目录
关于link
link 就是把 node_modules 中某个库的原生部分,加入到自己的原生项目中,例如:android的autolink是在yourapp/build.gradle、setting.gradle 添加第三方库、生成PackageList
关于 react-native link 、 Manual Linking、 autolink 的更多信息,可以参考这里
What is react-native link?,他们的目的都是link。本篇文章主要分析autolink 的源码,autolinking 是通过React-Native脚手架 来配合实现的,所以源码分析中,第2点,都是关于脚手架源码分析
autolink
autolink 的使用需要在两个文件中引入native_modules.gradle,如下:
setting.gradle
apply from: file("../node_modules/@react-native-community/cli-platform-android/native_modules.gradle");
//调用脚本中的方法
applyNativeModulesSettingsGradle(settings)
yourapp/build.gradle
apply from: file("../../node_modules/@react-native-community/cli-platform-android/native_modules.gradle");
//调用脚本中的方法
applyNativeModulesAppBuildGradle(project)
关于setting.gradle、build.gradle 执行时机的具体分析,可阅读我之前写的Gradle 源码分析
这里我们直接从native_modules.gradle 开始分析
源码分析
1、 native_modules.gradle
首先看一下 脚本中 applyNativeModulesSettingsGradle、applyNativeModulesAppBuildGradle 这两个函数
def projectRoot = rootProject.projectDir
//ReactNativeModules 是native_modules.gradle 中的类,后面会分析
def autoModules = new ReactNativeModules(logger, projectRoot)
/** -----------------------
* Exported Extensions
* ------------------------ */
ext.applyNativeModulesSettingsGradle = { DefaultSettings defaultSettings, String root = null ->
...
//作用是,和 手动在 setting.gradle 中include 第三方库 的效果一样。而是向 Gradle解析setting.gradle的内容时创建 的对象加入 第三方库的信息
autoModules.addReactNativeModuleProjects(defaultSettings)
}
ext.applyNativeModulesAppBuildGradle = { Project project, String root = null ->
...
//原理同setting.gradle的一样
autoModules.addReactNativeModuleDependencies(project)
def generatedSrcDir = new File(buildDir, "generated/rncli/src/main/java")
def generatedCodeDir = new File(generatedSrcDir, generatedFilePackage.replace('.', '/'))
task generatePackageList {
doLast {
autoModules.generatePackagesFile(generatedCodeDir, generatedFileName, generatedFileContentsTemplate)
}
}
//把generatePackageList 任务 放在build之前执行
preBuild.dependsOn generatePackageList
android {
sourceSets {
main {
java {
srcDirs += generatedSrcDir
}
}
}
}
}
这里先给出整篇的总流程,下面在逐一进入详细分析
1、native_modules.gradle脚本中会创建ReactNativeModules对象,在构造函数中,调用getReactNativeConfig来获取所有 node_modules中的原生库信息(包括packageName、构造函数等),第2、3点的函数都是调用该对象成员函数
2、调用addReactNativeModuleProjects,向setting.gradle 中引入库
3、调用addReactNativeModuleDependencies,向build.gradle中引入库
4、调用generatePackagesFile,生成PackageList 类,用于在MainApplication 初始化ReactNativeHost时 getPackages 中使用。(关于ReactNativeHost 在RN的作用,可查看我之前写的文章React Native 源码分析(一)——启动流程)
下面就开始分析,在创建ReactNativeModulesget对象时,调用的ReactNativeConfig,如何拿到、以及拿到哪些 原生工程的信息
2、getReactNativeConfig
2.1、getReactNativeConfig
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> getReactNativeConfig() {
if (this.reactNativeModules != null) return this.reactNativeModules
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> reactNativeModules = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>()
