一. 负载均衡Ribbon(理解记忆)
在刚才的案例中,我们启动了一个springcloud_01_goods ,然后通过DiscoveryClient来获取服务实例信息,然后获取ip和端口来访问。
但是实际环境中,往往会访问拥有很多个springcloud_01_goods 服务的集群。此时获取的服务列表中就会有多个,到底该访问哪一个呢?
一般这种情况下就需要编写负载均衡算法,在多个实例列表中进行选择。
不过Eureka中已经集成了负载均衡组件:Ribbon,简单配置即可使用。
1.1 什么是Ribbon
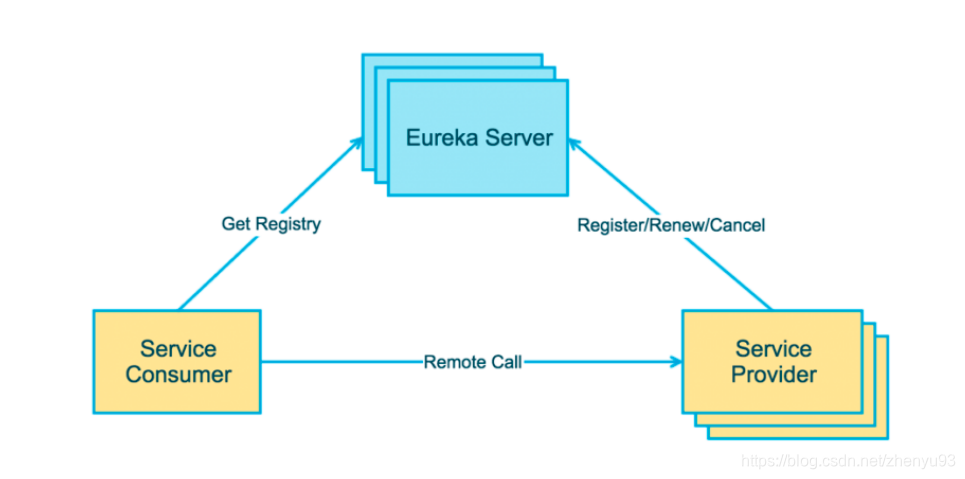
Ribbon是Netflix发布的负载均衡器,它有助于控制HTTP和TCP的客户端的行为。为Ribbon配置服务提供者地址后,Ribbon就可基于某种负载均衡算法,自动地帮助服务消费者去请求。Ribbon默认为我们提供了很多负载均衡算法,例如轮询、随机等。当然,我们也可为Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
1.2 Ribbon负载均衡
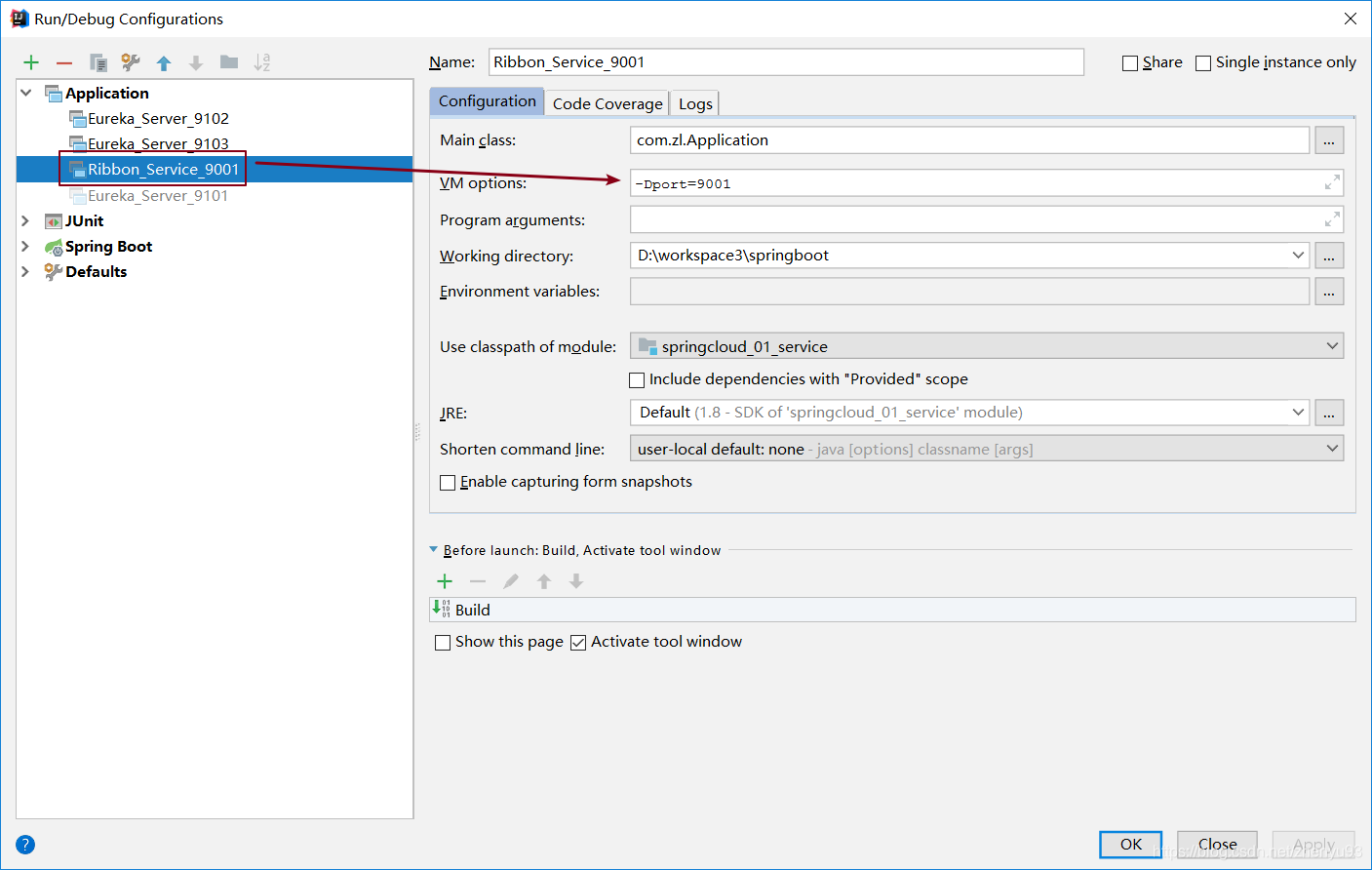
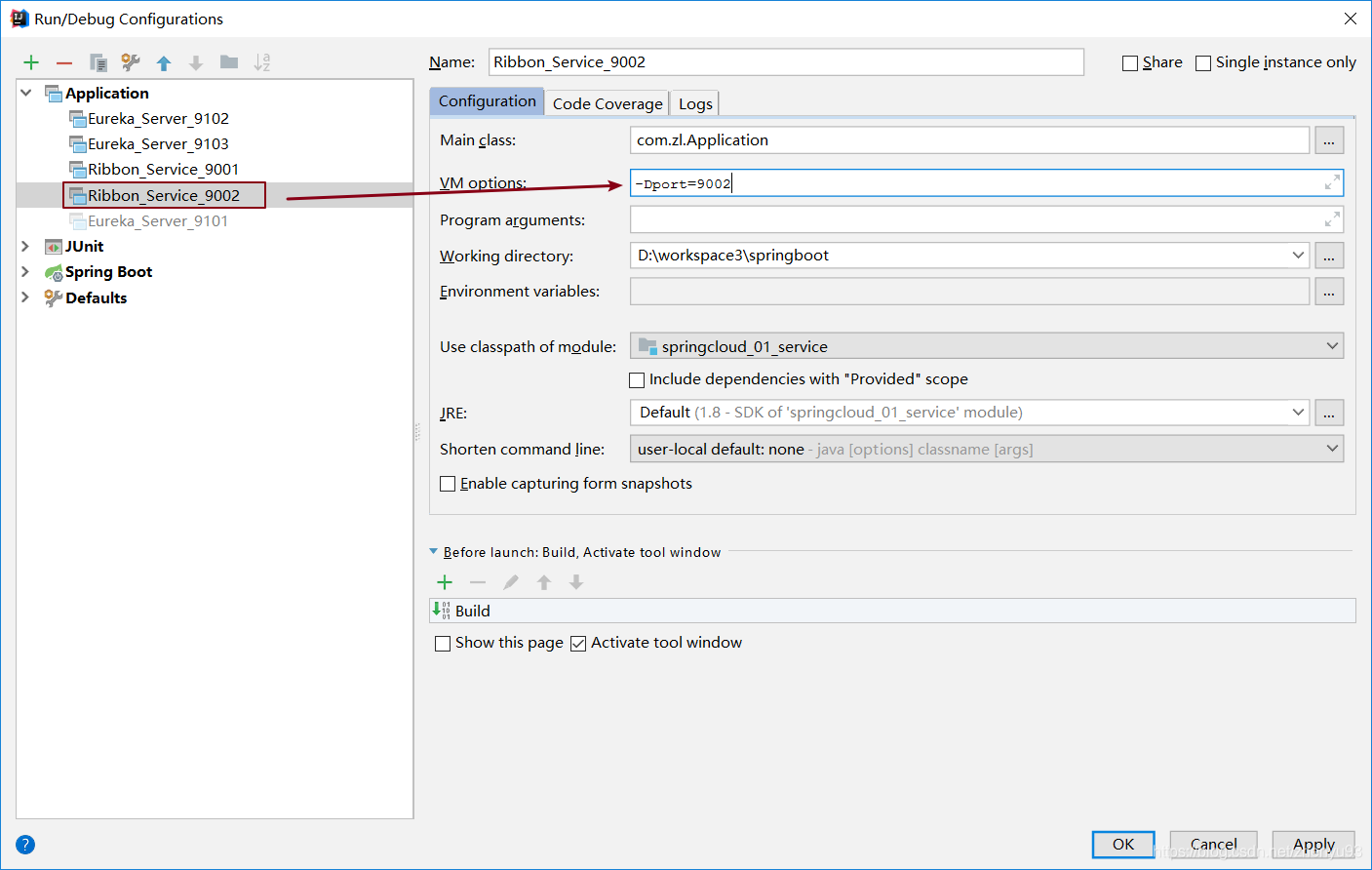
1.2.1 开启多个服务实例
Ribbon_Service_9001
Ribbon_Service_9002
1.2.2 开启负载均衡
添加负载均衡注解
因为Eureka中已经集成了Ribbon,所以我们无需引入新的依赖。
修改 springcloud_01_order项目下的启动类Application.java , 在获取RestTemplate的配置方法上添加@LoadBalanced注解:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-J7vfuQ4H-1613638354724)(assets/1570508963999.png)]
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
@Bean("restTemplate")
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
服务名称调用服务
修改springcloud_01_order项目下的OrderController类中服务的调用方式,直接通过服务名称调用服务;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Order findById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
//通过服务名称调用服务
String url = "http://springcloud_01_goods/user/" + id;
System.out.println(url);
return restTemplate.getForObject(url, User.class);
}
1.2.3 访问并测试
访问页面,查看结果;并可以在9001和9002的控制台查看执行情况:二边控制台均有输出 , 且数量基本一致 ;
1.3 内置负载均衡
Ribbon默认的负载均衡策略是轮询。Spring Boot也帮提供了修改负载均衡规则的配置入口 ;
在springcloud_01_order的配置文件中添加如下配置,就变成随机的了:
springcloud_01_goods:
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.BestAvailableRule
固定的格式 : 服务名称.ribbon.NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName=负载均衡类的类名 ;
Ribbon框架按照不同需求,已经为我们实现了许多均衡规则。以下规则能够实现大部分负载均衡需求的应用场景,如果有更复杂的需求,可以自己实现负载均衡。
| 内置负载均衡规则类 | 规则描述 |
|---|---|
| RoundRobinRule | 简单轮询服务列表来选择服务器。它是Ribbon默认的负载均衡规则。 |
| AvailabilityFilteringRule | 对以下两种服务器进行忽略: (1)在默认情况下,这台服务器如果3次连接失败,这台服务器就会被设置为“短路”状态。短路状态将持续30秒,如果再次连接失败,短路的持续时间就会几何级地增加。 (2)并发数过高的服务器。如果一个服务器的并发连接数过高,配置了AvailabilityFilteringRule规则的客户端也会将其忽略。 |
| WeightedResponseTimeRule | 为每一个服务器赋予一个权重值。服务器响应时间越长,这个服务器的权重就越小。这个规则会随机选择服务器,这个权重值会影响服务器的选择。 |
| ZoneAvoidanceRule | 以区域可用的服务器为基础进行服务器的选择。使用Zone对服务器进行分类,这个Zone可以理解为一个机房、一个机架等。 |
| BestAvailableRule | 忽略哪些短路的服务器,并选择并发数较低的服务器。 |
| RandomRule | 随机选择一个可用的服务器。 |
| RetryRule | 在一个配置时间段内,当选择server不成功,则一直尝试选择一个可用的server |
二. 服务调用Feign(掌握)
2.1 Feign概述
Feign 是一个声明式的 REST 客户端,它用了基于接口的注解方式,很方便实现客户端配置。
Feign 最初由 Netflix 公司提供,但不支持SpringMVC注解,后由 SpringCloud 对其封装,支持了SpringMVC注解,让使用者更易于接受
2.2 Feign快速入门(掌握)
在消费端引入 open-feign 依赖
<!--feign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
编写Feign调用接口
package com.itheima.consumer.feign;
import com.itheima.consumer.config.FeignLogConfig;
import com.itheima.consumer.domain.Goods;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
/**
*
* feign声明式接口。发起远程调用的。
*
String url = "http://FEIGN-PROVIDER/goods/findOne/"+id;
Goods goods = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Goods.class);
*
* 1. 定义接口
* 2. 接口上添加注解 @FeignClient,设置value属性为 服务提供者的 应用名称
* 3. 编写调用接口,接口的声明规则 和 提供方接口保持一致。
* 4. 注入该接口对象,调用接口方法完成远程调用
*/
@FeignClient(value = "FEIGN-PROVIDER")
public interface GoodsFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/goods/findOne/{id}")
public Goods findGoodsById(@PathVariable("id") int id);
}
在OrderController中注入feign客户端 , 实现服务调用
package com.itheima.consumer.controller;
import com.itheima.consumer.domain.Goods;
import com.itheima.consumer.feign.GoodsFeignClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/order")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private GoodsFeignClient goodsFeignClient;
@GetMapping("/goods/{id}")
public Goods findGoodsById(@PathVariable("id") int id){
/*
String url = "http://FEIGN-PROVIDER/goods/findOne/"+id;
// 3. 调用方法
Goods goods = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Goods.class);
return goods;*/
Goods goods = goodsFeignClient.findGoodsById(id);
return goods;
}
}
在启动类 添加 @EnableFeignClients 注解,开启Feign功能
package com.itheima.consumer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 激活DiscoveryClient
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients //开启Feign的功能
public class ConsumerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApp.class,args);
