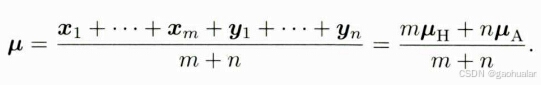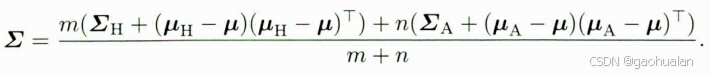直接法
不需要提取特征,将过去一段时间内的点云组成一个局部地图,将当前帧与局部地图进行配准。
NDT构建激光雷达里程计
建图
每隔一定距离或一定角度就取一个关键帧,再把最近的若干个关键帧拼成一个局部地图,作为NDT算法的配准目标。
src/ch7/direct_ndt_io.cc
添加地图
void DirectNDTLO::AddCloud(CloudPtr scan, SE3& pose) {
if (local_map_ == nullptr) {
// 第一个帧,直接加入local map
local_map_.reset(new PointCloudType);
// operator += 用来拼接点云
*local_map_ += *scan;
pose = SE3();
last_kf_pose_ = pose;
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
ndt_pcl_.setInputTarget(local_map_);
} else {
ndt_.SetTarget(local_map_);
}
return;
}
// 计算scan相对于local map的位姿
pose = AlignWithLocalMap(scan);
CloudPtr scan_world(new PointCloudType);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*scan, *scan_world, pose.matrix().cast<float>());
if (IsKeyframe(pose)) {
last_kf_pose_ = pose;
// 重建local map
scans_in_local_map_.emplace_back(scan_world);
if (scans_in_local_map_.size() > options_.num_kfs_in_local_map_) {
scans_in_local_map_.pop_front();
}
local_map_.reset(new PointCloudType);
for (auto& scan : scans_in_local_map_) {
*local_map_ += *scan;
}
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
ndt_pcl_.setInputTarget(local_map_);
} else {
ndt_.SetTarget(local_map_);
}
}
if (viewer_ != nullptr) {
viewer_->SetPoseAndCloud(pose, scan_world);
}
}
bool DirectNDTLO::IsKeyframe(const SE3& current_pose) {
// 只要与上一帧相对运动超过一定距离或角度,就记关键帧
SE3 delta = last_kf_pose_.inverse() * current_pose;
return delta.translation().norm() > options_.kf_distance_ ||
delta.so3().log().norm() > options_.kf_angle_deg_ * math::kDEG2RAD;
}
配准
用上两帧的相对运动作为运动模型,预测当前帧的位姿,作为NDT的位姿初值。
SE3 DirectNDTLO::AlignWithLocalMap(CloudPtr scan) {
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
ndt_pcl_.setInputSource(scan);
} else {
ndt_.SetSource(scan);
}
CloudPtr output(new PointCloudType());
SE3 guess;
bool align_success = true;
if (estimated_poses_.size() < 2) {
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
ndt_pcl_.align(*output, guess.matrix().cast<float>());
guess = Mat4ToSE3(ndt_pcl_.getFinalTransformation().cast<double>().eval());
} else {
align_success = ndt_.AlignNdt(guess);
}
} else {
// 从最近两个pose来推断
SE3 T1 = estimated_poses_[estimated_poses_.size() - 1];
SE3 T2 = estimated_poses_[estimated_poses_.size() - 2];
guess = T1 * (T2.inverse() * T1);
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
ndt_pcl_.align(*output, guess.matrix().cast<float>());
guess = Mat4ToSE3(ndt_pcl_.getFinalTransformation().cast<double>().eval());
} else {
align_success = ndt_.AlignNdt(guess);
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "pose: " << guess.translation().transpose() << ", "
<< guess.so3().unit_quaternion().coeffs().transpose();
if (options_.use_pcl_ndt_) {
