ReferenceLine
位于modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line.h
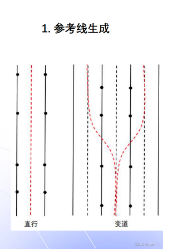
它是根据高清地图上的map_path_生成的,如下图:
- 默认情况下,只生成一条参考线
- 如果有变道,那么就生成多条参考线
其定义如下
数据成员
可以看到它有四个成员变量
| 数据类型 | 成员变量名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| std::vector< SpeedLimit> | speed_limit_; |
|
| std::vector< ReferencePoint> | reference_points_; |
|
| hdmap::Path | map_path_; |
|
| uint32_t | priority_ = 0; |
|
SpeedLimit
| 数据类型 | 成员变量名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| double | start_s = 0.0; | 起始点 |
| double | end_s = 0.0; | 终点 |
| double | speed_limit = 0.0; | 在[start_s,end_s]里的限速 |
除此之外,参考线还提供了一些方法,通过这些方法我们可以拼接参考线,也可以判断参考线所在位置的路的宽度,以及是否在路上等信息。我们先分析这些方法的功能实现,然后再介绍哪些场景需要用到这些功能。
重要方法
构造函数
我们可以看到有两种方式来生成ReferenceLine,可以通过一组参考点来生成,也可以通过地图路径来生成。这两者实际上是等价的。下面我们开始分析。
- 通过一组参考点生成,reference_points_直接拷贝赋值了,然后再用reference_points生成hdmap::MapPathPoint
- 通过地图路径生成参考线。遍历路径中的点,然后取
lane_waypoints中的第一个点,保存到参考线数组中
从上面可以可以看出,参考线上的点reference_points和高清地图上的点map_path_几乎一致。可以断定参考线是在map_path_的基础上生成的
缝合参考线(Stitch)
缝合参考线是把2段参考线连接起来,代码中也给出了下面2种情况。并且每次拼接的时候,会尽可能多的采用自身的参考线。最终效果如下:
* Example 1
* this: |--------A-----x-----B------|
* other: |-----C------x--------D-------|
* Result: |------A-----x-----B------x--------D-------|
* In the above example, A-B is current reference line, and C-D is the other
* reference line. If part B and part C matches, we update current reference
* line to A-B-D.
*
* Example 2
* this: |-----A------x--------B-------|
* other: |--------C-----x-----D------|
* Result: |--------C-----x-----A------x--------B-------|
* In the above example, A-B is current reference line, and C-D is the other
* reference line. If part A and part D matches, we update current reference
* line to C-A-B.
接下来我们分析下代码。
bool ReferenceLine::Stitch(const ReferenceLine& other) {
// 1. 找到起点的交点
auto first_point = reference_points_.front();
common::SLPoint first_sl;
if (!other.XYToSL(first_point, &first_sl)) {
AWARN << "Failed to project the first point to the other reference line.";
return false;
}
bool first_join = first_sl.s() > 0 && first_sl.s() < other.Length();
// 2. 找到终点的交点
auto last_point = reference_points_.back();
common::SLPoint last_sl;
if (!other.XYToSL(last_point, &last_sl)) {
AWARN << "Failed to project the last point to the other reference line.";
return false;
}
bool last_join = last_sl.s() > 0 && last_sl.s() < other.Length();
// 3. 如果起点和终点都没有交点,则退出
if (!first_join && !last_join) {
AERROR << "These reference lines are not connected.";
return false;
}
// 累积s值
const auto& accumulated_s = other.map_path().accumulated_s();
// 参考点
const auto& other_points = other.reference_points();
auto lower = accumulated_s.begin();
