什么是JUC
Java.util.Concurrent 包
进程和线程
- 区别:一个进程中可以有多个线程执行
- 线程状态
public enum State {
/**
* Thread state for a thread which has not yet started.
*/
NEW,(新建)
/**
* Thread state for a runnable thread. A thread in the runnable
* state is executing in the Java virtual machine but it may
* be waiting for other resources from the operating system
* such as processor.
*/
RUNNABLE,(准备就绪)
/**
* Thread state for a thread blocked waiting for a monitor lock.
* A thread in the blocked state is waiting for a monitor lock
* to enter a synchronized block/method or
* reenter a synchronized block/method after calling
* {@link Object#wait() Object.wait}.
*/
BLOCKED,(阻塞)
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread.
* A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the
* following methods:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Object#wait() Object.wait} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join() Thread.join} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#park() LockSupport.park}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>A thread in the waiting state is waiting for another thread to
* perform a particular action.
*
* For example, a thread that has called <tt>Object.wait()</tt>
* on an object is waiting for another thread to call
* <tt>Object.notify()</tt> or <tt>Object.notifyAll()</tt> on
* that object. A thread that has called <tt>Thread.join()</tt>
* is waiting for a specified thread to terminate.
*/
WAITING,(不见不散)
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time.
* A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of
* the following methods with a specified positive waiting time:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link #sleep Thread.sleep}</li>
* <li>{@link Object#wait(long) Object.wait} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join(long) Thread.join} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkNanos LockSupport.parkNanos}</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkUntil LockSupport.parkUntil}</li>
* </ul>
*/
TIMED_WAITING,(过时不候)
/**
* Thread state for a terminated thread.
* The thread has completed execution.
*/
TERMINATED;(终结)
}
- wait和sleep区别
sleep是Thread的静态方法;wait是Object的方法任何对象实例都可以调用
/**
* Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease
* execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to
* the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers. The thread
* does not lose ownership of any monitors.
*
* @param millis 参数是睡眠的毫秒数
* the length of time to sleep in milliseconds
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the value of {@code millis} is negative
*如果秒数是负的抛出异常
* @throws InterruptedException
* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is
* cleared when this exception is thrown.
*/
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notify()} method or the
* {@link java.lang.Object#notifyAll()} method for this object.
* In other words, this method behaves exactly as if it simply
* performs the call {@code wait(0)}.
* <p>
* The current thread must own this object's monitor. The thread
* releases ownership of this monitor and waits until another thread
* notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor to wake up
* either through a call to the {@code notify} method or the
* {@code notifyAll} method. The thread then waits until it can
* re-obtain ownership of the monitor and resumes execution.
* <p>
* As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are
* possible, and this method should always be used in a loop:
* <pre>
* synchronized (obj) {
* while (<condition does not hold>)
* obj.wait();
* ... // Perform action appropriate to condition
* }
* </pre>
* This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner
* of this object's monitor. See the {@code notify} method for a
* description of the ways in which a thread can become the owner of
* a monitor.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread is not
* the owner of the object's monitor.
* @throws InterruptedException if any thread interrupted the
* current thread before or while the current thread
* was waiting for a notification. The <i>interrupted
* status</i> of the current thread is cleared when
* this exception is thrown.
* @see java.lang.Object#notify()
* @see java.lang.Object#notifyAll()
*/
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {
wait(0);
}
sleep不会释放锁,也不需要占用锁;wait会释放锁,当被notify时
都可以被interrupted方法中断
4. 管程,就是Monitor监视器,也被称为锁。是一种同步机制,保证同一时间,只有一个线程访问被保护的数据或者代码。JVM中同步进入和退出都是基于管程对象实现的
5. 用户线程和守护线程
用户线程:自定义线程
守护线程:比如垃圾回收
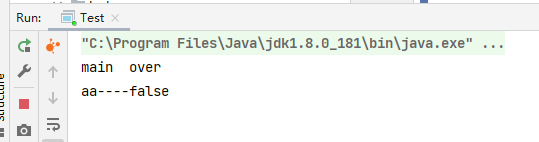
示例:主线程结束了,用户线程还在运行,jvm存活
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----" + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
while(true){
}
},"aa");
thread.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" over");
}
}
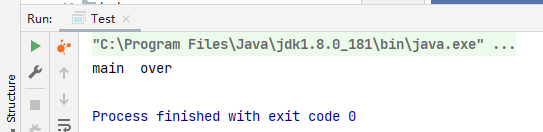
示例: 没有用户线程了,都是守护线程,jvm结束
package com.example.juclearn;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----" + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
while(true){
}
},"aa");
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" over");
}
}
========================= Lock接口 ==============================
Synchronized关键字
- 修饰一个代码块,被修饰的代码块称为同步语句块,作用范围是{}括起来的代码,作用对象是调用这个代码块的对象
- 修饰一个方法,被修饰的方法成为同步方法,作用范围是整个方法,作用对象是调用这个方法的对象。synchronized关键字不能被继承
- 修饰一个静态的方法,作用范围是整个静态方法,作用的对象是这个类的所有对象
- 修饰一个类,作用范围是synchronized后面括号括起来的部分,作用的对象是这个类的所有对象
