序言
从个人角度而已,了解学习优质开源项目的源码,可以学习其设计思想和提升自身代码质量。所以本次从vue-core 3.3alpha入手进行源码解析。
对于我而言,项目设计者和学习者是站在不同角度去看待源码,设计者基于功能、模块的设计思想去一步步实现,而学习者无法从设计思想上宏观看待源码,所以只能基于实际使用逆推其设计思想!
正文
按照官网所述
快速使用vue框架,首先调用 createApp创建app,并进行mount挂载到指定元素上,所以我们先从createApp开始解析。
解析前的准备
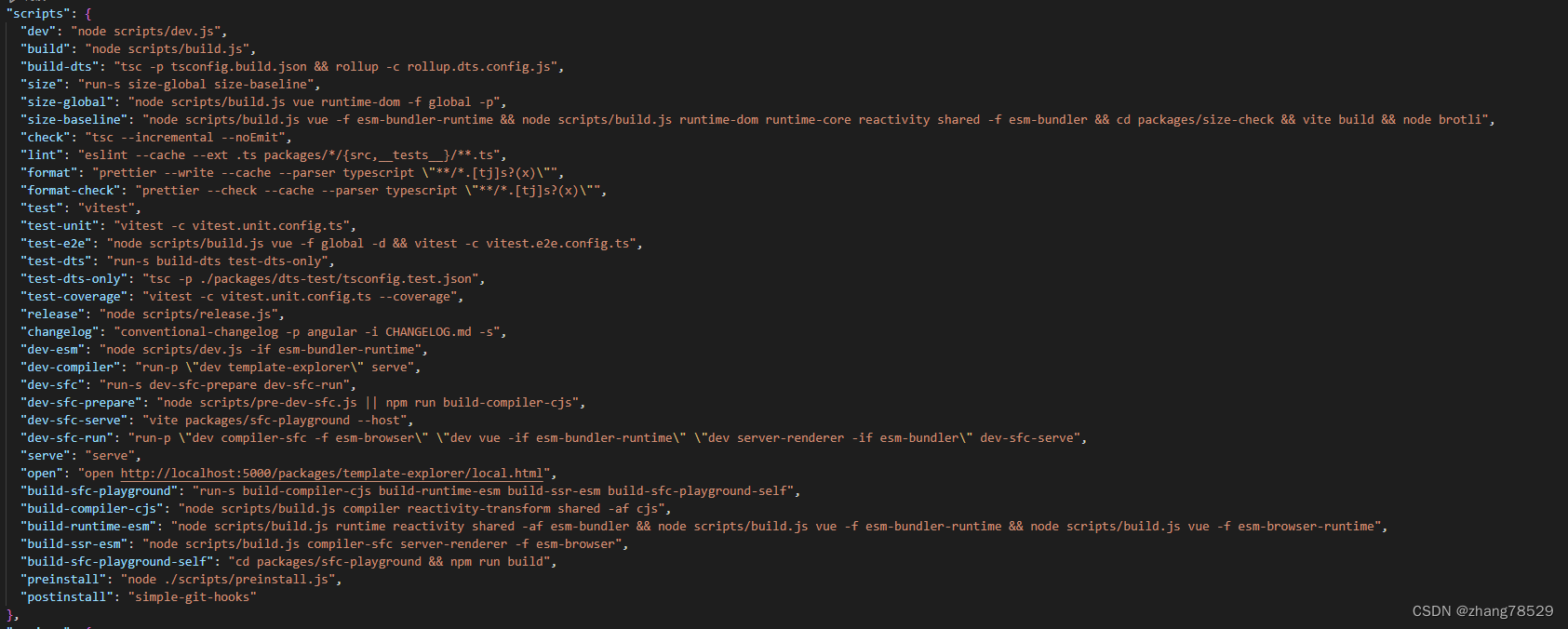
1.在开始解析之前,需要从github上clone项目
项目链接:GitHub - vuejs/core: 🖖 Vue.js is a progressive, incrementally-adoptable JavaScript framework for building UI on the web.2.克隆完成后,因为vue core是使用pnpm管理的单一代码库(monorepos),所以需要使用pnpm install进行依赖包安装
3.依赖包加载后,可以参照package.json中的配置
同时启动pnpm dev 和pnpm serve服务
dev服务:实时更新源码修改,便于调试
serve服务:启动本地服务器访问文件及页面
可以访问packages/vue/examples目录下页面进行调试,及新增调试页面
项目结构简介
正常启动调试界面,正式解析之前,需要对项目整体结构有所了解,便于解析源码时,理解其相互依赖关系。
本次解析以浏览器渲染为主,所以使用
1.compiler模块:解析器模块
- compiler-core
- compiler-dom
2.reactivity模块:响应式模块
- reactivity
3.runtime模块:运行时模块
- runtime-core
- runtime-dom
4.shared模块:公共函数模块
- shared
5.vue模块:集成模块
- vue
tip:packages/vue/examples目录下所使用的vue包皆是使用vue集成模块打包的库
源码解析
基于上述,可以从vue模块开始定位createApp函数是由runtime-dom/src的index.ts文件所导出
export const createApp = ((...args) => {
//ensureRenderer函数是懒汉单例模式,有renderer直接返回,无renderer则调用createRenderer创建并调用返回的createApp方法创建app对象
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)
if (__DEV__) {
//开发模式下开启本地组件标签名称检查
injectNativeTagCheck(app)
//开发模式下开启编译器配置检查
injectCompilerOptionsCheck(app)
}
//缓存mount方法
const { mount } = app
//重写mount方法
app.mount = (containerOrSelector: Element | ShadowRoot | string): any => {
//normalizeContainer基于containerOrSelector类型进行处理,字符串类型使用document.querySelector选择器获取元素,其他类型则直接返回
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
//没有container容器情况下则直接返回 不进行挂载
if (!container) return
//需要判断__COMPAT__条件的情况,主要是针对低版本兼容,先跳过
const component = app._component
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
component.template = container.innerHTML
if (__COMPAT__ && __DEV__) {
for (let i = 0; i < container.attributes.length; i++) {
const attr = container.attributes[i]
if (attr.name !== 'v-cloak' && /^(v-|:|@)/.test(attr.name)) {
compatUtils.warnDeprecation(
DeprecationTypes.GLOBAL_MOUNT_CONTAINER,
null
)
break
}
}
}
}
// 挂载前清空容器
container.innerHTML = ''
//调用缓存mount方法挂载
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)
if (container instanceof Element) {
//container为元素情况下,移除v-cloak属性 添加data-v-app属性
container.removeAttribute('v-cloak')
container.setAttribute('data-v-app', '')
}
return proxy
}
return app
}) as CreateAppFunction<Element>先从宏观角度看createApp函数,从上述代码可以看出该createApp是一个装饰器,用来创建app实例,并装饰扩展原app实例的mount方法。接下来我们再看ensureRenderer函数
//nodeOps包含dom元素的操作方法
import { nodeOps } from './nodeOps'
//patchProp主要是对元素的属性处理方法
import { patchProp } from './patchProp'
//extend是Object.assign的声明,主要用来合并patchProp和nodeOps
