前言
vue3 采用的 diff 算法名为快速 diff 算法,整个 diff 算法的过程可以大致分为以下5个阶段。
- 处理前置节点
- 处理后置节点
- 处理仅有新增节点
- 处理仅有删除节点
- 处理其他情况(新增 / 卸载 / 移动)
这里我们先定义新旧两个虚拟节点列表,接下来我们通过这两个列表来模拟下 vue3 的 diff 算法的整个过程。
1. 处理前置节点
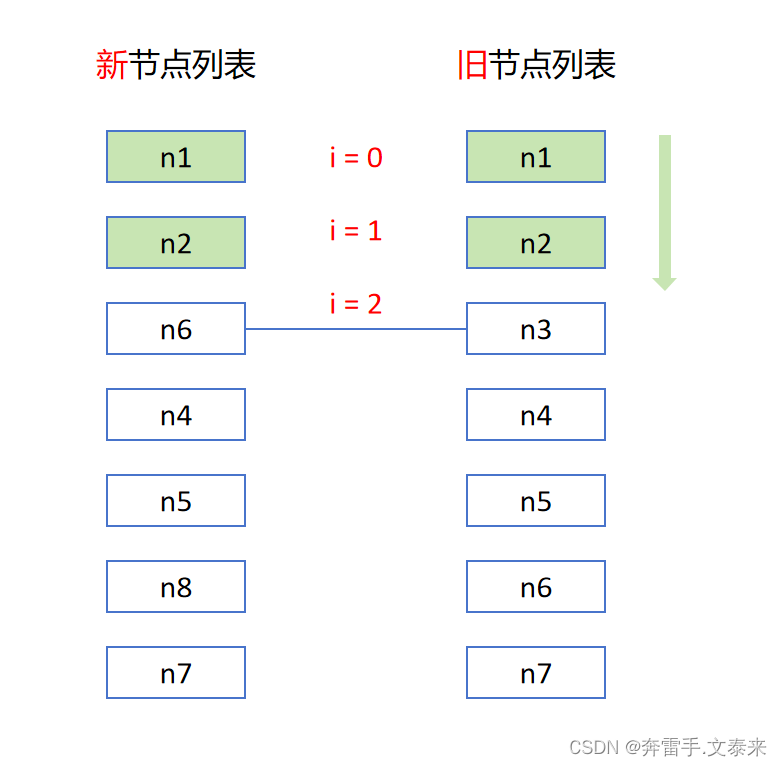
从前往后对比新旧两个节点,节点相同则 patch 打补丁更新
这里我们先定义一个 i 变量用于记录前置索引值并初始化 i = 0,逐个比较它们的节点是否相同。在遍历中可知当 i = 2 的时候新旧节点的值不一样那么我们就停在这里并记录当前 i = 2。经过这一步我们已经处理完成了前面两个节点。对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
let i = 0
const l2 = c2.length
let e1 = c1.length - 1 // prev ending index
let e2 = l2 - 1 // next ending index
// 1. sync from start
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i]
const n2 = c2[i]
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2,container)
} else {
break
}
i++
}
2. 处理后置节点
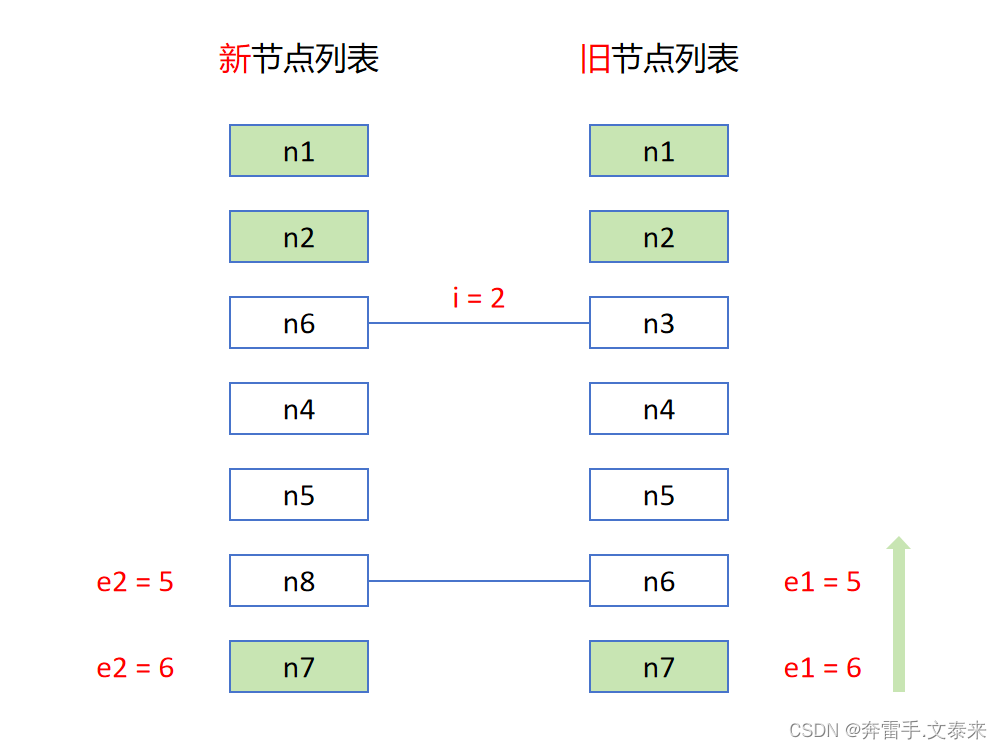
从后往前对比两个节点,节点相同则 patch 打补丁更新
这里我们定义一个 e1 e2 分别记录新旧节点列表的后置索引值。在遍历中可知当 e1 = 5 e2 = 5 的时候新旧节点的值不一样那么我们就停在这里并记录当前 e1 和 e2。经过这一步我们已经处理完成了后面一个节点。对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