LOG(INFO) << "trans prob: " << ndt_pcl_.getTransformationProbability();
}
estimated_poses_.emplace_back(guess);
return guess;
}
void DirectNDTLO::SaveMap(const std::string& map_path) {
if (viewer_) {
viewer_->SaveMap(map_path);
}
}
调用方式
src/ch7/test/test_ndt_lo.cc
/// 本程序以ULHK数据集为例
/// 测试以NDT为主的Lidar Odometry
/// 若使用PCL NDT的话,会重新建立NDT树
DEFINE_string(bag_path, "./dataset/sad/ulhk/test2.bag", "path to rosbag");
DEFINE_string(dataset_type, "ULHK", "NCLT/ULHK/KITTI/WXB_3D"); // 数据集类型
DEFINE_bool(use_pcl_ndt, false, "use pcl ndt to align?");
DEFINE_bool(use_ndt_nearby_6, false, "use ndt nearby 6?");
DEFINE_bool(display_map, true, "display map?");
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
FLAGS_stderrthreshold = google::INFO;
FLAGS_colorlogtostderr = true;
google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
sad::RosbagIO rosbag_io(fLS::FLAGS_bag_path, sad::Str2DatasetType(FLAGS_dataset_type));
sad::DirectNDTLO::Options options;
options.use_pcl_ndt_ = fLB::FLAGS_use_pcl_ndt;
options.ndt3d_options_.nearby_type_ =
FLAGS_use_ndt_nearby_6 ? sad::Ndt3d::NearbyType::NEARBY6 : sad::Ndt3d::NearbyType::CENTER;
options.display_realtime_cloud_ = FLAGS_display_map;
sad::DirectNDTLO ndt_lo(options);
rosbag_io
.AddAutoPointCloudHandle([&ndt_lo](sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::Ptr msg) -> bool {
sad::common::Timer::Evaluate(
[&]() {
SE3 pose;
ndt_lo.AddCloud(sad::VoxelCloud(sad::PointCloud2ToCloudPtr(msg)), pose);
},
"NDT registration");
return true;
})
.Go();
if (FLAGS_display_map) {
// 把地图存下来
ndt_lo.SaveMap("./data/ch7/map.pcd");
}
sad::common::Timer::PrintAll();
LOG(INFO) << "done.";
return 0;
}
此处没有用PCL自带的ndt,而是单独实现的ndt方法,好处:
1、可以设置体素的最近邻查找方法。不用PCL的k-d树查找,不存在k-d树构建的时间消耗。
2、可以自定义并行处理来提高效率。
增量NDT里程计
不重构NDT内部状态,不重建k-d树等数据结构,而是把配准好的点云更新到NDT的每个体素内部,更新高斯分布状态,再做下一步配准。
增量NDT类定义
src/ch7/ndt_inc.h
/**
* 增量版本的NDT
* 内部会维护增量式的voxels,自动删除较旧的voxel,往voxel里添加点云时,更新其均值和协方差估计
*/
class IncNdt3d {
public:
enum class NearbyType {
CENTER, // 只考虑中心
NEARBY6, // 上下左右前后
};
...
using KeyType = Eigen::Matrix<int, 3, 1>; // 体素的索引
/// 体素内置结构
struct VoxelData {
VoxelData() {}
VoxelData(const Vec3d& pt) {
pts_.emplace_back(pt);
num_pts_ = 1;
}
void AddPoint(const Vec3d& pt) {
pts_.emplace_back(pt);
if (!ndt_estimated_) {
num_pts_++;
}
}
std::vector<Vec3d> pts_; // 内部点,多于一定数量之后再估计均值和协方差
Vec3d mu_ = Vec3d::Zero(); // 均值
Mat3d sigma_ = Mat3d::Zero(); // 协方差
Mat3d info_ = Mat3d::Zero(); // 协方差之逆
bool ndt_estimated_ = false; // NDT是否已经估计
int num_pts_ = 0; // 总共的点数,用于更新估计
};
...
/// 获取一些统计信息
int NumGrids() const { return grids_.size(); }
/// 在voxel里添加点云,
void AddCloud(CloudPtr cloud_world);
/// 设置被配准的Scan
void SetSource(CloudPtr source) { source_ = source; }
/// 使用gauss-newton方法进行ndt配准
bool AlignNdt(SE3& init_pose);
...