HashMap<String, ArrayList> reactNativeModulesBuildVariants = new HashMap<String, ArrayList>()
//通过 require 引入cli库
def cliResolveScript = "console.log(require('react-native/cli').bin);"
String[] nodeCommand = ["node", "-e", cliResolveScript]
//找到cli库 bin.js 的路径
def cliPath = this.getCommandOutput(nodeCommand, this.root)
//调用bin.js 参数是config
String[] reactNativeConfigCommand = ["node", cliPath, "config"]
def reactNativeConfigOutput = this.getCommandOutput(reactNativeConfigCommand, this.root)
//下面对 node bin.js conofig 输出的结果进行处理
def json
try {
json = new JsonSlurper().parseText(reactNativeConfigOutput)
} catch (Exception exception) {
throw new Exception("Calling `${reactNativeConfigCommand}` finished with an exception. Error message: ${exception.toString()}. Output: ${reactNativeConfigOutput}");
}
def dependencies = json["dependencies"]
def project = json["project"]["android"]
if (project == null) {
throw new Exception("React Native CLI failed to determine Android project configuration. This is likely due to misconfiguration. Config output:\n${json.toMapString()}")
}
dependencies.each { name, value ->
def platformsConfig = value["platforms"];
def androidConfig = platformsConfig["android"]
if (androidConfig != null && androidConfig["sourceDir"] != null) {
this.logger.info("${LOG_PREFIX}Automatically adding native module '${name}'")
HashMap reactNativeModuleConfig = new HashMap<String, String>()
def nameCleansed = name.replaceAll('[~*!\'()]+', '_').replaceAll('^@([\\w-.]+)/', '$1_')
reactNativeModuleConfig.put("name", name)
reactNativeModuleConfig.put("nameCleansed", nameCleansed)
reactNativeModuleConfig.put("androidSourceDir", androidConfig["sourceDir"])
reactNativeModuleConfig.put("packageInstance", androidConfig["packageInstance"])
reactNativeModuleConfig.put("packageImportPath", androidConfig["packageImportPath"])
if (!androidConfig["buildTypes"].isEmpty()) {
reactNativeModulesBuildVariants.put(nameCleansed, androidConfig["buildTypes"])
}
this.logger.trace("${LOG_PREFIX}'${name}': ${reactNativeModuleConfig.toMapString()}")
reactNativeModules.add(reactNativeModuleConfig)
} else {
this.logger.info("${LOG_PREFIX}Skipping native module '${name}'")
}
}
return [reactNativeModules, reactNativeModulesBuildVariants, json["project"]["android"]["packageName"]];
}
}
使用下面这条命令,来查看node_modules中有哪些使用了原生的依赖
node ./node_modules/@react-native-community/cli/build/bin.js config
输出如下:(只贴出了一个库的信息)
{
"root": "/xxxxxxxxxxx",
"reactNativePath": "/xxxxxx/node_modules/react-native",
"dependencies": {
"react-native-code-push": {
"root": "/xxxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push",
"name": "react-native-code-push",
"platforms": {
"ios": {
"sourceDir": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push/ios",
"folder": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push",
"pbxprojPath": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push/ios/CodePush.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj",
"podfile": null,
"podspecPath": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push/CodePush.podspec",
"projectPath": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push/ios/CodePush.xcodeproj",
"projectName": "CodePush.xcodeproj",
"libraryFolder": "Libraries",
"sharedLibraries": [],
"plist": [],
"scriptPhases": [],
"configurations": []
},
"android": {
"sourceDir": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push/android",
"folder": "/xxxxx/node_modules/react-native-code-push",
"packageImportPath": "import com.microsoft.codepush.react.CodePush;",
"packageInstance": "new CodePush(BuildConfig.DEBUG ? BuildConfig.CODE_PUSH_KEY_DEV : BuildConfig.CODE_PUSH_KEY, getApplicationContext(), BuildConfig.DEBUG,BuildConfig.CODE_PUSH_SERVER)",
"buildTypes": []
}
},
"assets": [],
"hooks": {},
"params": []
}
}
主要是获取node bin.js conofig 输出的结果,然后按照一定格式输出,最终给addReactNativeModuleProjects、addReactNativeModuleDependencies、generatePackagesFile 使用。下面来分析一下bin.js 的执行过程。
这里拓展一下, 你可能听过react-native脚手架,现在它是指 react-native-community/cli, 全局安装后就可以使用 react-native命令,例如:npx react-native init AwesomeProject ,react-native 是一个js文件。
通过命令which react-native 来查看一下它的位置,最后指向了/node_modules/react-native/cli.js(这里不是全局安装的),cli.js 也很简单,调用了 node_modules/@react-native-community/cli/index.js中的run函数。
分析到这里,我们回过头看看 bin.js,它里面其实也是执行node_modules/@react-native-community/cli/index.js中的run函数。是脚手架的一个入口
关于如何调试
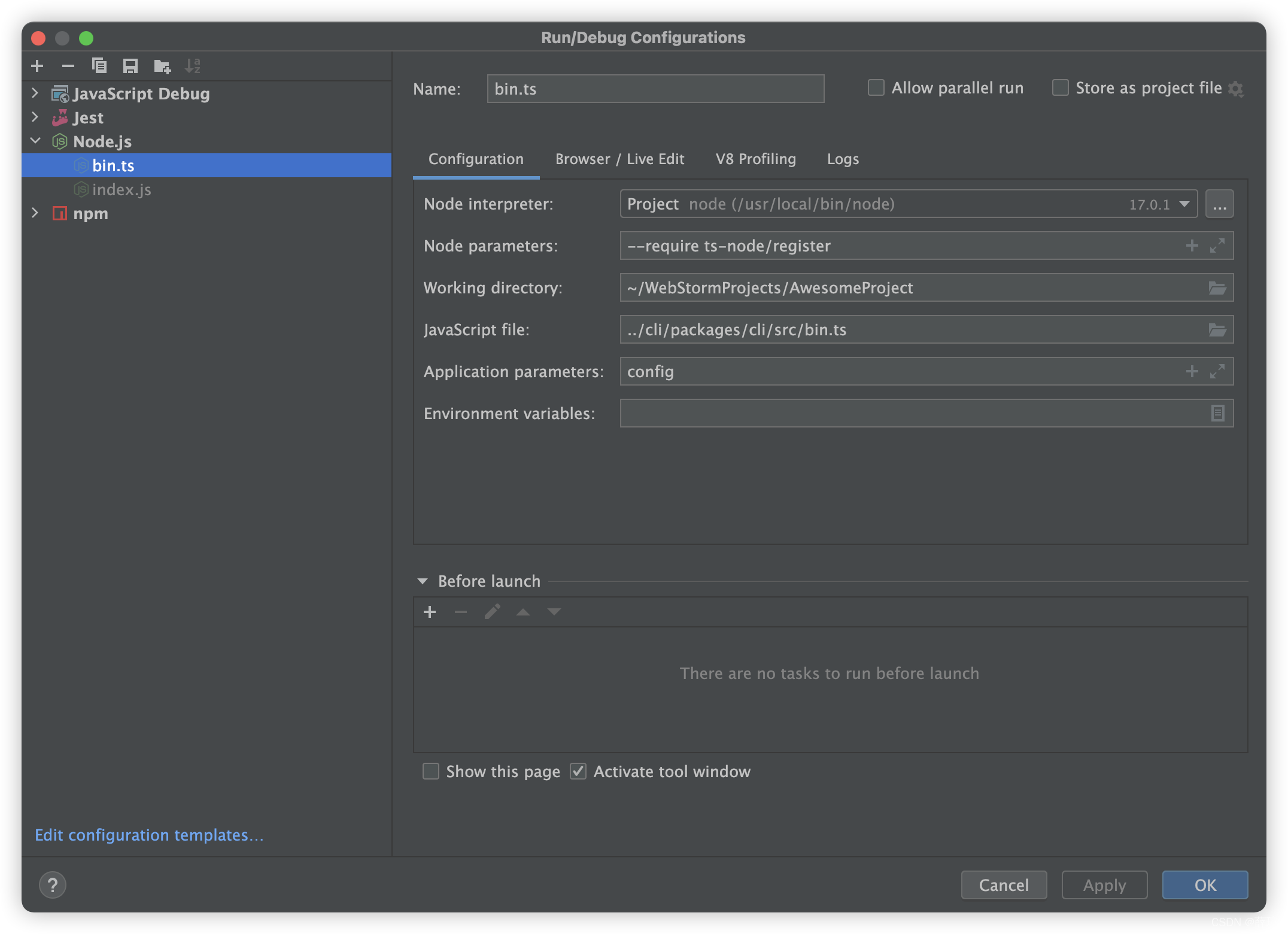
原计划从 node_modules/@react-native-community/cli/build/bin.js 开始分析,因为node_modules中的js代码,是由ts转换的,经常跳到d.ts文件中,看起来不顺畅。而且调试的时候,webstorm很聪明的定位到ts文件,但不知道文件在哪个目录下。所以后来还是决定在 react-native-community/cli 项目中来调试(如果你不会调试TS,看这里)。
如何在调试react-native-community/cli项目,因为部分流程会检测当前是否一个react-native工程,所以直接运行cli,很多流程走不到。我是这样配置的,AwesomeProject和cli在同级目录下
2.2、bin.js
下面就看一下react-native-community/cli 中关于Autolinking的主干流程,进入bin.ts后,流程如下
bin.ts run() -> 同级目录 index.ts run() -> setupAndRun()
2.3 setupAndRun
该函数作用是 添加各种命令,到commander中,commander 是一个命令处理库,先把命令名称、参数 、回调处理函数等 设置给commander。在commander.parse(process.argv) 时,根据命令名,来判断需要commander中的哪个命令来处理(调用回调函数)
下面看下代码:
async function setupAndRun() {
...省略一些 非主流程 的代码...
//添加detachedCommands中的每种命令,到commander中,
//在commander.parse(process.argv); 时
for (const command of detachedCommands) {
attachCommand(command);
}
try {
//加载配置,主要就是通过这里,去获取autolinking的信息。例如:package.json 依赖的第三方库,以及 android、ios项目的信息(包名、资源路径等)
//代码2.4分析
const config = loadConfig();
for (const command of [...projectCommands, ...config.commands]) {
// projectCommands 是默认命令对象的集合,每个命令对象都有的属性{name: 'config', func: xxx}
// name 表示这个命令的名称,func 表示 执行该命令时,触发的函数
// 代码2.5 介绍的config.ts ,就是projectCommands中的一员
//注册命令,后续在commander.parse 执行是,就可以根据命令行中的参数信息找到对应命令对象,执行函数
attachCommand(command, config);
}
} catch (error) {
...省略一些代码...
}
//命令行中的参数,会传入到这里。上门已经设置好了各种命令。这里根据命令行的信息,开始执行命令对应的回调函数
//代码2.5分析
commander.parse(process.argv);
//默认会有两个参数(也就是命令行中没有输入参数),这时输出help结果
if (commander.rawArgs.length === 2) {
commander.outputHelp();
}
...省略代码...
}
2.4 loadConfig
function loadConfig(projectRoot: string = findProjectRoot()): Config {
let lazyProject: ProjectConfig;
//从当前项目目录下,开始寻找react-native.config.js文件,
// 在react-native.config.js文件 可以配置依赖库的autolinking规则
const userConfig = readConfigFromDisk(projectRoot);
//初始化配置,最后跟下面的finalConfig 合并后返回
const initialConfig: Config = {
root: projectRoot,
//
get reactNativePath() {
return userConfig.reactNativePath
? path.resolve(projectRoot, userConfig.reactNativePath)
: resolveReactNativePath(projectRoot);
},
dependencies: userConfig.dependencies,
commands: userConfig.commands,
healthChecks: [],
platforms: userConfig.platforms,
//该函数是在命令执行后(也就是在代码2.5之后),才会执行。
//获取原生项目的信息,例如:包名、.gradle文件路径、manifest文件路径等。代码2.6分析
get project() {
if (lazyProject) {
return lazyProject;
}
lazyProject = {};
//finalConfig 在下面创建,
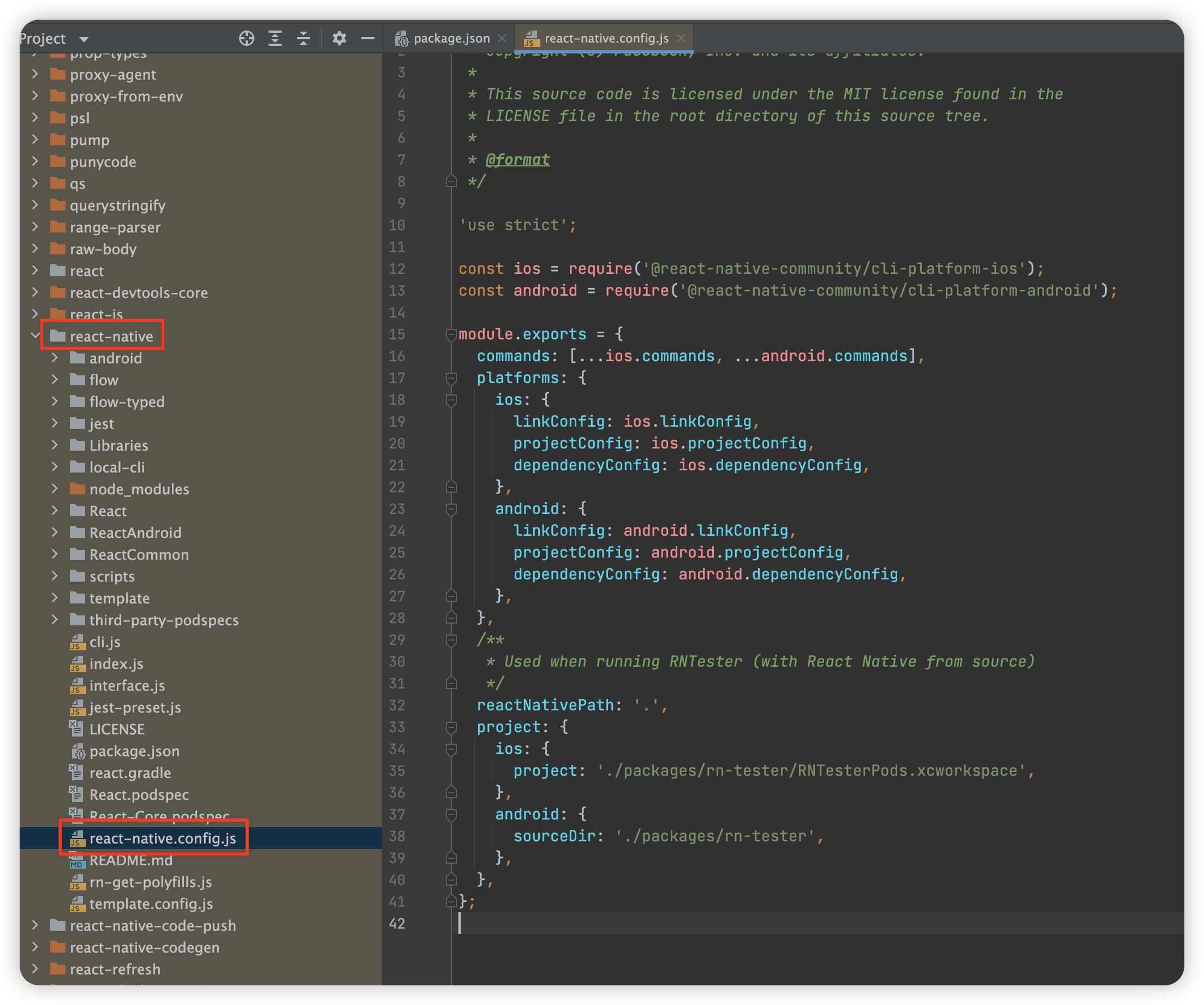
//finalConfig.platforms 内容,根源是在node—module/react-native/react-native.config.js 文件中配置的。详见下图2.4.1
for (const platform in finalConfig.platforms) {
const platformConfig = finalConfig.platforms[platform];
if (platformConfig) {
//获取原生项目的信息,在代码1.6分析。projectConfig 就是在react-native/react-native.config.js 是传入的
lazyProject[platform] = platformConfig.projectConfig(
projectRoot,
userConfig.project[platform] || {},
);
}
}
return lazyProject;
},
};
const finalConfig = Array.from(
new Set([
...Object.keys(userConfig.dependencies),
//这里从package.json中获取 RN依赖的第三方库
...findDependencies(projectRoot),
]),
).reduce((acc: Config, dependencyName) => {
const localDependencyRoot =
userConfig.dependencies[dependencyName] &&
userConfig.dependencies[dependencyName].root;
let root: string;
let config: UserDependencyConfig;
try {
root =
localDependencyRoot ||
resolveNodeModuleDir(projectRoot, dependencyName);
//获取当前依赖库下面的react-native.config.js 的配置信息
config = readDependencyConfigFromDisk(root);
} catch (error) {
...省略代码...
return acc;
}
const isPlatform = Object.keys(config.platforms).length > 0;
return assign({}, acc, {
//对每一个三方库,创建一个item,key是库名,value 是函数,用于获取库的原生信息(例如:创建库中类的对象)
dependencies: assign({}, acc.dependencies, {
//DependencyConfig 将会调用react-native/react-native.config.js 传入的 dependencyConfig
get [dependencyName](): DependencyConfig {
return getDependencyConfig(
root,
dependencyName,
finalConfig,
config,
userConfig,
isPlatform,
);
},
}),
commands: [...acc.commands, ...config.commands],
// 传入关于平台的信息,例如:React-native 如图2.4.1,projectConfig 获取原生项目的信息,dependencyConfig 获取第三方库的信息
//在2.6 和 2.7 介绍这两个
platforms: {
...acc.platforms,
...config.platforms,
},
healthChecks: [...acc.healthChecks, ...config.healthChecks],
}) as Config;
}, initialConfig);
return finalConfig;
}
下图 2.4.1
2.5 commander.parse(process.argv);
该函数是触发命令的执行,我们命令行 传入的参数是config,那么就会执行对应的回调
在代码2.3 中 config = loadConfig(); 传入到attachCommand,所以这里的action回调,是已经有了这些信息。下面我们进入cli-config/src/commads/config.ts 看看
config.ts
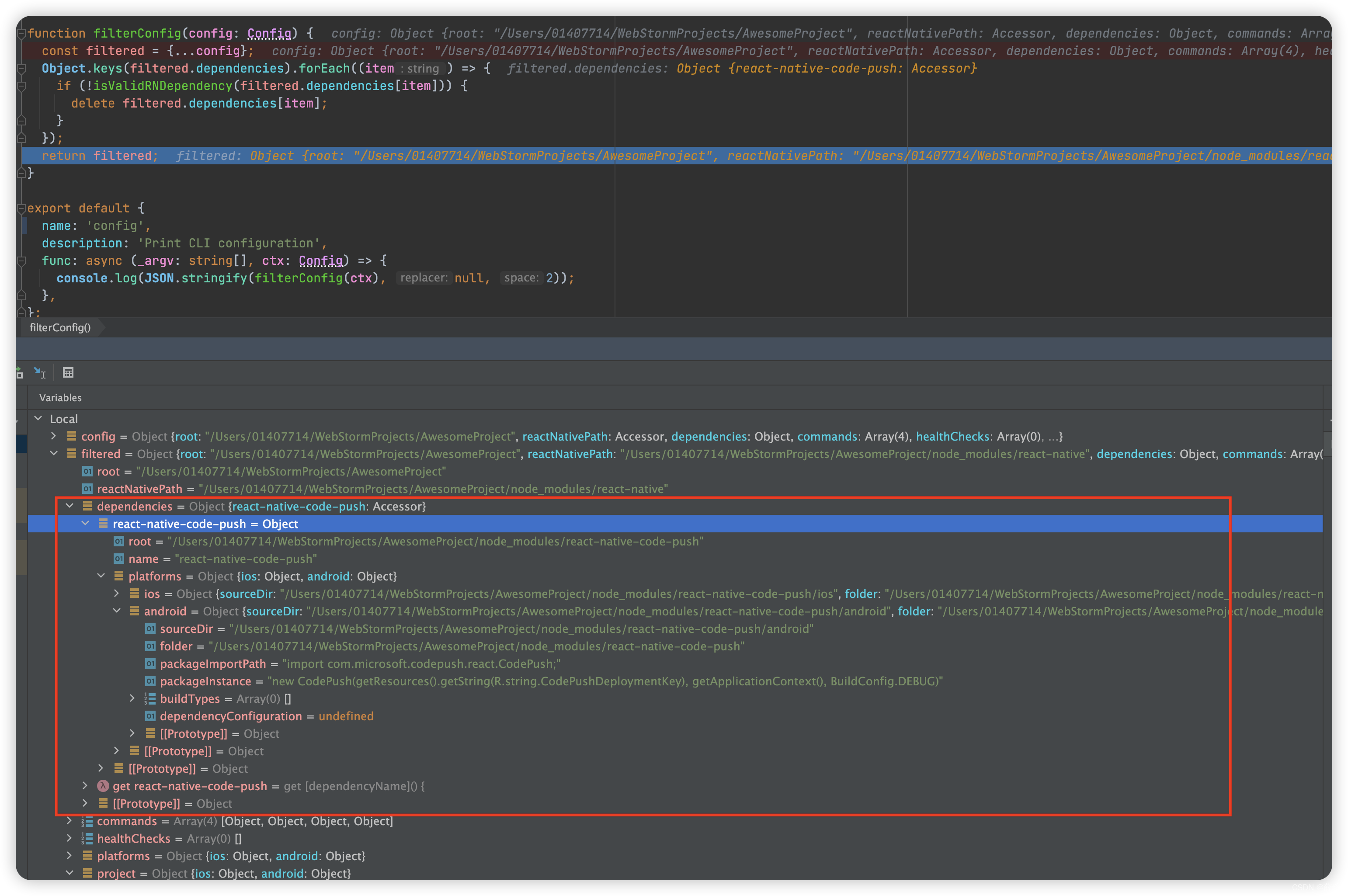
export default {
name: 'config',
description: 'Print CLI configuration',
func: async (_argv: string[], ctx: Config) => {
//filterConfig 就是去获取所有的内容
console.log(JSON.stringify(filterConfig(ctx), null, 2));
},
};
//config 参数内容如下图 1.5.2
function filterConfig(config: Config) {
// 触发 project函数
const filtered = {...config};
Object.keys(filtered.dependencies).forEach((item) => {
//触发 dependencies中每项的函数
if (!isValidRNDependency(filtered.dependencies[item])) {
delete filtered.dependencies[item];
}
});
return filtered;
}
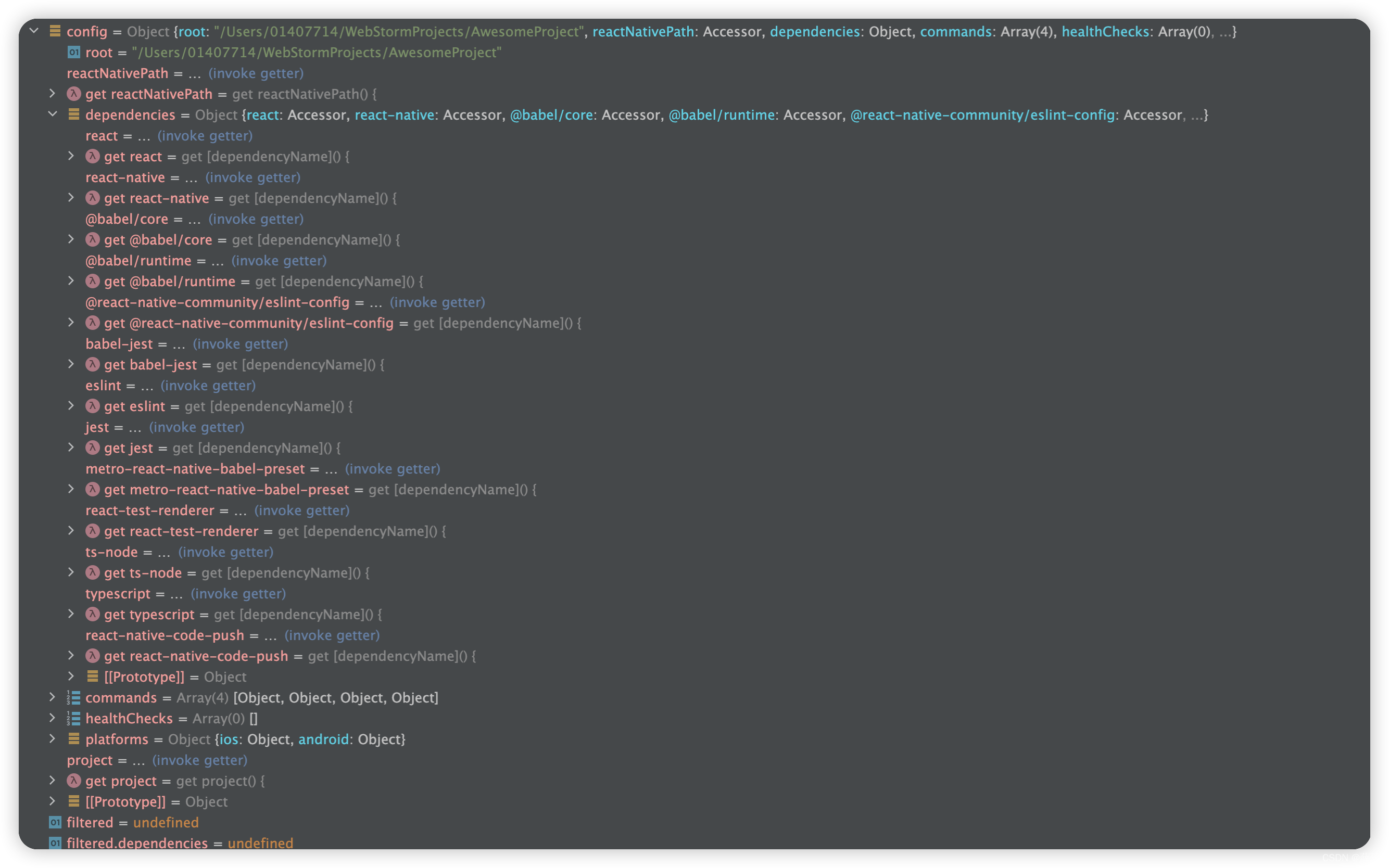
下图 2.5.2,可以看到
- project 是个函数,也就是代码2.4中initialConfig 中传入的。
- dependencies 中的每个item都是一个函数,他是 代码2.4 中finalConfig 传入的
通过代码2.4的分析,可以知道 project函数将会调用 projectConfig 获取原生项目的信息,dependencies中的每个item会调用 dependencyConfig 获取第三方库的信息。他们都是在 filterConfig 中触发的。
下面就来看一下 projectConfig 获取原生项目的信息、dependencyConfig 获取第三方库的信息 的代码
2.6 projectConfig
获取原生项目的信息,该函数是在 react-native/react-native.config.js 配置中传入的
拓展:在调试时发现,代码指向并没有到项目中的 packages/platform-android/src/config/index.ts ,而指向的是node_modules/@react-native-community/cli-platform-android/src/config/index.ts ,后者是前者的一个软连接,一番探索发现了一些技巧 1、 你所不知道的模块调试技巧 - npm link 2、【npm】简化本地文件引用路径
