单一坐标解析
上一节我们调用getRayIntersection方法获取了射线与场景的交点,其原理是先根据离屏相机进行一次离屏渲染,将结果写入到深度图纹理中,渲染结束后从深度图纹理中获取深度,然后根据深度值计算距离,最后根据距离计算坐标值,坐标值计算关键代码如下
const pickDepth = picking.getPickDepth(scene, i);
const depth = pickDepth.getDepth(context, 0, 0);
if (!defined(depth)) {
continue;
}
if (depth > 0.0 && depth < 1.0) {
const renderedFrustum = frustumCommandsList[i];
const near =
renderedFrustum.near *
(i !== 0 ? scene.opaqueFrustumNearOffset : 1.0);
const far = renderedFrustum.far;
const distance = near + depth * (far - near);
position = Ray.getPoint(ray, distance);
break;
}
其中最关键的就是getDepth方法,通过该方法获取到像素对应的深度值,然后根据深度值转为世界坐标值。因为是用于计算射线交点,所以只有一个坐标值,此时的深度纹理大小为 1x1,我们并没有直接设置这张深度图的大小,因为它会根据视口大小进行更新,默认的视口大小为1x1。
批量坐标解析
getRayIntersection方法用于拾取射线与场景的交点,所以只有一个结果值。而我们使用深度图是希望能批量获取点的高程值,所以我们需要对该方法进行一下修改,以达到我们的期望效果。
自定义离屏相机
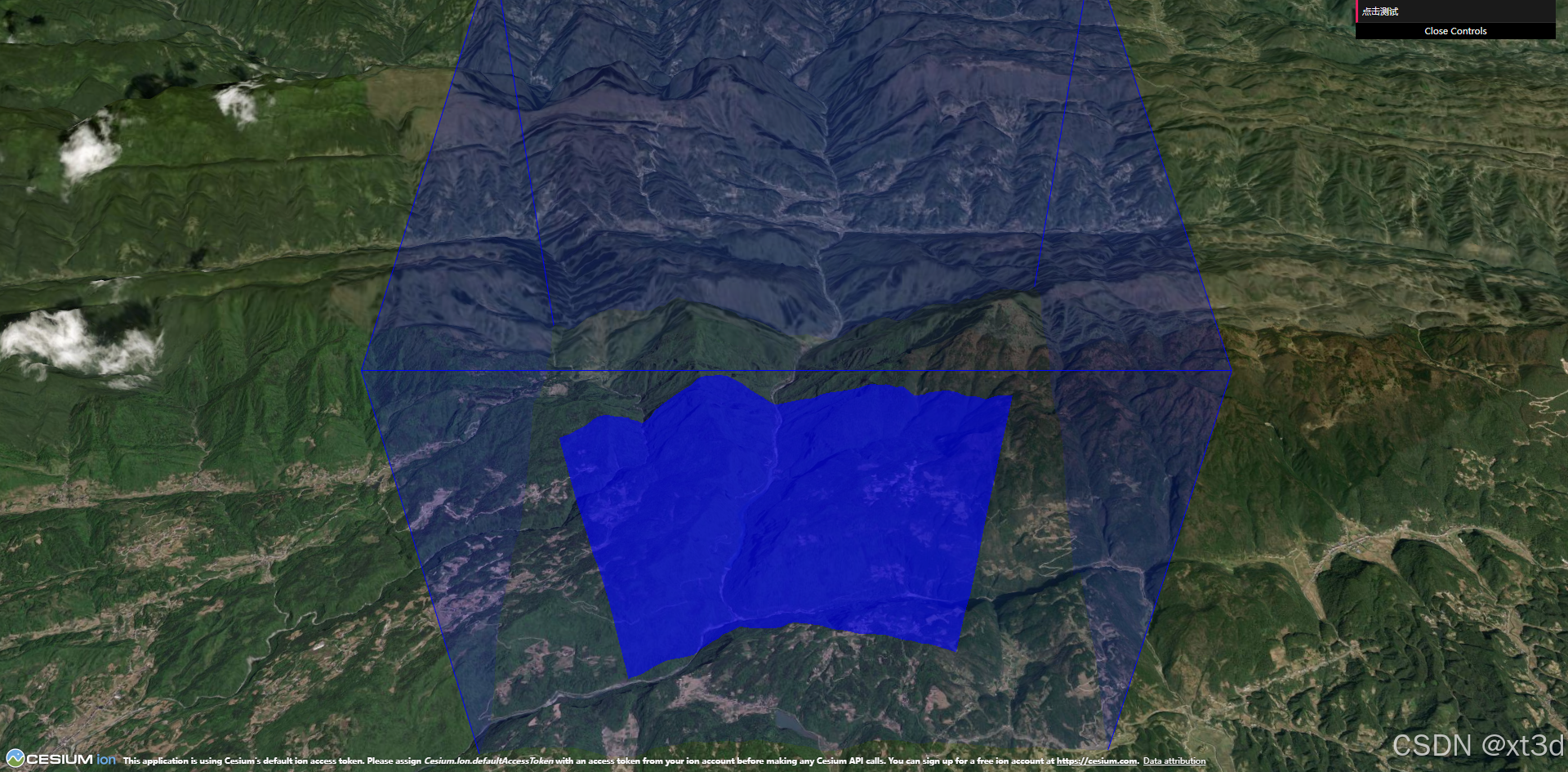
假定研究区域范围如下
let positions = [[110.91841340334987, 30.00563553427726, 852.0091102852589], [110.89473055638145, 30.010446441168135, 579.2311831160774], [110.87475288470749, 30.000617810741645, 678.046302939629], [110.88525405115537, 29.97371359878412, 248.6925509022207], [110.89707231953993, 29.978456909424786, 403.7668830135344], [110.9198256224335, 29.97377121630911, 712.4432989443915], [110.92939046684437, 30.003520348332533, 1062.8462515370425]] ;
positions = Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegreesArrayHeights([].concat.apply([], positions));
首先需要设置离屏相机,一般将离屏相机设置在感兴趣的研究区域,从上往下看,我们将其封装为一个方法
function createOffscreenCamera() {
//创建相机 (正交投影)
const offscreenCamera = new Cesium.Camera(viewer.scene);
//设置相机的位置
let center = new Cesium.Cartesian3();
let n = positions.length;
let centerPosition = new Cesium.Cartesian3();
positions.forEach(p => {
