引言
- 今天又是新的一周了,今天继续加油,起的挺早的,背完书睡了一会,整的有点懵,先把今天的算法题做了!
- 不知道今天字节一面,能不能通过,不过据说好难呀,字节是大厂里面最难面试的!
- 看了一下他的内容,感觉要求还是很高的,重点要求高可用高并发,尤其是消息队列那一部分,什么kafka这些暂时还不会,权当接受鞭笞了吧!
- 一紧张,一个上午啥也不想干,就想停在这里,这样可不行呀!
复习
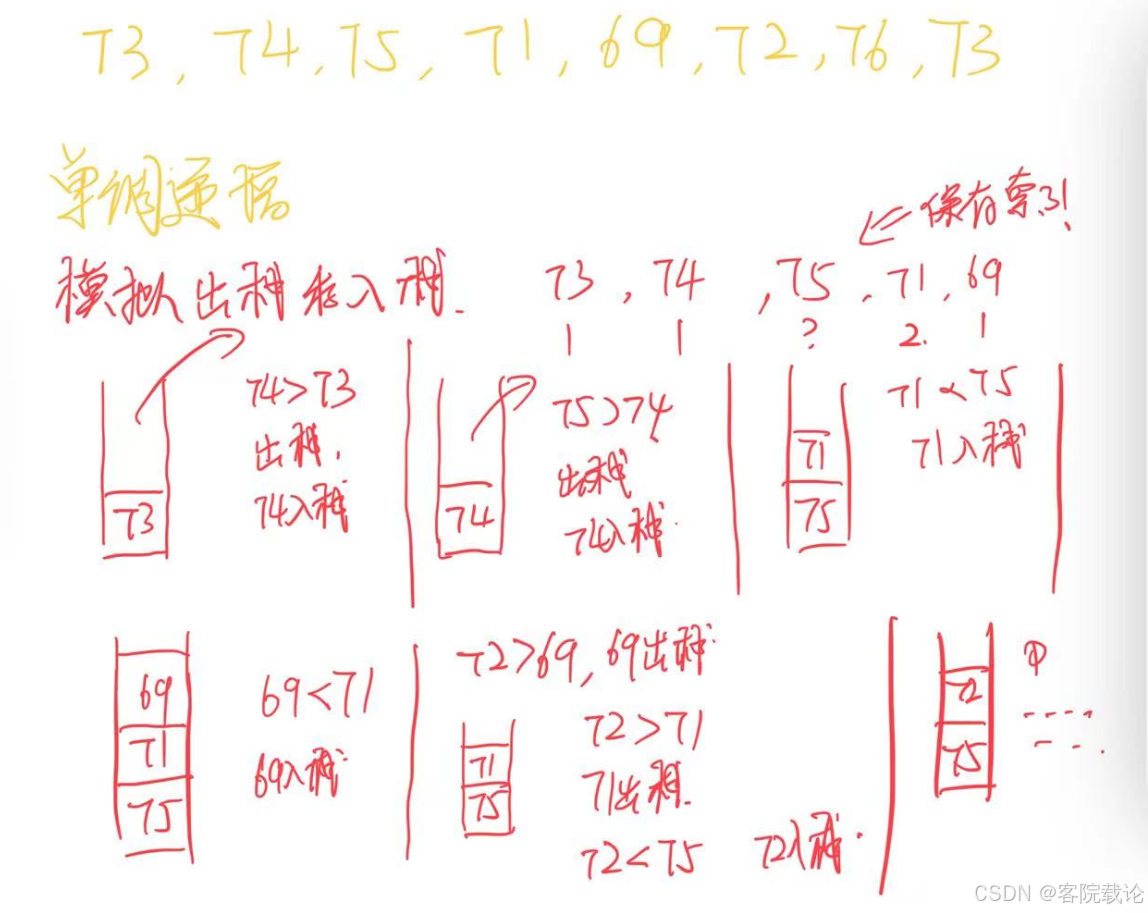
快速排序模版题——数组中第K大的元素
回顾实现
- 规定了时间复杂度是O(n),所以这里是基于快排实现的,快排的时间复杂度是O(nlogn),但是这里每次都取一半,最终的结果逼近2n,就是O(n)时间复杂度,这里直接使用快排的模板去做。
- 实现如下
模板记录 - 这里的模板写错了,应该是以j作为分割线,因为最终肯定是j移动到中间的
- 进行交换的之后,要判定i和j之间的相对关系
class Solution {
public:
int quicksort(vector<int> &nums,int l,int r,int k){
if(l >= r) return nums[k];
int i - l - 1 ,j = r + 1 ,x =(l + r) >>1;
while(i < j){
do i++;while(nums[i] < nums[x]);
do j --;while(nums[j] > nums[x]);
swap(nums[i],nums[j]);
}
quicksort(nums,l,x - 1,k),quicksort(nums,x + 1,r,k);
}
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
return quicksort(nums,0,nums.size() - 1,k);
}
};
void quick_sort(int q[],int l,int r){
if(l >= r) return ;
// 确定中间值、左边界、右边界
// 中间元素不参加排序,i是从x的左侧一个开始,j是从x的右侧开始
int i = l - 1,j = r + 1,x = q[l + r >> 1];
while(i < j){
do i ++; while(q[i] < x);
do j -- ;while(q[j] > x);
