配置文件
yml 和 properties
- spring boot 支持2中配置文件:
*.yaml/*.yml、*.properties - 配置文件的默认名:application
- yml格式:application.yml
- properties:application.properties
properties 配置
位置:%maven%/src/main/resources/
-
配置内容:
key=value- key 内容任意值,一般采用包命名方式。例如:jdbc.driver
#端口号
server.port=9090
#数据源配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc://localhost:3306/ssm_db1
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=1234
yml 配置
- 配置文件位置:
配置内容:key: value
#实例
A:
B:
C:
key: value
#端口号
server:
port: 9091
#数据源
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc://localhost:3306/ssm_db1
username: root
password: 1234
yml 高级使用
-
yml支持的数据类型
# 自定义数据 user: username: tom age: 12 birthday: 1997/10/10 vip: true valueList: - MyBatis - SpringMVC - SpringBoot ageArray: - 18 - 20 - 22 userList: # 复杂写法 List<Map> -> [{name:tom,age:20},{name:Jack,age:22}] - name: tom age: 20 - name: Jack age: 22
2.1.2 配置内容获取
- 通常使用2种方式:@Value、@ConfigurationProperties
- @Value:一个一个值的获取,通过key获得value,key为properties文件key书写方式
- @ConfigurationProperties,确定前缀,一次性加载一组内容。
1) @Value 获得一个值
package com.czxy.boot.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class OneConfig {
/**
* 获得配置文件中的内容 ${key:默认值}
*/
@Value("${server.port:8000}")
private Integer port;
/**
* 打印获得内容
* @return
*/
@Bean
public String oneDemo() {
System.out.println("port端口号:" + port);
return "";
}
}
2)@ConfigurationProperties 获得一组值
package com.czxy.boot.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
public class UserConfig {
private String username;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private boolean vip;
private List<String> valueList;
private String[] ageArray;
private List<Map<String,String>> userList;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public boolean isVip() {
return vip;
}
public void setVip(boolean vip) {
this.vip = vip;
}
public List<String> getValueList() {
return valueList;
}
public void setValueList(List<String> valueList) {
this.valueList = valueList;
}
public String[] getAgeArray() {
return ageArray;
}
public void setAgeArray(String[] ageArray) {
this.ageArray = ageArray;
}
public List<Map<String, String>> getUserList() {
return userList;
}
public void setUserList(List<Map<String, String>> userList) {
this.userList = userList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserConfig{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' +
", vip=" + vip +
", valueList=" + valueList +
", ageArray=" + Arrays.toString(ageArray) +
", userList=" + userList +
'}';
}
@Bean
public String userDemo() {
System.out.println(this);
return "";
}
}
配置文件优先级
1 yml 和 properties优先级
- properties 优先级大于 yml (properties覆盖了yml的内容)
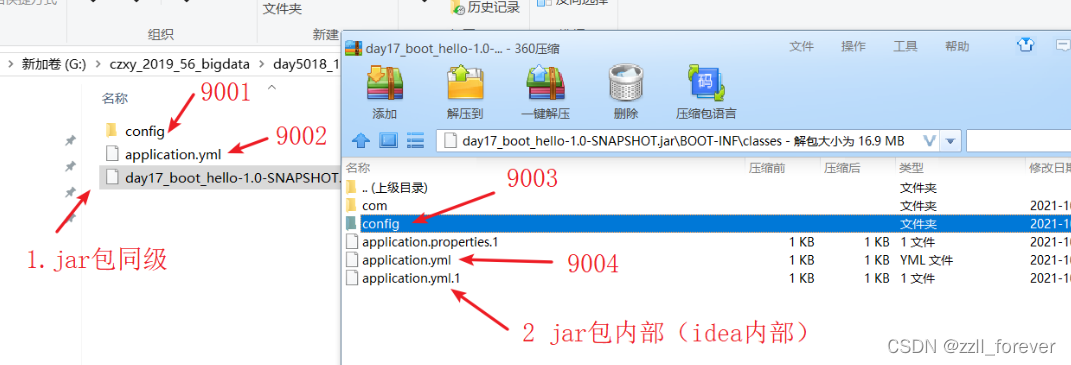
2 位置优先级
-
配置文件存放的位置不同,优先级不同。
-
file:./config/:项目jar包所在目录的config目录
-
file:./ :项目jar包所在的同级目录
-
classpath:/config:classpath(resource)目录下config目录
-
classpath:/:classpath(resource)目录下
-
-
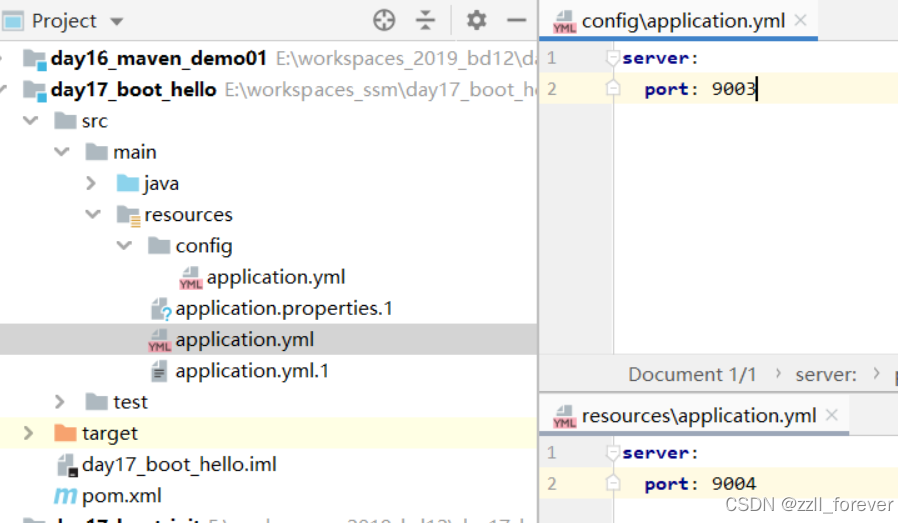
idea环境下优先级
完整的配置优先级的对比(优先级:9001 > 9002 > 9003 > 9004)
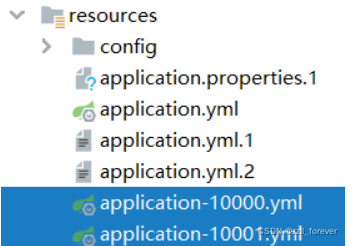
多环境配置
-
需要为不同的环境编写配置文件
application-{profile}.yml
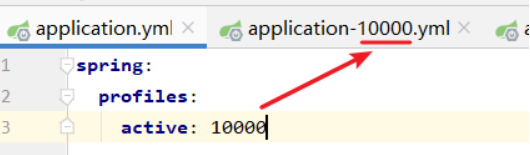
启动不同的配置 -
方式1:application.yml 文件配置
-
spring: profiles: active: 10000 -
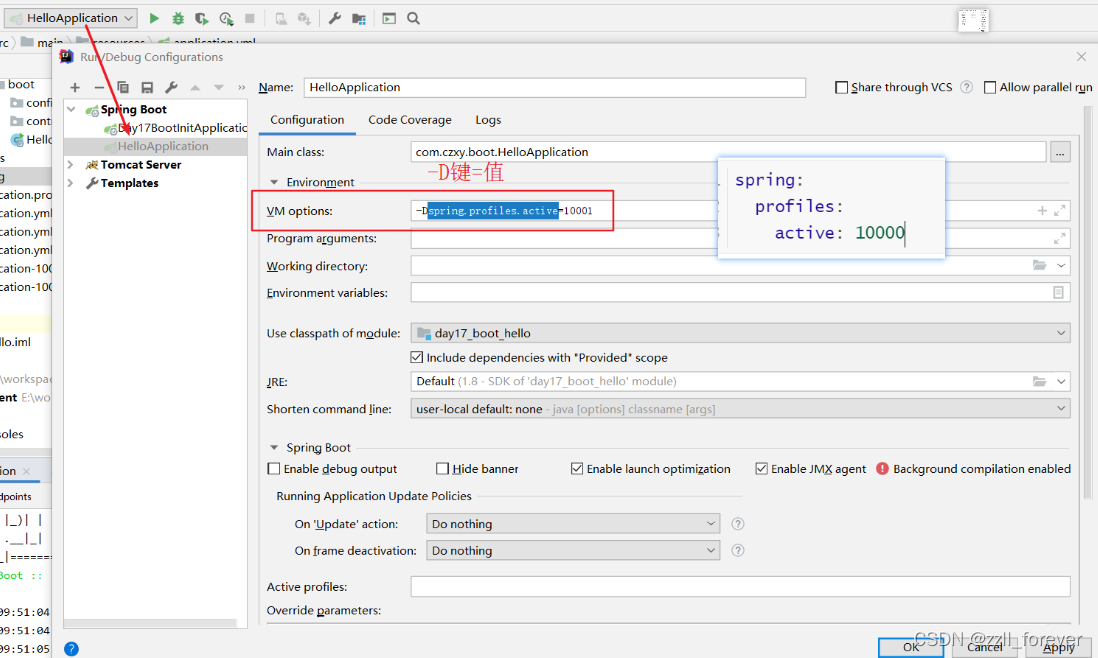
方式2:在idea中,配置启动类的参数
-
方式3:在cmd中,配置jar包的参数
java -jar -Dspring.profiles.active=10000 xxx.jar
部署
项目部署
- 将spring boot项目打包成可运行的jar。
- 仅需要在pom.xml文件中,添加一个插件,并配置启动类。
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<!-- 配置启动类 -->
<mainClass>com.czxy.boot.HelloApplication</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
热部署
-
现状:编写controller后,需要重启才能生效。
-
热部署:当修改部分内容后,自动部署,不用重启就可以访问。
-
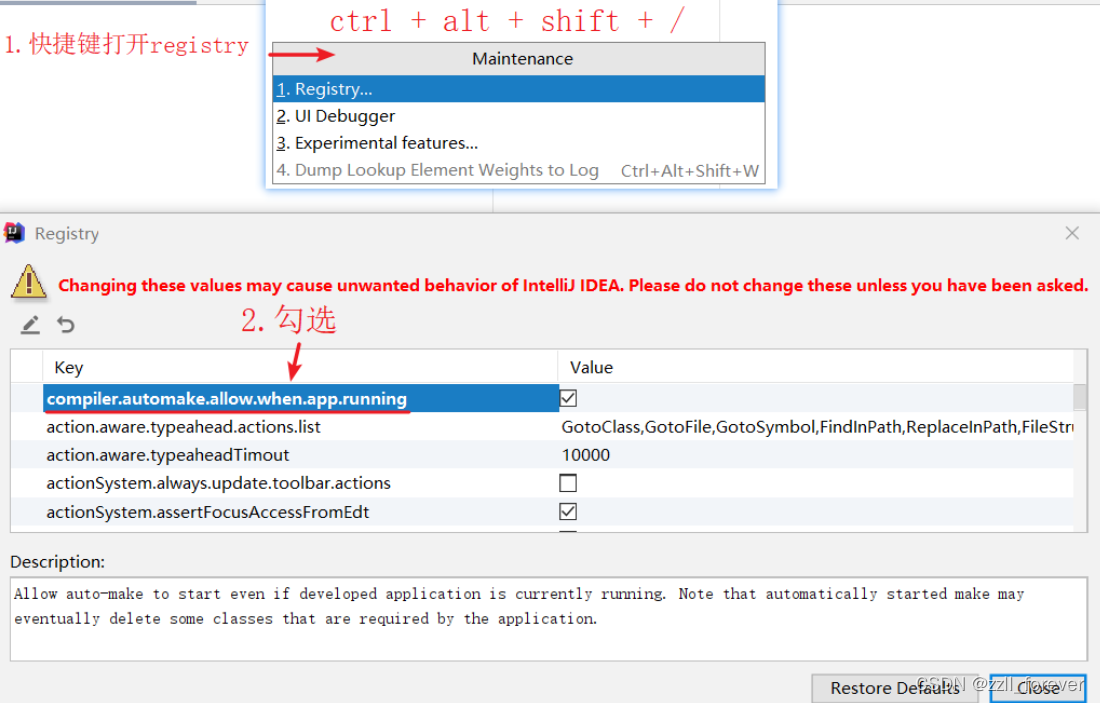
步骤:
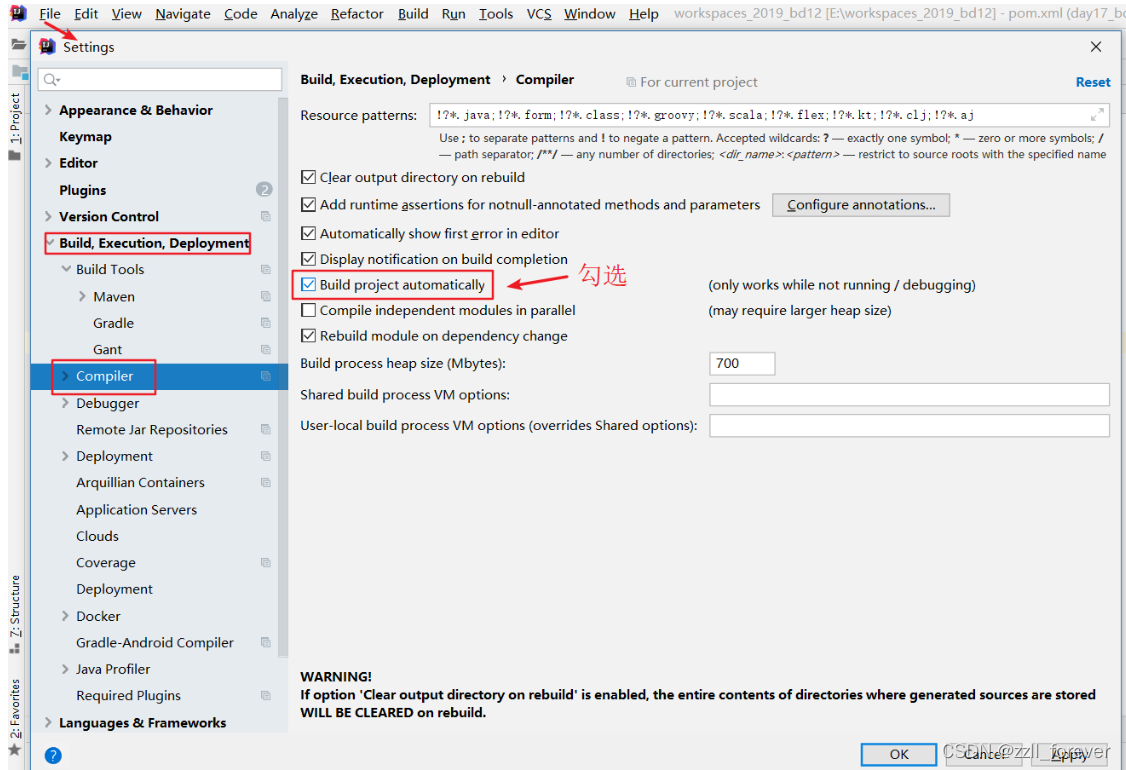
- 开启auto make自动编译(一次性)
- 设置自动编译项目(跟项目)
- 添加依赖
-
步骤:
- 开启auto make自动编译(一次性)
- 设置自动编译项目(跟项目)
3.添加依赖
- 开启auto make自动编译(一次性)
<!-- 热部署模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<!-- 这个需要为 true -->
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
整合测试
-
spring boot 整合 Junit
-
步骤:
- 添加依赖
- 编写测试用例
-
实现:
-
添加依赖
<!--test 启动器--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> -
编写测试用例
package com.czxy.boot.service; import com.czxy.boot.HelloApplication; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // spring 整合 Junit @SpringBootTest(classes = HelloApplication.class) // spring boot 整合 Junit public class TestUserService { @Resource private UserService userService; @Test public void testSave() { userService.save(); } }
-