centerPosition = Cesium.Cartesian3.add(centerPosition, p, centerPosition);
})
centerPosition = Cesium.Cartesian3.multiplyByScalar(centerPosition, 1 / n, centerPosition);//中心点
//获取中心点的法线
let normal = Cesium.Ellipsoid.WGS84.geodeticSurfaceNormal(centerPosition);
//中心点向上平移5000米
centerPosition = Cesium.Cartesian3.add(centerPosition, Cesium.Cartesian3.multiplyByScalar(normal, 5000, new Cesium.Cartesian3()), centerPosition);
offscreenCamera.position = centerPosition;
//相机方向 从上往下看
offscreenCamera.direction = Cesium.Cartesian3.negate(normal, normal);
//设置相机上方向 (这里使用类似正北的方向)
let d = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(centerPosition);
let up = Cesium.Cartesian3.subtract(Cesium.Cartesian3.fromRadians(d.longitude, d.latitude + 0.005, d.height), centerPosition, new Cesium.Cartesian3())
up = Cesium.Cartesian3.normalize(up, up);
offscreenCamera.up = up;
offscreenCamera.frustum = new Cesium.OrthographicFrustum({
width: range,
aspectRatio: 1,
near: 0.1,
far: 10000
});
//可视化相机
viewer.scene.primitives.add(new Cesium.DebugCameraPrimitive({
camera: offscreenCamera,
color: Cesium.Color.BLUE,
updateOnChange: false,//不更新
show: true,
}));
return offscreenCamera;
}
let offscreenCamera= createOffscreenCamera();
示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
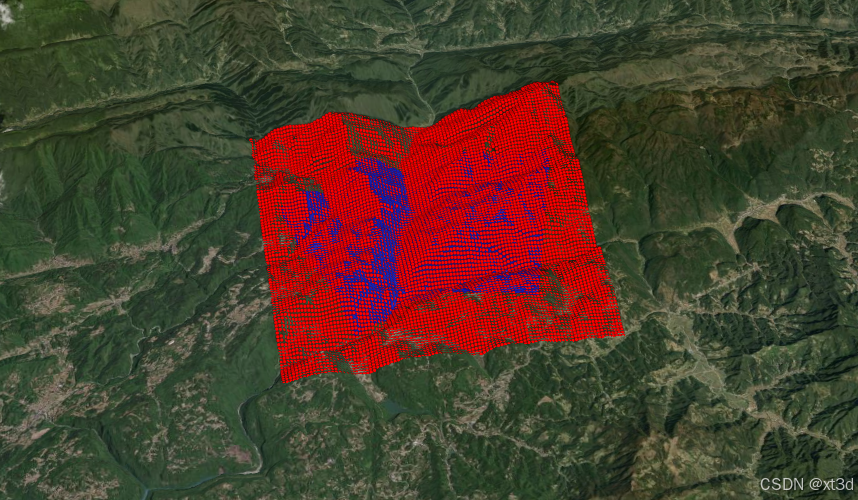
设置纹理大小
需要修改默认的纹理大小,使其能够存储多个值,在创建 Picking对象时设置其视口大小即可。
const depthTextureSize=100;
function creatPicking() {
const picking = new Cesium.Picking(viewer.scene);
const view = picking._pickOffscreenView;
...
view.camera = offscreenCamera;
return picking;
}
let picking = creatPicking();
离屏渲染
参考getRayIntersection方法,将离屏渲染的代码封装成一个方法,离屏渲染中使用自定义的相机。
function offscreenRender(camera, picking) {