Synchronized实现卖票例子
package com.example.juclearn;
/**
* 多线程编程实现卖票例子 3个售货员卖30张票
*/
/**
* 第一步,创建资源类,在类中创建属性和操作方法
*/
class Ticket{
private int number = 30;
/**
* 售票方法
*/
public synchronized void sale(){
if (number > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖第"+ (30-number--+1) +"张票,还剩" + number + "张");
}
}
}
public class TestSynchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
// 创建多个线程 调用资源类的方法
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++){
ticket.sale();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++){
ticket.sale();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++){
ticket.sale();
}
}
}, "CC").start();
}
}
Lock接口
- 实现了比使用synchronized方法和语句可获得的更广泛的锁定操作
- 实现类有ReentrantLock(可重入锁)、ReentrantreadWriteLock.ReadLock、ReentrantreadWriteLock.WriteLock
- Lock 和Synchronized区别
Lock不是Java语言内置的,是一个类;Synchronized是Java语言的关键字,是内置的
synchronized不需要用户手动释放锁;Lock必须手动释放锁,否则会出现死锁
Lock可以让等待锁的线程响应中断;Synchronized会让等待的线程一直等待下去
Lock可以得知有没有获得锁;Synchronized不能
Lock可以提高多个线程进行读操作的效率
package com.example.juclearn.lock;
/**
* 多线程编程实现卖票例子 3个售货员卖30张票
*/
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 第一步,创建资源类,在类中创建属性和操作方法
*/
class Ticket{
private int number = 30;
private final ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* 售票方法
*/
public void sale(){
reentrantLock.lock();
try {
if (number > 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖第"+ (30-number--+1) +"张票,还剩" + number + "张");
}
}finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建多个线程 调用资源类的方法
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
},"CC").start();
}
}
注:start方法最终调用的本地方法,何时调用由操作系统决定
========================= 线程间通信 ============================
多线程编程步骤:
1 创建资源类,创建属性和方法
2 在资源类中判断、干活、通知(新增)
3 创建多个线程,调用资源类的操作方法
Synchronized实现案例
实例:有两个线程其中一个线程实现对值 +1,另一个线程实现对值 -1
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
class Share {
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if (number != 0){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if (number != 1){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadComDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
}
}
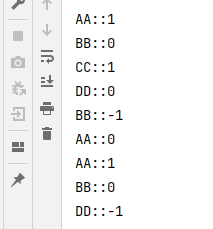
上述代码只有两个线程,当有四个线程时会存在问题,代码如下
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
class Share {
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if (number != 0){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if (number != 1){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadComDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"CC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"DD").start();
}
}
原因:wait和notify 实现中断和虚假唤醒是有可能的,而且此方法应始终在循环中使用
改进:wait在哪里睡在哪里醒,必须要放在循环里才会再次判断
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
class Share {
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void incr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
while (number != 0){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decr() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
while (number != 1){
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ThreadComDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"CC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"DD").start();
}
}
Lock实现案例
package com.example.juclearn.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class Share{
private int number = 0;
// 创建可重人锁
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 得到Condition对象
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void incr() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 0){
condition.await();
}
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
condition.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decr() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 1){
condition.await();
}
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + number);
condition.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ThreadComDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Share share = new Share();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.incr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"CC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
share.decr();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"DD").start();
}
}
===================== 线程间定制化通信 ===========================
实现功能:启动三个线程,按照如下要求
AA打印2次,BB打印3次,CC打印4次
AA打印2次,BB打印3次,CC打印4次
AA打印2次,BB打印3次,CC打印4次
…
进行10轮
package com.example.juclearn.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class ShareResource{
private int flag = 1;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
public void print2(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 1){
condition1.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"第"+loop+"次");
}
// 修改标志位
flag = 2;
// 通知BB线程
condition2.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print3(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 2){
condition2.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"第"+loop+"次");
}
flag = 3;
// 通知CC线程
condition3.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print4(int loop) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 3){
condition3.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"第"+loop+"次");
}
flag = 1;
// 通知AA线程
condition1.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ThreadCusComDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareResource.print2(i+1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareResource.print3(i+1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareResource.print4(i+1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"CC").start();