static constexpr double kStitchingError = 1e-1;
if (first_join) {
// 4. 如果横向偏移大于0.1m,则退出
if (first_sl.l() > kStitchingError) {
AERROR << "lateral stitching error on first join of reference line too "
"big, stitching fails";
return false;
}
lower = std::lower_bound(accumulated_s.begin(), accumulated_s.end(),
first_sl.s());
// 4.1 因为this的起点在other之后,插入other的起点到this的起点
size_t start_i = std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(), lower);
reference_points_.insert(reference_points_.begin(), other_points.begin(),
other_points.begin() + start_i);
}
if (last_join) {
// 5.1 如果横向偏移大于0.1m,则退出
if (last_sl.l() > kStitchingError) {
AERROR << "lateral stitching error on first join of reference line too "
"big, stitching fails";
return false;
}
// 5.2 因为this的终点小于other的终点,把other终点拼接到参考线的终点
auto upper = std::upper_bound(lower, accumulated_s.end(), last_sl.s());
auto end_i = std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(), upper);
reference_points_.insert(reference_points_.end(),
other_points.begin() + end_i, other_points.end());
}
map_path_ = MapPath(std::move(std::vector<hdmap::MapPathPoint>(
reference_points_.begin(), reference_points_.end())));
return true;
}
分割参考线(Segment)
分割参考线的方法是根据起点s,向前和向后的查看距离把参考线进行分割。 有2个方法,我们只看其中一个就可以了。
bool ReferenceLine::Segment(const double s, const double look_backward,
const double look_forward) {
const auto& accumulated_s = map_path_.accumulated_s();
// 1. 查找向后的索引(look_backward)
auto start_index =
std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(),
std::lower_bound(accumulated_s.begin(), accumulated_s.end(),
s - look_backward));
// 2. 查找向前的索引(look_forward)
auto end_index =
std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(),
std::upper_bound(accumulated_s.begin(), accumulated_s.end(),
s + look_forward));
// 3. 如果只有一个点
if (end_index - start_index < 2) {
AERROR << "Too few reference points after shrinking.";
return false;
}
// 4. 更新当前的参考线,并且返回成功
reference_points_ =
std::vector<ReferencePoint>(reference_points_.begin() + start_index,
reference_points_.begin() + end_index);
map_path_ = MapPath(std::vector<hdmap::MapPathPoint>(
reference_points_.begin(), reference_points_.end()));
return true;
}
其他方法:待分析
GetReferencePoint
GetFrenetPoint
GetReferencePoints
GetNearestReferenceIndex
GetLaneSegments
GetApproximateSLBoundary
SL坐标到XY坐标相互转换
// 根据s值获取参考点(会根据s进行插值)
ReferencePoint GetReferencePoint(const double s) const;
// 根据x,y找到最近的点,并且进行插值
ReferencePoint GetReferencePoint(const double x, const double y) const;
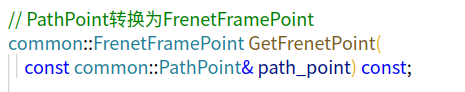
// PathPoint转换为FrenetFramePoint
common::FrenetFramePoint GetFrenetPoint(
const common::PathPoint& path_point) const;
//
std::pair<std::array<double, 3>, std::array<double, 3>> ToFrenetFrame(
