在上篇中,我们使用闭散列技术解决了哈希冲突并实现了哈希表。然而,我们发现闭散列并不理想,因此本篇将探讨如何通过开散列方法来处理哈希冲突。
🌈个人主页:是店小二呀
🌈C语言专栏:C语言
🌈C++专栏: C++
🌈初阶数据结构专栏: 初阶数据结构
🌈高阶数据结构专栏: 高阶数据结构
🌈Linux专栏: Linux
🌈喜欢的诗句:无人扶我青云志 我自踏雪至山巅
一、开散列(哈希桶)
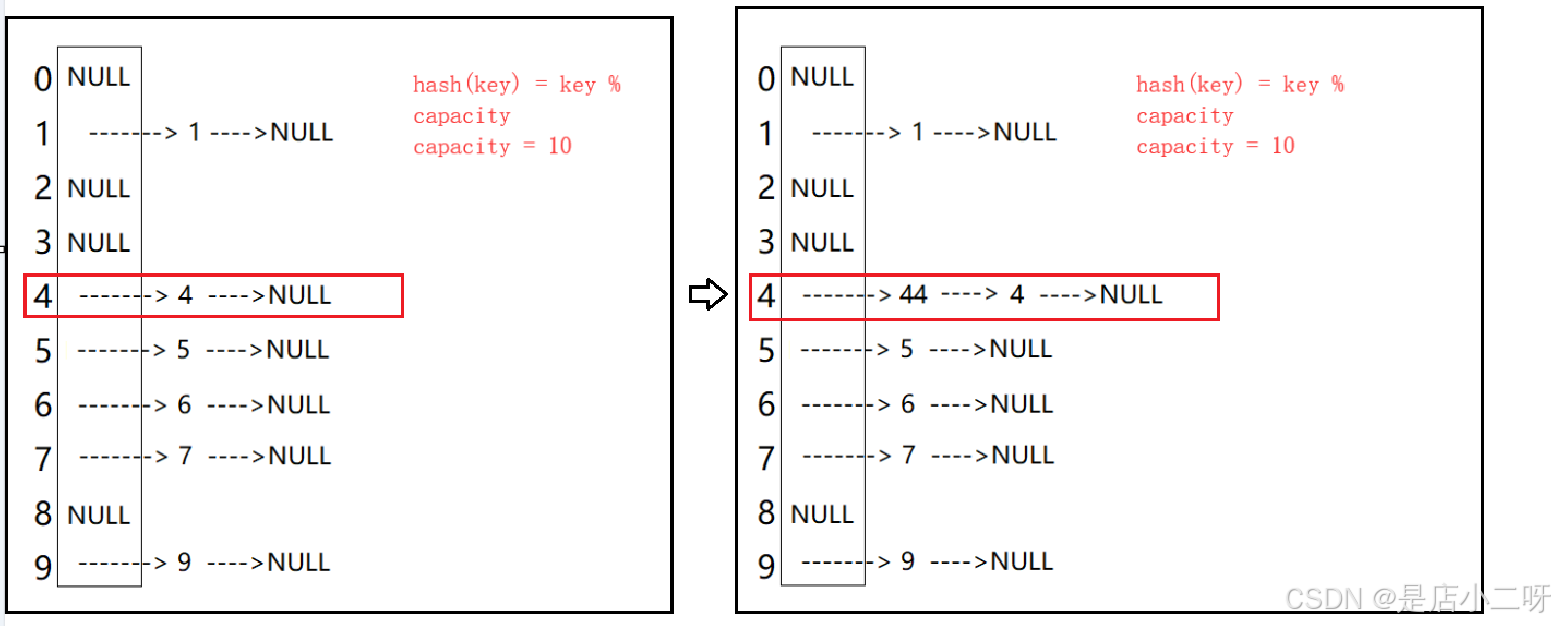
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
从上图可以看出,开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素
二、实现哈希表
2.1 哈希表基本构架
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace hash_buck
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V> _next;
};
template<class K, class V,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10,nullptr);
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
//vector<list<..>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}
这里如果想实现哈希桶结构,可以使用一个个节点连接起来或者直接套上一个链表容器。这里为了更好地实现迭代器,我们选择第一种方式,第二种方式实现迭代器有一丝麻烦。
开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素 ,并没有顺序之分。
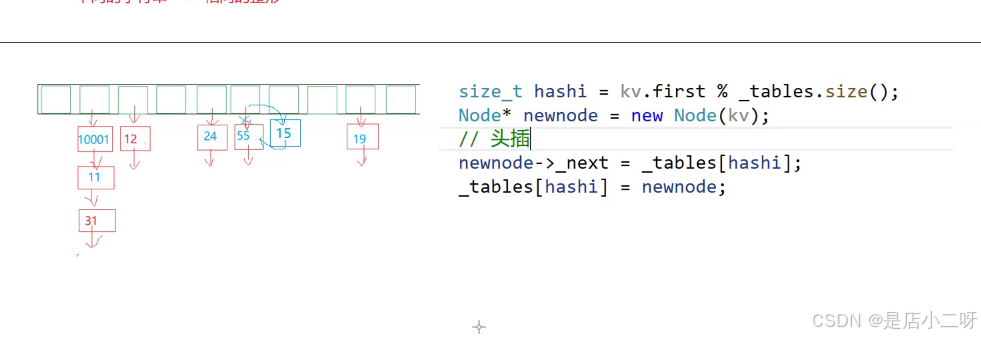
2.2 哈希表插入数据
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
//进行头插操作
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
_tables[hashi]->_next = newnode;
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
}
这里链表节点只需要单纯地存储数据,那么只需要设计单链表即可,没有必要设双向链表。对于单链表插入数据,一般推荐采用头插,由于尾插需要找尾比较麻烦。
2.3 哈希表析构函数
这里涉及堆上空间资源的开辟,一般需要涉及析构函数进行资源处理。
由于vector容器元素为内置类型,析构函数对内置类型不进行处理,那么就导致指向空间没有得到释放,需要显式写析构函数,完成资源释放。
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
2.4 哈希表扩容
由于哈希桶去解决哈希冲突对于哈希表空间需要相对比较小,不同于开发定址法去解决哈希冲突占用表内空间,而是表中一个指针指向一个空间。
【负载因子满足1即可扩容】:_n == _tables.size()
【第一个方案】:复用Insert完成CV操作
//扩容逻辑
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//这里可以忽略类型
HashTable NewTable;
NewTable._tables.resize(n * 10);
//CV工作
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
NewTable.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
_tables.swap(NewTable);
}
【缺陷】:如果存在一万个节点,意味着需要复制一万个节点又要释放一万个节点,显得很浪费
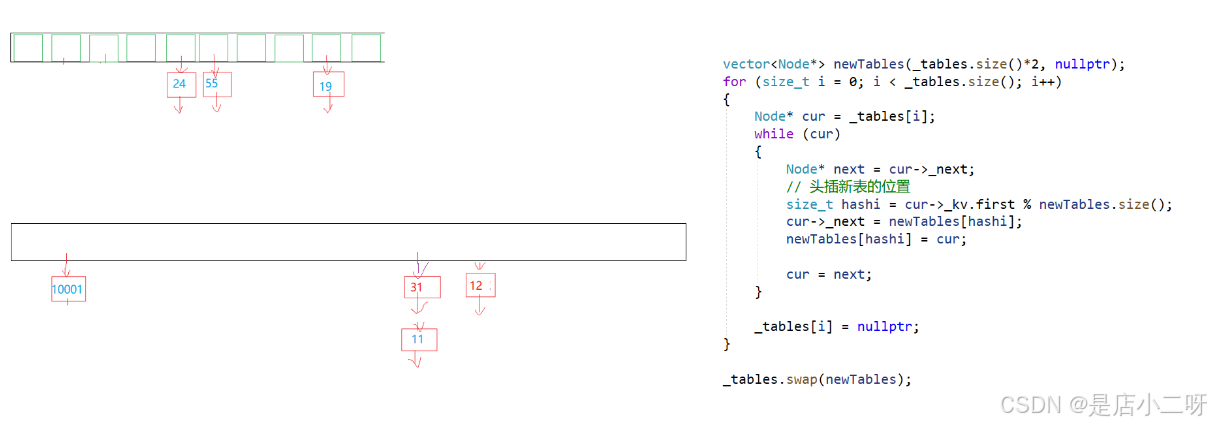
【第二个方案】:直接将节点拿下来
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<Node*> NewTable(n * 10, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
cur->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(NewTable);
}
关于这段代码是比较难懂,每个指针指向一块空间,先cur->next = newTables[hashi]抓住新表的位置,newTables[hashi] = cur新表将旧表节点拿下来,可以好好理解拿下来的逻辑,得到了这个地址,这个地址指向一块节点。
这里会导致newTables[hashi]和_tables[i]共同指向一块空间,虽然不会去使用旧表去影响到新表,为了保险起见,可以将旧表这块位置指针置空。
2.5 哈希表删除数据
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
这里删除数据,无非需要考虑两种情况的删除,一种是删除第一个节点,另一种是删除其他节点prev->_next = cur->_next。在删除节点需要前后兼顾,保存下前驱指针指向节点。
2.6 哈希桶中查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return &cur->_kv.first;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
三、HashTable.h
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace hash_bucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V> _next;
};
template<class K, class V,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10,nullptr);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
//扩容逻辑
//if (_n == _tables.size())
//{
// //这里可以忽略类型
// HashTable NewTable;
// NewTable._tables.resize(n * 10);
//
// //CV工作
// for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
// {
// Node* cur = _tables[i];
// while (cur)
// {
// NewTable.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
// cur = cur->_next;
// }
// }
// _tables.swap(NewTable);
//}
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<Node*> NewTable(n * 10, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
// 头插新表的位置
size_t hashi = hs(kot(cur->_data)) % NewTable.size();
cur->_next = NewTable[hashi];
NewTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(NewTable);
}
//进行头插操作
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
_tables[hashi]->_next = newnode;
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return &cur->_kv.first;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}
以上就是本篇文章的所有内容,在此感谢大家的观看!这里是店小二呀C++笔记,希望对你在学习C++语言旅途中有所帮助!