if(i < j) swap(q[i],q[j]);
}
quick_sort(q,l,j),quick_sort(q,j + 1,r);
}
这个模板有几个特征需要注意
- 如果数量是奇数的话,最终j就是第k个已经排序好的元素
- 如果数量是偶数的话,左右边界会互换,然后左右边界并不一定是已经排序好的元素,所以要始终进行重排序
注意,是第k大的元素,就是要从大到小进行排序,这里搞错了,搞反了!!
class Solution {
public:
int quicksort(vector<int> &nums,int l,int r,int k){
if(l == r) return nums[k];
int i = l - 1 ,j = r + 1 ,x =nums[(l + r) >>1];
while(i < j){
do i++;while(nums[i] > x);
do j --;while(nums[j] < x);
if (i < j) swap(nums[i],nums[j]);
}
if(i == j && j == k) return nums[k];
if(j < k) return quicksort(nums,j + 1,r,k);
else return quicksort(nums,l,j,k);
}
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
return quicksort(nums,0,nums.size() - 1,k - 1);
}
};
LRU缓存的实现
注意
- 一个人是如何在一个地方跌倒了两次的,命运总是如此巧合,在腾讯的时候就面试过这道题,然后在字节的时候又来了,太真实了!兄弟!
- 没必要了,这道题你怎么都得背下来,不仅仅是背下来,你还得在clion中再写一遍!从头写一遍!
个人实现
- 今天手撕部分主要有以下两个缺点
- leetcode官网用习惯了,连类的构造函数都不会写了,正常手撕代码题,并不会像leetcode一样,给你打好一个框架
- 我的命名方式太差了,居然和平常些算法题一样,怎么简单怎么来了,完全没有意义!不要省这个时间,然后键盘好好用用!老师打错字,打慢点没事的!
下面是我个人实现
- 上一次没有好好做,然后这一次做了才发现一个问题,就是没有办法好好确认最后一个节点的指针的坐标,所以就没有办法进行节点清除
- 很多地方,写的都是不对的,有很大的问题,并没有判定是否为空!不然就是非法内存访问了!
class LRUCache {
public:
struct Node{
int value;
Node* pre;
Node* next;
Node(int v):value(v),pre(nullptr),next(nullptr){};
};
int capacity;
int cur_capacity;
unordered_map<int,Node*> dict;
Node* dummy;
Node* tail;
LRUCache(int capacity){
this->capacity = capacity;
this->cur_capacity = 0;
this->dummy = new Node(-1);
this->tail = dummy;
}
void moveFirst(Node* node_move){
// remove the node_move in the list
if(node_move->next) node_move->next->pre = node_move->pre;
node_move->pre->next = node_move->next;
// move the node_move to first
node_move->pre = dummy;
dummy->next = node_move;
Node* temp = dummy->next;
if(temp){
node_move->next = temp;
temp->pre = node_move;
}
}
int get(int key){
// analysis the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0) return -1;
// move the Node to the first
moveFirst(dict[key]);
return dict[key]->value;
}
void put(int key,int value){
// judge the whether the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0){
// the key does not exists
dict[key] = new Node(value);
if(cur_capacity == 0) tail = dict[key];
// the capacity is not full
if(cur_capacity < capacity) {
dict[key]->next = dummy->next;
dict[key]->pre = dummy;
dummy->next = dict[key];
if(dummy->next) dummy->next->pre = dict[key];
cur_capacity ++;
}else{
// the cache is full ,remove the tail node;
tail = tail->pre;
delete tail->next;
}
}else{
dict[key]->value = value;
moveFirst(dict[key]);
}
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
总结
- 这里写的真的是糟糕,有几个地方是有问题的,具体以下几个部分
- 指针那里的操作还是有很大的问题,不是不理解,是感觉自己不规范,每次都忘记判定下一个next指针是否为空,然后做了很多不必要的判断
- 第二个就是,命名也没有很规范
参考实现
- 这里的思路基本上是一致的,主要是看看他怎么实现删除最后一个节点的,以及如何维护不同指针的!
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class LRUCache{
public:
struct Node{
// int value; 多个变量,同类型,同行进行命名
int key,val;
Node *left,*right; // 指针的命名这里也是有问题的,就是
// Node* right;
// Node(int v):value(v),pre(nullptr),next(nullptr){};
Node(int _key,int _val):key(_key),val(_val),left(NULL),right(NULL){};
} *L ,*R;
unordered_map<int,Node*> dict;
int num;// 这个cache的容量大小
LRUCache(int capacity){
num = capacity;
// 同时建立头节点和尾节点,这样能够防止空指针,比我的高明多了
L = new Node(-1,-1),R = new Node(-1,-1);
L->right = R,R->left = L;
}
void insert(Node *p){
// insert new node to the first
// assign the left and right point of the node
p->right = L->right;
p->left = L;
// assign the left the node
L->right->left = p;
L->right = p;
}
void remove(Node *p){
// remove the final node
p->right->left = p->left;
p->left->right = p->right;
}
int get(int key){
// analysis the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0) return -1;
// remove the node and insert the node again
auto p = dict[key];
remove(p);
insert(p);
return p->val;
}
void put(int key,int value){
// judge the whether the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0){
// judge the size of cache by the dict
if(dict.size() == num){
// the cache is full
auto p = R->left;
remove(p);
dict.erase(key);
delete p;
}
// insert new node to cache
auto p = new Node(key,value);
insert(p);
dict[key] = p;
}else{
auto p = dict[key];
p->val = value;
// refresh the node access time
remove(p);
insert(p);
}
}
};
int main(){
LRUCache lru(2) ;
lru.put(1,3);
lru.put(1,4);
lru.put(1,5);
cout<<lru.get(1)<<endl;
lru.put(4,5);
cout<<lru.get(3)<<endl;
return 0;
}
总结
-
下面就上面几个问题进行逐个回答,解释一下
-
为了防止出现空指针的判定
- 这里创建了一个头节点和尾节点,我在面试的时候想到了,但是觉得可能会浪费空间,所以就想多写一些逻辑进行判定,但是效果并不好的。
-
通过字典来判定当前的cache的数量
- 我在面试的时候是通过的一个新的变量n来维护对应的cache长度,但是这里完全没有必要,只需要通过字典进行维护即可,因为字典保存的是有效的字典空间
- 字典的大小 小于阈值,就不需要判定是否需要删除最后一个元素,只有达到阈值,才需要删除目标元素!
