模拟实现list
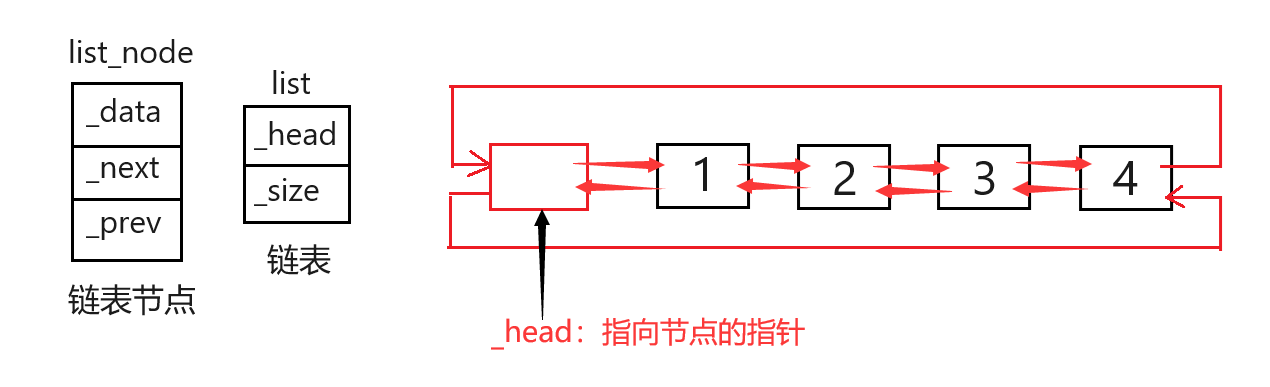
一.list成员变量
由于STL中的list容器本质是带有哨兵位头节点的双向循环链表,早已在数据结构篇幅实现。那么在C++中封装成类就好办好多了,结构图如下:
namespace xzy
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
T _data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}
二.构造函数
1.无参(默认)构造
- 节点的无参(默认)构造:初始化节点。
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
,_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
{}
- list的无参(默认)构造:实现
带有哨兵位头节点的双向循环链表结构。
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
—_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
2.有参构造
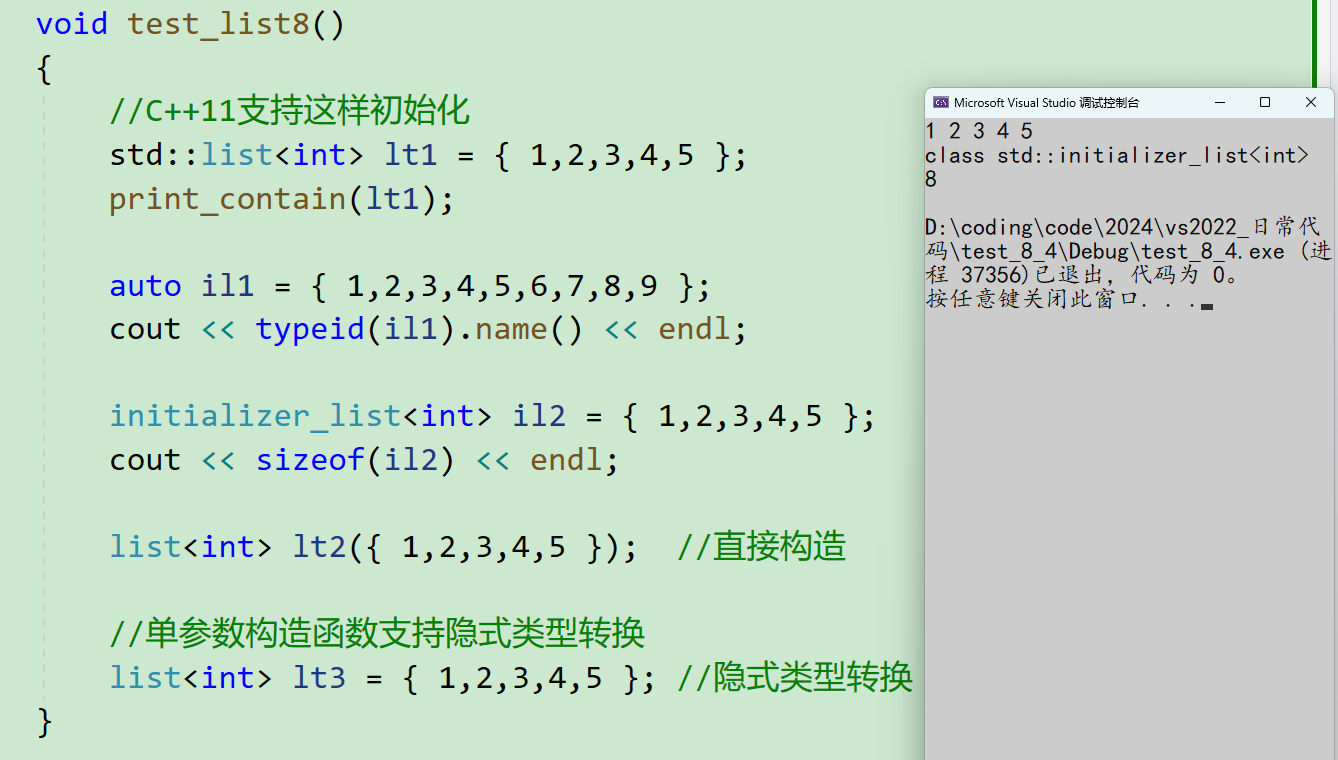
C++11支持下面这样构造:
list(initializer_list<T> il)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : il)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
3.拷贝构造
注意:要准备循环结构。
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
三.析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
四.list对象的容量操作
1.size
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
2.empty
bool empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
3.clear
void clear()
{
auto it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
五.list迭代器的实现
1.普通迭代器
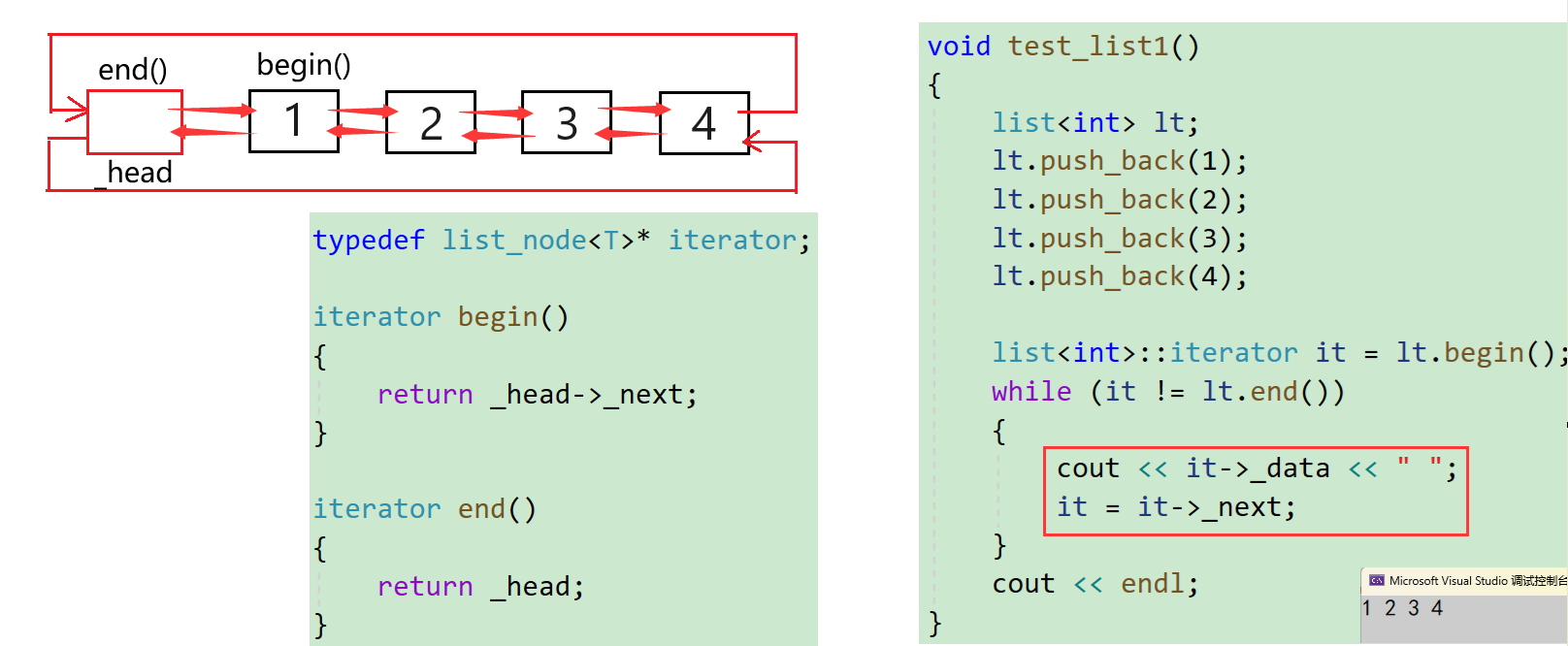
根据string和vecor迭代器的实现:无非就是begin()与end()返回iterator(指针),通过解引用指针和++指针进行遍历。
但是list不同,因为string和vector在内存时连续存储的,而list不是连续的。
- ++指针:找不到下一个节点。
- 解引用指针:是节点,并非数据。
- 查找下一个节点+访问数据:通过->。
但是产生迭代器就是为了统一各种容器。方便遍历容器,获得数据。如下代码:
为了模拟实现SLT中的list,内置类型指针不满足需求,利用自定义类型进行重载*和前置++,而重载最少需要一个类类型的对象。所以对节点的指针进行封装,类为list_iterator(成员变量:Node * _node)尝试实现:
例如list_iterator的对象it,*it:获取数据;++it:下一个位置的迭代器。
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
,_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
{}
T _data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
};
template<class T>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
/*iterator it;
it._node = _head->_next;
return it;*/
/*iterator it(_head->_next);
return it;*/
//return iterator(_head->_next); //匿名迭代器
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
注意:单参数构造函数支持隐式类型转换
单参数构造函数:list_iterator(Node* node)。
隐式类型转换:传入_head(节点的指针)隐式类型转换为迭代器。
类似string(const char* str); string s1 = “hello world”; 字符指针隐式类型转换为string。
如果数据类型是自定义类型并非内置类型,则重载*只能得到自定义类型,将借用.操作符获取自定义类型中的数据,也可以重载<<获取数据。如下:
class AA
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const AA& a);
private:
int _a1 = 1;
int _a2 = 1;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const AA& a)
{
out << a._a1 << " " << a._a2 << endl;
return out;
}
int main()
{
list<AA> lt;
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
list<AA>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << endl;
cout << *it << endl; //*it类型为AA,自定义类型无法直接输出,需要重载<<
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
也可以在list_iterator中重载->,用T*接收数据的地址,也就是自定义类型的地址,通过->访问数据。
T* operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
int main()
{
list<AA> lt;
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
lt.push_back(AA());
list<AA>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;
//cout << it->->_a1 << ":" << it->->_a2 << endl;
//本来应该是两个->,为了可读性,只需一个箭头
cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;
++it;
}
return 0;
}
2.const修饰的迭代器
- const iterator:迭代器本身不能修改,无法实现++it。
- const_iterator:指向的数据不能修改,无法实现(*it)++。
namespace xzy
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
T _data;
list_node* _next;
list_node* _prev;
};
template<class T>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
struct list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_const_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
const T* operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;
typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
private:
list_node<T>* _head;
size_t _size;
};
template<class Container>
void print_contain(const Container& con)
{
//模版按需实例化
typename Container::const_iterator it = con.begin();
while (it != con.end())
{
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
print_contain(lt);
list<int>::const_iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//(*it)++; 不能修改
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
}
3.模版写法
namespace xzy
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
T _data;
list_node* _next;
list_node* _prev;
};
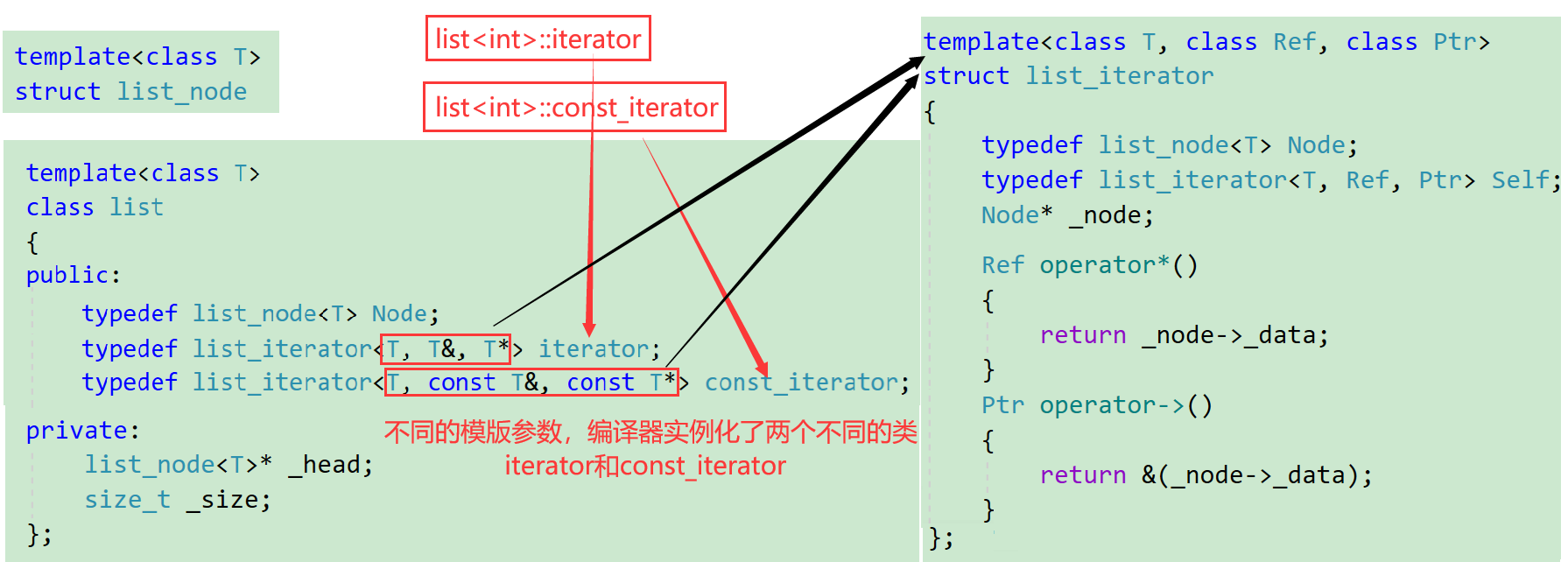
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
private:
list_node<T>* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}
六.list对象的增删查改操作
1.push_back
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//1.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//2.寻找尾节点
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//3.尾插新节点
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
//insert(end(), x);
}
2.push_front
void push_front(const T& x)
{
//1.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//2.定位头节点的下一个节点
Node* next = _head->_next;
//3.头插新节点
_head->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = _head;