}
}
======================= 集合的线程安全 =========================
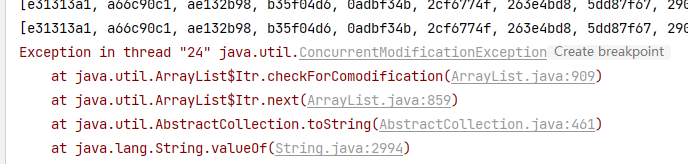
ArrayList的线程不安全及解决方式
ArrayList的 add 方法源码,没有加Synchronized 表明方法是线程不安全的
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
package com.example.juclearn.collectionsafe;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
public class ArrayListSafe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 解决方法1 Vector
// List<String> list = new Vector<>();
// 解决方法2 Collections
// List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
// 解决方式3 CopyOnWriteArrayList
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,8);
list.add(key);
System.out.println(list);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
HashSet线程不安全及解决方案
package com.example.juclearn.collectionsafe;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
public class HashSetSafe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
// 解决方案 使用
Set<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,8);
set.add(key);
System.out.println(set);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
HashMap线程不安全及解决方案
package com.example.juclearn.collectionsafe;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class HashMapSafe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
// 解决方案 使用ConcurrentHashMap
Map<String,String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
String key = String.valueOf(i);
new Thread(()->{
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,8);
map.put(key,value);
System.out.println(map);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
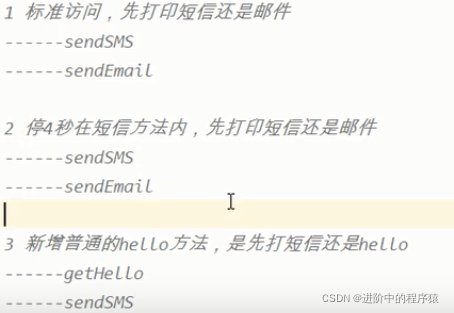
==================== Synchronized 锁的八种情况======================
Synchronized的具体表现形式
- 普通同步方法,锁的是当前对象的实例【相当于是房间门】
- 静态同步方法,锁的是当前类的Class对象(字节码文件)【相当于是单元门】
- 同步方法块,锁的是Synchronized括号里配置的对象
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class Phone{
public static synchronized void senSMS() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println("--sendSMS---");
}
public synchronized void sendEmail(){
System.out.println("---sendEmail---");
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("sayHello---");
}
}
public class EightTypeForSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
Phone phone2 = new Phone();
new Thread(()->{
try {
phone.senSMS();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"AA").start();
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone2.sendEmail();
},"BB").start();
}
}
公平锁和非公平锁
非公平锁:会出现线程饿死情况,效率高
公平锁:效率低
源码
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
* 默认是非公平锁
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
* given fairness policy.
*
* @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy
* 如果参数是true 表明创建的是公平锁
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
公平锁源码
/**
* Sync object for fair locks
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
非公平锁源码
/**
* Sync object for non-fair locks
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
可重入锁
- Synchronized证明可重入锁。可重入锁理解起来相当于我们打开了房间大门,剩下房间内部的所有门都可以随意进入。
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
public class SyncForReentrantLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "外层");
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "中层");
synchronized (o) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "内层");
}
}
}
},"AA").start();
}
}
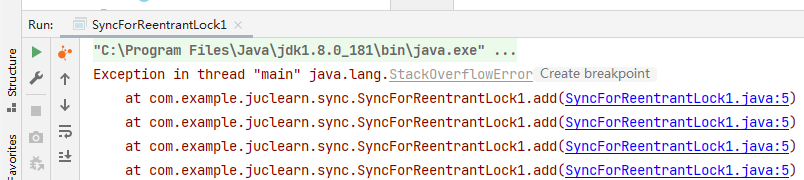
synchronized修饰的方法可以递归调用,导致StackOverFlow
package com.example.juclearn.sync;
public class SyncForReentrantLock1 {
public synchronized void add() {
add();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SyncForReentrantLock1 syncForReentrantLock1 = new SyncForReentrantLock1();
syncForReentrantLock1.add();
}
}
- Lock证明可重入锁
package com.example.juclearn.lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class LockForReentrantLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
try{
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "外层");
try {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "内层");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
死锁
- 定义:两个或两个以上线程在执行过程中,因为争夺资源而造成的一种互相等待的现象,如果没有外力干涉,无法再执行下去。
- 产生原因:
系统资源不足
进程运行推进顺序不合适
资源分配不当
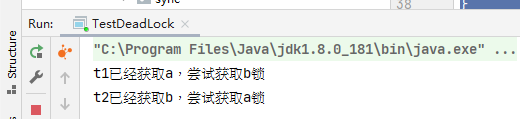
package com.example.juclearn.deadlock;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object a = new Object();
Object b = new Object();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (a) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已经获取a,尝试获取b锁");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (b){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已经获取b锁");
}
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (b) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已经获取b,尝试获取a锁");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (a){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"已经获取a锁");
}
}
},"t2").start();
}
}
- 验证是否是死锁:jps + jstack
E:\juc>jstack 9408
2022-04-17 12:33:17
Full thread dump Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (25.181-b13 mixed mode):
"DestroyJavaVM" #13 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000212a800 nid=0x24dc waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"t2" #12 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000a9f9800 nid=0x1904 waiting for monitor entry [0x000000000b4ff000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock.lambda$main$1(TestDeadLock.java:33)