即使增加了最大生存时间,也不需要单独额外判定,只需要在获取元素的时候判定一下即可,因为没有必要删除过期的元素!!
- 获取当前系统运行时间相关操作
- ctime包的clock_t对象,使用clock()函数获取对应的时间戳
- 使用double来保存时间的长度
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 获取程序开始时间
clock_t start = clock();
// 模拟一些操作
for (volatile int i = 0; i < 100000000; ++i);
// 获取程序结束时间
clock_t end = clock();
// 计算运行时间
double duration = double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
cout << "Program run time: " << duration << " seconds" << endl;
return 0;
}
增加了过期时间的相关操作
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class LRUCache{
public:
struct Node{
// int value; 多个变量,同类型,同行进行命名
int key,val;
Node *left,*right; // 指针的命名这里也是有问题的,就是
clock_t useTime;
// Node* right;
// Node(int v):value(v),pre(nullptr),next(nullptr){};
Node(int _key,int _val):key(_key),val(_val),left(NULL),right(NULL),useTime(0){};
} *L ,*R;
unordered_map<int,Node*> dict;
int num;// 这个cache的容量大小
double duraTime;
LRUCache(int capacity,double duration){
num = capacity;
duraTime = duration; // assign the life of the node
// 同时建立头节点和尾节点,这样能够防止空指针,比我的高明多了
L = new Node(-1,-1),R = new Node(-1,-1);
L->right = R,R->left = L;
}
void insert(Node *p){
// insert new node to the first
// assign the left and right point of the node
p->right = L->right;
p->left = L;
// assign the left the node
L->right->left = p;
L->right = p;
// refresh the StartTiem
p->useTime = clock();
}
void remove(Node *p){
// remove the final node
p->right->left = p->left;
p->left->right = p->right;
}
int get(int key){
// analysis the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0) return -1;
auto p = dict[key];
p->useTime = clock();
remove(p);
// judge whether the node exists
if((clock() - p->useTime) > duraTime) {
delete p;
dict.erase(key);
return -1;
}
// remove the node and insert the node again
insert(p);
return p->val;
}
void put(int key,int value){
// judge the whether the key exists
if(dict.count(key) == 0){
// judge the size of cache by the dict
if(dict.size() == num){
// the cache is full
auto p = R->left;
remove(p);
dict.erase(key);
delete p;
}
// insert new node to cache
auto p = new Node(key,value);
p->useTime = clock();
insert(p);
dict[key] = p;
}else{
auto p = dict[key];
p->val = value;
p->useTime = clock();
// refresh the node access time
remove(p);
insert(p);
}
}
};
int main(){
LRUCache lru(2,2000000.00) ;
lru.put(1,3);
lru.put(1,4);
lru.put(1,5);
cout<<lru.get(1)<<endl;
lru.put(4,5);
cout<<lru.get(3)<<endl;
return 0;
}
下面是Java版本的
import java.util.*;
class LRUCache {
class Node {
int key, val;
Node left, right;
long useTime;
Node(int _key, int _val) {
key = _key;
val = _val;
left = null;
right = null;
useTime = 0;
}
}
private Node L, R;
private Map<Integer, Node> dict;
private int num;
private double duraTime;
public LRUCache(int capacity, double duration) {
num = capacity;
duraTime = duration; // assign the life of the node
// 同时建立头节点和尾节点,这样能够防止空指针,比我的高明多了
L = new Node(-1, -1);
R = new Node(-1, -1);
L.right = R;
R.left = L;
dict = new HashMap<>();
}
private void insert(Node p) {
// insert new node to the first
