第3章 链表
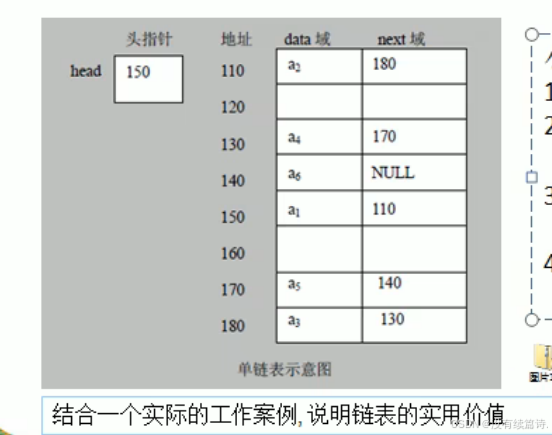
链表是有序的列表,但是它在内存中的存储不一定是连续的
-
链表是以节点的方法来存储的
-
每个节点包含date域,next域:指向下一个节点
-
链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储
-
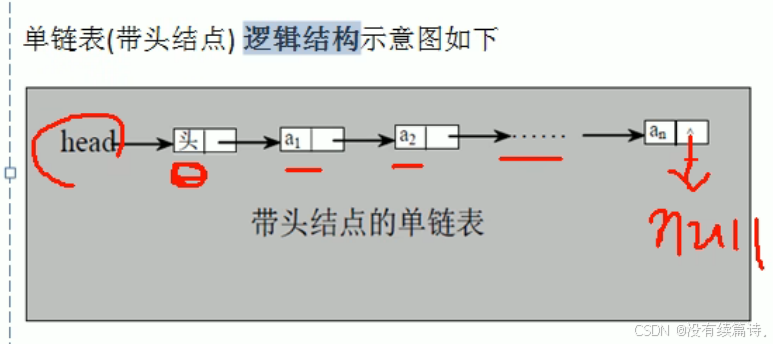
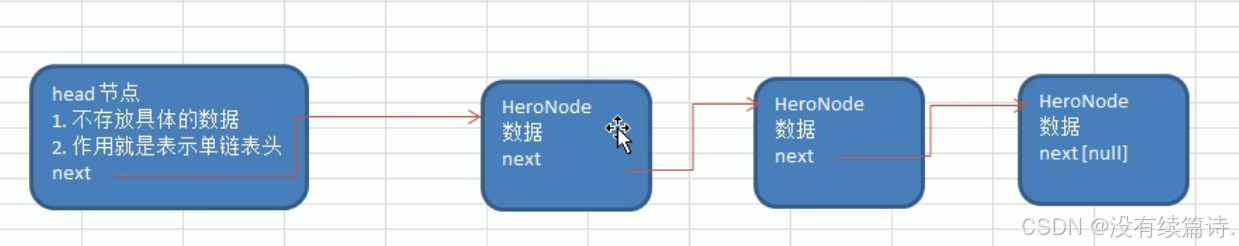
链表分为头节点的链表和没有头节点的链表根据实际需求来定
内存实际结构
3.1单链表
简单单链表实现
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero1 = new Hero("张三", 20);
Hero hero2 = new Hero("李四", 30);
Hero hero3 = new Hero("王五", 40);
SingleLinkedList list = new SingleLinkedList();
list.addHero(hero1);
list.addHero(hero2);
list.addHero(hero3);
list.print();
}
}
class Hero{
private String name;
private int age;
Hero next;
public Hero(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
class SingleLinkedList{
private Hero head=new Hero("",0);
public void addHero(Hero hero){//添加英雄
Hero temp = head;
if(temp.next == null){
temp.next = hero;
return;
}
while(temp.next!=null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = hero;
}
public void print(){//遍历英雄
Hero temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
System.out.println(temp.next.toString());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}3.2按顺序插入和删除排序单链表
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero1 = new Hero("张三", 30);
Hero hero2 = new Hero("李四", 20);
Hero hero3 = new Hero("王五", 10);
SingleLinkedList list = new SingleLinkedList();
list.addHero(hero1);
list.addHero(hero2);
list.addHero(hero3);
list.print();
System.out.println("==============");
list.deleteHero(hero2);
list.print();
}
}
class Hero{
private String name;
private int age;
Hero next;
public Hero(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Hero getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Hero next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
class SingleLinkedList{
private Hero head=new Hero("",0);
public void addHero(Hero hero){//添加英雄
Hero temp = head;
if(temp.next == null){
temp.next = hero;
return;
}
while(temp.next!=null){
if(temp.next.getAge()>hero.getAge()){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
hero.next = temp.next;
temp.next=hero;
}
public void deleteHero(Hero hero){//删除英雄
Hero temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
if(temp.next.getAge()==hero.getAge()){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public void print(){//遍历英雄
Hero temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
System.out.println(temp.next.toString());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}3.3企业面试题实现单链表一些功能
有链表数据反转和链表长度和链表特定索引查询
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero1 = new Hero("张三", 30);
Hero hero2 = new Hero("李四", 20);
Hero hero3 = new Hero("王五", 10);
SingleLinkedList list = new SingleLinkedList();
list.addHero(hero1);
list.addHero(hero2);
list.addHero(hero3);
list.print();
System.out.println("==============");
reserve(list.head);
list.print();
}
public static Hero reserve(Hero heroHead) {
Hero endHero = new Hero("",0);
