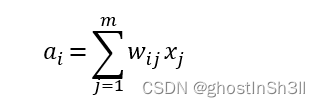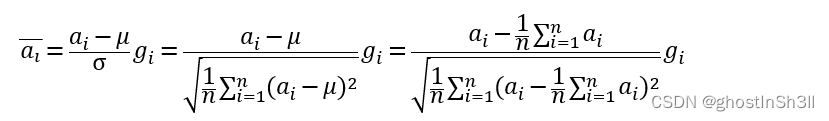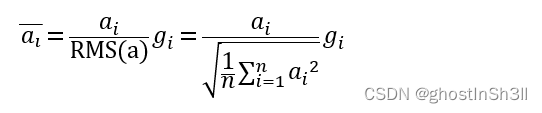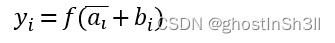ImageBind-LLM: Multi-modality Instruction Tuning 论文阅读笔记
本文主要基于LLaMA和ImageBind工作,结合多模态信息和文本指令来实现一系列任务。训练中仅使用图像文本信息作为多模态信息提取能力的训练数据(only leverage the vision-language data for multi-modality instruction tuning)。Github代码 link.
Method 方法
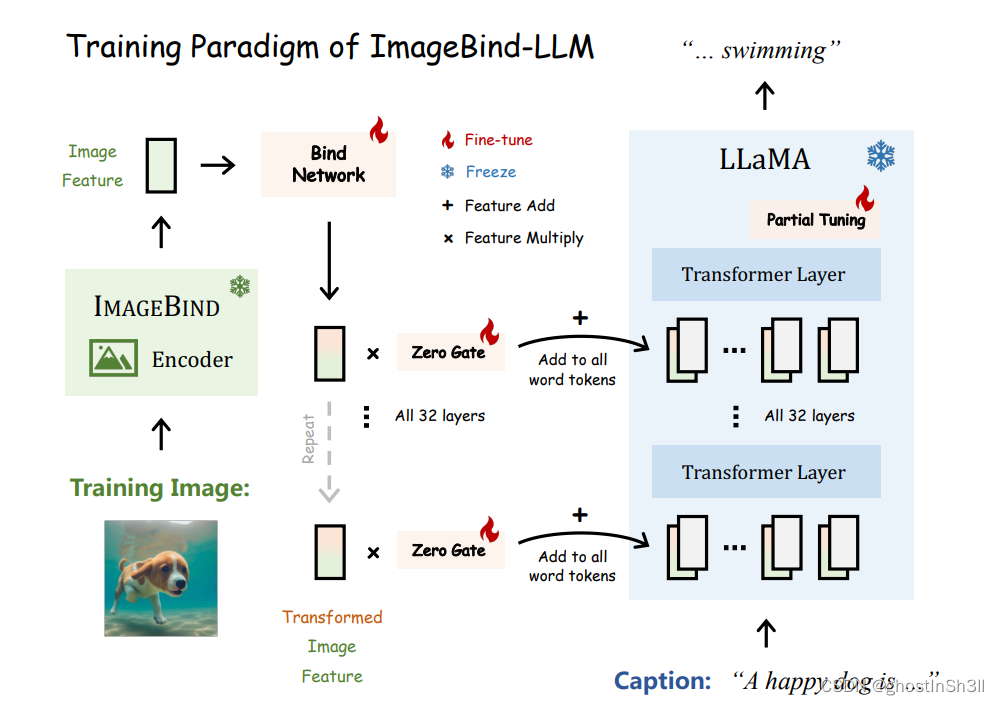
对于一个图像文本对,
- 使用来自ImageBind工作、预训练好、冻结参数的图像encoder来提取全局的图像特征(utilize the frozen image encoder of ImageBind to extract the global image feature)。
- 使用一个可学习的bind network来对齐 前面ImageBind encoder 和 后面LLaMA的特征空间,得到处理后的transformed image feature(adopt a learnable bind network to align the embedding space between LLaMA and ImageBind’s image encoder)。
- 将图像特征(多模态数据特征)transformed image feature与LLaMA的文本知识融合:将transformed image feature与LLaMA中每个transformer层的每个word tokens相加(the transformed image feature is added to the word tokens at all transformer layers in LLaMA)。并且设置了一个初始值为0、可学习的门参数
g
z
e
r
o
g_{zero}
gzero来控制特征融合的程度,
T j = T I ∗ g z e r o + T W j T^j=T_I*g_{zero} + T{_W}{^j} Tj=TI∗gzero+TWj
门参数的设置可以使得模型训练初期保持稳定,门参数的数值一般随着训练会逐渐增加。
所以整个模型可以分为两个阶段的训练,
- vision-language pretraining on image-caption data to learn the image-conditioned response capacity
基于ImageBind的encoder,模型也可以理解图像之外其他模态的信息 - multi-modality instruction tuning on visual instruction data
基于non-instruction model LLaMA,输入文本指令(language instruction)来学习长句生成能力(long-sentence generation quality)。本阶段仅使用图像文本数据来微调模型,并且冻结Imagebind encoder和Bind network的参数。
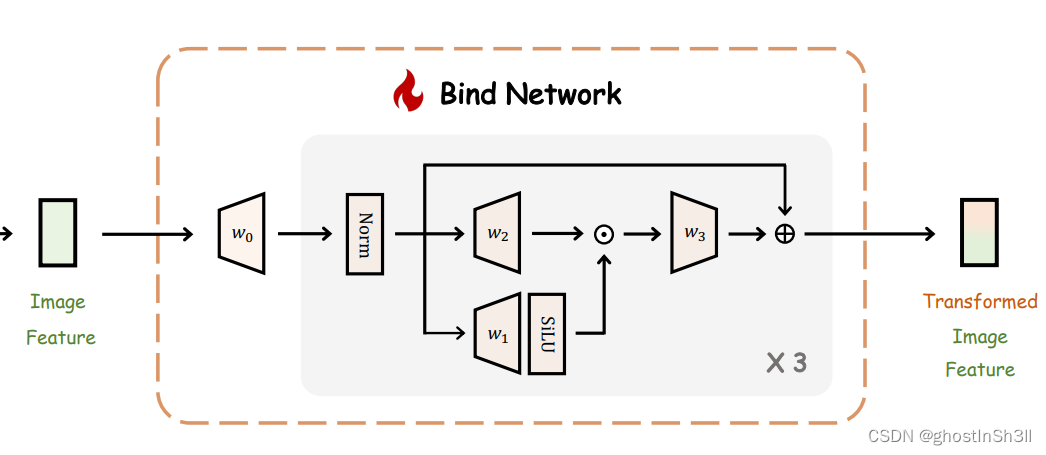
Bind Network
主要作用是对齐ImageBind和LLaMA之间的特征空间。
代码实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Define the RMSNorm
class RMSNorm(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, eps: float = 1e-6):
super().__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(dim))
def _norm(self, x):
return x * torch.rsqrt(x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True) + self.eps)
def forward(self, x):
output = self._norm(x.float()).type_as(x)
return output * self.weight
# Define the repeated feedforward block in bind network
class FeedForwardBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, hidden_dim: int):
