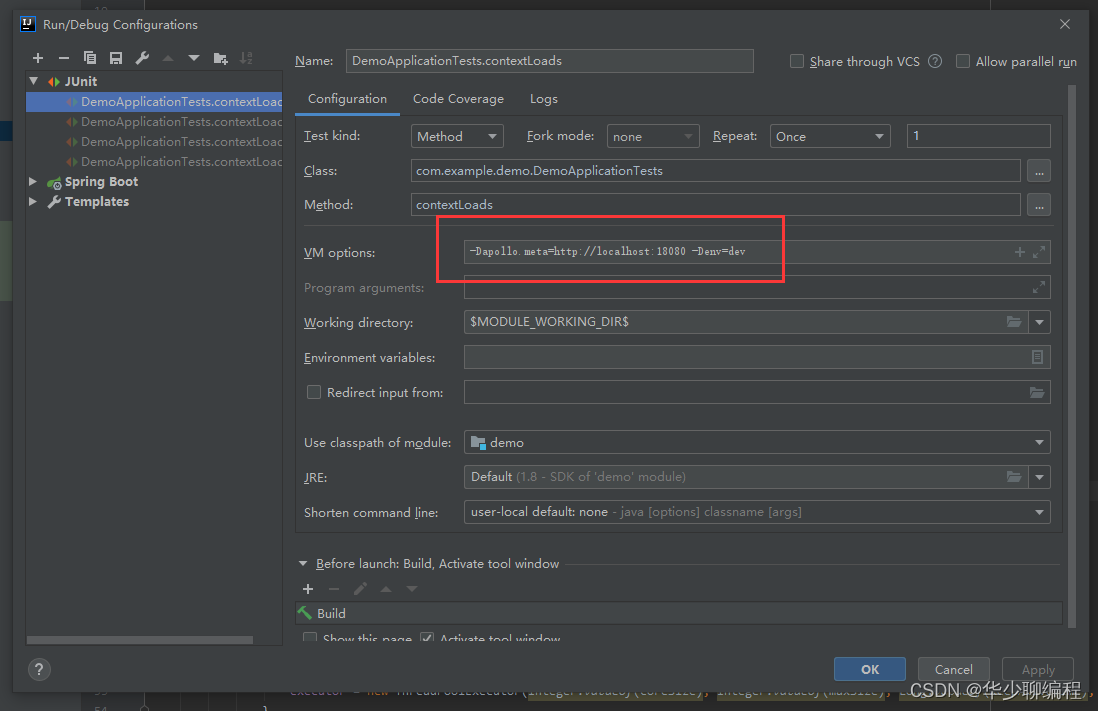
最后,修改配置信息成功立即显示在控制台,我们需要在以下操作一步,添加 -Dapollo.meta=http://localhost:18080 -Denv=dev,18080 这个对应 apollo-configservice 文件中配置的 端口号,不然就算配置了信息服务也获取不到数据。