Hero tempHead = heroHead.next;//临时结点存放原链表第一个节点
Hero next=null;//用来存放原链表第二个节点
while (tempHead != null) {
next=tempHead.next;//存放原链表第二个节点
tempHead.next=endHero.next;//将第二个节点指向最终链表的第一个节点
endHero.next=tempHead;//将最终节点指向当前第一个节点
tempHead=next;//将节点改成第二个节点
}
return heroHead.next=endHero.next;
}
}
class Hero{
private String name;
private int age;
Hero next;
public Hero(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Hero getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Hero next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
class SingleLinkedList{
Hero head=new Hero("",0);
public void addHero(Hero hero){//添加英雄
Hero temp = head;
if(temp.next == null){
temp.next = hero;
return;
}
while(temp.next!=null){
if(temp.next.getAge()>hero.getAge()){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
hero.next = temp.next;
temp.next=hero;
}
public void deleteHero(Hero hero){//删除英雄
Hero temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
if(temp.next.getAge()==hero.getAge()){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public void print(){//遍历英雄
Hero temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null){
System.out.println(temp.next.toString());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
public Hero getHero(int index){//查看倒数第几个英雄
Hero temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<this.getLength()-index;i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
public int getLength(){//查看链表长度
Hero temp = head;
int length = 0;
while(temp.next!=null){
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
}4.4单链表实现逆序打印
思路:
-
先将单链表进行反转操作,然后再遍历即可,这样做的问题会破坏原来的单链表结构,不建议
-
可以利用栈这个数据结构,将各个节点压入到栈中然后利用先进后出的特点,就实现了逆序打印的效果
演示
public static void reservePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){
return ;
}
HeroNode cur=head.next;
Stack<HeroNode> heroNodes = new Stack<>();
while (cur!=null){
heroNodes.push(cur);//压入栈
cur=cur.next;
}
while (heroNodes.size()>0){
System.out.println(heroNodes.pop());//弹出栈
}
}4.5双向链表实现及功能
-
遍历方式和单链表一样,但是可以从后向前
-
添加 temp.next=newHeroNode newHeroNode.pre=temp;
-
修改思路和单聊表一样
-
删除
-
因为是双向链表,因此,我们可以实现自我删除某个节点
-
直接找到要删除的节点比如temp
-
temo.pre.next=temp.next
-
temp.next.pre=temp.pre
-
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode h1 = new HeroNode(1, "小明");
HeroNode h2 = new HeroNode(2, "小红");
HeroNode h3 = new HeroNode(3, "小蓝");
HeroNode h4 = new HeroNode(4, "小绿");
DoubleLinkedList d = new DoubleLinkedList();
d.add(h1);
d.add(h2);
d.list();
System.out.println("==========");
d.unList();
}
}
//双向链表存放
class DoubleLinkedList{
private HeroNode tail=new HeroNode(0,"");
private HeroNode head= new HeroNode(0,"");
public void add(HeroNode h){//添加元素
if(head.next==null){
head.next=h;
tail=h;
return;
}
HeroNode temp=head;
while (temp.next!=null){
if(h.a<=temp.next.a){
temp.next.pre=h;
h.next=temp.next;
temp.next=h;
h.pre=temp;
return;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
temp.next=h;
h.pre=temp;
tail=h;
}