// 2. sync from end
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1]
const n2 = c2[e2]
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(n1, n2,container)
} else {
break
}
e1--
e2--
}
3. 处理仅有新增节点
新节点还没遍历完而旧节点已遍历结束
在遍历过程中会出现 i > e1 && i <= e2 的情况(旧的少 新的多),这种情况代表有节点需要被新增。对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
if (i > e1) {
if (i <= e2) {
const nextPos = e2 + 1 // 插入的位置
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? c2[nextPos].el : parentAnchor // 参照物
while (i <= e2) {
patch(null, c2[i],container, anchor)
i++
}
}
}
4. 处理仅有删除节点
新节点已遍历结束而旧节点还没遍历完
在遍历过程中同样也会出现 i > e2 的情况(旧的多 新的少),这种情况代表有节点需要被删除。对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
i++
}
}
5. 处理其他情况(新增 / 卸载 / 移动)
在完成前置、后置预处理,部分边界情况后,最后我们来处理有新增、卸载、移动的复杂情况。让我们来看下 vue3 是如何完成这种复杂情况的操作。我们先定义如下几个变量
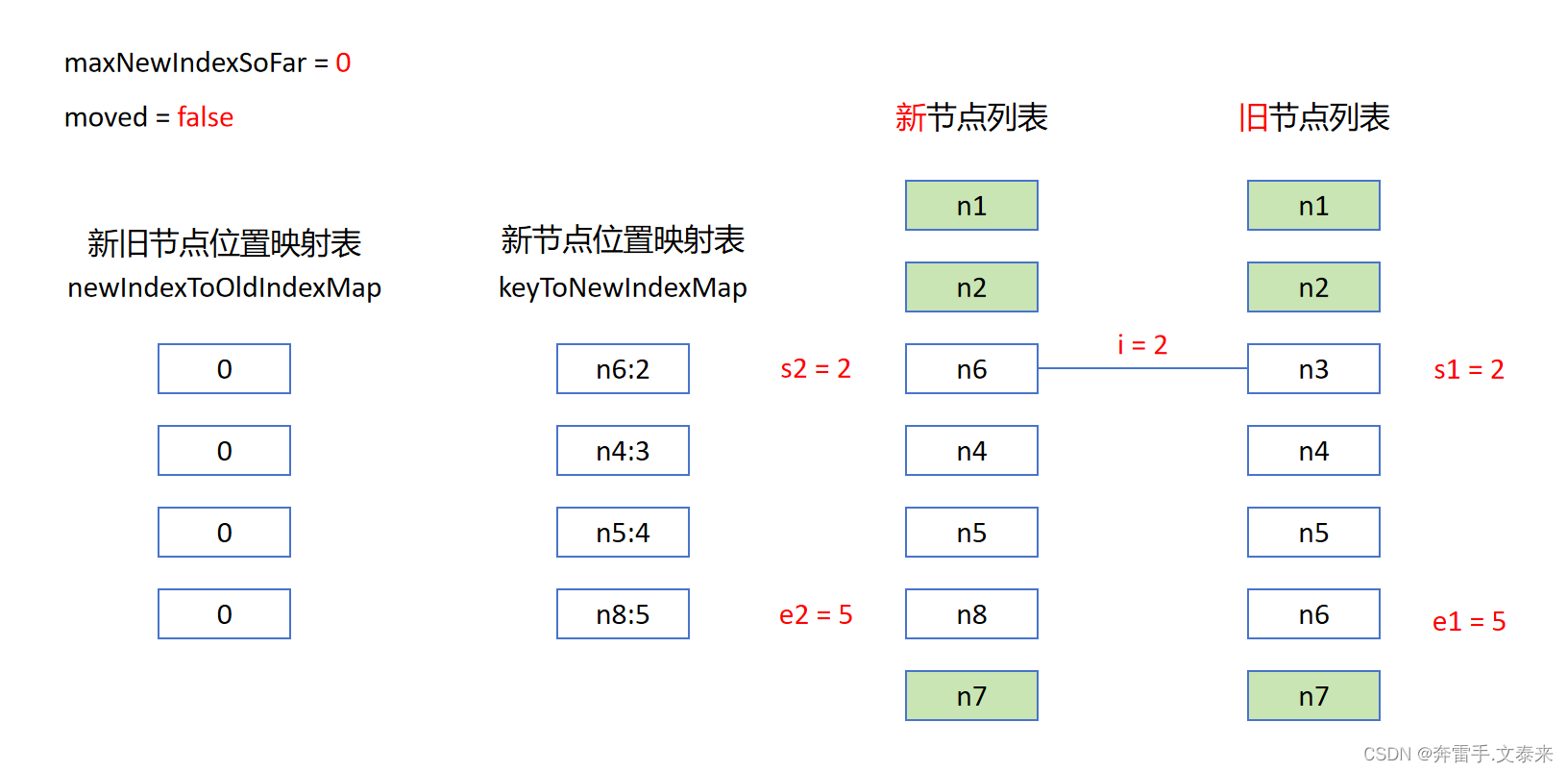
5.1 定义位置映射表
s1s2分别记录新旧节点列表要处理部分的起始位置。keyToNewIndexMap用于保存新节点与位置的索引关系。moved = false表示移动标识。maxNewIndexSoFar = 0用于记录新节点中当前的最远位置,目的是用于判断新旧节点在遍历过程中是否呈现递增趋势,如果不是则证明节点产生了移动,需要设置moved = true后续进行移动处理。newIndexToOldIndexMap用于记录新旧节点位置的映射关系,初始值都为 0,如果处理完之后还是保持 0 这个值的话则判定为新节点后续需要挂载。
const s1 = i // prev starting index
const s2 = i // next starting index
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
const keyToNewIndexMap = new Map()
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = c2[i]
if (nextChild.key != null) {
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}
// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer present
let j
let patched = 0
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1
let moved = false
// used to track whether any node has moved
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0
// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>
// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1
// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has
// no corresponding old node.