const rendererOptions = extend({ patchProp }, nodeOps)
//懒汉式单例,用来创建renderer,并配置rendererOptions
function ensureRenderer() {
return (
renderer ||
(renderer = createRenderer<Node, Element | ShadowRoot>(rendererOptions))
)
}ensureRenderer除了是懒汉式单例外,最主要的功能是注入nodeOps元素操作方法和patchProp元素属性的处理方法(nodeOps,patchProp内容比较常规,这里不详细叙述)。
项目中第一次使用createApp函数,renderer是绝对不存在的,所以现在详细说明下createRenderer函数做了什么
//createRenderer函数在runtime-core/renderer.ts文件下
//createRenderer函数是对baseCreateRenderer函数的再封装,明确类型定义,与createHydrationRenderer函数区分开来
export function createRenderer<
HostNode = RendererNode,
HostElement = RendererElement
>(options: RendererOptions<HostNode, HostElement>) {
return baseCreateRenderer<HostNode, HostElement>(options)
}从上述代码可以看出createRenderer是对baseCreateRenderer再封装,因此接下来便来详细解析一下baseCreateRenderer
function baseCreateRenderer(
options: RendererOptions,
createHydrationFns?: typeof createHydrationFunctions
): any {
// 编译时特性标志检查,可跳过
if (__ESM_BUNDLER__ && !__TEST__) {
initFeatureFlags()
}
//获取全局对象,用户端为浏览器时,target指向的是window
const target = getGlobalThis()
//设置全局对象的__VUE__属性为true
target.__VUE__ = true
//开发模式下的配置,可跳过
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
setDevtoolsHook(target.__VUE_DEVTOOLS_GLOBAL_HOOK__, target)
}
//对createRenderer传入的nodeOps,patchProp方法重命名
const {
insert: hostInsert,
remove: hostRemove,
patchProp: hostPatchProp,
createElement: hostCreateElement,
createText: hostCreateText,
createComment: hostCreateComment,
setText: hostSetText,
setElementText: hostSetElementText,
parentNode: hostParentNode,
nextSibling: hostNextSibling,
setScopeId: hostSetScopeId = NOOP,
insertStaticContent: hostInsertStaticContent
} = options
//此处内部函数定义较多,具体函数在调用时再解析
return {
render,
hydrate,
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate)
}
}
baseCreateRenderer内部主要是对外部配置进行重命名,规范命名空间,同时定义了很多内部方法(虚拟节点的处理等,也就是备受关注的diff算法函数),baseCreateRenderer返回一个对象,包含了render、hydrate、createApp方法,没错,此处的createApp即ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)所调用的createApp方法,so...,打开runtime-core/apiCreateApp.ts看看createAppAPI主要干了什么吧
export function createAppAPI<HostElement>(
render: RootRenderFunction<HostElement>,
hydrate?: RootHydrateFunction
): CreateAppFunction<HostElement> {
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
//如果传入的根组件不是函数,则进行属性拷贝
if (!isFunction(rootComponent)) {
rootComponent = extend({}, rootComponent)
}
//如果根组件的属性不是一个对象的话,进行置空,在开发模式下警告提示
if (rootProps != null && !isObject(rootProps)) {
__DEV__ && warn(`root props passed to app.mount() must be an object.`)
rootProps = null
}
// 创建app上下文环境
const context = createAppContext()
// 创建一个Set集合用来缓存安装的插件
const installedPlugins = new Set()
// 用来判断app是否挂载
let isMounted = false
const app: App = (context.app = {//上下文context与app相互绑定
// 自增型唯一uid
_uid: uid++,
// 根组件
_component: rootComponent as ConcreteComponent,
// 根组件属性
_props: rootProps,
// 根组件容器
_container: null,
// 上下文
_context: context,
// 实例
_instance: null,
// vue版本
version,
//app的config同context的config
get config() {
return context.config
},
//无法设置congfig,开发模式下警告
set config(v) {
if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`app.config cannot be replaced. Modify individual options instead.`
)
}
},
//注册插件,缓存到installedPlugins中
use(plugin: Plugin, ...options: any[]) {
if (installedPlugins.has(plugin)) {//如果插件已注册,且在开发模式下,警告提示
__DEV__ && warn(`Plugin has already been applied to target app.`)
} else if (plugin && isFunction(plugin.install)) {//如果传入的插件有install方法,则注册插件且调用install方法
installedPlugins.add(plugin)
plugin.install(app, ...options)
} else if (isFunction(plugin)) {//如果传入的插件本身就是一个函数,则注册插件和直接调用
installedPlugins.add(plugin)
plugin(app, ...options)
} else if (__DEV__) {//其他情况下,在开发模式下警告提示
warn(
`A plugin must either be a function or an object with an "install" ` +
`function.`
)
}
return app
},
//注册mixin到context的mixins集中
mixin(mixin: ComponentOptions) {
if (__FEATURE_OPTIONS_API__) {
if (!context.mixins.includes(mixin)) {//如果上下文中的mixins集中不包含参数mixin则注册
context.mixins.push(mixin)
} else if (__DEV__) {//否则在开发模式下警告提示
warn(
'Mixin has already been applied to target app' +
(mixin.name ? `: ${mixin.name}` : '')
)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn('Mixins are only available in builds supporting Options API')
}
return app
},
//注册组件到context的components集中
component(name: string, component?: Component): any {
if (__DEV__) {//开发模式下,验证名称是否vue的关键字slot 和component还有上下文配置的是否是原生标签名
validateComponentName(name, context.config)
}
if (!component) {//无component参数情况下,则根据name返回component
return context.components[name]
}
if (__DEV__ && context.components[name]) {//开发模式下,会提示已注册的组件
warn(`Component "${name}" has already been registered in target app.`)
}
//将组件注册到上下文的组件集
context.components[name] = component
// 返回app
return app
},
//注册组件到context的components集中
directive(name: string, directive?: Directive) {
if (__DEV__) {//开发模式下 验证名称是否使用了vue的保留关键字
validateDirectiveName(name)
}
if (!directive) {//无参数directive情况下,根据name返回directive
return context.directives[name] as any
}
if (__DEV__ && context.directives[name]) {//开发模式下,提示已组成的指令
warn(`Directive "${name}" has already been registered in target app.`)
}
//将指令注册到上下文的指令集
context.directives[name] = directive
// 返回app
return app
},
mount(
rootContainer: HostElement,
isHydrate?: boolean,
isSVG?: boolean
): any {
if (!isMounted) {//未挂载情况下开始挂载
if (__DEV__ && (rootContainer as any).__vue_app__) {
warn(
`There is already an app instance mounted on the host container.\n` +
` If you want to mount another app on the same host container,` +
` you need to unmount the previous app by calling \`app.unmount()\` first.`
)
}
//创建根虚拟节点
const vnode = createVNode(
rootComponent as ConcreteComponent,
rootProps
)
//根虚拟节点的appContext指向上下文
vnode.appContext = context
// HMR root reload
if (__DEV__) {//开发模式下,定义reload方法,render克隆的vnode
context.reload = () => {
render(cloneVNode(vnode), rootContainer, isSVG)
}
}
if (isHydrate && hydrate) {
hydrate(vnode as VNode<Node, Element>, rootContainer as any)
} else {
//调用baseCreateRenderer中render函数进行渲染
render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG)
}
//渲染后,状态变成已挂载
isMounted = true
//app的_container指向根节点容器
app._container = rootContainer
//根节点容器的__vue_app__属性指向app
;(rootContainer as any).__vue_app__ = app
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
app._instance = vnode.component
devtoolsInitApp(app, version)
}
return getExposeProxy(vnode.component!) || vnode.component!.proxy
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`App has already been mounted.\n` +
`If you want to remount the same app, move your app creation logic ` +
`into a factory function and create fresh app instances for each ` +
`mount - e.g. \`const createMyApp = () => createApp(App)\``
)
}
},
//卸载
unmount() {
if (isMounted) {
render(null, app._container)
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
app._instance = null
devtoolsUnmountApp(app)
}
delete app._container.__vue_app__
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`Cannot unmount an app that is not mounted.`)
}
},
//注入全局属性到context的provides中
provide(key, value) {
if (__DEV__ && (key as string | symbol) in context.provides) {
warn(
`App already provides property with key "${String(key)}". ` +
`It will be overwritten with the new value.`
)
}
context.provides[key as string | symbol] = value
return app
}
})
if (__COMPAT__) {
installAppCompatProperties(app, context, render)
}
return app
}
}
export function createAppContext(): AppContext {
return {
app: null as any,//与全局app相互绑定
config: {
isNativeTag: NO,
performance: false,
globalProperties: {},
optionMergeStrategies: {},
errorHandler: undefined,
warnHandler: undefined,
compilerOptions: {}
},
mixins: [],//全局mixin集
components: {},//全局组件集
directives: {},//全局指令集
provides: Object.create(null),//提供依赖集
optionsCache: new WeakMap(),//配置缓存
propsCache: new WeakMap(),//属性缓存
emitsCache: new WeakMap()//事件缓存
}
}参考上面2段注释内容,大家可以明白这里返回的createApp函数,主要是创建全局上下文context对象和app对象并且相互绑定关联,并在app对象中定义use、mixin、component、directive、mount、unmount、provide等方法
截止此处,大家应该已经大致了解了创建应用的整体流程
总结
创建应用createApp函数,主要作用是
- 导入外部定义的dom节点操作方法和dom元素属性操作方法
- 创建app对象和context对象
- 通过app对象定义的方法,配置全局组件、mixin、指令等和挂载、卸载功能
下一篇:vue-core 3.3alpha版本源码解析2--挂载应用(mount)_zhang78529的博客-CSDN博客