简介
react-native-swiper是基于ScrollView封装的swiper组件,用于图片滑动展示、轮播图等场景。具体示例详见react-native-swiper。
核心功能
react-native-swiper实现了三大核心功能:分页、循环滚动、自动播放。
核心原理
分页
分页功能其实是由android和ios实现的,通过pagingEnable这个props来控制是否开启分页,当值为true时开启,如果用户不手动设置为false,react-native-swiper默认传入true。
循环滚动
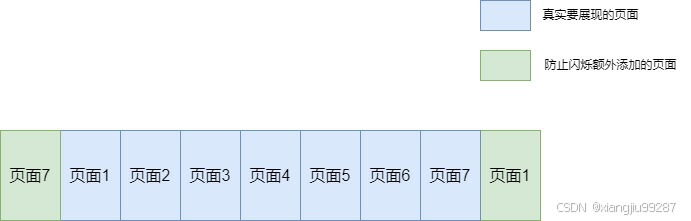
可以预想,在现有的ScrollView中我们无法实现从最后一页到第一页的滚动,所以react-native-swiper在最后一页后额外增加了第一页的内容;同理,为了实现从第一页到最后一页的滚动,在第一页前额外增加了最后一页的内容。
像这种跟视图展现相关的代码我们在render中可以看到。
render() {
...
if (total > 1) {
// Re-design a loop model for avoid img flickering
pages = Object.keys(children)
if (loop) {
pages.unshift(total - 1 + '')
pages.push('0')
}
...
}
...
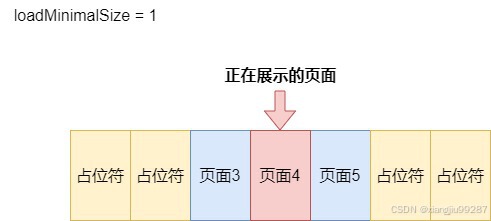
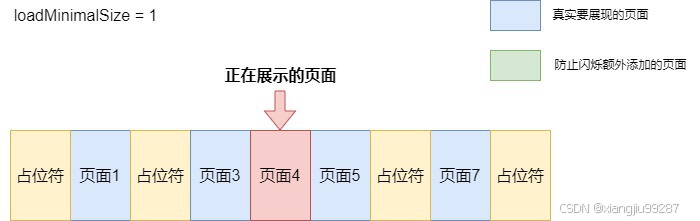
}值得一提的是,为了优化性能,react-native-swiper还支持最小化加载。当我们传入loadMinimal: true时,只会加载视口页面和前后各1 loadMinimalSize大小的页面,其他页面用占位符来代替,loadMinimalSize默认为1。
如果开启了循环滚动,那么真实的第一页和最后一页将始终被渲染,后续会介绍原因。
相关代码。
if (
(i >= index + loopVal - loadMinimalSize &&
i <= index + loopVal + loadMinimalSize) ||
// The real first swiper should be keep
(loop && i === 1) ||
// The real last swiper should be keep
// 这里作者应该是写错了,等号右边应该是total
(loop && i === total - 1)
) {
return (
<View style={pageStyle} key={i}>
{children[page]}
</View>
)
}以上的逻辑涉及到两个问题。
1. 启用了最小化加载,实际加载的页面和index有关,那么,在滚动的过程中需要维护index。
2. 首尾各新增了一页,那么用户在滚动到额外增加的页面时,我们需要手动将其挪到对应的真实页面。
先来解决第一个问题,index应该和视口可见的图片下标保持同步,而视口的切换是由于滑动这个行为导致的,所以应该在滑动结束后更新下标。
根据render函数的返回值可以找到渲染scrollView的方法renderScrollView。
return (
<View style={[styles.container, containerStyle]} onLayout={this.onLayout}>
{this.renderScrollView(pages)}
{showsPagination &&
(renderPagination
? renderPagination(index, total, this)
: this.renderPagination())}
{this.renderTitle()}
{showsButtons && this.renderButtons()}
</View>
)在renderScrollView中我们可以找到动画结束后触发的回调函数this.onScrollEnd。
renderScrollView = pages => {
return (
<ScrollView
ref={this.refScrollView}
{...this.props}
{...this.scrollViewPropOverrides()}
contentContainerStyle={[styles.wrapperIOS, this.props.style]}
contentOffset={this.state.offset}
onScrollBeginDrag={this.onScrollBegin}
onMomentumScrollEnd={this.onScrollEnd}
onScrollEndDrag={this.onScrollEndDrag}
style={this.props.scrollViewStyle}
>
{pages}
</ScrollView>
)在onScrollEnd这个方法中,我们可以看到他核心就是调用了三个方法。
updateIndex:更新index(对应第一个问题)
autoplay:自动播放
loopJump: 当滚动到额外增加的页面时,手动将其挪动到对应的真实页面(对应第二个问题)
onScrollEnd = e => {
...
this.updateIndex(e.nativeEvent.contentOffset, this.state.dir, () => {
this.autoplay()
this.loopJump()
})
...
}先来看一下updateIndex的逻辑。
通过新旧offset相减算出是左滑还是右滑,再除以元素的宽度,得到下标是+1还是-1。由于快速连续滑动可能导致计算不准确,所以这里调用了parseInt和Math.round以保证正确性。
在算出新的index后,调用setState进行更新,setState会引起重新渲染。
updateIndex = (offset, dir, cb) => {
...
// offset记录的是最新的位置
// this.internals.offset记录的是旧有位置
const diff = offset[dir] - (this.internals.offset[dir] || 0)
const step = dir === 'x' ? state.width : state.height
let loopJump = false
// Do nothing if offset no change.
if (!diff) return
// Note: if touch very very quickly and continuous,
// the variation of `index` more than 1.
// parseInt() ensures it's always an integer
index = parseInt(index + Math.round(diff / step))
if (this.props.loop) {
// index记录的是真实页面的下标,不包括额外增加的页面
// index <= -1代表从第一页滚动到了最后一页
if (index <= -1) {
// 所以在这里我们把下标更新为真实页面的最后一页
index = state.total - 1
offset[dir] = step * state.total
loopJump = true
} else if (index >= state.total) {
// 同理,这里发生的是从最后一页滚动到了第一页
index = 0
offset[dir] = step
loopJump = true
}
}
const newState = {}
newState.index = index
newState.loopJump = loopJump
this.internals.offset = offset
// only update offset in state if loopJump is true
if (loopJump) {
// 以下是处理loopJump的代码,我认为作用是和下面的loopJump方法一致的
// 以下代码的触发时间比loopJump方法早,滚动体验会更流畅,我认为loopJump方法是冗余的
// 不知道为什么要将同样的功能实现两遍,可能是为了健壮性吧
if (offset[dir] === this.internals.offset[dir]) {
newState.offset = { x: 0, y: 0 }
newState.offset[dir] = offset[dir] + 1
this.setState(newState, () => {
this.setState({ offset: offset }, cb)
})
} else {
newState.offset = offset
this.setState(newState, cb)
}
} else {
this.setState(newState, cb)
}
}将上面处理loopjump的代码摘出来单独说一下。
由于在上文已经赋值this.internals.offset = offset,所以我认为在loopJump为true时,只会走到以下分支。
newState.offset = { x: 0, y: 0 }
newState.offset[dir] = offset[dir] + 1
this.setState(newState, () => {
this.setState({ offset: offset }, cb)
})那么为何要将offset存入state呢?
其实就是因为我们可以通过修改contentOffset实现无动画跳转,由额外增加的页面跳转到对应的真实页面。由于这个跳转的速度是非常快的,所以我们要保证滚动到的第一页或最后一页一定是已经渲染好的,这里就说明了为什么在开启了loadMinimal时,真实的第一页和最后一页始终被渲染。
renderScrollView = pages => {
return (
<ScrollView
...
contentOffset={this.state.offset}
...
>
{pages}
</ScrollView>
)
}那么为什么要将offset先+1再-1呢?因为state中offset不是实时更新的,只有在onLayout和发生了loopJump才会更新,我们第一次发生loopJump和第二次发生loopJump的offset是一致的,两次传入一样的offset不会触发滚动(这个应该是anroid和ios上的实现逻辑)。
再来看一下loopJump的逻辑。
核心逻辑就是直接调用scrollTo方法,在禁用动画的情况下将其滚动到对应位置。
loopJump = () => {
// 未发生循环跳转,直接返回
if (!this.state.loopJump) return
// 其实可以不用判断this.props.loop,因为如果loop为false根本无法进行循环跳转
const i = this.state.index + (this.props.loop ? 1 : 0)
const scrollView = this.scrollView
this.loopJumpTimer = setTimeout(
() => {
// 历史原因,曾经在anroid端是基于ViewPagerAndroid做的封装
if (scrollView.setPageWithoutAnimation) {
scrollView.setPageWithoutAnimation(i)
} else {
if (this.state.index === 0) {
// 粗暴的滚动,禁用动画,其实会出现一下闪屏,体验不是很好
scrollView.scrollTo(
this.props.horizontal === false
? { x: 0, y: this.state.height, animated: false }
: { x: this.state.width, y: 0, animated: false }
)
} else if (this.state.index === this.state.total - 1) {
this.props.horizontal === false
? this.scrollView.scrollTo({
x: 0,
y: this.state.height * this.state.total,
animated: false
})
: this.scrollView.scrollTo({
x: this.state.width * this.state.total,
y: 0,
animated: false
})
}
}
},
// Important Parameter
// ViewPager 50ms, ScrollView 300ms
scrollView.setPageWithoutAnimation ? 50 : 300
)
}自动播放
autoplay主要就是判断是否满足自动滚动的条件,满足则调用scrollBy方法。
autoplay = () => {
if (
// 无法自动播放的情况
// 1. 只有一个页面
// 2. 未开启自动播放
// 3. 正在滚动
// 4. 不能循环滚动 且 自动滚动方向向前且当前处于第一页 || 自动滚动方向向后且当前处于最后一页
!Array.isArray(this.state.children) ||
!this.props.autoplay ||
this.internals.isScrolling ||
this.state.autoplayEnd
)
return
this.autoplayTimer && clearTimeout(this.autoplayTimer)
this.autoplayTimer = setTimeout(() => {
// 以上所说的第四种情况
if (
!this.props.loop &&
(this.props.autoplayDirection
? this.state.index === this.state.total - 1
: this.state.index === 0)
)
return this.setState({ autoplayEnd: true })
// 核心方法
this.scrollBy(this.props.autoplayDirection ? 1 : -1)
}, this.props.autoplayTimeout * 1000)
}scrollBy方法其实就是调用了ScrollView的scrollTo方法,在启用动画的情况下滚动到下一页/上一页。
scrollBy = (index, animated = true) => {
if (this.internals.isScrolling || this.state.total < 2) return
const state = this.state
const diff = (this.props.loop ? 1 : 0) + index + this.state.index
let x = 0
let y = 0
if (state.dir === 'x') x = diff * state.width
if (state.dir === 'y') y = diff * state.height
this.scrollView && this.scrollView.scrollTo({ x, y, animated })
// update scroll state
this.internals.isScrolling = true
this.setState({
autoplayEnd: false
})
...
}总结
react-native-swiper虽然自称是the best swiper for react native,但其实在轮播的时候会有明显的闪屏,快速滑动的时候也会存在active dot和active page不同步的问题。此外,源码在逻辑上也存在一些错误和死代码(如果我没理解错的话)。如果有swiper的更佳实践,还请大家留言呀~