}
}
2.3 Feign超时配置(掌握)
Feign 底层依赖于 Ribbon 实现负载均衡和远程调用。
Ribbon默认1秒超时。
超时配置:
# 设置Ribbon的超时时间
ribbon:
ConnectTimeout: 1000 # 连接超时时间 默认1s 默认单位毫秒
ReadTimeout: 3000 # 逻辑处理的超时时间 默认1s 默认单位毫秒
2.4 Feign日志记录(了解)
Feign 只能记录 debug 级别的日志信息。
# 设置当前的日志级别 debug,feign只支持记录debug级别的日志
logging:
level:
com.itheima: debug
定义Feign日志级别Bean
FeignLogConfig
package com.itheima.consumer.config;
import feign.Logger;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FeignLogConfig {
/*
NONE,不记录
BASIC,记录基本的请求行,响应状态码数据
HEADERS,记录基本的请求行,响应状态码数据,记录响应头信息
FULL;记录完成的请求 响应数据
*/
@Bean
public Logger.Level level(){
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
启用该Bean:
package com.itheima.consumer.feign;
import com.itheima.consumer.config.FeignLogConfig;
import com.itheima.consumer.domain.Goods;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
/**
*
* feign声明式接口。发起远程调用的。
*
String url = "http://FEIGN-PROVIDER/goods/findOne/"+id;
Goods goods = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Goods.class);
*
* 1. 定义接口
* 2. 接口上添加注解 @FeignClient,设置value属性为 服务提供者的 应用名称
* 3. 编写调用接口,接口的声明规则 和 提供方接口保持一致。
* 4. 注入该接口对象,调用接口方法完成远程调用
*/
@FeignClient(value = "FEIGN-PROVIDER",configuration = FeignLogConfig.class)
public interface GoodsFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/goods/findOne/{id}")
public Goods findGoodsById(@PathVariable("id") int id);
}
三. 服务熔断Hystrix
3.1 Hystrix概述
Hystix 是 Netflix 开源的一个延迟和容错库,用于隔离访问远程服务、第三方库,防止出现级联失败(雪崩)。
3.1.1 雪崩效应
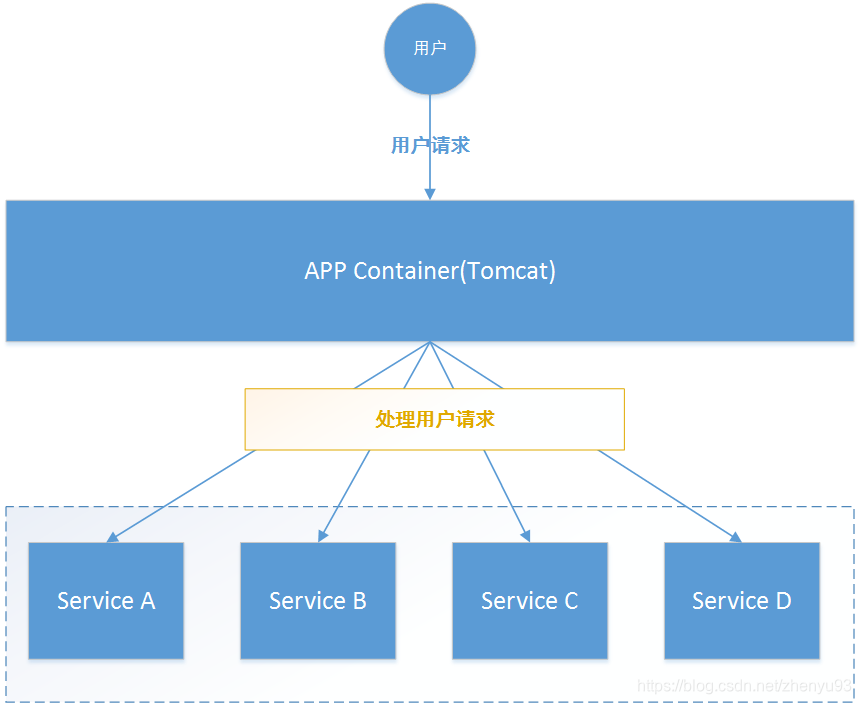
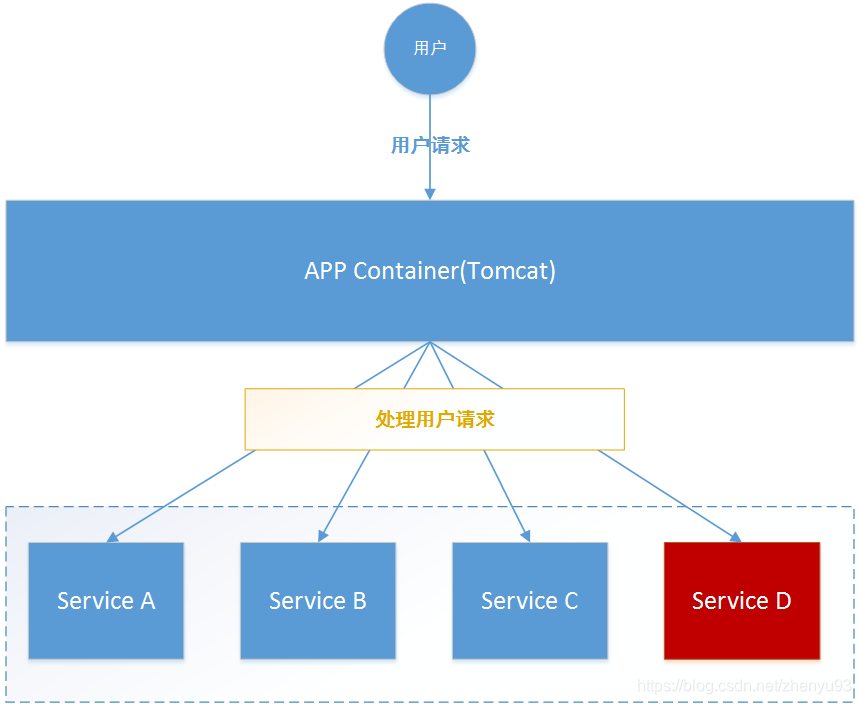
微服务中,服务间调用关系错综复杂,一个请求,可能需要调用多个微服务接口才能实现,会形成非常复杂的调用链路:
如图,一次业务请求,需要调用A、B、C、D 四个服务,这四个服务又可能调用其它服务。
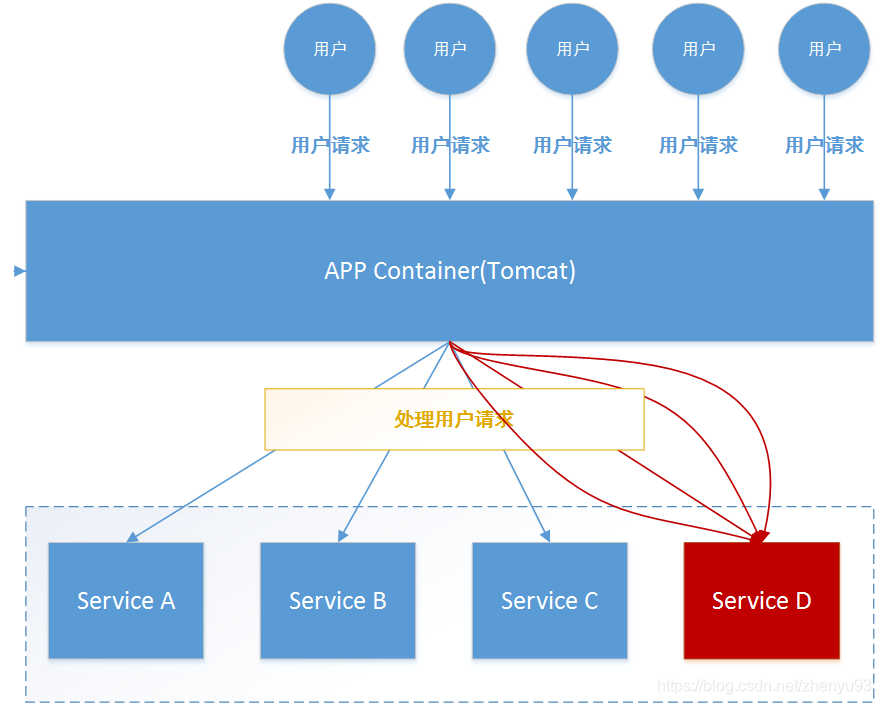
如果此时,某个服务出现异常:
如上图所示: 微服务D发生异常,请求阻塞,用户请求就不会得到响应,则tomcat的这个线程不会释放,于是越来越多的用户请求到来,越来越多的线程就会阻塞:
因为服务器支持的线程和并发数有限,请求一直阻塞,会导致服务器资源耗尽,从而导致所有其它服务都不可用,形成雪崩效应。
这就好比,一个汽车生产线,生产不同的汽车,需要使用不同的零件,如果某个零件因为种种原因无法使用,那么就会造成整台车无法装配,陷入等待零件的状态,直到零件到位,才能继续组装。 此时如果有很多个车型都需要这个零件,那么整个工厂都将陷入等待的状态,导致所有生产都陷入瘫痪。一个零件的波及范围不断扩大。
总结 : 雪崩就是指一个服务失败,导致整条链路的服务都失败的情形
3.1.2 避免雪崩问题
Hystrix解决雪崩问题的手段主要是服务降级,包括:
-
隔离
线程池隔离
信号量隔离
-
降级: 异常,超时
-
熔断
-
限流
3.1.3 Hystrix隔离原理
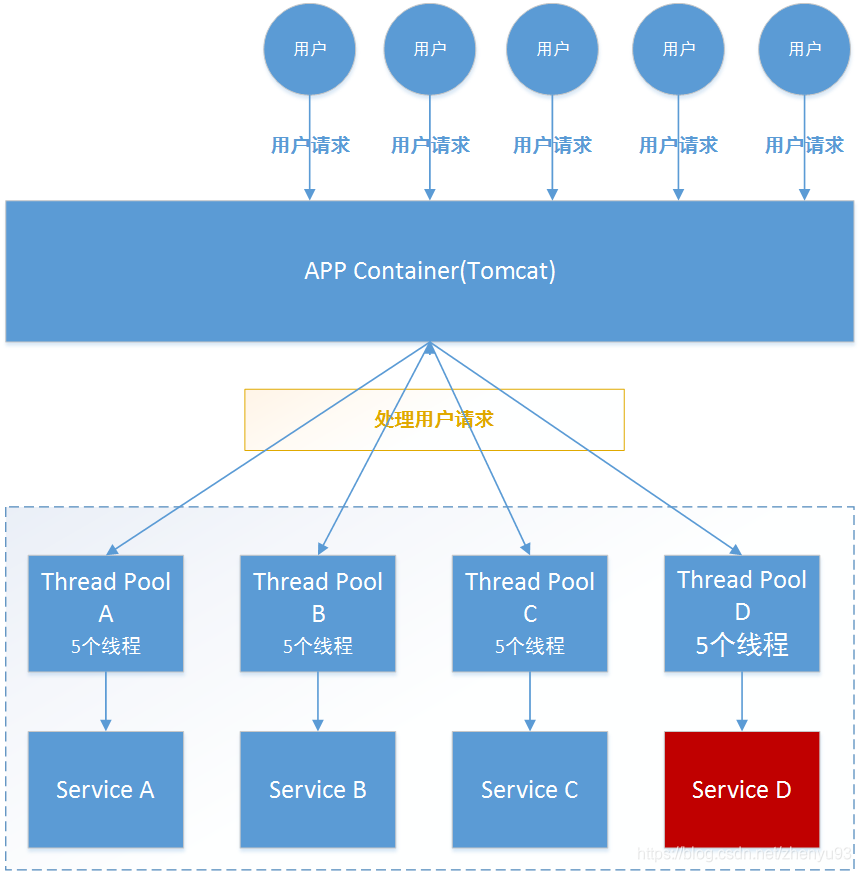
