目录
前言
规则引擎,顾名思义是针对我们业务系统中配置的各种规则进行统一管理,通过该引擎进行调度计算,可以动态调整规则的表达式内容,而不影响业务系统代码,常见的业务典型场景有电商中促销活动,单品折扣、整场活动满减或满折,用户参与活动赠送赠品,以及在投放业务中根据规则回传事件等场景
一、QLExpress是什么?
由阿里的电商业务规则、表达式(布尔组合)、特殊数学公式计算(高精度)、语法分析、脚本二次定制等强需求而设计的一门动态脚本引擎解析工具。 在阿里集团有很强的影响力,同时为了自身不断优化、发扬开源贡献精神,于2012年开源。
QLExpress脚本引擎被广泛应用在阿里的电商业务场景,具有以下的一些特性:
- 1、线程安全,引擎运算过程中的产生的临时变量都是threadlocal类型。
- 2、高效执行,比较耗时的脚本编译过程可以缓存在本地机器,运行时的临时变量创建采用了缓冲池的技术,和groovy性能相当。
- 3、弱类型脚本语言,和groovy,javascript语法类似,虽然比强类型脚本语言要慢一些,但是使业务的灵活度大大增强。
- 4、安全控制,可以通过设置相关运行参数,预防死循环、高危系统api调用等情况。
- 5、代码精简,依赖最小,250k的jar包适合所有java的运行环境,在android系统的低端pos机也得到广泛运用。
二、使用步骤
1.引入POM
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>QLExpress</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency>2.入门案例
代码如下(示例):
public class QlExpressTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExpressRunner runner = new ExpressRunner();
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
context.put("a", 1);
context.put("b", 2);
context.put("c", 3);
String express = "a + b * c";
Object r = runner.execute(express, context, null, true, false);
System.out.println(r);
}
}运行输出:
7
进程已结束,退出代码0
二、使用进阶
一、运行原理
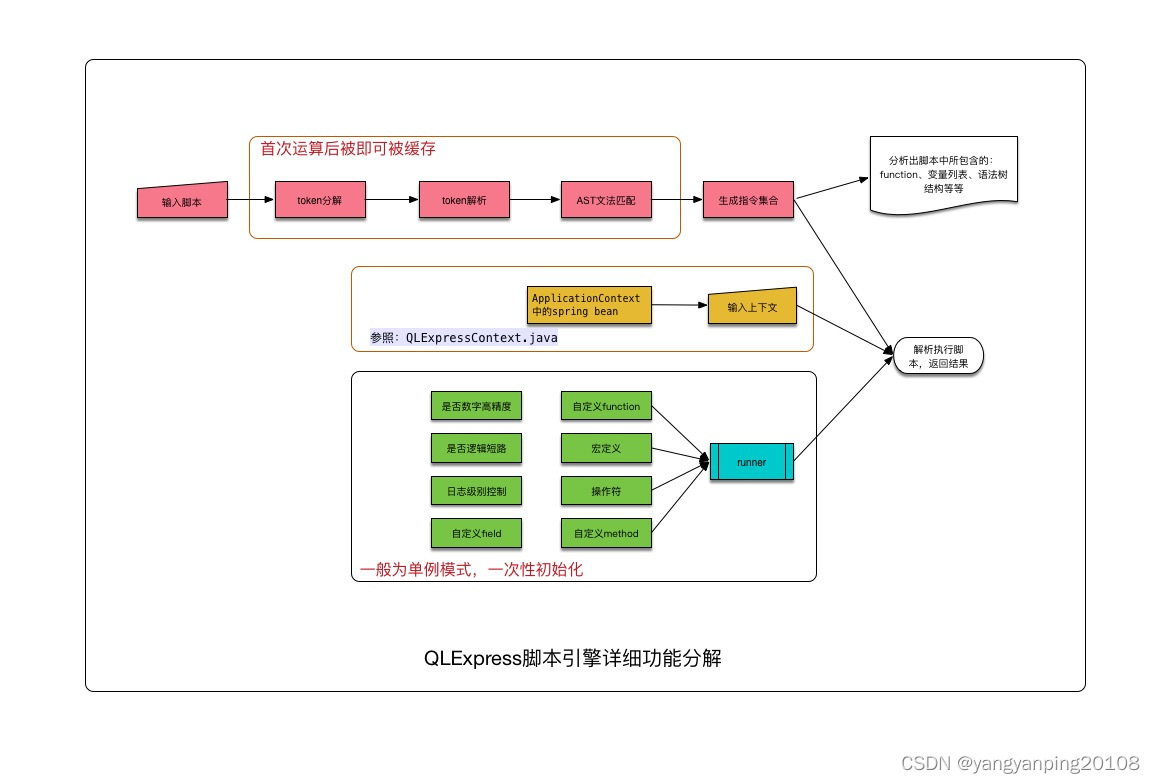
QLExpressRunner如下图所示,从语法树分析、上下文、执行过程三个方面提供二次定制的功能扩展。
二、调用入参
/**
* 执行一段文本
* @param expressString 程序文本
* @param context 执行上下文,可以扩展为包含ApplicationContext
* @param errorList 输出的错误信息List
* @param isCache 是否使用Cache中的指令集,建议为true
* @param isTrace 是否输出详细的执行指令信息,建议为false
* @param aLog 输出的log
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
Object execute(String expressString, IExpressContext<String, Object> context, List<String> errorList, boolean isCache, boolean isTrace);三、与spring框架的无缝集成
上下文参数 IExpressContext context 非常有用,它允许put任何变量,然后在脚本中识别出来。
在实际中我们很希望能够无缝的集成到spring框架中,可以仿照下面的例子。
QLExpress 上下文定义类
/**
* QLExpress 上下文定义类
*
* @author yangyanping
* @date 2023-07-27
*/
public class QLExpressContext extends HashMap<String, Object> implements IExpressContext<String, Object> {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public QLExpressContext(Map<String, Object> properties, ApplicationContext context) {
super(properties);
this.applicationContext = context;
}
@Override
public Object get(Object name) {
Object result;
result = super.get(name);
try {
if (result == null && this.applicationContext != null && this.applicationContext.containsBean((String) name)) {
result = this.applicationContext.getBean((String) name);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object put(String name, Object object) {
super.put(name, object);
return object;
}
}QLExpress 管理类
/**
* QLExpress 管理器
*
* @author yangyanping
* @date 2023-07-26
* https://blog.csdn.net/AiMaiShanHuHai/article/details/127160286
*/
@Slf4j
public class QLExpressManager implements InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private ExpressRunner runner;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Object execute(String statement, Map<String, Object> context) throws Exception {
IExpressContext expressContext = new QLExpressContext(context != null ? context : Collections.EMPTY_MAP, applicationContext);
return runner.execute(statement, expressContext, null, true, false);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
runner = new ExpressRunner(false, false);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("大于", ">", null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("小于", "<", null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("等于", "==", null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("大于等于", ">=", null);
runner.addOperatorWithAlias("小于等于", "<=", null);
Map<String, RuleHandler> beanMap = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(RuleHandler.class);
beanMap.values().forEach(bean -> {
Method[] methods = bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
QlRule qlRule = method.getAnnotation(QlRule.class);
if (qlRule == null) {
continue;
}
try {
runner.addFunctionOfClassMethod(qlRule.methodName(), bean.getClass().getName(), method.getName(),
method.getParameterTypes(), null);
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("runner.addFunctionOfClassMethod", ex);
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}QLRule 注解
/**
* QLRule 注解,Spring启动时扫描
*
* @author yangyanping
* @date 2023-07-27
*/
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface QlRule {
/**
* 方法名称
*/
String methodName();
/**
* 方法描述
*/
String desc() default "";
}规则接口类定义
/**
* 规则处理器
*
* @author yangyanping
* @date 2023-07-27
*/
public interface RuleHandler {
}四、案例场景
规则处理器接口
/**
* 规则处理器接口
*
* @author yangyanping
* @date 2023-07-27
*/
public interface AbstractRuleHandler extends RuleHandler {
/**
* 根据渠道创意查询
*/
BigDecimal doHandler(Integer type, String channelType);
}订单金额统计查询
@Component
public class OrderMoneyHandler implements AbstractRuleHandler {
@Override
@QlRule(methodName = "doHandler", desc = "订单金额统计查询")
public BigDecimal doHandler(Integer type, String channelType) {
return null;
}
}订单总数统计查询
@Component
public class OrderCountHandler implements AbstractRuleHandler {
@Override
@QlRule(methodName = "doHandler", desc = "订单总数统计查询")
public BigDecimal doHandler(Integer type, String channelType, String creativeId) {
return null;
}
}五、案例场景
public class QlExpressTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DefaultContext<String, Object> context = new DefaultContext<>();
//阈值1000
context.put("threshold", 1000);
context.put("name", "orderMoney");
context.put("channelType", "mobile");
context.put("type", 1);
String qlExpress = "" +
"if(name ==\"orderMoney\" ) { " +
"actual = orderMoneyHandler.doHandler(type,channelType); " +
"} else if(name ==\"orderCount\" ) { " +
"actual = orderCountHandler.doHandler(type,channelType); " +
"}" +
"" +
"return actual >= threshold; ";
Object result = qlExpressManager.execute(qlExpress, context);
}
}六、热部署
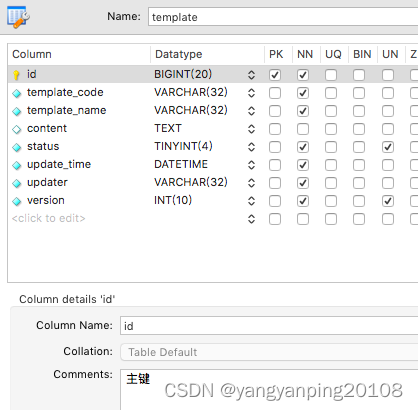
在实际开发中,我们可以把qlExpress 脚本保存到数据库中,业务的变动无需发布服务即可生效。
实现服务的热部署功能。
模版表设计如下: