【C++进阶】封装红黑树实现map和set
🥕个人主页:开敲🍉
🔥所属专栏:C++🥭
🌼文章目录🌼
1. 源码及框架分析
SGI-STL30版本源代码,map和set的源代码在map/set/stl_map.h/stl_set.h/stl_tree.h等几个头文件中。
map和set的实现结构框架核心部分截取出来如下:
// set
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_set.h>
#include <stl_multiset.h>
// map
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_TREE_H
#include <stl_tree.h>
#endif
#include <stl_map.h>
#include <stl_multimap.h>
// stl_set.h
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
public:
// typedefs:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing set
};
// stl_map.h
template <class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
public:
// typedefs:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
private:
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,
select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t; // red-black tree representing map
};
// stl_tree.h
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
color_type color;
base_ptr parent;
base_ptr left;
base_ptr right;
};
// stl_tree.h
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc
= alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
public:
// insert⽤的是第⼆个模板参数左形参
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);
// erase和find⽤第⼀个模板参数做形参
size_type erase(const key_type& x);
iterator find(const key_type& x);
protected:
size_type node_count; // keeps track of size of tree
link_type header;
};
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
Value value_field;
};① 通过下图对框架的分析,我们可以看到源码中rb_tree用了⼀个巧妙的泛型思想实现,rb_tree是实现key的搜索场景,还是key/value的搜索场景不是直接写死的,而是由第⼆个模板参数Value决定_rb_tree_node中存储的数据类型。
② set实例化rb_tree时第二个模板参数给的是key,map实例化rb_tree时第二个模板参数给的是
pair<const key, T>,这样⼀颗红黑树既可以实现key搜索场景的set,也可以实现key/value搜索场景的map。
③ 要注意⼀下,源码里面模板参数是用T代表value,而内部写的value_type不是我们我们日常
key/value场景中说的value,源码中的value_type反⽽是红黑树结点中存储的真实的数据的类型。
④ rb_tree第⼆个模板参数Value已经控制了红黑树结点中存储的数据类型,为什么还要传第⼀个模板参数Key呢?尤其是set,两个模板参数是⼀样的,这是很多同学这时的⼀个疑问。要注意的是对于map和set,find/erase时的函数参数都是Key,所以第⼀个模板参数是传给find/erase等函数做形参的类型的。对于set而言两个参数是⼀样的,但是对于map而言就完全不⼀样了,map insert的是pair对象,但是find和ease的是Key对象。
2. 模拟实现map和set
2.1 实现出复用红黑树的框架,并支持insert
① 参考源码框架,map和set复用之前我们实现的红黑树。
② 我们这里相比源码调整⼀下,key参数就用K,value参数就用V,红黑树中的数据类型,我们使用T。(源码中的命名风格实在令人抓狂)
③ 其次因为RBTree实现了泛型不知道T参数导致是K,还是pair<K, V>,那么insert内部进行插入逻辑比较时,就没办法进行比较,因为pair的默认支持的是key和value⼀起参与比较,我们需要时的任何时候只比较key,所以我们在map和set层分别实现⼀个MapKeyOfT和SetKeyOfT的仿函数传给RBTree的KeyOfT,然后RBTree中通过KeyOfT仿函数取出T类型对象中的key,再进行比较,具体细节参考如下代码实现。
// 源码中pair⽀持的<重载实现
template <class T1, class T2>
bool operator< (const pair<T1,T2>& lhs, const pair<T1,T2>& rhs)
{ return lhs.first<rhs.first || (!(rhs.first<lhs.first) &&
lhs.second<rhs.second); }
// Mymap.h
namespace bit
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}// Myset.h
namespace bit
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
return key;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode//红黑树
{
T _data;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
: _data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{}
};
// 实现步骤:
// 1、实现红⿊树
// 2、封装map和set框架,解决KeyOfT
// 3、iterator
// 4、const_iterator
// 5、key不⽀持修改的问题
// 6、operator[]
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
p
rivate :
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
Node* _root = nullptr;
public:
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
} K
eyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
} e
lse if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
} e
lse
{
return false;
}
} c
ur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
// 新增结点。颜⾊给红⾊
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
} e
lse
{
parent->_left = cur;
} c
ur->_parent = parent;
//...
return true;
}
}2.2 支持iterator的实现
iterator核心源码:
struct __rb_tree_base_iterator
{
typedef __rb_tree_node_base::base_ptr base_ptr;
base_ptr node;
void increment()
{
if (node->right != 0) {
node = node->right;
while (node->left != 0)
node = node->left;
} e
lse{
base_ptr y = node->parent;
while (node == y->right) {
node = y;
y = y->parent;
} i
f(node->right != y)
node = y;
}
} v
oid decrement()
{
if (node->color == __rb_tree_red &&
node->parent->parent == node)
node = node->right;
else if (node->left != 0) {
base_ptr y = node->left;
while (y->right != 0)
y = y->right;
node = y;
} e
lse{
base_ptr y = node->parent;
while (node == y->left) {
node = y;
y = y->parent;
} n
ode = y;
}
}
};
template <class Value, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __rb_tree_iterator : public __rb_tree_base_iterator
{
typedef Value value_type;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value, Value&, Value*> iterator;
__rb_tree_iterator() {}
__rb_tree_iterator(link_type x) { node = x; }
__rb_tree_iterator(const iterator& it) { node = it.node; }
reference operator*() const { return link_type(node)->value_field; }
#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR
pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
#endif /* __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR */
self& operator++() { increment(); return *this; }
self& operator--() { decrement(); return *this; }
inline bool operator==(const __rb_tree_base_iterator& x,
const __rb_tree_base_iterator& y) {
return x.node == y.node;
} i
nline bool operator!=(const __rb_tree_base_iterator& x,
const __rb_tree_base_iterator& y) {
return x.node != y.node;
}iterator实现思路分析:
① iterator实现的大框架跟list的iterator思路是一致的,用⼀个类型封装结点的指针,再通过重载运算符实现,迭代器像指针⼀样访问的行为。
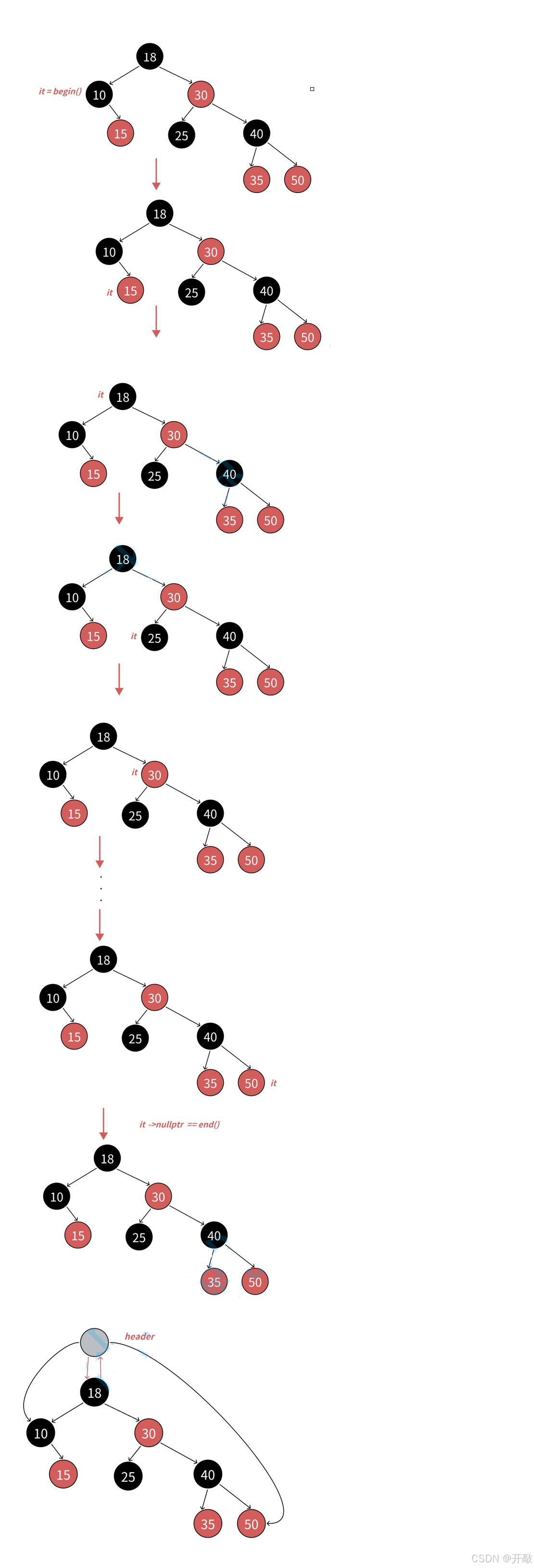
② 这里的难点是operator++和operator--的实现。之前使用部分,我们分析了,map和set的迭代器走的是中序遍历,左子树->根结点->右子树,那么begin()会返回中序第⼀个结点的iterator也就是10所在结点的迭代器。
③ 迭代器++的核心逻辑就是不看全局,只看局部,只考虑当前中序局部要访问的下一个结点。
④ 迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右子树不为空,代表当前结点已经访问完了,要访问下⼀个结点是右子树的中序第⼀个,一棵树中序第一个是最左结点,所以直接找右子树的最左结点即可。
⑤ 迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右子树空,代表当前结点已经访问完了且当前结点所在的子树也访问完了,要访问的下一个结点在当前结点的祖先里面,所以要沿着当前结点到根的祖先路径向上找。
⑥ 如果当前结点是父亲的左,根据中序左子树->根结点->右子树,那么下一个访问的结点就是当前结点的父亲;如下图:it指向25,25右为空,25是30的左,所以下一个访问的结点就是30。
⑦ 如果当前结点是父亲的右,根据中序左子树->根结点->右子树,当前当前结点所在的⼦树访问完了,当前结点所在父亲的子树也访问完了,那么下一个访问的需要继续往根的祖先中去找,直到找到孩⼦是父亲左的那个祖先就是中序要问题的下一个结点。如下图:it指向15,15右为空,15是10的右,15所在⼦树话访问完了,10所在子树也访问完了,继续往上找,10是18的左,那么下⼀个访问的结点就是18。
⑧ end()如何表示呢?如下图:当it指向50时,++it时,50是40的右,40是30的右,30是18的右,18到根没有父亲,没有找到孩子是父亲左的那个祖先,这是父亲为空了,那我们就把it中的结点指针置为nullptr,我们用nullptr去充当end。需要注意的是stl源码空,红黑树增加了⼀个哨兵位头结点做为end(),这哨兵位头结点和根互为父亲,左指向最左结点,右指向最右结点。相比我们用nullptr作为end(),差别不大,他能实现的,我们也能实现。只是--end()判断到结点时空,特殊处理一下,让迭代器结点指向最右结点。具体参考迭代器--实现。
⑨ 迭代器--的实现跟++的思路完全类似,逻辑正好反过来即可,因为他访问顺序是右子树->根结点->左子树,具体参考下面代码实现。
⑩ set的iterator也不支持修改,我们把set的第二个模板参数改成const K即可, RBTree<K,
const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
⑪ map的iterator不支持修改key但是可以修改value,我们把map的第二个模板参数pair的第⼀个参数改成const K即可, RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
实际上支持iterator还有非常多的细节要处理,具体看下面的代码。
2.3 map支持[]
① map要支持[]主要修改insert返回值支持,修改RBTree中的insert返回值为pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
② 有了insert支持,[]实现就很简单了,具体实现参考下面代码。
2.4 Mymap和myset代码实现
//Mymap
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace gjk
{
template <class K,class V>
class Mymap
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& data)
{
return _t.Insert(data);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}//Myset
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace gjk
{
template <class K>
class Myset
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& data)
{
return _t.Insert(data);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}//RBTree
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
//枚举存储颜色
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
namespace gjk
{
template <class T>
class RBTreeNode
{
public:
T _data;//存储的值
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;//左孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;//右孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;//父亲
Color _col;//颜色
RBTreeNode(const T& data,Color col = RED)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
,_col(col)
{}
};
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node,Node* root)
:_node(node)
,_root(root)
{}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min && min->_left) min = min->_left;
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator++(int)//后置++
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min && min->_left) min = min->_left;
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (!_node)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_right) cur = cur->_right;
_node = cur;
}
else if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max && max->_right) max = max->_right;
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
if (!_node)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_right) cur = cur->_right;
_node = cur;
}
else if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max && max->_right) max = max->_right;
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
template <class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*> Iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left) cur = cur->_left;
return Iterator(cur, _root);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left) cur = cur->_left;
return ConstIterator(cur, _root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);
}
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (!_root)
{
_root = new Node(data,BLACK);
return make_pair(Iterator(_root, _root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)//插入节点
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else return make_pair(Iterator(cur, _root), true);
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* flag = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data)) parent->_left = cur;
else parent->_right = cur;
//处理两个红连在一起的情况
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
if (parent->_left == cur)//新增节点插入在parent左边的情况
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (grandfather->_right == parent) uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在并且颜色为红
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//uncle不存在或者颜色为黑
{
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//新增节点插入在parent右边的情况
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (grandfather->_right == parent) uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在并且颜色为红
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (grandfather->_right == parent)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(Iterator(flag, _root), true);
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)//右单旋
{
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subR;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (subR) subR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
subL->_parent = pparent;
if (pparent)
{
if (pparent->_left == parent) pparent->_left = subL;
else pparent->_right = subL;
}
else _root = subL;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)//左单旋
{
Node* pparent = parent->_parent;
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subL;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (subL) subL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
subR->_parent = pparent;
if (pparent)
{
if (pparent->_left == parent) pparent->_left = subR;
else pparent->_right = subR;
}
else _root = subR;
}
int leafnodesize()//叶子节点个数
{
int sum = 0;
LeafNodeSize(_root,sum);
return sum;
}
int nodesize()//节点个数
{
int sum = 0;
NodeSize(_root, sum);
return sum;
}
void printf()
{
Printf(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void find(const T& data)
{
Find(_root,data);
}
bool isRBTree()
{
return IsRBTree(_root);
}
void blacknodenum(vector<int>& arr)
{
BlackNodeNum(_root,arr,0);
}
private:
void Printf(Node* cur)
{
if (!cur) return;
Printf(cur->_left);
cout << cur->_val << " ";
Printf(cur->_right);
}
void Find(Node* cur,const T& data)//查找
{
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_val > data) cur = cur->_left;
else if (cur->_val < data) cur = cur->_right;
else
{
cout << data << "->" << cur->_val << endl;
return;
}
}
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
bool IsRBTree(Node* cur)//验证红黑树
{
if (!cur) return true;
if (cur->_parent && cur->_col == RED && cur->_col == cur->_parent->_col) return false;
return IsRBTree(cur->_left) && IsRBTree(cur->_right);
}
bool IsLeafNode(Node* cur)
{
return !cur->_left && !cur->_right;
}
void LeafNodeSize(Node* cur,int& sum)
{
if (!cur) return;
if (IsLeafNode(cur))
{
sum++;
return;
}
LeafNodeSize(cur->_left, sum);
LeafNodeSize(cur->_right, sum);
}
void NodeSize(Node* cur,int& sum)
{
if (!cur) return;
sum++;
NodeSize(cur->_left,sum);
NodeSize(cur->_right,sum);
}
void BlackNodeNum(Node* cur,vector<int>& sum,int num)
{
if (!cur)
{
sum.push_back(num);
return;
}
if (cur->_col == BLACK) num++;
BlackNodeNum(cur->_left, sum, num);
BlackNodeNum(cur->_right, sum, num);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;//根节点
};
}创作不易,点个赞呗,蟹蟹啦~