private:
/// 根据最近邻的类型,生成附近网格
void GenerateNearbyGrids();
/// 更新体素内部数据, 根据新加入的pts和历史的估计情况来确定自己的估计
void UpdateVoxel(VoxelData& v);
CloudPtr source_ = nullptr;
Options options_;
using KeyAndData = std::pair<KeyType, VoxelData>; // 预定义
std::list<KeyAndData> data_; // 真实数据,会缓存,也会清理
std::unordered_map<KeyType, std::list<KeyAndData>::iterator, hash_vec<3>> grids_; // 栅格数据,存储真实数据的迭代器
std::vector<KeyType> nearby_grids_; // 附近的栅格
bool flag_first_scan_ = true; // 首帧点云特殊处理
};
添加点云
src/ch7/ndt_inc.cc
void IncNdt3d::AddCloud(CloudPtr cloud_world) {
std::set<KeyType, less_vec<3>> active_voxels; // 记录哪些voxel被更新
for (const auto& p : cloud_world->points) {
auto pt = ToVec3d(p);
auto key = CastToInt(Vec3d(pt * options_.inv_voxel_size_));
auto iter = grids_.find(key);
if (iter == grids_.end()) {
// 栅格不存在
data_.push_front({key, {pt}});
grids_.insert({key, data_.begin()});
if (data_.size() >= options_.capacity_) {
// 删除一个尾部的数据
grids_.erase(data_.back().first);
data_.pop_back();
}
} else {
// 栅格存在,添加点,更新缓存
iter->second->second.AddPoint(pt);
data_.splice(data_.begin(), data_, iter->second); // 更新的那个放到最前
iter->second = data_.begin(); // grids时也指向最前
}
active_voxels.emplace(key);
}
// 更新active_voxels
std::for_each(std::execution::par_unseq, active_voxels.begin(), active_voxels.end(),
[this](const auto& key) { UpdateVoxel(grids_[key]->second); });
flag_first_scan_ = false;
}
更新体素
更新体素,更新高斯分布,维护索引。
void IncNdt3d::UpdateVoxel(VoxelData& v) {
if (flag_first_scan_) {
if (v.pts_.size() > 1) {
math::ComputeMeanAndCov(v.pts_, v.mu_, v.sigma_, [this](const Vec3d& p) { return p; });
v.info_ = (v.sigma_ + Mat3d::Identity() * 1e-3).inverse(); // 避免出nan
} else {
v.mu_ = v.pts_[0];
v.info_ = Mat3d::Identity() * 1e2;
}
v.ndt_estimated_ = true;
v.pts_.clear();
return;
}
if (v.ndt_estimated_ && v.num_pts_ > options_.max_pts_in_voxel_) {
return;
}
if (!v.ndt_estimated_ && v.pts_.size() > options_.min_pts_in_voxel_) {
// 新增的voxel
math::ComputeMeanAndCov(v.pts_, v.mu_, v.sigma_, [this](const Vec3d& p) { return p; });
v.info_ = (v.sigma_ + Mat3d::Identity() * 1e-3).inverse(); // 避免出nan
v.ndt_estimated_ = true;
v.pts_.clear();
} else if (v.ndt_estimated_ && v.pts_.size() > options_.min_pts_in_voxel_) {
// 已经估计,而且还有新来的点
Vec3d cur_mu, new_mu;
Mat3d cur_var, new_var;
math::ComputeMeanAndCov(v.pts_, cur_mu, cur_var, [this](const Vec3d& p) { return p; });
math::UpdateMeanAndCov(v.num_pts_, v.pts_.size(), v.mu_, v.sigma_, cur_mu, cur_var, new_mu, new_var);
v.mu_ = new_mu;
v.sigma_ = new_var;
v.num_pts_ += v.pts_.size();
v.pts_.clear();
// check info
Eigen::JacobiSVD svd(v.sigma_, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Vec3d lambda = svd.singularValues();
if (lambda[1] < lambda[0] * 1e-3) {
lambda[1] = lambda[0] * 1e-3;
}
if (lambda[2] < lambda[0] * 1e-3) {
lambda[2] = lambda[0] * 1e-3;
}
Mat3d inv_lambda = Vec3d(1.0 / lambda[0], 1.0 / lambda[1], 1.0 / lambda[2]).asDiagonal();
v.info_ = svd.matrixV() * inv_lambda * svd.matrixU().transpose();
}
}
高斯分布合并
均值合并的公式
协方差合并的公式
src/common/math_util.h
/**
* 高斯分布合并
* @tparam S scalar type
* @tparam D dimension
* @param hist_m 历史点数
* @param curr_n 当前点数
* @param hist_mean 历史均值
* @param hist_var 历史方差
* @param curr_mean 当前均值
* @param curr_var 当前方差
* @param new_mean 新的均值
* @param new_var 新的方差
*/
template <typename S, int D>
void UpdateMeanAndCov(int hist_m, int curr_n, const Eigen::Matrix<S, D, 1>& hist_mean,
const Eigen::Matrix<S, D, D>& hist_var, const Eigen::Matrix<S, D, 1>& curr_mean,
const Eigen::Matrix<S, D, D>& curr_var, Eigen::Matrix<S, D, 1>& new_mean,
Eigen::Matrix<S, D, D>& new_var) {
assert(hist_m > 0);
assert(curr_n > 0);
new_mean = (hist_m * hist_mean + curr_n * curr_mean) / (hist_m + curr_n);
new_var = (hist_m * (hist_var + (hist_mean - new_mean) * (hist_mean - new_mean).template transpose()) +
curr_n * (curr_var + (curr_mean - new_mean) * (curr_mean - new_mean).template transpose())) /
(hist_m + curr_n);
}
特征法
特征提取
1、计算点的曲率。
2、将点云一周分为6个区间;每个区间,进行特征提取。根据曲率,区分角点、平面点。
3、角点、平面点分开存放,总共2个pcd文件。
src/ch7/loam-like/feature_extraction.cc
void FeatureExtraction::Extract(FullCloudPtr pc_in, CloudPtr pc_out_edge, CloudPtr pc_out_surf) {
int num_scans = 16;
std::vector<CloudPtr> scans_in_each_line; // 分线数的点云
for (int i = 0; i < num_scans; i++) {
scans_in_each_line.emplace_back(new PointCloudType);
}
for (auto &pt : pc_in->points) {
assert(pt.ring >= 0 && pt.ring < num_scans);
PointType p;
p.x = pt.x;
p.y = pt.y;
p.z = pt.z;
p.intensity = pt.intensity;
scans_in_each_line[pt.ring]->points.emplace_back(p);
}
// 处理曲率
for (int i = 0; i < num_scans; i++) {
if (scans_in_each_line[i]->points.size() < 131) {
continue;
}
std::vector<IdAndValue> cloud_curvature; // 每条线对应的曲率
int total_points = scans_in_each_line[i]->points.size() - 10;
for (int j = 5; j < (int)scans_in_each_line[i]->points.size() - 5; j++) {
// 两头留一定余量,采样周围10个点取平均值
double diffX = scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 5].x + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 4].x +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 3].x + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 2].x +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 1].x - 10 * scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j].x +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 1].x + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 2].x +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 3].x + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 4].x +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 5].x;
double diffY = scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 5].y + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 4].y +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 3].y + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 2].y +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 1].y - 10 * scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j].y +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 1].y + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 2].y +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 3].y + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 4].y +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 5].y;
double diffZ = scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 5].z + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 4].z +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 3].z + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 2].z +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j - 1].z - 10 * scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j].z +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 1].z + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 2].z +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 3].z + scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 4].z +
scans_in_each_line[i]->points[j + 5].z;
IdAndValue distance(j, diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ);
cloud_curvature.push_back(distance);
}
// 对每个区间选取特征,把360度分为6个区间
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
int sector_length = (int)(total_points / 6);
int sector_start = sector_length * j;