每一个信息的获取,都是优先获取配置文件中的,如果没有,再去调用函数获取。整体逻辑很简单,就不注释了
export function projectConfig(
root: string,
userConfig: AndroidProjectParams = {},
): AndroidProjectConfig | null {
const src = userConfig.sourceDir || findAndroidDir(root);
if (!src) {
return null;
}
const sourceDir = path.join(root, src);
const appName = getAppName(sourceDir, userConfig.appName);
const manifestPath = userConfig.manifestPath
? path.join(sourceDir, userConfig.manifestPath)
: findManifest(path.join(sourceDir, appName));
if (!manifestPath) {
return null;
}
const packageName = userConfig.packageName || getPackageName(manifestPath);
if (!packageName) {
throw new Error(`Package name not found in ${manifestPath}`);
}
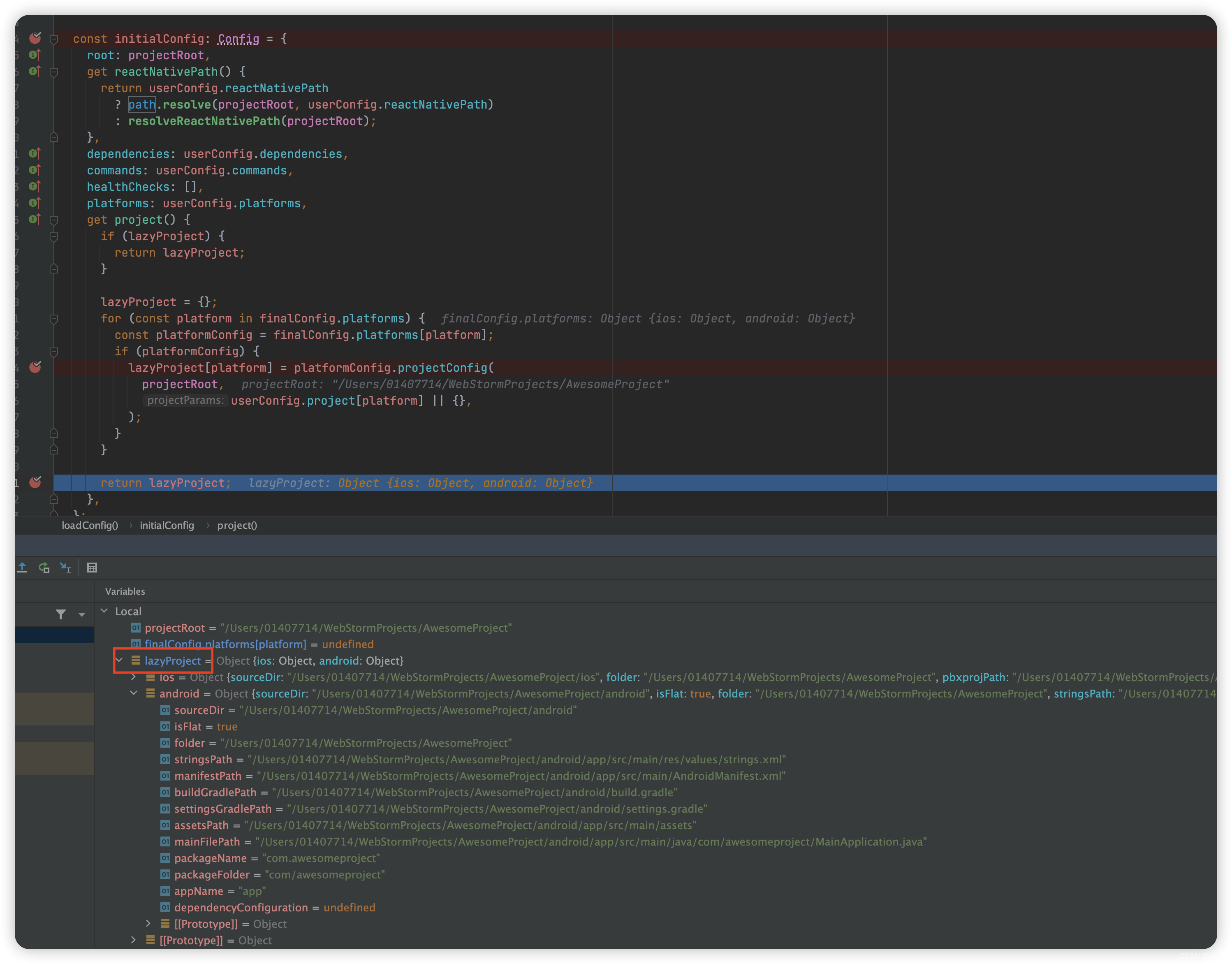
return {
sourceDir,
appName,
packageName,
dependencyConfiguration: userConfig.dependencyConfiguration,
};
}
下图 2.5.2 projectConfig 执行完成后,拿到的信息,是这样子的
2.7 dependencyConfig
代码2.5中filtered.dependencies[item] 触发的是 代码2.4中 传入的getDependencyConfig 函数,
function getDependencyConfig(
root: string,
dependencyName: string,
finalConfig: Config,
config: UserDependencyConfig,
userConfig: UserConfig,
isPlatform: boolean,
): DependencyConfig {
return merge(
{
root,
name: dependencyName,
platforms: Object.keys(finalConfig.platforms).reduce(
(dependency, platform) => {
const platformConfig = finalConfig.platforms[platform];
dependency[platform] =
// Linking platforms is not supported
isPlatform || !platformConfig
? null
//这里的dependencyConfig 才是react-native/react-native.config.js 传入的函数
: platformConfig.dependencyConfig(
root,
config.dependency.platforms[platform],
);
return dependency;
},
{} as Config['platforms'],
),
},
userConfig.dependencies[dependencyName] || {},
) as DependencyConfig;
}
platformConfig.dependencyConfig 调用的函数也是在 packages/platform-android/src/config/index.ts 中
优先从依赖库中的react-native.config.js 获取,若无,再调用函数获取
export function dependencyConfig(
root: string,
userConfig: AndroidDependencyParams = {},
): AndroidDependencyConfig | null {
const src = userConfig.sourceDir || findAndroidDir(root);
if (!src) {
return null;
}
const sourceDir = path.join(root, src);
const manifestPath = userConfig.manifestPath
? path.join(sourceDir, userConfig.manifestPath)
: findManifest(sourceDir);
if (!manifestPath) {
return null;
}
const packageName = userConfig.packageName || getPackageName(manifestPath);
const packageClassName = findPackageClassName(sourceDir);
/**
* This module has no package to export
*/
if (!packageClassName) {
return null;
}
const packageImportPath =
userConfig.packageImportPath ||
`import ${packageName}.${packageClassName};`;
const packageInstance =
userConfig.packageInstance || `new ${packageClassName}()`;
const buildTypes = userConfig.buildTypes || [];
const dependencyConfiguration = userConfig.dependencyConfiguration;
return {
sourceDir,
packageImportPath,
packageInstance,
buildTypes,
dependencyConfiguration,
};
}
下面看一下,最后获取的内容:图2.7.1
命令执行完成,返回信息到2.1中的 reactNativeConfigOutput,进行一些解析赋值,Autolinking需要的原生信息,已经拿到,下面就是根据这些信息,执行上面提到的总流程的第3、4、5步,这些就非常简单了
先来看第2步autoModules.addReactNativeModuleProjects(defaultSettings)
3 、addReactNativeModuleProjects
效果是 添加三方库信息到setting.gradle
void addReactNativeModuleProjects(DefaultSettings defaultSettings) {
//reactNativeModule 中保存是,每个库的信息,
reactNativeModules.forEach { reactNativeModule ->
//nameCleansed 库名称,对应图2.7.1 中的红框中的dependencies 的react-native-code-push这一项的key值。就是react-native-code-push
String nameCleansed = reactNativeModule["nameCleansed"]
//对应react-native-code-push这一项的platforms.android.sourceDir
String androidSourceDir = reactNativeModule["androidSourceDir"]
//和在setting.gradle中,引入本地库是一样的,只不过这里是在编译器赋值的
defaultSettings.include(":${nameCleansed}")
defaultSettings.project(":${nameCleansed}").projectDir = new File("${androidSourceDir}")
}
}
再来看总流程的第3步addReactNativeModuleDependencies,
4 、addReactNativeModuleProjects
添加三方库信息到 build.gradle中
void addReactNativeModuleDependencies(Project appProject) {
reactNativeModules.forEach { reactNativeModule ->
def nameCleansed = reactNativeModule["nameCleansed"]
appProject.dependencies {
//reactNativeModulesBuildVariants 是从脚手架获取的,意味着可以通过配置来决定。
//对应图2.7.1 react-native-code-push这一项的platforms.android.buildTypes
if (reactNativeModulesBuildVariants.containsKey(nameCleansed)) {
//为每一种buildVariant,添加依赖
reactNativeModulesBuildVariants
.get(nameCleansed)
.forEach { buildVariant ->
"${buildVariant}Implementation" project(path: ":${nameCleansed}")
}
} else {
// TODO(salakar): are other dependency scope methods such as `api` required?
implementation project(path: ":${nameCleansed}")
}
}
}
}
5、generatePackagesFile
调用generatePackagesFile,生成PackageList 类,用于在MainApplication 初始化ReactNativeHost时 getPackages 中使用
参数 generatedFileContentsTemplate 是一个字符串,内容就是PackageList的模板代码。 它把需要import的第三方库,用字符串{{ packageImports }} 先代替。
generatePackagesFile 函数收集第三方库信息后,替换字符串中所得内容,最后把字符串,写入文件即可。
void generatePackagesFile(File outputDir, String generatedFileName, String generatedFileContentsTemplate) {
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>[] packages = this.reactNativeModules
String packageName = this.packageName
String packageImports = ""
String packageClassInstances = ""
if (packages.size() > 0) {
def interpolateDynamicValues = {
it
.replaceAll(~/([^.\w])(BuildConfig|R)([^\w])/, {
wholeString, prefix, className, suffix ->
"${prefix}${packageName}.${className}${suffix}"
})
}
packageImports = packages.collect {
"// ${it.name}\n${interpolateDynamicValues(it.packageImportPath)}"
}.join('\n')
packageClassInstances = ",\n " + packages.collect {
interpolateDynamicValues(it.packageInstance)
}.join(",\n ")
}
String generatedFileContents = generatedFileContentsTemplate
.replace("{{ packageImports }}", packageImports)
.replace("{{ packageClassInstances }}", packageClassInstances)
outputDir.mkdirs()
final FileTreeBuilder treeBuilder = new FileTreeBuilder(outputDir)
treeBuilder.file(generatedFileName).newWriter().withWriter { w ->
w << generatedFileContents
}
}
代码3、4是在gradle同步的时候,就会执行。代码5 是依赖build任务,所以需要编译项目,才能生成
刚开始是想断点调试native-module.gralde,但是断点进入build.gradle中后,在native-module.gralde中就是断不下来。后来询问了react-native-community/cli的一个贡献者,他使用打日志的方式,感觉这种方式太麻烦了,所以顺便请教一下大神,如何断点调试build.gradle引用的其他脚本。
至此,Autolinking的源码就分析完了,请点赞、评论 支持一下,欢迎吐槽,U·ェ·U