// used for determining longest stable subsequence
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched)
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
5.2 更新位置映射表并判断节点是否有移动
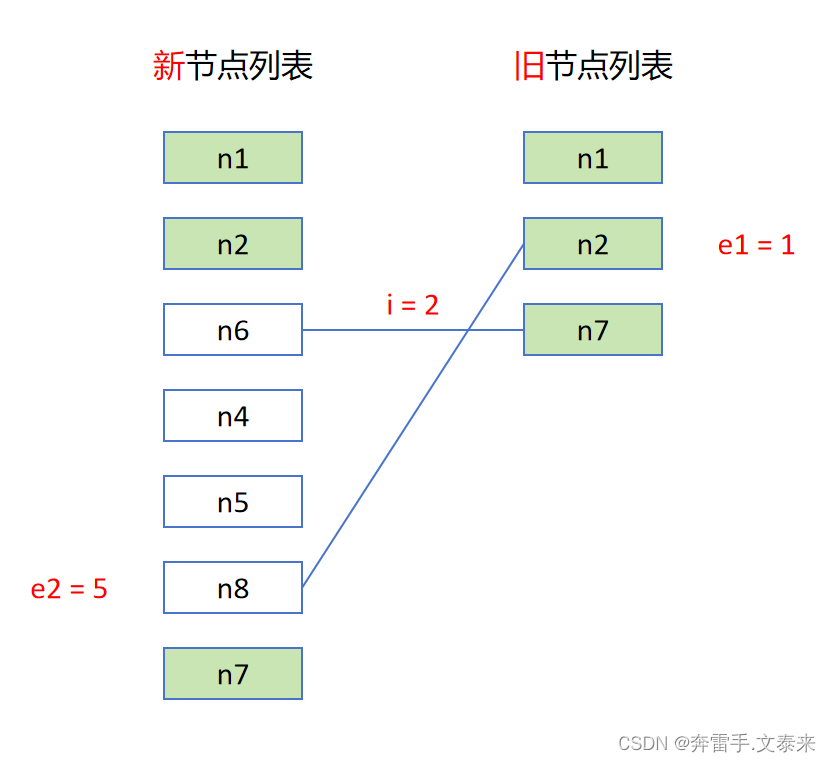
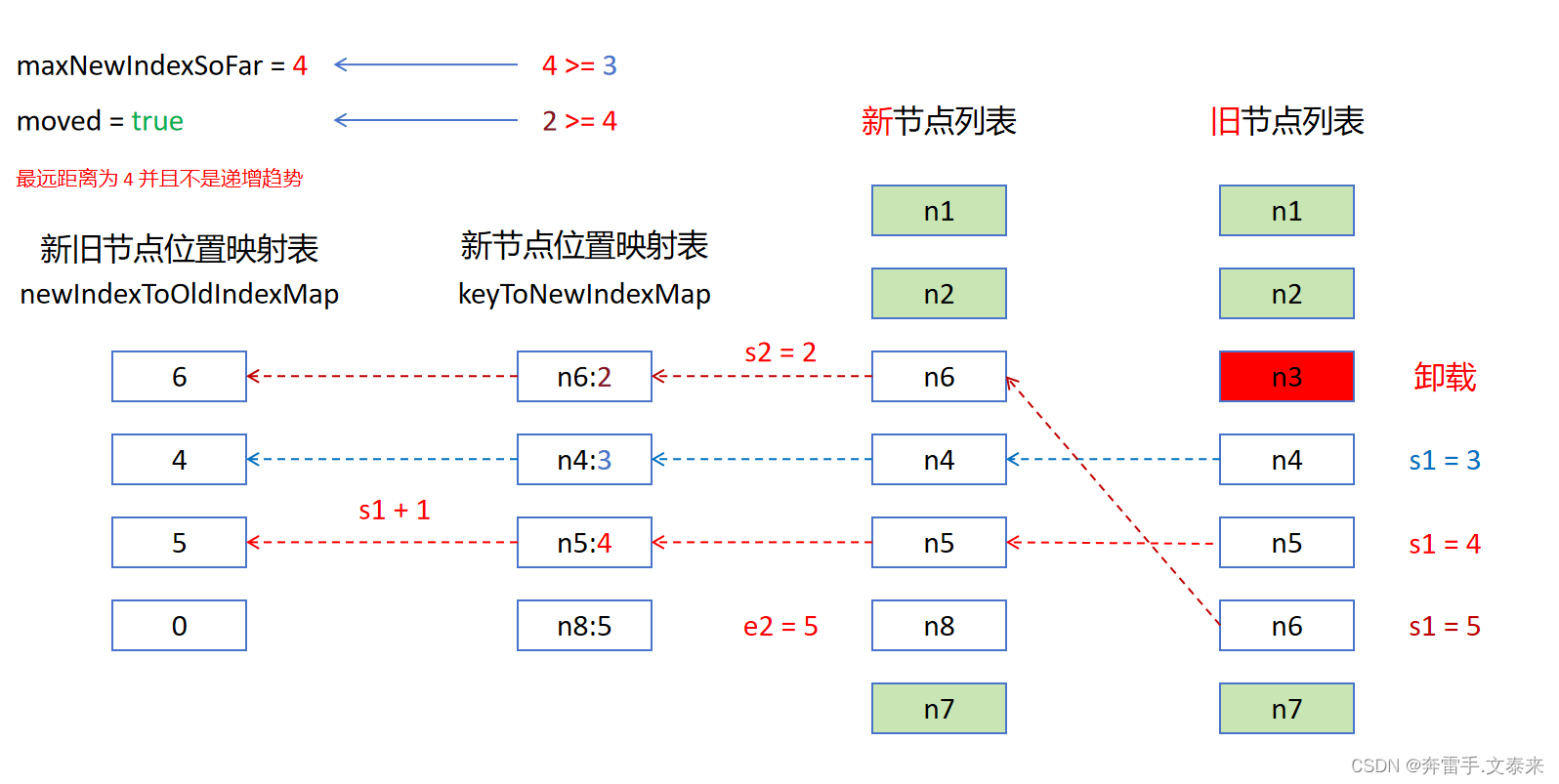
接下来我们从旧节点列表中依次取值并判断获取到的值是否存在于新节点列表中其结果只会包含两种情况:存在和不存在。
- 不存在:直接卸载该节点。
- 存在:
1. 更新newIndexToOldIndexMap对应下标的值。
2. 对比新节点位置索引值和当前最远位置如果newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar则更新maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex的值,否则的话更新moved = true。
对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removal
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