- waiting to lock <0x00000000d5ed4fe8> (a java.lang.Object)
- locked <0x00000000d5ed4ff8> (a java.lang.Object)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock$$Lambda$2/883049899.run(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"t1" #11 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000a9f7800 nid=0x21a4 waiting for monitor entry [0x000000000b3ae000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock.lambda$main$0(TestDeadLock.java:19)
- waiting to lock <0x00000000d5ed4ff8> (a java.lang.Object)
- locked <0x00000000d5ed4fe8> (a java.lang.Object)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock$$Lambda$1/495053715.run(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"Service Thread" #10 daemon prio=9 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000999b800 nid=0x1174 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C1 CompilerThread2" #9 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000000990e000 nid=0x24e8 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread1" #8 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000000990d800 nid=0x7fc waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread0" #7 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000000990c800 nid=0x2668 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Monitor Ctrl-Break" #6 daemon prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00000000098e8000 nid=0x226c runnable [0x000000000a15f000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead0(Native Method)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead(SocketInputStream.java:116)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:171)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:141)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.readBytes(StreamDecoder.java:284)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.implRead(StreamDecoder.java:326)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.read(StreamDecoder.java:178)
- locked <0x00000000d5f365a8> (a java.io.InputStreamReader)
at java.io.InputStreamReader.read(InputStreamReader.java:184)
at java.io.BufferedReader.fill(BufferedReader.java:161)
at java.io.BufferedReader.readLine(BufferedReader.java:324)
- locked <0x00000000d5f365a8> (a java.io.InputStreamReader)
at java.io.BufferedReader.readLine(BufferedReader.java:389)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMainV2$1.run(AppMainV2.java:48)
"Attach Listener" #5 daemon prio=5 os_prio=2 tid=0x00000000097c2800 nid=0x2014 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Signal Dispatcher" #4 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000008377000 nid=0x1a6c runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Finalizer" #3 daemon prio=8 os_prio=1 tid=0x0000000008360000 nid=0x24a8 in Object.wait() [0x00000000097ae000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x00000000d5d08ed0> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:144)
- locked <0x00000000d5d08ed0> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:165)
at java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread.run(Finalizer.java:216)
"Reference Handler" #2 daemon prio=10 os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000008319000 nid=0x253c in Object.wait() [0x000000000959f000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x00000000d5d06bf8> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Object.java:502)
at java.lang.ref.Reference.tryHandlePending(Reference.java:191)
- locked <0x00000000d5d06bf8> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler.run(Reference.java:153)
"VM Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x000000000830d800 nid=0x998 runnable
"GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000213f000 nid=0x2628 runnable
"GC task thread#1 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002141000 nid=0x7c4 runnable
"GC task thread#2 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002142800 nid=0x1948 runnable
"GC task thread#3 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002144000 nid=0x25f0 runnable
"VM Periodic Task Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x000000000999e000 nid=0x24a0 waiting on condition
JNI global references: 316
Found one Java-level deadlock:
=============================
"t2":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000000000835cd98 (object 0x00000000d5ed4fe8, a java.lang.Object),
which is held by "t1"
"t1":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000000000835f418 (object 0x00000000d5ed4ff8, a java.lang.Object),
which is held by "t2"
Java stack information for the threads listed above:
===================================================
"t2":
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock.lambda$main$1(TestDeadLock.java:33)
- waiting to lock <0x00000000d5ed4fe8> (a java.lang.Object)
- locked <0x00000000d5ed4ff8> (a java.lang.Object)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock$$Lambda$2/883049899.run(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"t1":
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock.lambda$main$0(TestDeadLock.java:19)
- waiting to lock <0x00000000d5ed4ff8> (a java.lang.Object)
- locked <0x00000000d5ed4fe8> (a java.lang.Object)
at com.example.juclearn.deadlock.TestDeadLock$$Lambda$1/495053715.run(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
Found 1 deadlock.