super().__init__()
# normalize the input
self.norm = RMSNorm(dim)
# Define 3 linear projection layers whose parameters are w1, w2 and w3 respectively.
self.w1 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim, bias=False)
self.w2 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim, bias=False)
self.w3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
# cascade linear linears with RMSNorm, SiLU activation functions and residual connections
x = self.norm(x)
return x + self.w3(F.silu(self.w1(x)) * self.w2(x))
class bind_network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, args):
super.__init__()
self.image_dim = args.image_dim # e.g., 1024, encoded by ImageBind
self.model_dim = args.model_dim # e.g., 4096
self.ffn_dim = self.model_dim * 4 #
self.linear_0 = nn.Linear(self.image_dim, self.model_dim)
self.feed_forward_1 = FeedForwardBlock(dim=self.model_dim, hidden_dim=self.ffn_dim)
self.feed_forward_2 = FeedForwardBlock(dim=self.model_dim, hidden_dim=self.ffn_dim)
self.feed_forward_3 = FeedForwardBlock(dim=self.model_dim, hidden_dim=self.ffn_dim)
def forward(self, image_feature):
# image_feature, (1,C1) / (1,image_dim)
# Adopt the linear projection layer at first
image_feature = self.linear_0(image_feature) # image_feature, (1, model_dim)
# Cascade 3 projection blocks
image_feature = self.feed_forward_1(image_feature)
image_feature = self.feed_forward_2(image_feature)
transformed_image_feature = self.feed_forward_3(image_feature)
return transformed_image_feature
RMSNorm的原理及与Layer Norm的对比
计算过程,对于输入向量 x ∈ R m x∈R^m x∈Rm,
- 首先计算输入向量与权重矩阵的加权和,
- 标准化 Normalization
LayerNorm的计算方法,
RMSNorm的计算方法,
故RMSNorm完整减少了计算加权和平均值μ的步骤,保证模型与输入向量和权重解耦、训练过程中梯度稳定及模型收敛速度的前提下,减少了额外的计算开销,加速7%~64%的网络训练(具体的提升指标受硬件、网络结构、其他部分计算开销等影响)。
- 加上偏置和激活函数,获得该层的输出
Related Word / Prior Work
LLaMA-Adapter
模型输入图像 (image inputs),输出文本(language responses)。
Pipeline:
- 使用预训练好的encoder来提取图像特征;
- 将图像特征输入LLaMA进行微调。具体的实现方法是将图像特征作为token,拼接到LLaMA输入的word tokens前(LLaVA和MiniGPT-4中也使用同样的concat做法,这样导致数据长度变长、需调用self-attention mechanism,所以会导致额外的计算和训练难度的提示);并且在每一个attention layer前,设置一个初始值为0的、可学习的门参数(zero-initialized gating factor)来调节特征拼接的程度。
局限:只能解决简单的视觉问答(visual question answering scenarios)问题,例如ScienceQA