int sector_end = sector_length * (j + 1) - 1;
if (j == 5) {
sector_end = total_points - 1;
}
std::vector<IdAndValue> sub_cloud_curvature(cloud_curvature.begin() + sector_start,
cloud_curvature.begin() + sector_end);
ExtractFromSector(scans_in_each_line[i], sub_cloud_curvature, pc_out_edge, pc_out_surf);
}
}
}
void FeatureExtraction::ExtractFromSector(const CloudPtr &pc_in, std::vector<IdAndValue> &cloud_curvature,
CloudPtr &pc_out_edge, CloudPtr &pc_out_surf) {
// 按曲率排序
std::sort(cloud_curvature.begin(), cloud_curvature.end(),
[](const IdAndValue &a, const IdAndValue &b) { return a.value_ < b.value_; });
int largest_picked_num = 0;
int point_info_count = 0;
/// 按照曲率最大的开始搜,选取曲率最大的角点
std::vector<int> picked_points; // 标记被选中的角点,角点附近的点都不会被选取
for (int i = cloud_curvature.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int ind = cloud_curvature[i].id_;
if (std::find(picked_points.begin(), picked_points.end(), ind) == picked_points.end()) {
if (cloud_curvature[i].value_ <= 0.1) {
break;
}
largest_picked_num++;
picked_points.push_back(ind);
if (largest_picked_num <= 20) {
pc_out_edge->push_back(pc_in->points[ind]);
point_info_count++;
} else {
break;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= 5; k++) {
double diffX = pc_in->points[ind + k].x - pc_in->points[ind + k - 1].x;
double diffY = pc_in->points[ind + k].y - pc_in->points[ind + k - 1].y;
double diffZ = pc_in->points[ind + k].z - pc_in->points[ind + k - 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05) {
break;
}
picked_points.push_back(ind + k);
}
for (int k = -1; k >= -5; k--) {
double diffX = pc_in->points[ind + k].x - pc_in->points[ind + k + 1].x;
double diffY = pc_in->points[ind + k].y - pc_in->points[ind + k + 1].y;
double diffZ = pc_in->points[ind + k].z - pc_in->points[ind + k + 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05) {
break;
}
picked_points.push_back(ind + k);
}
}
}
/// 选取曲率较小的平面点
for (int i = 0; i <= (int)cloud_curvature.size() - 1; i++) {
int ind = cloud_curvature[i].id_;
if (std::find(picked_points.begin(), picked_points.end(), ind) == picked_points.end()) {
pc_out_surf->push_back(pc_in->points[ind]);
}
}
}
特征法激光雷达里程计的实现
分别为角点、平面点构建2个局部地图,使用ICP进行配准。
src/ch7/loam-like/loam_like_odom.h
class LoamLikeOdom {
public:
struct Options {
Options() {}
int min_edge_pts_ = 20; // 最小边缘点数
int min_surf_pts_ = 20; // 最小平面点数
double kf_distance_ = 1.0; // 关键帧距离
double kf_angle_deg_ = 15; // 旋转角度
int num_kfs_in_local_map_ = 30; // 局部地图含有多少个关键帧
bool display_realtime_cloud_ = true; // 是否显示实时点云
// ICP 参数
int max_iteration_ = 5; // 最大迭代次数
double max_plane_distance_ = 0.05; // 平面最近邻查找时阈值
double max_line_distance_ = 0.5; // 点线最近邻查找时阈值
int min_effective_pts_ = 10; // 最近邻点数阈值
double eps_ = 1e-3; // 收敛判定条件
bool use_edge_points_ = true; // 是否使用边缘点
bool use_surf_points_ = true; // 是否使用平面点
};
explicit LoamLikeOdom(Options options = Options());
/**
* 往里程计中添加一个点云,内部会分为角点和平面点
* @param full_cloud
*/
void ProcessPointCloud(FullCloudPtr full_cloud);
void SaveMap(const std::string& path);
private:
/// 与局部地图进行配准
SE3 AlignWithLocalMap(CloudPtr edge, CloudPtr surf);
/// 判定是否为关键帧
bool IsKeyframe(const SE3& current_pose);
Options options_;
int cnt_frame_ = 0;
int last_kf_id_ = 0;
CloudPtr local_map_edge_ = nullptr, local_map_surf_ = nullptr; // 局部地图的local map
std::vector<SE3> estimated_poses_; // 所有估计出来的pose,用于记录轨迹和预测下一个帧
SE3 last_kf_pose_; // 上一关键帧的位姿
std::deque<CloudPtr> edges_, surfs_; // 缓存的角点和平面点
CloudPtr global_map_ = nullptr; // 用于保存的全局地图
std::shared_ptr<FeatureExtraction> feature_extraction_ = nullptr;
std::shared_ptr<PCLMapViewer> viewer_ = nullptr;
KdTree kdtree_edge_, kdtree_surf_;
};
构建局部地图
src/ch7/loam-like/loam_like_odom.cc
void LoamLikeOdom::ProcessPointCloud(FullCloudPtr cloud) {
LOG(INFO) << "processing frame " << cnt_frame_++;
// step 1. 提特征
CloudPtr current_edge(new PointCloudType), current_surf(new PointCloudType);
feature_extraction_->Extract(cloud, current_edge, current_surf);
if (current_edge->size() < options_.min_edge_pts_ || current_surf->size() < options_.min_surf_pts_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "not enough edge/surf pts: " << current_edge->size() << "," << current_surf->size();
return;
}
LOG(INFO) << "edge: " << current_edge->size() << ", surf: " << current_surf->size();
if (local_map_edge_ == nullptr || local_map_surf_ == nullptr) {
// 首帧特殊处理
local_map_edge_ = current_edge;
local_map_surf_ = current_surf;
kdtree_edge_.BuildTree(local_map_edge_);
kdtree_surf_.BuildTree(local_map_surf_);
edges_.emplace_back(current_edge);
surfs_.emplace_back(current_surf);
return;
}
/// 与局部地图配准
SE3 pose = AlignWithLocalMap(current_edge, current_surf);
CloudPtr scan_world(new PointCloudType);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*ConvertToCloud<FullPointType>(cloud), *scan_world, pose.matrix());
CloudPtr edge_world(new PointCloudType), surf_world(new PointCloudType);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*current_edge, *edge_world, pose.matrix());
pcl::transformPointCloud(*current_surf, *surf_world, pose.matrix());
if (IsKeyframe(pose)) {
LOG(INFO) << "inserting keyframe";
last_kf_pose_ = pose;
last_kf_id_ = cnt_frame_;
// 重建local map
edges_.emplace_back(edge_world);
surfs_.emplace_back(surf_world);
if (edges_.size() > options_.num_kfs_in_local_map_) {
edges_.pop_front();
}
if (surfs_.size() > options_.num_kfs_in_local_map_) {
surfs_.pop_front();
}
local_map_surf_.reset(new PointCloudType);
local_map_edge_.reset(new PointCloudType);
for (auto& s : edges_) {
*local_map_edge_ += *s;
}
for (auto& s : surfs_) {
*local_map_surf_ += *s;
}
local_map_surf_ = VoxelCloud(local_map_surf_, 1.0);
local_map_edge_ = VoxelCloud(local_map_edge_, 1.0);
LOG(INFO) << "insert keyframe, surf pts: " << local_map_surf_->size()
<< ", edge pts: " << local_map_edge_->size();
kdtree_surf_.BuildTree(local_map_surf_);
kdtree_edge_.BuildTree(local_map_edge_);
*global_map_ += *scan_world;
}
LOG(INFO) << "current pose: " << pose.translation().transpose() << ", "
<< pose.so3().unit_quaternion().coeffs().transpose();
if (viewer_ != nullptr) {
viewer_->SetPoseAndCloud(pose, scan_world);
}
}
bool LoamLikeOdom::IsKeyframe(const SE3& current_pose) {
if ((cnt_frame_ - last_kf_id_) > 30) {
return true;
}
// 只要与上一帧相对运动超过一定距离或角度,就记关键帧
SE3 delta = last_kf_pose_.inverse() * current_pose;
return delta.translation().norm() > options_.kf_distance_ ||
delta.so3().log().norm() > options_.kf_angle_deg_ * math::kDEG2RAD;
}
配准
SE3 LoamLikeOdom::AlignWithLocalMap(CloudPtr edge, CloudPtr surf) {
// 这部分的ICP需要自己写
SE3 pose;
if (estimated_poses_.size() >= 2) {
// 从最近两个pose来推断
SE3 T1 = estimated_poses_[estimated_poses_.size() - 1];
SE3 T2 = estimated_poses_[estimated_poses_.size() - 2];
pose = T1 * (T2.inverse() * T1);
}
int edge_size = edge->size();
int surf_size = surf->size();
// 我们来写一些并发代码
for (int iter = 0; iter < options_.max_iteration_; ++iter) {
std::vector<bool> effect_surf(surf_size, false);
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 6>> jacob_surf(surf_size); // 点面的残差是1维的
std::vector<double> errors_surf(surf_size);
std::vector<bool> effect_edge(edge_size, false);
