1. 写在前面
日常工作中,锁用的非常多,今天就和大家一起来看下ReentrantLock,看完这边文章我们基本能够解答下面的疑问:
- 什么是 ReentrantLock?
- ReentrantLock 和 synchronized 有什么区别?
- 如何使用 ReentrantLock?
- 什么是公平锁和非公平锁?
- 什么是可重入性?
- ReentrantLock 的 lockInterruptibly 方法有什么作用?
- ReentrantLock 的 tryLock 方法有什么作用?
- ReentrantLock 的 newCondition 方法有什么作用?
- ReentrantLock 的底层实现原理是什么?
2. 全局视角
ReentrantLock 是 Java 并发包(java.util.concurrent.locks)中的一个类,它提供了一个可重入的互斥锁。ReentrantLock 的实现依赖于 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS),这是一个用于构建锁和其他同步器的框架。
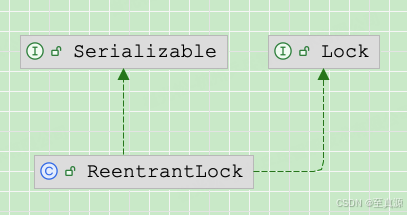
ReentrantLock 类的继承结构相对简单,它直接继承自 Object 类,并实现了 Lock 接口和 Serializable 接口。
- ReentrantLock:实现了 Lock 接口和 Serializable 接口。它通过内部类 Sync 来实现具体的锁机制。
- Lock 接口:定义了锁的基本操作,如 lock、unlock、tryLock 和 newCondition 等。
- Serializable 接口:使 ReentrantLock 可以被序列化。
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS):一个用于实现依赖于 FIFO 队列的阻塞锁和相关同步器的框架。ReentrantLock 的内部类 Sync 继承自 AQS,并实现了具体的同步逻辑。
3. 从日常用法说起
3.1 创建锁
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ReentrantLockExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() {
lock.lock(); // 获取锁
try {
// 临界区代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is doing something");
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 释放锁
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockExample example = new ReentrantLockExample();
Runnable task = example::doSomething;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
3.2 可重入性
ReentrantLock 是可重入的,这意味着同一个线程可以多次获取同一个锁,而不会被自己阻塞。
public class ReentrantLockReentrancyExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void outer() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("Outer method");
inner();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void inner() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("Inner method");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockReentrancyExample example = new ReentrantLockReentrancyExample();
example.outer();
}
}
3.3 可中断锁
使用 lockInterruptibly 方法可以在获取锁的过程中响应中断。
public class ReentrantLockInterruptiblyExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly(); // 可中断地获取锁
try {
// 临界区代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is doing something");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockInterruptiblyExample example = new ReentrantLockInterruptiblyExample();
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
example.doSomething();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " was interrupted");
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread2.interrupt(); // 中断线程2
}
}
3.4 尝试获取锁
使用 tryLock 方法可以尝试获取锁,如果锁可用则获取锁并返回 true,否则立即返回 false。
public class ReentrantLockTryLockExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() {
if (lock.tryLock()) { // 尝试获取锁
try {
// 临界区代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is doing something");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " could not get the lock");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockTryLockExample example = new ReentrantLockTryLockExample();
Runnable task = example::doSomething;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
3.5 定时尝试获取锁
使用 tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 方法可以在指定的时间内尝试获取锁。
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ReentrantLockTimedTryLockExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void doSomething() {
try {
if (lock.tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { // 尝试在2秒内获取锁
try {
// 临界区代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is doing something");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " could not get the lock");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " was interrupted");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockTimedTryLockExample example = new ReentrantLockTimedTryLockExample();
Runnable task = example::doSomething;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
3.6 使用 Condition 对象
ReentrantLock 提供了 newCondition 方法,可以创建一个 Condition 对象,用于实现更复杂的等待/通知机制。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ReentrantLockConditionExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is waiting");
condition.await(); // 等待
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is done waiting");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void signal() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is signaling");
condition.signal(); // 唤醒等待的线程
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLockConditionExample example = new ReentrantLockConditionExample();
Runnable awaitTask = () -> {
try {
example.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(awaitTask);
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒
Runnable signalTask = example::signal;
Thread thread2 = new Thread(signalTask);
thread2.start();
}
}
3.7 公平锁与非公平锁
默认情况下,ReentrantLock 是非公平锁,可以通过构造函数参数 true 来创建公平锁。
public class ReentrantLockFairnessExample {
private final ReentrantLock lock;
public ReentrantLockFairnessExample(boolean fair) {
this.lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
}
public void doSomething() {
lock.lock();
try {
// 临界区代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is doing something");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockFairnessExample example = new ReentrantLockFairnessExample(true); // 创建公平锁
Runnable task = example::doSomething;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
4. 底层实现原理
ReentrantLock 是一个可重入的锁,它的实现依赖于内部的 Sync 类。Sync 继承自 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,并且有两个子类 NonfairSync 和 FairSync,分别实现非公平锁和公平锁。代码如下:
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;
private final Sync sync;
// 默认构造函数创建非公平锁
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
// 带参数的构造函数,可以选择公平锁或非公平锁
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
// 获取锁
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
// 可中断地获取锁
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
// 尝试获取锁
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
// 尝试在指定时间内获取锁
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
// 释放锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// 创建一个新的Condition对象
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
// 内部类Sync,继承自AQS
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
// 尝试获取锁,由子类实现
abstract void lock();
// 非公平锁尝试获取锁
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 尝试释放锁
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// 创建一个新的Condition对象
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
// 获取当前持有锁的线程
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();
}
// 获取锁的持有计数
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}
// 判断锁是否被持有
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}
// 反序列化时重置锁的状态
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}
// 非公平锁的实现
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
// 获取锁
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
// 尝试获取锁
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
// 公平锁的实现
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
// 获取锁
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
// 尝试获取锁
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
4.1 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS) 类
AQS 是 ReentrantLock 的底层实现基础。它维护了一个 FIFO 队列,用于管理等待线程,并提供了获取和释放锁的基本操作。以下是 AQS 的关键方法:
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;
// 获取锁
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
// 释放锁
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 尝试获取锁,由子类实现
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// 尝试释放锁,由子类实现
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// 添加等待节点
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
// 将节点插入队列
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
// 获取队列中的节点
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 释放下一个节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
}
4.2 锁的获取
- ReentrantLock 的 lock() 方法调用了 Sync 类的 lock() 方法。
- 非公平锁(NonfairSync)的 lock() 方法首先尝试直接获取锁(CAS 操作),如果失败则调用 acquire(1)。
- 公平锁(FairSync)的 lock() 方法直接调用 acquire(1)。
- acquire(1) 方法是 AQS 提供的,它会尝试获取锁,如果失败则将当前线程加入等待队列,并进行自旋等待。
4.3 锁的释放
- ReentrantLock 的 unlock() 方法调用了 Sync 类的 release(1) 方法。
- release(1) 方法是 AQS 提供的,它会尝试释放锁,如果锁完全释放(计数为 0),则唤醒等待队列中的下一个线程。
4.4 公平锁与非公平锁
- 公平锁在获取锁时会检查等待队列中是否有前驱节点,如果有则当前线程必须等待
- 非公平锁则直接尝试获取锁,不考虑等待队列中的其他线程
4.5 重入性
ReentrantLock 是可重入的,因为同一个线程可以多次获取同一个锁。每次获取锁时,计数器 state 增加 1,释放锁时计数器减少 1,直到计数器为 0 时锁才真正释放。
4.6 条件变量
ReentrantLock 提供了 newCondition() 方法来创建条件变量。条件变量通过 ConditionObject 实现,依赖于 AQS 的 ConditionObject 类。
5. 细节
5.1 ReentrantLock 和 synchronized 有什么区别?
- 功能:ReentrantLock 提供了更多的功能,如可定时锁、可中断锁和公平锁等,而 synchronized 相对简单。
- 性能:在高并发情况下,ReentrantLock 通常比 synchronized 性能更好。
- 灵活性:ReentrantLock 可以在代码中显式地获取和释放锁,而 synchronized 是隐式的。
- 条件变量:ReentrantLock 提供了 Condition 类,可以实现更复杂的等待/通知机制,而 synchronized 只能使用 wait 和 notify。
5.2 什么是公平锁和非公平锁?
- 公平锁:公平锁按线程请求的顺序获取锁,避免线程饥饿。ReentrantLock 可以通过构造函数参数 true 来创建公平锁。
- 非公平锁:非公平锁不保证线程获取锁的顺序,可能会导致线程饥饿。默认情况下,ReentrantLock 是非公平锁。
5.3 什么是可重入性?
可重入性是指同一个线程可以多次获取同一个锁,而不会被自己阻塞。ReentrantLock 和 synchronized 都是可重入的。例如,一个线程可以在持有锁的情况下再次获取该锁。
5.4 ReentrantLock 的 lockInterruptibly 方法有什么作用?
lockInterruptibly 方法允许线程在获取锁的过程中被中断。与 lock 方法不同,lockInterruptibly 方法可以响应中断。
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
// 临界区代码
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 处理中断
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
系列文章
7.jdk源码阅读之ConcurrentHashMap(上)