const common::TrajectoryPoint& traj_point) const;
// 查找起点和终点分别为start_s和end_s的参考点
std::vector<ReferencePoint> GetReferencePoints(double start_s,
double end_s) const;
// 获取离s最近的索引
size_t GetNearestReferenceIndex(const double s) const;
// 离s最近的ReferencePoint
ReferencePoint GetNearestReferencePoint(const common::math::Vec2d& xy) const;
ReferencePoint GetNearestReferencePoint(const double s) const;
// 根据起点s和终点s获取LaneSegment
std::vector<hdmap::LaneSegment> GetLaneSegments(const double start_s,
const double end_s) const;
// 获取box在参考线上的投影框
bool GetApproximateSLBoundary(const common::math::Box2d& box,
const double start_s, const double end_s,
SLBoundary* const sl_boundary) const;
bool GetSLBoundary(const common::math::Box2d& box,
SLBoundary* const sl_boundary) const;
bool GetSLBoundary(const hdmap::Polygon& polygon,
SLBoundary* const sl_boundary) const;
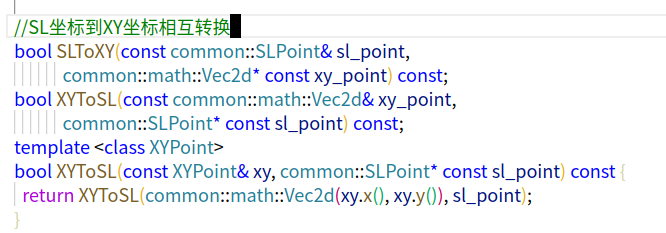
// SL坐标到XY坐标相互转换
bool SLToXY(const common::SLPoint& sl_point,
common::math::Vec2d* const xy_point) const;
bool XYToSL(const common::math::Vec2d& xy_point,
common::SLPoint* const sl_point) const;
// 获取s距离处路的宽度
bool GetLaneWidth(const double s, double* const lane_left_width,
double* const lane_right_width) const;
// 获取s距离处的偏移
bool GetOffsetToMap(const double s, double* l_offset) const;
// 获取s距离处路的宽度
bool GetRoadWidth(const double s, double* const road_left_width,
double* const road_right_width) const;
// 获取s距离处路的类型
hdmap::Road::Type GetRoadType(const double s) const;
// 获取s距离处道路
void GetLaneFromS(const double s,
std::vector<hdmap::LaneInfoConstPtr>* lanes) const;
// 获取乘车宽度
double GetDrivingWidth(const SLBoundary& sl_boundary) const;
// 是否在路上
bool IsOnLane(const common::SLPoint& sl_point) const;
bool IsOnLane(const common::math::Vec2d& vec2d_point) const;
template <class XYPoint>
bool IsOnLane(const XYPoint& xy) const {
return IsOnLane(common::math::Vec2d(xy.x(), xy.y()));
}
bool IsOnLane(const SLBoundary& sl_boundary) const;
bool IsOnRoad(const common::SLPoint& sl_point) const;
bool IsOnRoad(const common::math::Vec2d& vec2d_point) const;
bool IsOnRoad(const SLBoundary& sl_boundary) const;
// 是否堵路了
bool IsBlockRoad(const common::math::Box2d& box2d, double gap) const;
// 是否有重叠
bool HasOverlap(const common::math::Box2d& box) const;
// 查找s处的速度限制
double GetSpeedLimitFromS(const double s) const;
// 添加start_s到end_s处的速度限制,并且进行排序
void AddSpeedLimit(double start_s, double end_s, double speed_limit);
重要补充
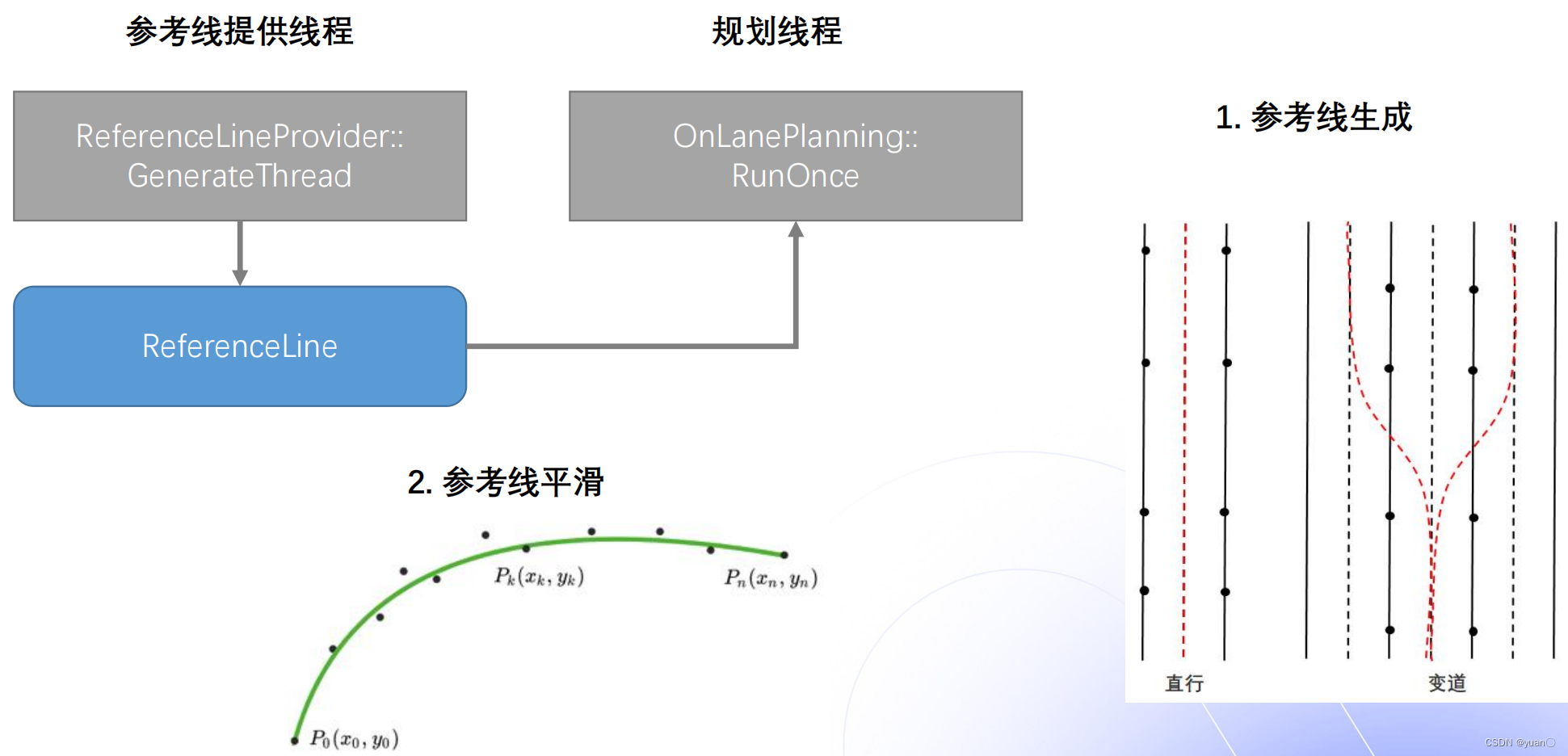
ReferenceLine由ReferenceLineProvider专门负责生成。主要有两个步骤:
- 参考线生成线程将会生成ReferenceLine
- 一般生成一条参考线;当有变道发生时,生成多条参考线。
- 然后会对参考线进行一定的平滑,,常见的参考线平滑方式有:离散点的平滑(Apollo采用)、螺旋线的平滑以及样条曲线的平滑。
- 规划线程会使用平滑参考线来规划出一条轨迹
如下图: