开心一刻
老公酷爱网络游戏,老婆无奈,只得告诫他:你玩就玩了,但是千万不可以在游戏里找老婆,不然,哼哼。。。
老公嘴角露出了微笑:放心吧亲爱的,我绝对不会在游戏里找老婆的!因为我有老公!
老婆:......
前情回顾
大家还记得上篇博文讲了什么吗,我们来一起简单回顾下:
SecurityManager是shiro的核心,负责与shiro的其他组件进行交互;SessionManager是session的真正管理者,负责shiro的session管理;
SessionsSecurityManager的start方法中将session的创建委托给了具体的sessionManager,是创建session的关键入口。
SimpleSession是shiro完完全全的自己实现,是shiro对session的一种拓展;实现了ValidatingSession接口,具有自我校验的功能;一般不对外暴露,暴露的往往是他的代理:DelegatingSession;SimpleSession有几个属性值得重点关注下,如下
id:就是session id;
startTimestamp:session的创建时间;
stopTimestamp:session的失效时间;
lastAccessTime:session的最近一次访问时间,初始值是startTimestamp
timeout:session的有效时长,默认30分钟
expired:session是否到期
attributes:session的属性容器
查询
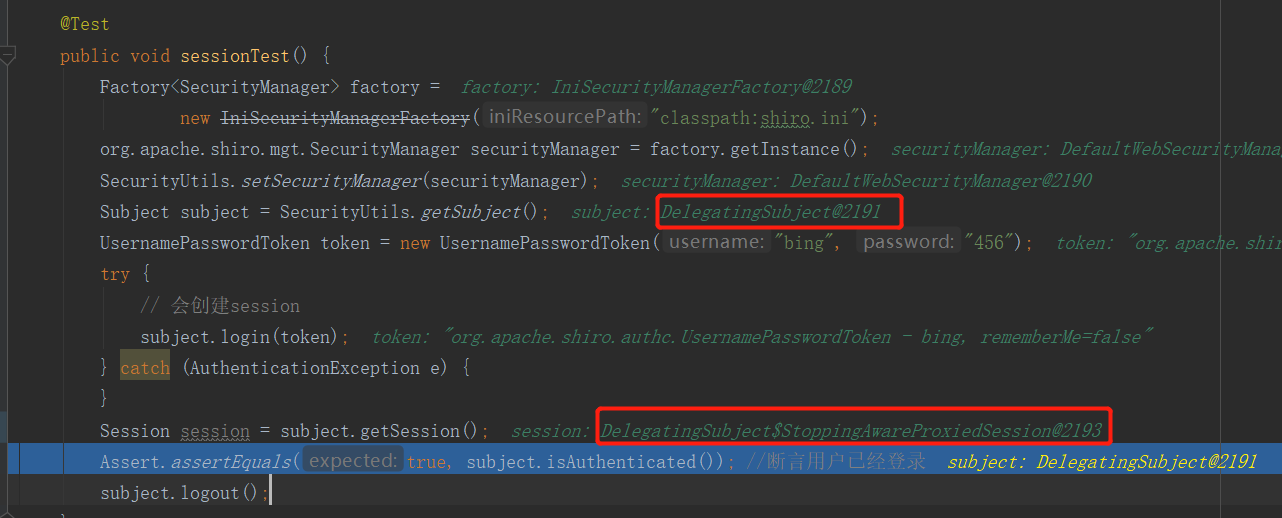
session的创建完成后,会将session(SimpleSession类型)对象的代理对象(DelegatingSession)装饰成StoppingAwareProxiedSession对象,然后绑定到subject(类型是DelegatingSubject);
Session session = subject.getSession();返回的就是绑定在当前subjuct的session。注意subject的实际类型是:DelegatingSubject,如下图
刷新
shiro的Session接口提供了一个touch方法,负责session的刷新;session的代理对象最终会调用SimpleSession的touch():
public void touch() { this.lastAccessTime = new Date(); // 更新最后被访问时间为当前时间 }
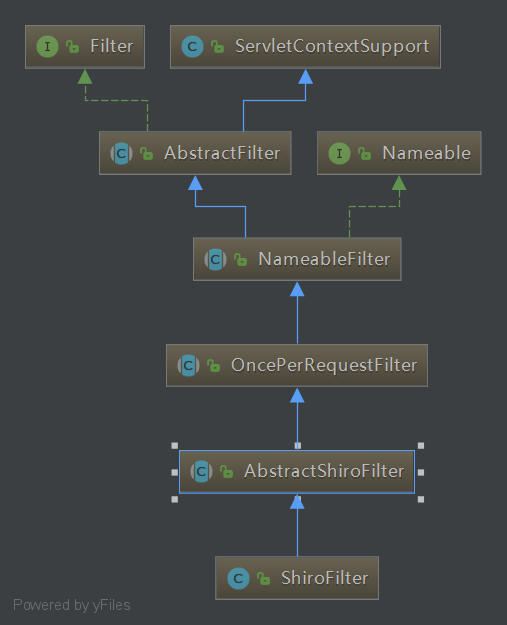
但是touch方法是什么时候被调用的呢?JavaSE需要我们自己定期的调用session的touch() 去更新最后访问时间;如果是Web应用,每次进入ShiroFilter都会自动调用session.touch()来更新最后访问时间,ShiroFilter的类图如下:
ShiroFilter自动调用session.touch()如下
过期
如果是让我们自己实现session过期的判断,我们会怎么做了?我们来看看shiro是怎么做的,或许我们能够从中学到一些经验。
启动校验定时任务
还记得AbstractValidatingSessionManager中createSession方法吗?在调用doCreateSession方法之前调用enableSessionValidationIfNecessary(),enableSessionValidationIfNecessary代码如下
private void enableSessionValidationIfNecessary() { // 获取session验证调度器 SessionValidationScheduler scheduler = getSessionValidationScheduler(); // session验证调度器开启 && (调度器为空或调度器不可用) if (isSessionValidationSchedulerEnabled() && (scheduler == null || !scheduler.isEnabled())) { enableSessionValidation(); // 开启session验证 } }
第一次创建session的时候,如果session验证调度器启用(默认是启用),那么调用enableSessionValidation(),enableSessionValidation代码如下

protected synchronized void enableSessionValidation() { SessionValidationScheduler scheduler = getSessionValidationScheduler(); // 获取调取器 if (scheduler == null) { scheduler = createSessionValidationScheduler(); // 创建调取器,实际类型是ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler setSessionValidationScheduler(scheduler); // 将调度器绑定到sessionManager } // it is possible that that a scheduler was already created and set via 'setSessionValidationScheduler()' // but would not have been enabled/started yet if (!scheduler.isEnabled()) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Enabling session validation scheduler..."); } scheduler.enableSessionValidation(); // 启动定时任务,验证session afterSessionValidationEnabled(); // 什么也没做,供继承,便于拓展 } }
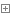
ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler类图如下,它实现了Runnable接口
调用scheduler的enableSessionValidation(),enableSessionValidation方法如下

public void enableSessionValidation() { if (this.interval > 0l) { // 创建ScheduledExecutorService this.service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(new ThreadFactory() { private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1); public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { Thread thread = new Thread(r); thread.setDaemon(true); thread.setName(threadNamePrefix + count.getAndIncrement()); return thread; } }); // 初始化service interval时长之后开始执行this的run方法,每隔interval执行一次;注意interval的单位是TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS this.service.scheduleAtFixedRate(this, interval, interval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // this就是ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler自己 } this.enabled = true; }
session校验
定时(默认每隔60分钟)的调用ExecutorServiceSessionValidationScheduler的run方法,run方法中调用sessionManager的validateSessions方法来完成session的验证,validateSessions方法如下

/** * @see ValidatingSessionManager#validateSessions() */ public void validateSessions() { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Validating all active sessions..."); } int invalidCount = 0; // 从sessionDao中获取全部的session // sessionDao可以是默认的MemorySessionDAO,也可以是我们定制的CachingSessionDAO Collection<Session> activeSessions = getActiveSessions(); if (activeSessions != null && !activeSessions.isEmpty()) { // 一个一个校验 for (Session s : activeSessions) { try { //simulate a lookup key to satisfy the method signature. //this could probably stand to be cleaned up in future versions: SessionKey key = new DefaultSessionKey(s.getId()); validate(s, key); // 真正校验的方法 } catch (InvalidSessionException e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { boolean expired = (e instanceof ExpiredSessionException); String msg = "Invalidated session with id [" + s.getId() + "]" + (expired ? " (expired)" : " (stopped)"); log.debug(msg); } invalidCount++; // 统计上次到这次定时任务间隔内过期的session个数 } } } if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { String msg = "Finished session validation."; if (invalidCount > 0) { msg += " [" + invalidCount + "] sessions were stopped."; } else { msg += " No sessions were stopped."; } log.info(msg); } }
validate方法如下

protected void validate(Session session, SessionKey key) throws InvalidSessionException { try { doValidate(session); // 真正校验session } catch (ExpiredSessionException ese) { onExpiration(session, ese, key); // 从sessionDao中删除过期的session throw ese; // 抛出异常供上层统计用 } catch (InvalidSessionException ise) { onInvalidation(session, ise, key); // 从sessionDao中删除不合法的session throw ise; // 抛出异常供上层统计用 } }
通过捕获doValidate()抛出的异常来剔除过期的或不合法的session,并将异常接着往上抛,供上层统计过期数量。注意:ExpiredSessionException的父类是StoppedSessionException,而StoppedSessionException的父类是InvalidSessionException。
doValidate方法如下

protected void doValidate(Session session) throws InvalidSessionException { if (session instanceof ValidatingSession) { ((ValidatingSession) session).validate(); // 校验session是否过期 } else { // 若session不是ValidatingSession类型,则抛出IllegalStateException异常 String msg = "The " + getClass().getName() + " implementation only supports validating " + "Session implementations of the " + ValidatingSession.class.getName() + " interface. " + "Please either implement this interface in your session implementation or override the " + AbstractValidatingSessionManager.class.getName() + ".doValidate(Session) method to perform validation."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } }
若session不是ValidatingSession类型,则抛出IllegalStateException异常
validate方法如下

public void validate() throws InvalidSessionException { //check for stopped: if (isStopped()) { // sesson已经停止了,则抛出StoppedSessionException;理论上来讲不会出现这种情况,但程序的事没有100%保障 //timestamp is set, so the session is considered stopped: String msg = "Session with id [" + getId() + "] has been " + "explicitly stopped. No further interaction under this session is " + "allowed."; throw new StoppedSessionException(msg); } //check for expiration if (isTimedOut()) { // 校验是否过期,校验方法是:lastAccessTime是否小于(当前时间 - session有效时长) expire(); // 更新session的stopTimestamp为当前时间,session的expired为true //throw an exception explaining details of why it expired: Date lastAccessTime = getLastAccessTime(); long timeout = getTimeout(); Serializable sessionId = getId(); DateFormat df = DateFormat.getInstance(); String msg = "Session with id [" + sessionId + "] has expired. " + "Last access time: " + df.format(lastAccessTime) + ". Current time: " + df.format(new Date()) + ". Session timeout is set to " + timeout / MILLIS_PER_SECOND + " seconds (" + timeout / MILLIS_PER_MINUTE + " minutes)"; if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace(msg); } throw new ExpiredSessionException(msg); // 抛出ExpiredSessionException供上层使用 } }
校验总结
1、sesion的有效时长默认30分钟;定时任务默认是每60分钟执行一次,第一次执行是在定时器初始化完成60分钟后执行;
2、session不是ValidatingSession类型,则抛出IllegalStateException异常;session已经停止了则抛出StoppedSessionException;session过期则抛出ExpiredSessionException异常;理论上来讲IllegalStateException与StoppedSessionException不会被抛出,应该全是ExpiredSessionException异常;ExpiredSessionException继承自StoppedSessionException,而StoppedSessionException又继承自IllegalStateException;
3、校验session的时候,抛出了异常,将其捕获,从sessionDao中删除对应的session,并使过期数量自增1
删除
夹杂在过期定时任务中,与过期是同时进行的,利用的异常机制;当然session操作的时候sessionManager也有session的校验,伴随着就有session的删除。
疑问
定时任务默认每60分钟执行一次,而session有效时长默认是30分钟,那么定时任务执行的间隔内肯定有session过期了,而我们在这个间隔内操作了过期的session怎么办?
其实这个问题应该这么来问:在定时任务间隔期间,对session的操作有没有做校验处理?答案是肯定的。
通过上面的讲解我们知道:session的操作通过代理之后,都会来到sessionManager,sessionManager通过处理之后再到SimpleSession;AbstractNativeSessionManager中将session操作放给SimpleSession之前,都会调用lookupSession方法,跟进lookupSession你会发现,里面也有session的校验。
所以session的校验,不只是定制任务在执行,很多session的操作都有做session的校验。
总结
1、一般我们操作subject是DelegatingSubject类型,DelegatingSubject中将subject的操作委托给了securityManager;一般操作的session是session的代理,代理将session操作委托给sessionManager,sesionManager校验之后再转交给SimpleSession;
2、session过期定时任务默认60分钟执行一次,所session已过期或不合法,则抛出对应的异常,上层通过捕获异常从sessionDao中删除session
3、不只定时任务做session的校验,session的基本操作都在sessionManager中有做session的校验
参考
《跟我学shiro》