public void upDate(int a){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
HeroNode temp=head;
while (temp.next!=null){
if(temp.next.a==a){
System.out.println("请输入要改成的序号和名字");
temp.next.a=sc.nextInt();
temp.next.name=sc.nextLine();
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这个年龄的值");
}
public void unList(){
HeroNode temp=tail;
while (temp!=null){
System.out.println(temp.toString());
temp=temp.pre;
}
}
public void list(){
HeroNode temp=head;
while (temp.next!=null){
System.out.println(temp.next.toString());
temp=temp.next;
}
}
}
class HeroNode{
public int a;
public String name;
public HeroNode next;
public HeroNode pre;
public HeroNode(int a, String name){
this.a=a;
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (a+" "+name );
}
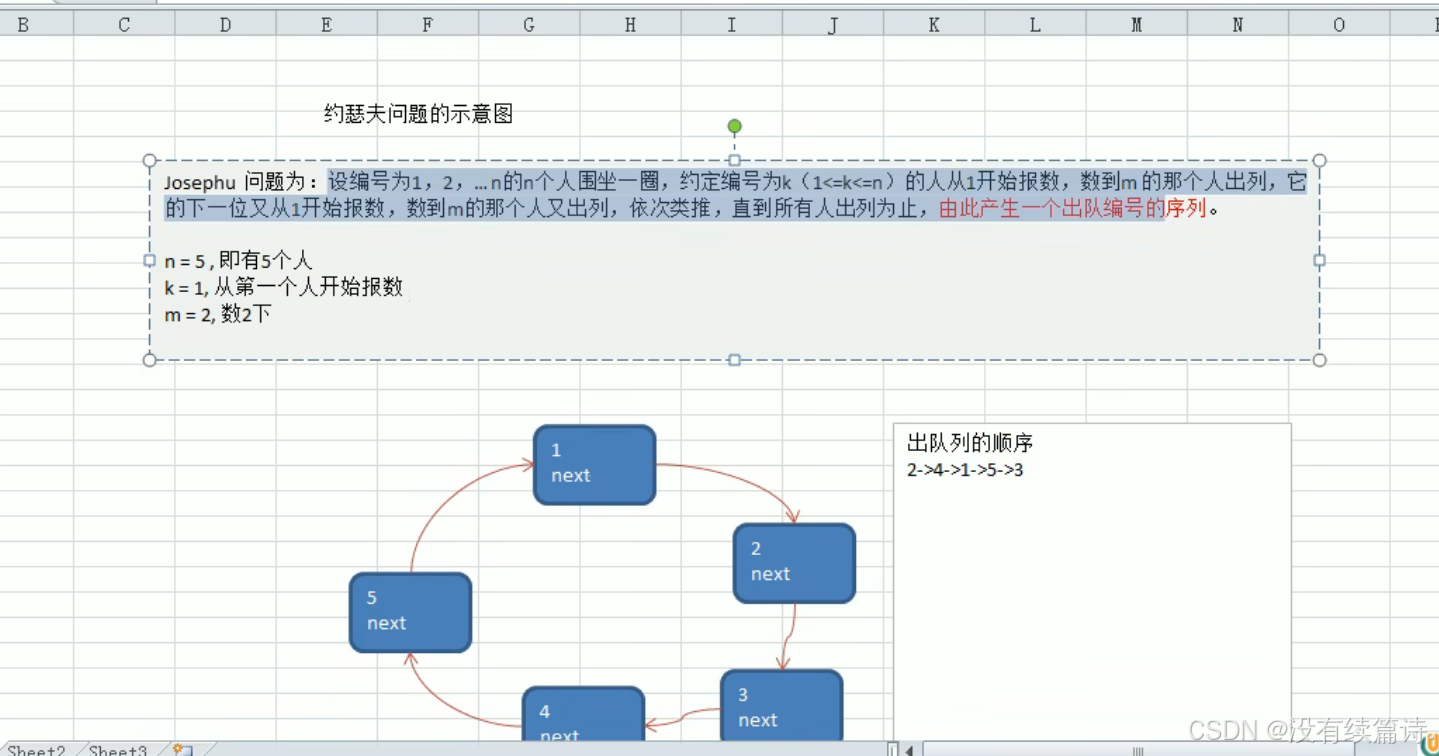
}4.6双向链表约瑟夫问题
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Josepfu j = new Josepfu();
j.addBoy(5);
j.showBoy();
}
}
class Boy{
private int age;
private Boy next;
public Boy(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
class Josepfu{
private Boy first=null;
public void addBoy(int num){// 添加数据
Boy curBoy=null;
for (int i = 1; i <=num ; i++) {
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
if(i>1){
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
}else {
first=boy;
boy.setNext(first);
}
curBoy=boy;
}
}
public void showBoy(){//遍历孩子年龄
Boy curBoy=first;
while (true){
System.out.println(curBoy.getAge());
if(curBoy.getNext()==first){
break;
}
curBoy=curBoy.getNext();
}
}
}import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Josepfu j = new Josepfu();
j.addBoy(5);
j.showBoy();
}
}
class Boy{
private int age;
private Boy next;
public Boy(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
class Josepfu{
private Boy first=null;
public void addBoy(int num){// 添加数据
Boy curBoy=null;
for (int i = 1; i <=num ; i++) {
Boy boy = new Boy(i);
if(i>1){
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
}else {
first=boy;
boy.setNext(first);
}
curBoy=boy;
}
}
public void showBoy(){//遍历孩子年龄
Boy curBoy=first;
while (true){
System.out.println(curBoy.getAge());
if(curBoy.getNext()==first){
break;
}
curBoy=curBoy.getNext();
}
}
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){//从第几个人开始 报几个数 一共多少个人
if(startNo<1||first==null||countNum>nums){
System.out.println("数据不符合");
return;
}
Boy helper=first;
while (true){
if(helper.getNext()==first){
break;
}
helper=helper.getNext();
}
while (true){
if(helper.getNext()==first){
break;
}
helper=helper.getNext();
}
for (int i = 1; i <startNo ; i++) {//报数前,先让first和helper移动k-1次
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
while (first.getNext()!=first){//当小孩报数时让first和helper同时移动
for (int i = 0; i <countNum-1 ; i++) {
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
System.out.println("出圈元素为"+first.getAge());
first=first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
}
System.out.println("最后留下的小孩"+first.getAge());
}
}