const { scene } = viewer;
const { context, frameState } = scene;
const view = picking._pickOffscreenView;
let sceneView = scene.view;
scene.view = view;
Cesium.BoundingRectangle.clone(view.viewport, scratchRectangle);
const passState = view.pickFramebuffer.begin(scratchRectangle, view.viewport);
scene.jobScheduler.disableThisFrame();
scene.updateFrameState();
frameState.invertClassification = false;
frameState.passes.pick = true;
frameState.passes.offscreen = true;
frameState.tilesetPassState = pickTilesetPassState;
context.uniformState.update(frameState);
scene.updateEnvironment();
scene.updateAndExecuteCommands(passState, Cesium.Color.TRANSPARENT);
scene.resolveFramebuffers(passState);
const ray = new Cesium.Ray(camera.position, camera.direction);
scene.view = sceneView;
context.endFrame();
return positions;
}
解析坐标值
在渲染完成后就可以对坐标进行解析了,这里也将其封装成一个方法。
function pickPositions(ray, picking, scene, width, height, depthTextureSize) {
const res = [];
const { context } = scene;
if (!context.depthTexture) { return res; }
const view = picking._pickOffscreenView;
const { camera } = view;
const numFrustums = view.frustumCommandsList.length;
const offset = new Cesium.Cartesian3();
for (let i = 0; i < numFrustums; ++i) {
// 获取每个视锥体的深度缓存
const pickDepth = picking.getPickDepth(scene, i);
const depths = getDepths(context, 0, 0, depthTextureSize, depthTextureSize, pickDepth.framebuffer);
for (let j = 0, len = depths.length; j < len; j++) {
const depth = depths[j];
if (Cesium.defined(depth) && depth > 0.0 && depth < 1.0) {
// 根据视锥体远近截面计算出相机到物体表面的距离
const renderedFrustum = view.frustumCommandsList[i];
const near = renderedFrustum.near * (j !== 0 ? scene.opaqueFrustumNearOffset : 1.0);
...
const point = new Cesium.Cartesian3();
Cesium.Cartesian3.multiplyByScalar(camera.up, rowScalar, offset);
Cesium.Cartesian3.add(offset, camera.position, point);
Cesium.Cartesian3.multiplyByScalar(camera.right, columnScalar, offset);
Cesium.Cartesian3.add(offset, point, point);
// 利用射线获取坐标高程
const clonedRay = Cesium.Ray.clone(ray);
clonedRay.origin = point;
const position = Cesium.Ray.getPoint(clonedRay, distance);
if (!res[j]) {
res[j] = position;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
方法中调用了一个getDepths方法,用于从深度图中获取深度数组,可以参考PickDepth.prototype.getDepth方法。
const packedDepthScale = new Cesium.Cartesian4(1.0, 1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 65025.0, 1.0 / 16581375.0); // 1, 1 / 255, 1 / (255^2), 1 / (255^3)
function getDepths(context, x, y, width, height, framebuffer) {
// 获取颜深度缓存中的所有像素值
const pixels = context.readPixels({
x,
y,
width,
height,
framebuffer
});
const packedDepthArray = Cesium.Cartesian4.unpackArray(pixels);
//像素值转深度值
return packedDepthArray.map((t) => {
Cesium.Cartesian4.divideByScalar(t, 255.0, t);
return Cesium.Cartesian4.dot(t, packedDepthScale);
});
}
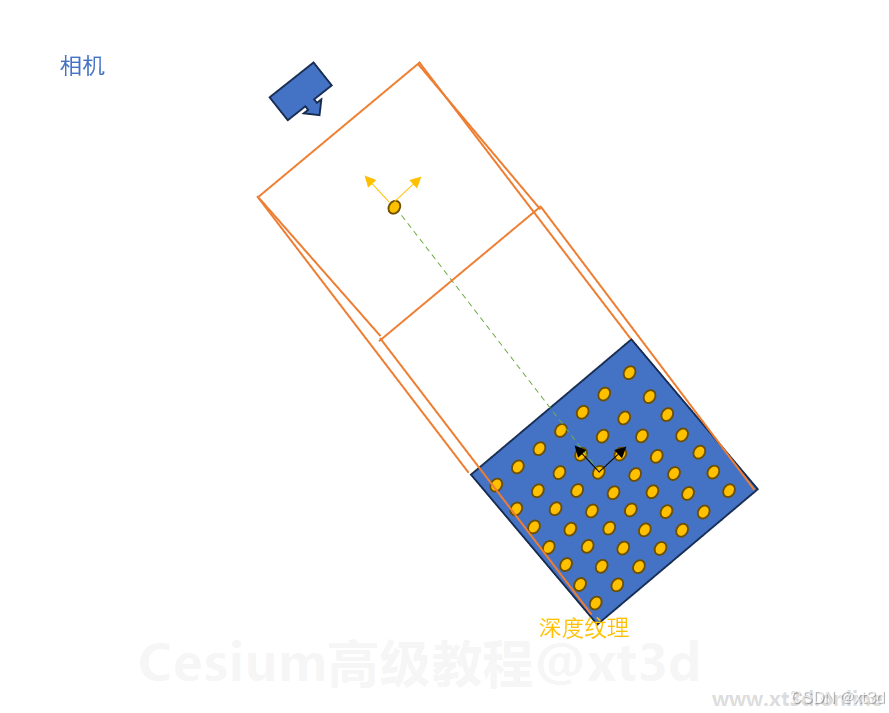
坐标解析的核心就是先将像素点映射到相机平面的世界坐标,然后根据深度值计算距离,将这个平面上的坐标进行平移即可得到正确的坐标值,原理图如下
示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
更多内容见 Cesium高级教程-教程简介