// assign the left and right point of the node
p.right = L.right;
p.left = L;
// assign the left the node
L.right.left = p;
L.right = p;
// refresh the StartTiem
p.useTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
private void remove(Node p) {
// remove the final node
p.right.left = p.left;
p.left.right = p.right;
}
public int get(int key) {
// analysis the key exists
if (!dict.containsKey(key)) return -1;
Node p = dict.get(key);
p.useTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
remove(p);
// judge whether the node exists
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() - p.useTime) > duraTime) {
dict.remove(key);
return -1;
}
// remove the node and insert the node again
insert(p);
return p.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
// judge the whether the key exists
if (!dict.containsKey(key)) {
// judge the size of cache by the dict
if (dict.size() == num) {
// the cache is full
Node p = R.left;
remove(p);
dict.remove(p.key);
}
// insert new node to cache
Node p = new Node(key, value);
p.useTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
insert(p);
dict.put(key, p);
} else {
Node p = dict.get(key);
p.val = value;
p.useTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// refresh the node access time
remove(p);
insert(p);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache lru = new LRUCache(2, 2000000.00);
lru.put(1, 3);
lru.put(1, 4);
lru.put(1, 5);
System.out.println(lru.get(1)); // 应该打印 5
lru.put(4, 5);
System.out.println(lru.get(3)); // 应该打印 -1 因为 key 3 不存在
}
}
新作
栈——每日温度
注意
- 返回的是系列中第一个会单调递增的元素的索引,如果是零,后续没有比他大的元素了
- 数组长度的是 1 0 5 10^5 105,这里有可能会超时
- 温度的区间是30到100,并不会出现越界
个人实现
- 这里的思路就很明确了,感觉类似单调递增队列,不过数据长度没有限制,想想看怎么实现哈!
- 这里算是给了一点提示吧,因为这个章节就是和栈相关的,所以这里使用栈来实现,具体思路如下
- 使用一个保存索引的队列来维护
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temp) {
int m = temp.size();
vector<int> f(m );
stack<int> upst;
upst.push(0);
for(int i = 1;i < temp.size();i ++){
// compare the top elements
while(!upst.empty() && temp[i] > temp[upst.top()]){
f[upst.top()] = i - upst.top();
upst.pop();
}
upst.push(i);
}
return f;
}
};
总结
- 哇靠,难得那么顺,可能这题比较简单?不过好歹是中等题!还能提前做完,真舒服!
参考实现
- 他说这道题就是单调栈的模版题,然后花了一分半写了单调栈的模板,然后改了几个参数,就结束了。
- 这里好好看看他给的模版吧!
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temp) {
int m = temp.size();
vector<int> f(m);
stack<int> upst;
for(int i = temp.size() - 1;i >= 0;i --){
while(!upst.empty() && temp[i] >= temp[upst.top()]) upst.pop();
if(upst.size()) f[i] = upst.top() - i;
upst.push(i);
}
return f;
}
};
内存效率确实更高了
总结
- 但是我觉得这个题目比较难记,虽然和我的思路大致是相同的,但是想起来总有点怪怪的,想想看怎么记下来会更好记,脑袋不好用,记不住事情。
- 右边第一个大于我的元素,左大弹(左边元素大,弹出栈),答栈顶(答案就是栈顶元素)
- 能记就记,记不住就用我们自己的方法
- 说到模版题了,再去回忆一个模板题,基于快速排序实现的。
总结
- 以后的所有代码都要在clion中实现一下,因为手撕代码要求你能从头开始运行一个程序,是从零开始的!所以,你写习惯了idle没意义!
- 今天面试对我来说,获益匪浅,字节的老师真的很棒,我觉得虽然过不了,但是让我成长了不少
- 后续所有的算法题,都要使用java写一遍,
- 写一个完整的对象,注意自己的命名细节
- 重视自己的编程习惯
- 不要紧张,有想法赶快实现,总共就20分钟,你想那么多干嘛
明天抽时间,好好再过一遍面试的题目,进一步加深我们的面试题目的回答深度
- 心态还是不够好,前面的八股说的七零八落的,后面的手撕就紧张了,很多东西都没有想明白,就开始落手了,其实练了那么久,算法能力并没有那么差。
- 我算是知道为什么自己会记得那么乱了,两个语言生命对象的方式不同,我老是记混!明天加油!