Hystrix之所以能够防止雪崩的本质原因,是其运用了资源隔离模式,我们可以用蓄水池做比喻来解释什么是资源隔离。生活中一个大的蓄水池由一个一个小的池子隔离开来,这样如果某一个水池的水被污染,也不会波及到其它蓄水池,如果只有一个蓄水池,水池被污染,整池水都不可用了。软件资源隔离如出一辙,如果采用资源隔离模式,将对远程服务的调用隔离到一个单独的线程池后,若服务提供者不可用,那么受到影响的只会是这个独立的线程池。
-
Hystrix为每个依赖服务调用分配一个小的线程池,如果线程池已满调用将被立即拒绝,默认不采用排队,加速失败判定时间。
-
用户的请求将不再直接访问服务,而是通过线程池中的空闲线程来访问服务,如果线程池已满,或者请求超
时,则会进行降级处理,什么是服务降级?服务降级:优先保证核心服务,而非核心服务不可用或弱可用。
当用户的请求故障时,不会被阻塞,更不会无休止的等待或者看到系统崩溃,至少可以看到一个执行结果
服务降级虽然会导致请求失败,但是不会导致阻塞,而且最多会影响这个依赖服务对应的线程池中的资源,对其它服务没有影响。
触发Hystrix服务降级的情况:
- 线程池已满
- 请求超时
3.2 Hystrix降级实现(掌握)
3.2.1 提供方降级
Hystix 降级:当服务发生异常或调用超时,返回默认数据
服务提供方降级
在服务提供方,引入 hystrix 依赖
<!-- hystrix -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
定义降级方法
/**
* 定义降级方法:
* 1. 方法的返回值需要和原方法一样
* 2. 方法的参数需要和原方法一样
*/
public Goods findOne_fallback(int id){
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("降级了~~~");
return goods;
}
使用 @HystrixCommand 注解配置降级方法
/**
* 降级:
* 1. 出现异常
* 2. 服务调用超时
* * 默认1s超时
*
* @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "findOne_fallback")
* fallbackMethod:指定降级后调用的方法名称
*/
@GetMapping("/findOne/{id}")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "findOne_fallback",commandProperties = {
//设置Hystrix的超时时间,默认1s
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value = "3000")
})
public Goods findOne(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//1.造个异常
int i = 3/0;
try {
//2. 休眠2秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Goods goods = goodsService.findOne(id);
goods.setTitle(goods.getTitle() + ":" + port);//将端口号,设置到了 商品标题上
return goods;
}
hystrix:
command:
default:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 2000 # 熔断超时设置,默认为1秒
在启动类上开启Hystrix功能:@EnableCircuitBreaker
package com.itheima.provider;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
/**
* 启动类
*/
@EnableEurekaClient //该注解 在新版本中可以省略
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCircuitBreaker // 开启Hystrix功能
public class ProviderApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApp.class,args);
}
}
3.2.2-消费方降级
消费方一般使用feign调用服务, feign 组件中已经集成了 hystrix 组件。我们不需要再引入依赖
定义feign 调用接口实现类,复写方法,即 降级方法
GoodsFeignClientFallback
package com.itheima.consumer.feign;
import com.itheima.consumer.domain.Goods;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* Feign 客户端的降级处理类
* 1. 定义类 实现 Feign 客户端接口
* 2. 使用@Component注解将该类的Bean加入SpringIOC容器
*/
@Component
public class GoodsFeignClientFallback implements GoodsFeignClient {
@Override
public Goods findGoodsById(int id) {
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("又被降级了~~~");
return goods;
}
}
在 @FeignClient 注解中使用 fallback 属性设置降级处理类。
GoodsFeignClient
package com.itheima.consumer.feign;
import com.itheima.consumer.domain.Goods;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@FeignClient(value = "HYSTRIX-PROVIDER",fallback = GoodsFeignClientFallback.class)
public interface GoodsFeignClient {
@GetMapping("/goods/findOne/{id}")
public Goods findGoodsById(@PathVariable("id") int id);
}
配置开启 feign.hystrix.enabled = true
application.yml
# 开启feign对hystrix的支持
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
3.3 Hystrix熔断(理解记忆)
3.3.1 熔断概念
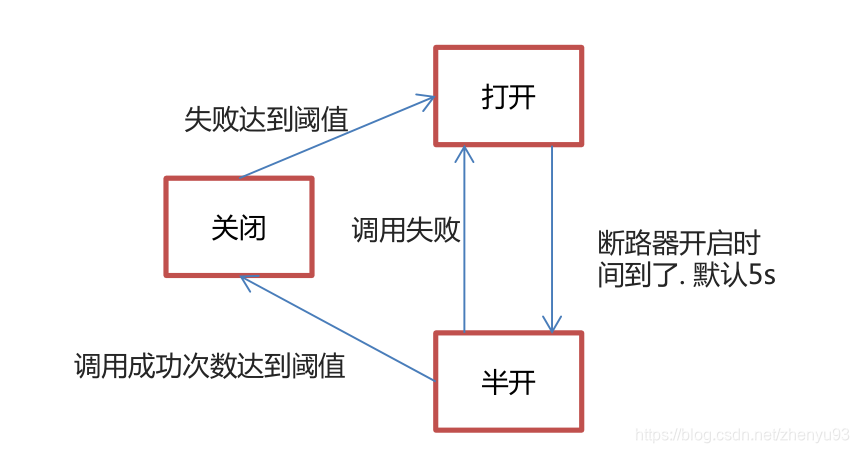
• Hystrix 熔断机制,用于监控微服务调用情况,当失败的情况达到预定的阈值(5秒失败20次),会打开
断路器,拒绝所有请求,直到服务恢复正常为止。
断路器三种状态:打开、半开、关闭
3.3.2 熔断演示
修改服务提供方的方法,演示熔断机制
熔断配置
circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds:监控时间
circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold:失败次数
circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage:失败率
GoodsController
package com.itheima.provider.controller;
import com.itheima.provider.domain.Goods;
import com.itheima.provider.service.GoodsService;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixProperty;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Goods Controller 服务提供方
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/goods")
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
@Value("${server.port}")
private int port;
/**
* 降级:
* 1. 出现异常
* 2. 服务调用超时
* * 默认1s超时
*
* @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "findOne_fallback")
* fallbackMethod:指定降级后调用的方法名称
*/
@GetMapping("/findOne/{id}")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "findOne_fallback",commandProperties = {
//设置Hystrix的超时时间,默认1s
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value = "3000"),
//监控时间 默认5000 毫秒
@HystrixProperty(name="circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds",value = "5000"),
//失败次数。默认20次
@HystrixProperty(name="circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold",value = "20"),
//失败率 默认50%
@HystrixProperty(name="circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage",value = "50") })
public Goods findOne(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//如果id == 1 ,则出现异常,id != 1 则正常访问
if(id == 1){
//1.造个异常
int i = 3/0;
}
/*try {
//2. 休眠2秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
Goods goods = goodsService.findOne(id);
goods.setTitle(goods.getTitle() + ":" + port);//将端口号,设置到了 商品标题上
return goods;
}
/**
* 定义降级方法:
* 1. 方法的返回值需要和原方法一样
* 2. 方法的参数需要和原方法一样
*/
public Goods findOne_fallback(int id){
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("降级了~~~");
return goods;
}
}
注意 : 以上配置如果配置在@HystrixCommand注解中, 只对当前方法有效, 如果想对所有控制方法配置降级参数, 可以在application.yml总统一配置 , 配置如下 :
hystrix:
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
errorThresholdPercentage: 50 # 触发熔断错误比例阈值,默认值50%
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 10000 # 熔断后休眠时长,默认值5秒
requestVolumeThreshold: 10 # 熔断触发最小请求次数,默认值是20
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 2000 # 熔断超时设置,默认为1秒
3.3.3 熔断监控
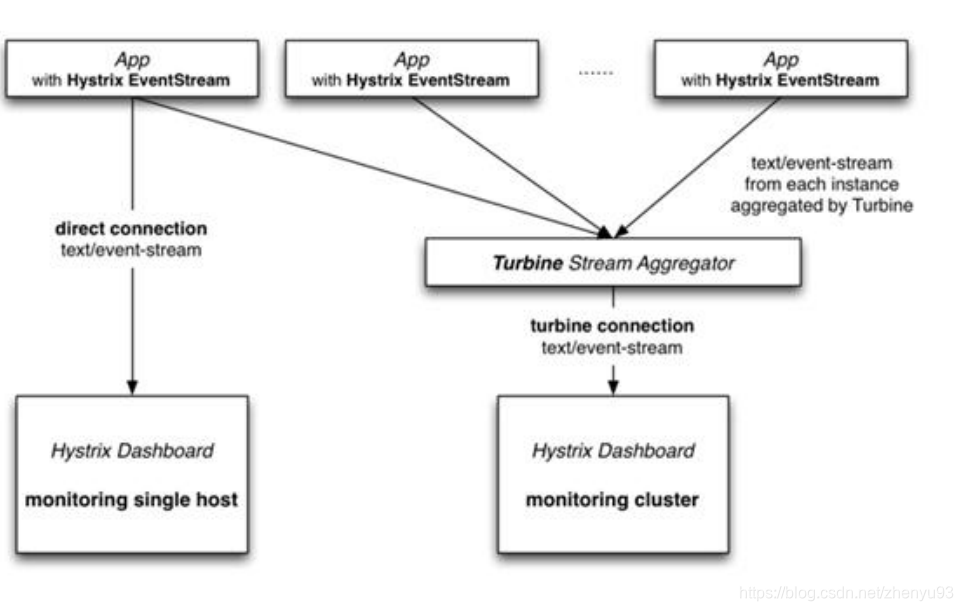
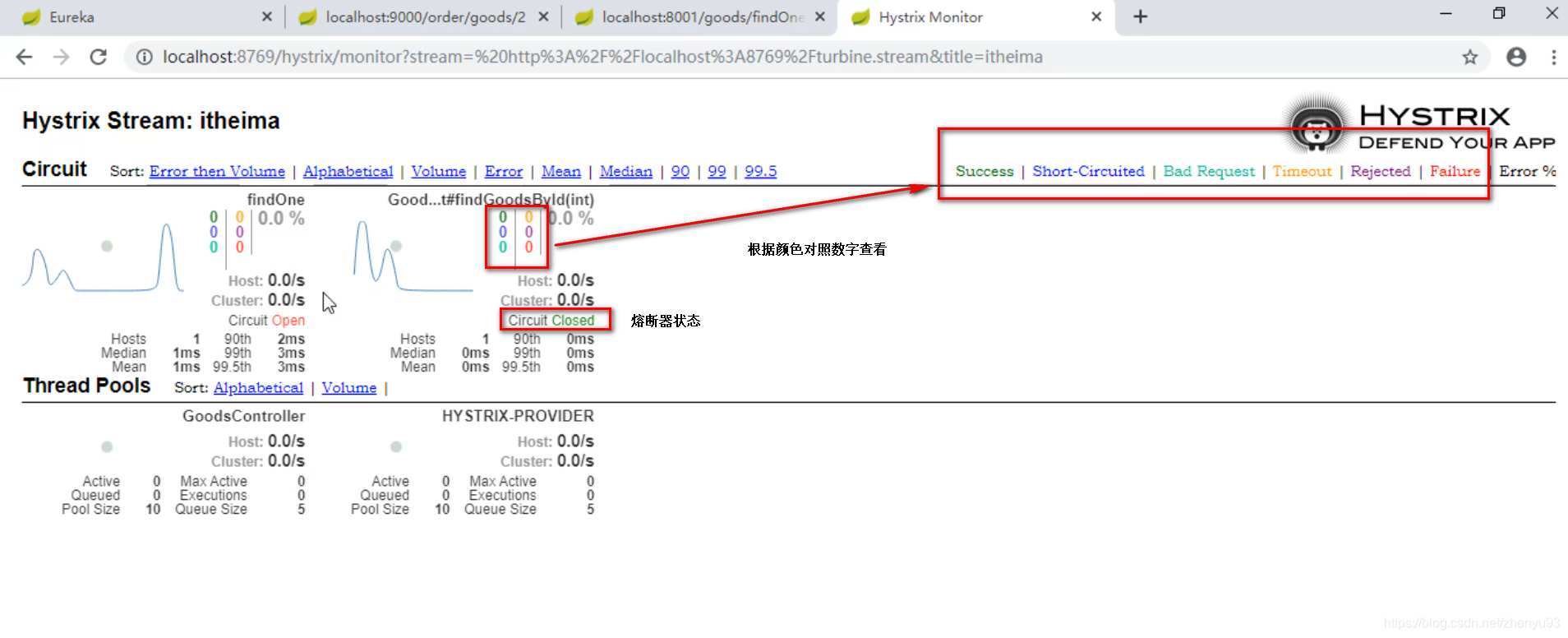
Hystrix 提供了 Hystrix-dashboard 功能,用于实时监控微服务运行状态。
但是Hystrix-dashboard只能监控一个微服务。
Netflix 还提供了 Turbine ,进行聚合监控。
熔断器监控安装 请查看Turbine搭建步骤.md
四. 服务网关Gateway
4.1 Gateway概述
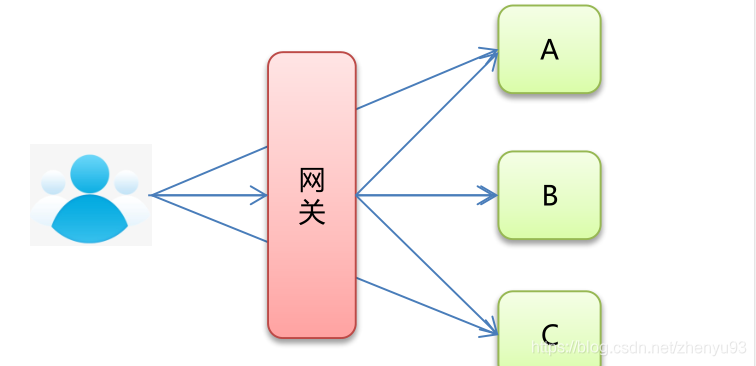
网关旨在为微服务架构提供一种简单而有效的统一的API路由管理方式。
在微服务架构中,不同的微服务可以有不同的网络地址,各个微服务之间通过互相调用完成用户请求,客户端可能通过调用N个微服务的接口完成一个用户请求。
存在的问题:
1.客户端多次请求不同的微服务,增加客户端的复杂性
2.认证复杂,每个服务都要进行认证
3.http请求不同服务次数增加,性能不高
网关就是系统的入口,封装了应用程序的内部结构,为客户端提供统一服务,一些与业务本身功能无关的公共逻辑可以在这里实现,诸如认证、鉴权、监控、缓存、负载均衡、流量管控、路由转发等
在目前的网关解决方案里,有Nginx+ Lua、Netflix Zuul 、Spring Cloud Gateway等等
4.2 Gateway快速入门
4.2.1 创建网关模块项目
4.2.2 引入网关依赖
<dependencies>
<!--引入gateway 网关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- eureka-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.2.3 编写启动引导类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class,args);
}
}
4.2.4 编写配置文件
创建并编写application.yml配置文件
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway-server
cloud:
# 网关配置
gateway:
# 路由配置:转发规则
routes: #集合。
# id: 唯一标识。默认是一个UUID
# uri: 转发路径
# predicates: 条件,用于请求网关路径的匹配规则
- id: gateway-provider
uri: http://localhost:8001/
predicates:
- Path=/goods/**
4.3 Gateway静态路由
application.yml 中的uri是写死的,就是静态路由
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway-server
cloud:
# 网关配置
gateway:
# 路由配置:转发规则
routes: #集合。
# id: 唯一标识。默认是一个UUID
# uri: 转发路径
# predicates: 条件,用于请求网关路径的匹配规则
# filters:配置局部过滤器的
- id: gateway-provider
# 静态路由
uri: http://localhost:8001/
predicates:
- Path=/goods/**
4.4 Gateway动态路由
启动类添加@EnableEurekaClient
package com.itheima.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class ApiGatewayApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiGatewayApp.class,args);
}
}
引入eureka-client配置 , 在application.yml 中修改uri属性:uri: lb://服务名称
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway-server
cloud:
# 网关配置
gateway:
# 路由配置:转发规则
routes: #集合。
# id: 唯一标识。默认是一个UUID
# uri: 转发路径
# predicates: 条件,用于请求网关路径的匹配规则
# filters:配置局部过滤器的
- id: gateway-provider
# 静态路由
# uri: http://localhost:8001/
# 动态路由
uri: lb://GATEWAY-PROVIDER
predicates:
- Path=/goods/**
4.5 Gateway微服务名称配置
application.yml中配置微服务名称配置
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
# 微服务名称配置
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true # 设置为true 请求路径前可以添加微服务名称
lower-case-service-id: true # 允许为小写
4.6 Gateway过滤器
4.6.1 过滤器概述
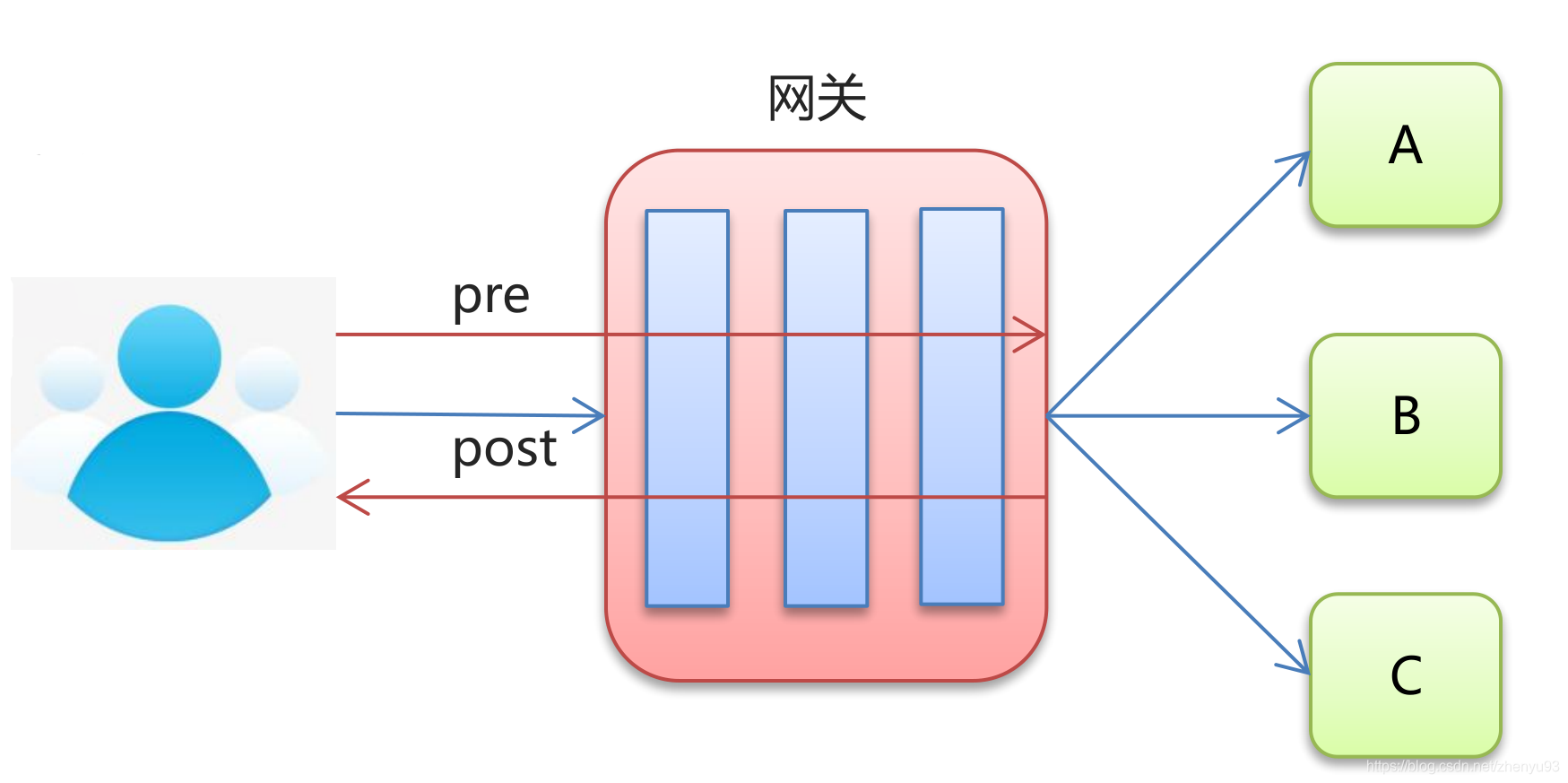
Gateway 支持过滤器功能,对请求或响应进行拦截,完成一些通用操作。
Gateway 提供两种过滤器方式:“pre”和“post”
- pre 过滤器,在转发之前执行,可以做参数校验、权限校验、流量监控、日志输出、协议转换等。
- post 过滤器,在响应之前执行,可以做响应内容、响应头的修改,日志的输出,流量监控等。
Gateway 还提供了两种类型过滤器
- GatewayFilter:局部过滤器,针对单个路由
- GlobalFilter :全局过滤器,针对所有路由
4.6.2 局部过滤器
GatewayFilter 局部过滤器,是针对单个路由的过滤器。
在Spring Cloud Gateway 组件中提供了大量内置的局部过滤器,对请求和响应做过滤操作。
遵循约定大于配置的思想,只需要在配置文件配置局部过滤器名称,并为其指定对应的值,就可以让其生效。
具体配置参见gateway内置过滤器工厂.md
**修改网关配置文件 , application.yml **
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway-server
cloud:
# 网关配置
gateway:
# 路由配置:转发规则
routes: #集合。
# id: 唯一标识。默认是一个UUID
# uri: 转发路径
# predicates: 条件,用于请求网关路径的匹配规则
# filters:配置局部过滤器的
- id: gateway-provider
# 静态路由
# uri: http://localhost:8001/
# 动态路由
uri: lb://GATEWAY-PROVIDER
predicates:
- Path=/goods/**
filters:
- AddRequestParameter=username,zhangsan
gateway-provider模块中GoodsController中的findOne添加username参数
public Goods findOne(@PathVariable("id") int id,String username){
System.out.println(username);
//如果id == 1 ,则出现异常,id != 1 则正常访问
if(id == 1){
//1.造个异常
int i = 3/0;
}
/*try {
//2. 休眠2秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
Goods goods = goodsService.findOne(id);
goods.setTitle(goods.getTitle() + ":" + port);//将端口号,设置到了 商品标题上
return goods;
}
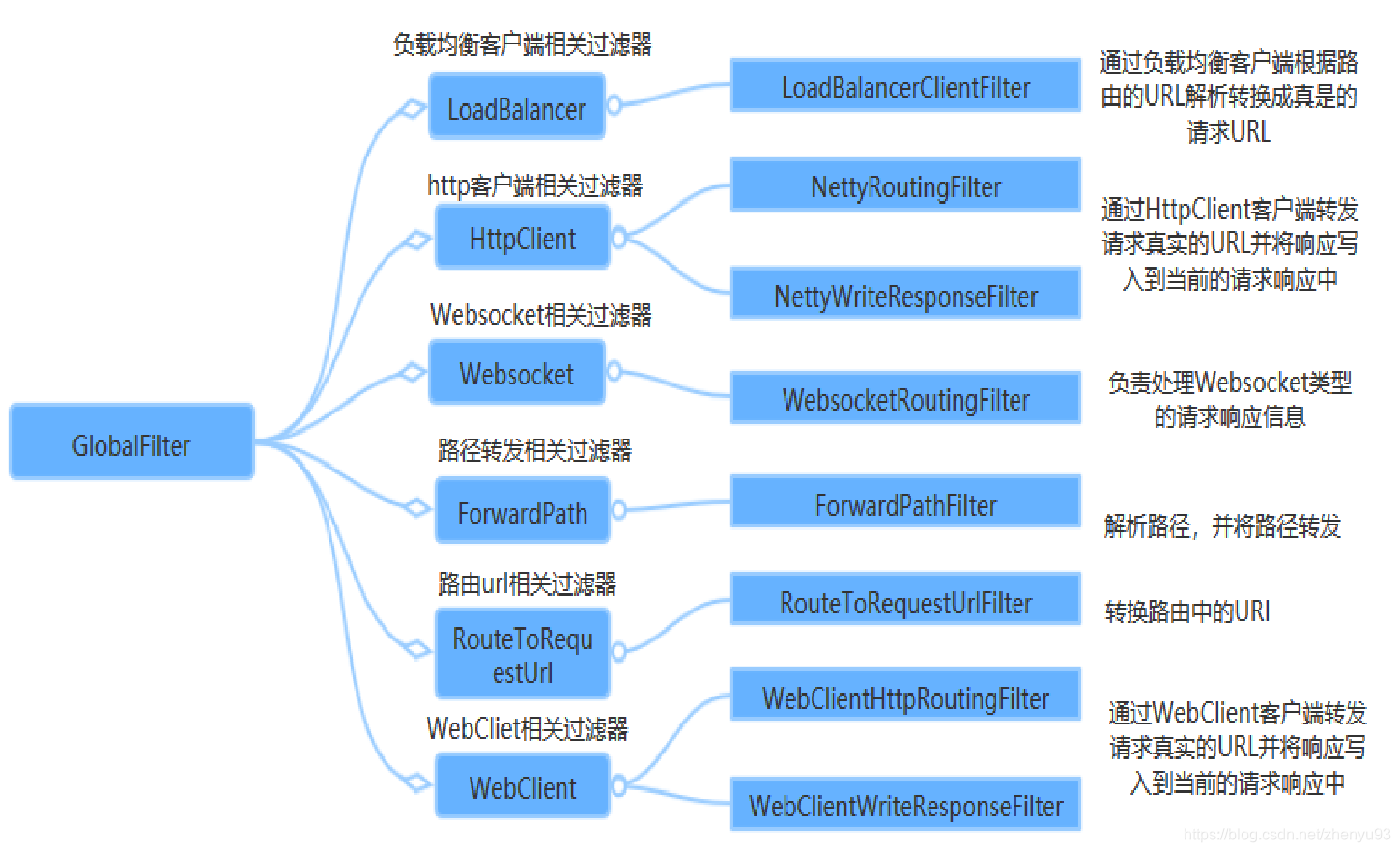
4.6.3 全局过滤器
GlobalFilter 全局过滤器,不需要在配置文件中配置,系统初始化时加载,并作用在每个路由上。
Spring Cloud Gateway 核心的功能也是通过内置的全局过滤器来完成。
自定义全局过滤器步骤:
- 定义类实现 GlobalFilter 和 Ordered接口
- 复写方法
- 完成逻辑处理
MyFilter
package com.itheima.gateway.filter;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Component
public class MyFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
System.out.println("自定义全局过滤器执行了~~~");
return chain.filter(exchange);//放行
}
/**
* 过滤器排序
* @return 数值越小 越先执行
*/
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
4.6.4 过滤器应用案例
需求 : 对系统的所有微服务进行权限认证 , 只有登录之后的用户才能够访问微服务
@Component
public class AuthenticationFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate ;
/**
*
* @param exchange 网关与web环境交换机
* @param chain 过滤器链
* @return
*/
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
String method = request.getMethodValue();
String path = request.getURI().getPath();
//登陆请求直接放行
if(method.equalsIgnoreCase("post") && path.endsWith("/user")){
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
//获取请求中携带的token数据
List<String> headers = request.getHeaders().get("token");
//用户未携带token , 直接返回错误信息给客户端
if(headers==null || headers.size()<=0){
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
//获取客户端发送的token
String token = headers.get(0);
//判断token是否存在 , 如果不存在说明未登录,或者登陆状态过期
Boolean flag = redisTemplate.hasKey(token);
if(!flag){
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
//放行 , 访问资源
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}