continue
}
let newIndex
if (prevChild.key != null) {
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
} else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
if (
newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&
isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j] as VNode)
) {
newIndex = j
break
}
}
}
if (newIndex === undefined) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
} else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex
} else {
moved = true
}
patch(prevChild, c2, container,null)
patched++
}
}
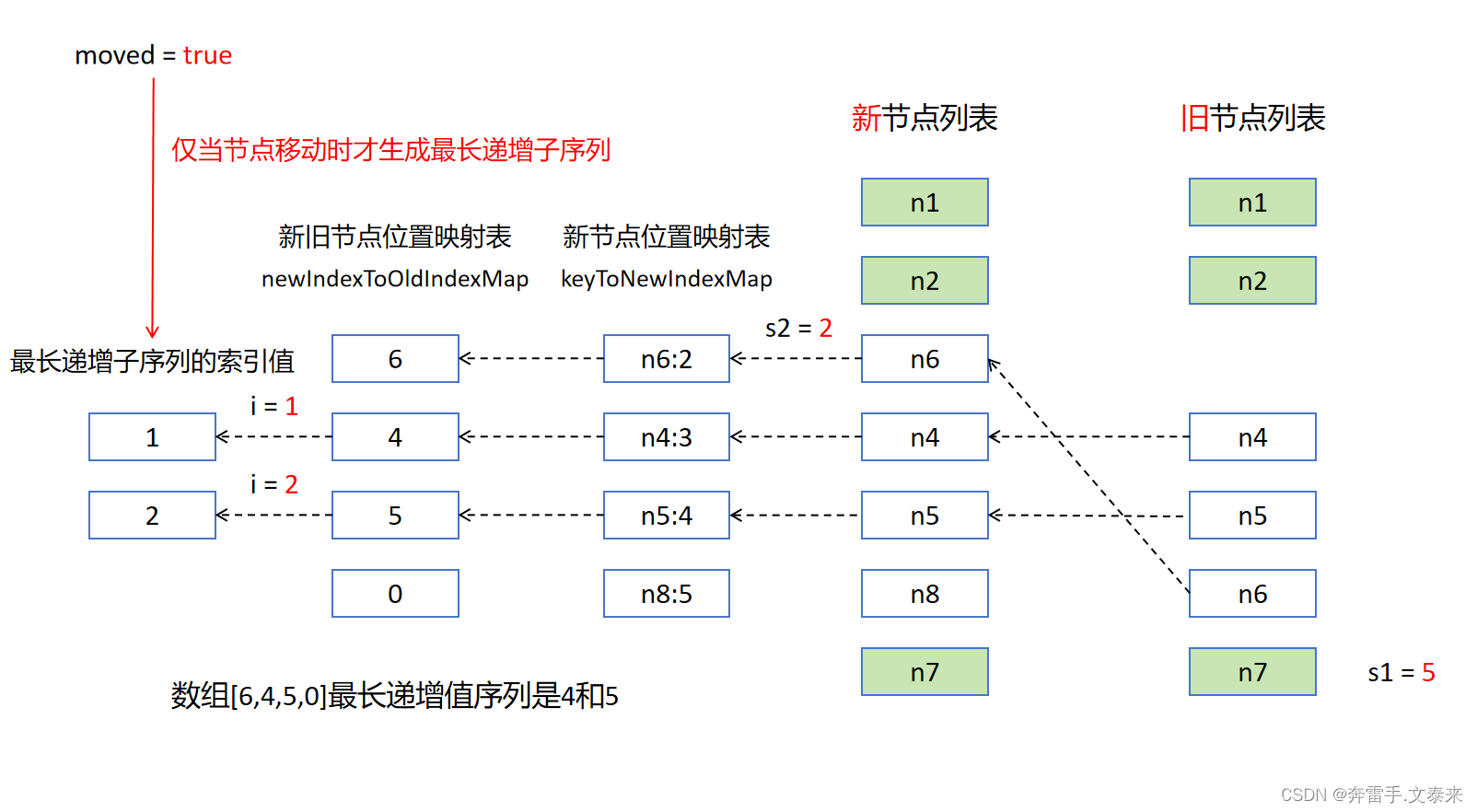
5.3 生成最长递增子序列