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6>> jacob_edge(edge_size); // 点线的残差是3维的
std::vector<Vec3d> errors_edge(edge_size);
std::vector<int> index_surf(surf_size);
std::iota(index_surf.begin(), index_surf.end(), 0); // 填入
std::vector<int> index_edge(edge_size);
std::iota(index_edge.begin(), index_edge.end(), 0); // 填入
// gauss-newton 迭代
// 最近邻,角点部分
if (options_.use_edge_points_) {
std::for_each(std::execution::par_unseq, index_edge.begin(), index_edge.end(), [&](int idx) {
Vec3d q = ToVec3d(edge->points[idx]);
Vec3d qs = pose * q;
// 检查最近邻
std::vector<int> nn_indices;
kdtree_edge_.GetClosestPoint(ToPointType(qs), nn_indices, 5);
effect_edge[idx] = false;
if (nn_indices.size() >= 3) {
std::vector<Vec3d> nn_eigen;
for (auto& n : nn_indices) {
nn_eigen.emplace_back(ToVec3d(local_map_edge_->points[n]));
}
// point to point residual
Vec3d d, p0;
if (!math::FitLine(nn_eigen, p0, d, options_.max_line_distance_)) {
return;
}
Vec3d err = SO3::hat(d) * (qs - p0);
if (err.norm() > options_.max_line_distance_) {
return;
}
effect_edge[idx] = true;
// build residual
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6> J;
J.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = -SO3::hat(d) * pose.so3().matrix() * SO3::hat(q);
J.block<3, 3>(0, 3) = SO3::hat(d);
jacob_edge[idx] = J;
errors_edge[idx] = err;
}
});
}
/// 最近邻,平面点部分
if (options_.use_surf_points_) {
std::for_each(std::execution::par_unseq, index_surf.begin(), index_surf.end(), [&](int idx) {
Vec3d q = ToVec3d(surf->points[idx]);
Vec3d qs = pose * q;
// 检查最近邻
std::vector<int> nn_indices;
kdtree_surf_.GetClosestPoint(ToPointType(qs), nn_indices, 5);
effect_surf[idx] = false;
if (nn_indices.size() == 5) {
std::vector<Vec3d> nn_eigen;
for (auto& n : nn_indices) {
nn_eigen.emplace_back(ToVec3d(local_map_surf_->points[n]));
}
// 点面残差
Vec4d n;
if (!math::FitPlane(nn_eigen, n)) {
return;
}
double dis = n.head<3>().dot(qs) + n[3];
if (fabs(dis) > options_.max_plane_distance_) {
return;
}
effect_surf[idx] = true;
// build residual
Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 6> J;
J.block<1, 3>(0, 0) = -n.head<3>().transpose() * pose.so3().matrix() * SO3::hat(q);
J.block<1, 3>(0, 3) = n.head<3>().transpose();
jacob_surf[idx] = J;
errors_surf[idx] = dis;
}
});
}
// 累加Hessian和error,计算dx
// 原则上可以用reduce并发,写起来比较麻烦,这里写成accumulate
double total_res = 0;
int effective_num = 0;
Mat6d H = Mat6d::Zero();
Vec6d err = Vec6d::Zero();
for (const auto& idx : index_surf) {
if (effect_surf[idx]) {
H += jacob_surf[idx].transpose() * jacob_surf[idx];
err += -jacob_surf[idx].transpose() * errors_surf[idx];
effective_num++;
total_res += errors_surf[idx] * errors_surf[idx];
}
}
for (const auto& idx : index_edge) {
if (effect_edge[idx]) {
H += jacob_edge[idx].transpose() * jacob_edge[idx];
err += -jacob_edge[idx].transpose() * errors_edge[idx];
effective_num++;
total_res += errors_edge[idx].norm();
}
}
if (effective_num < options_.min_effective_pts_) {
LOG(WARNING) << "effective num too small: " << effective_num;
return pose;
}
Vec6d dx = H.inverse() * err;
pose.so3() = pose.so3() * SO3::exp(dx.head<3>());
pose.translation() += dx.tail<3>();
// 更新
LOG(INFO) << "iter " << iter << " total res: " << total_res << ", eff: " << effective_num
<< ", mean res: " << total_res / effective_num << ", dxn: " << dx.norm();
if (dx.norm() < options_.eps_) {
LOG(INFO) << "converged, dx = " << dx.transpose();
break;
}
}
estimated_poses_.emplace_back(pose);
return pose;
}
参考资料:
1、书籍:《自动驾驶与机器人中的SLAM技术:从理论到实践》
2、代码:https://github.com/gaoxiang12/slam_in_autonomous_driving/tree/master/src/ch7