newnode->_next = next;
next->_prev = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
//insert(begin(), x);
}
3.insert
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
//1.保存结构体pos的指针和pos的前一个节点的指针
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//2.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//3.插入新节点
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
return newnode; //隐式类型转换
}
4.pop_back
void pop_back()
{
//1.保存要删除的节点的指针和前一个节点的指针
Node* del = _head->_prev;
Node* prev = del->_prev;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
prev->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = prev;
delete del;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
//erase(--end());
}
5.pop_front
void pop_front()
{
//1.保存要删除的节点的指针和后一个节点的指针
Node* del = _head->_next;
Node* next = del->_next;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
_head->_next = next;
next->_prev = _head;
delete del;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
//erase(begin());
}
6.erase
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
//注意:不能删除哨兵位的头节点
assert(pos != end());
//1.保存pos节点的前后节点的指针
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
return next; //隐式类型转换
}
七.operator=
1.传统写法
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> lt)
{
clear();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
return *this;
}
2.现代写法
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
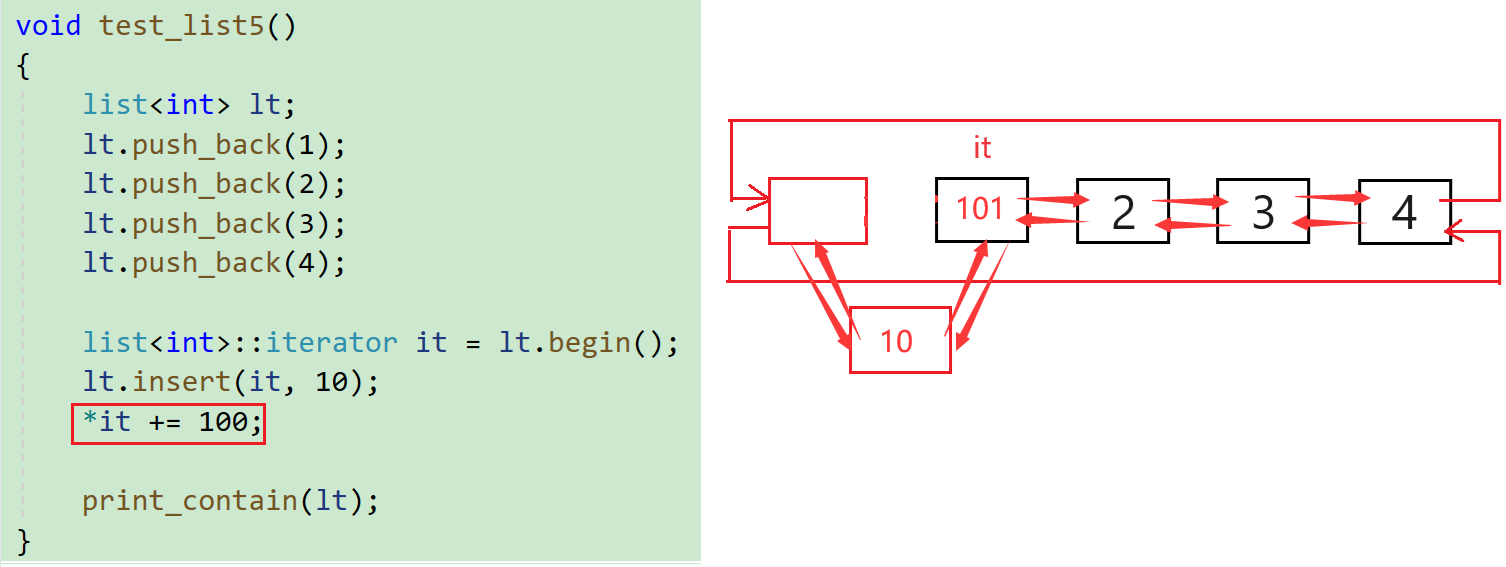
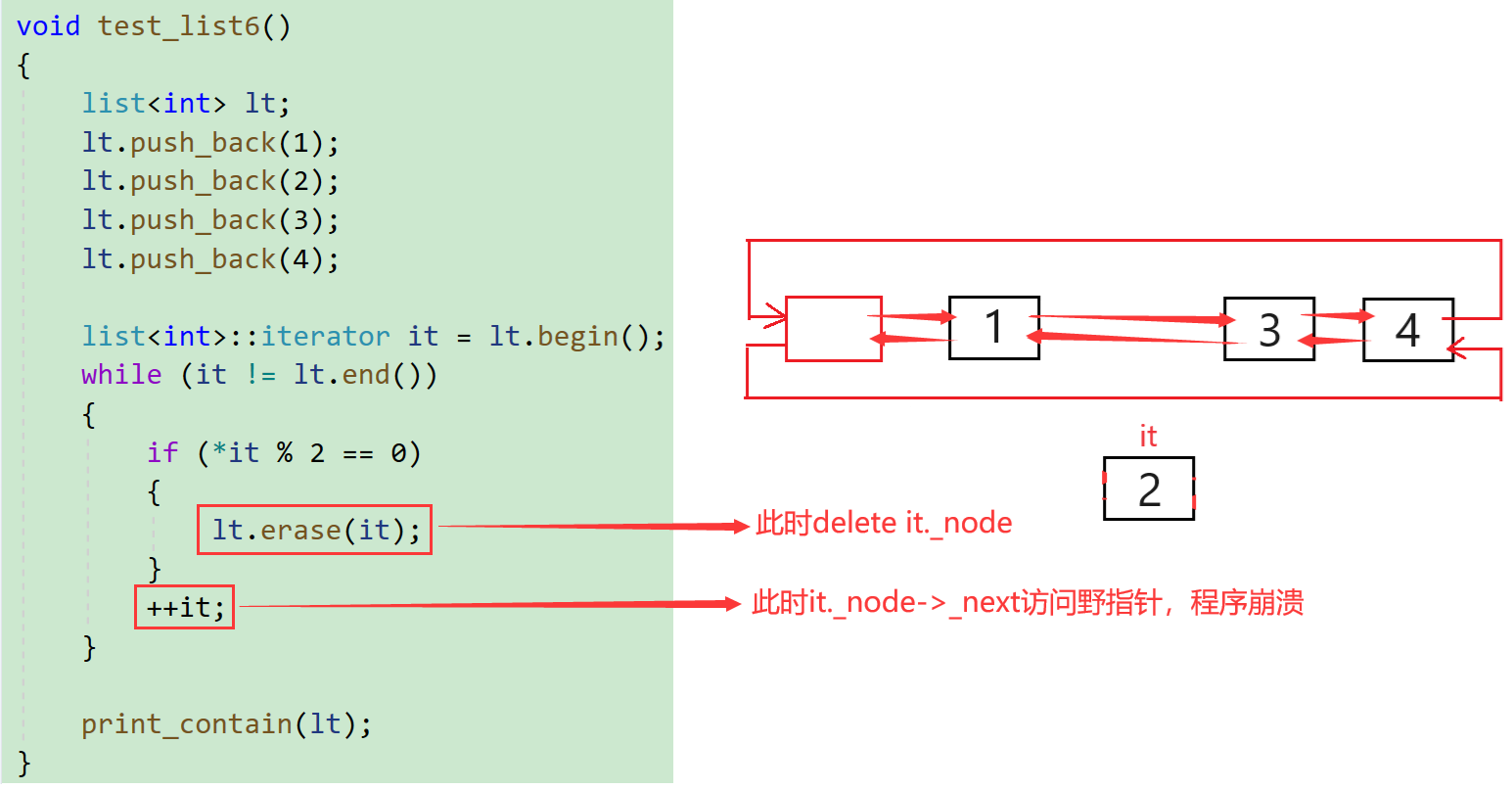
八.list迭代器失效问题
前面说过,此处可将迭代器暂时理解成类似于指针,迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节点被删除了。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