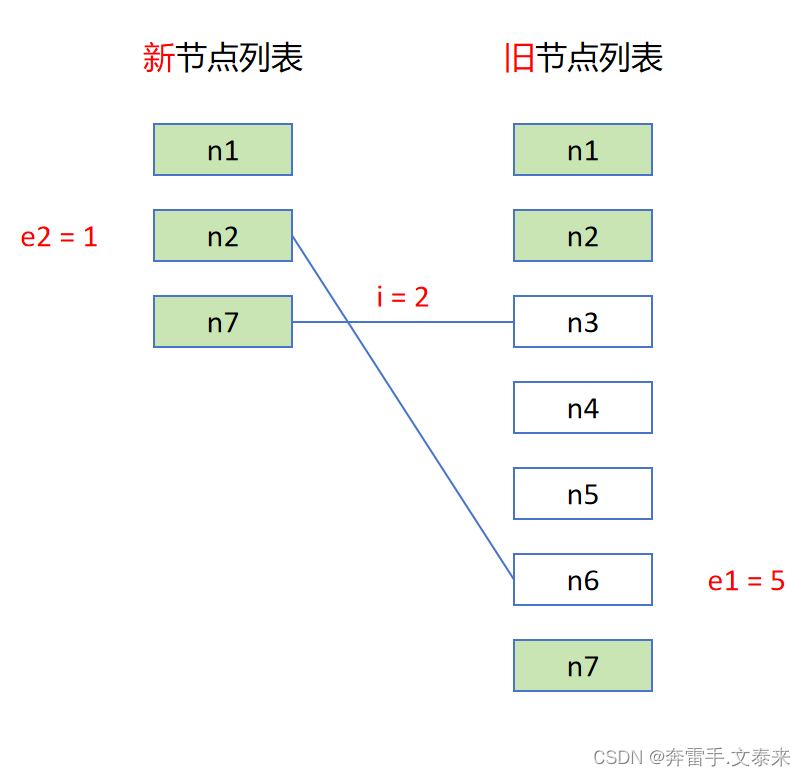
需要注意的是仅当节点移动时才生成最长递增子序列,其目的是让节点可以做到最小限度的移动操作。
接下来从后开始往前遍历处理新旧节点位置映射表:
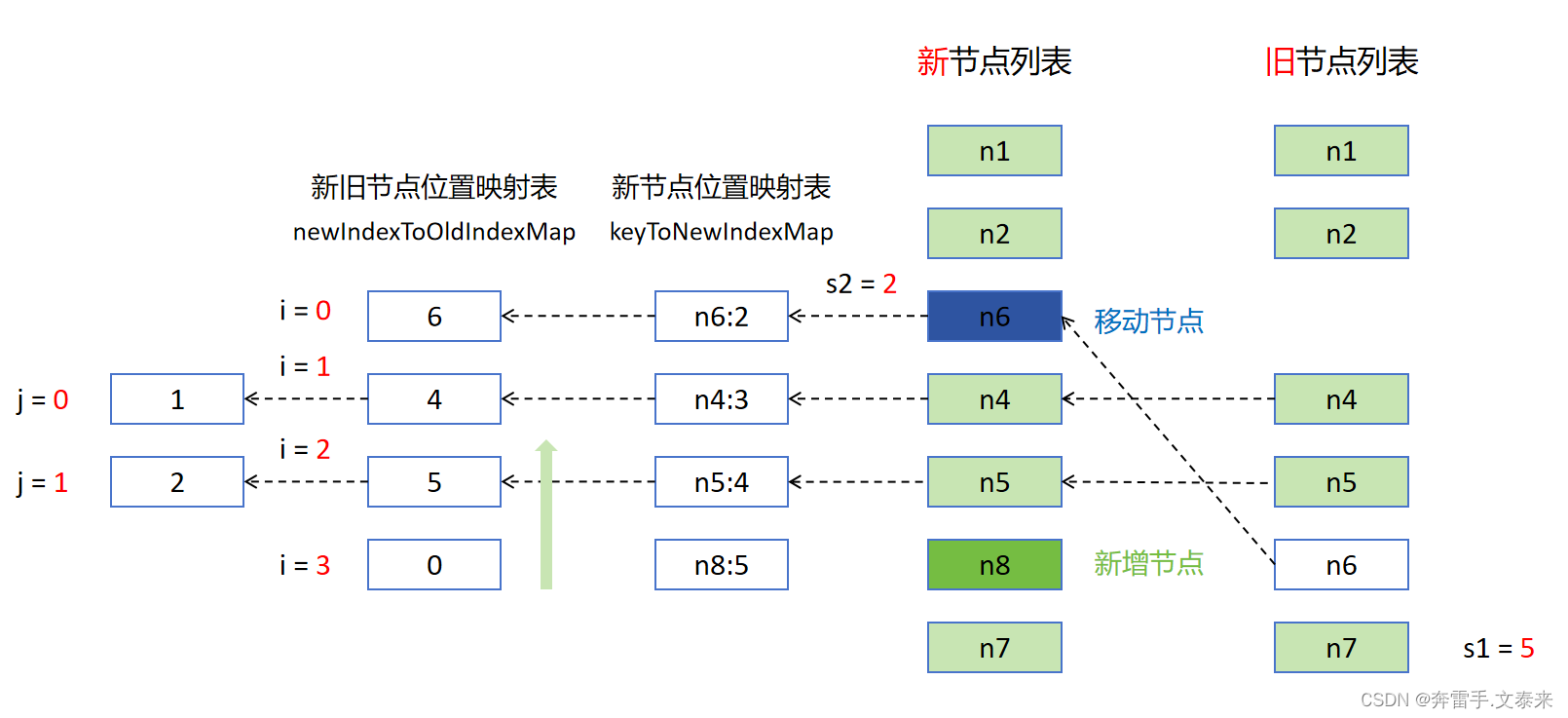
i = 3对应的位置值为 0 表示该节点为新节点后续需要挂载。i = 2处于最长递增子序列j = 1的地方,直接跳过,同时i和j需要同时往上移动。i = 1处于最长递增子序列j = 0的地方,直接跳过,同时i和j需要同时往上移动。i = 0对应的位置值为 6,i = 0不处于最长递增子序列中因此该节点需要移动。
整个过程只是新挂载了 n8 节点、卸载了 n3 节点、移动了 n6 节点,其他均为原地 patch 更新,这样的处理使性能得到了极大的提升。
对应的 vue3 源码在这里:
// 5.3 move and mount
// generate longest stable subsequence only when nodes have moved
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1
// looping backwards so that we can use last patched node as anchor
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex]
const anchor = nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? c2[nextIndex + 1.el : parentAnchor
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// mount new
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor)
} else if (moved) {
// move if:
// There is no stable subsequence (e.g. a reverse)
// OR current node is not among the stable sequence
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, MoveType.REORDER)
} else {
j--
}
}
}
由于 vue3 diff 算法源码内容较多这里就不在贴出来,最后附上源码链接感兴趣的小伙伴可以深入的了解下。
总结
以上就是 vue3 diff 算法的大致流程,本篇文章为 【前端面试】Vue3 DOM Diff】的文字记录版。如有不明白或者是写错的地方还希望大家可以指出来,最后码字不易,希望大家可以素质三连。