正确代码如下:
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = lt.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
print_contain(lt);
}
九.list与vector的对比
vector与list都是STL中非常重要的序列式容器,由于两个容器的底层结构不同,导致其特性以及应用场景不同,其主要不同如下:
| 容器 | vector | list |
|---|---|---|
| 底层结构 | 动态顺序表,一段连续空间 | 带头结点的双向循环链表 |
| 随机访问 | 支持随机访问,访问某个元素效率O(1) | 不支持随机访问,访问某个元素效率O(N) |
| 插入和删除 | 任意位置插入和删除效率低,需要搬移元素,时间复杂度为O(N),插入时有可能需要增容,增容:开辟新空间,拷贝元素,释放旧空间,导致效率更低 | 任意位置插入和删除效率高,不需要搬移元素,时间复杂度为O(1) |
| 空间利用率 | 底层为连续空间,不容易造成内存碎片,空间利用率高,缓存利用率高 | 底层节点动态开辟,小节点容易造成内存碎片,空间利用率低,缓存利用率低 |
| 迭代器 | 原生态指针 | 对原生态指针(节点指针)进行封装 |
| 迭代器失效 | 在插入元素时,要给所有的迭代器重新赋值,因为插入元素有可能会导致重新扩容,致使原来迭代器失效,删除时,当前迭代器需要重新赋值否则会失效 | 插入元素不会导致迭代器失效,删除元素时,只会导致当前迭代器失效,其他迭代器不受影响 |
| 使用场景 | 需要高效存储,支持随机访问,不关心插入删除效率 | 大量插入和删除操作,不关心随机访问 |
十.源代码
list.h
//#pragma once
#ifndef __LIST_H___
#define __LIST_H___
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace xzy
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
T _data;
list_node* _next;
list_node* _prev;
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list(initializer_list<T> il)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : il)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
/*list<T>& operator=(const list<T> lt)
{
clear();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
return *this;
}*/
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
auto it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//1.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//2.寻找尾节点
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//3.尾插新节点
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
//insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
//1.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//2.定位头节点的下一个节点
Node* next = _head->_next;
//3.头插新节点
_head->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = _head;
newnode->_next = next;
next->_prev = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
//insert(begin(), x);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
//1.保存结构体pos的指针和pos的前一个节点的指针
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//2.创建要插入的节点
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//3.插入新节点
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
//4.节点数自增一个
++_size;
return newnode;
}
void pop_back()
{
//1.保存要删除的节点的指针和前一个节点的指针
Node* del = _head->_prev;
Node* prev = del->_prev;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
prev->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = prev;
delete del;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
//erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
//1.保存要删除的节点的指针和后一个节点的指针
Node* del = _head->_next;
Node* next = del->_next;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
_head->_next = next;
next->_prev = _head;
delete del;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
//erase(begin());
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
//注意:不能删除哨兵位的头节点
assert(pos != end());
//1.保存pos节点的前后节点的指针
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
//2.修改指针的指向+删除节点
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
//3.节点数自减一个
--_size;
return next;
}
private:
list_node<T>* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}